一、递归
1. 代码示例:
public class RecursionTest {public static void main(String[] args) {test(10);}// 递归方法public static void test(int n){if(n>2){test(n-1);}System.out.println("n="+n);}}
2. 执行结果
3. 逻辑讲解:
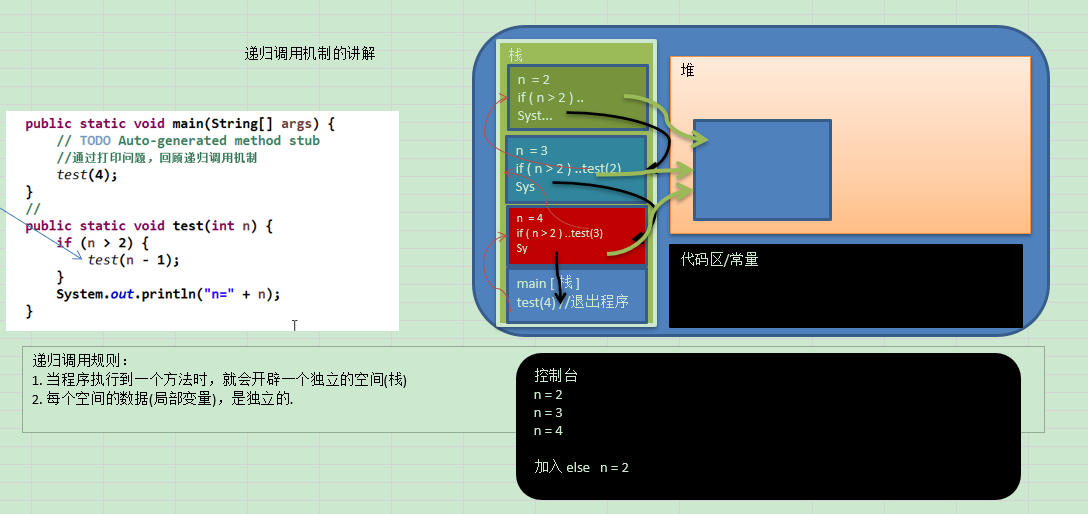
解析:
当n=4时,会在test(3)处重新创建一个栈
当n=3时,会在test(2)处重新创建一个栈
当n=2时,在判断n>2之后,执行打印程序;
执行完打印程序后,当前的n=2的栈弹出;执行n=3时的栈。此时再执行打印程序;
依此类推;
4. 递归能解决的问题

5. 实际运用—-迷宫问题
package com.atguigu.Recursion;public class MiGongDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 先创建二维数组模拟迷宫,八行七列// 地图int[][] map = new int[8][7];// 使用1表示墙,先把上下置为1for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {map[0][i] = 1;map[7][i] = 1;}// 左右也置为1for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {map[j][0] = 1;map[j][7] = 1;}// 设置挡板map[3][1] = 1;map[3][2] = 1;}// 使用递归给小球找路/*** localMap: 输入地图* int i,int j: 起始位置* 约定: 当map[i][j]=0时表示该点还没走过,当为1时,表示是墙,不能走,当为3时,思路走不通* 在走迷宫时,需要确定一个策略(方法):下-->左-->上-->右,如果该点走不通再回溯*/public static boolean findWay(int[][] localMap,int i,int j){if(localMap[6][5]==2){return true;}else{if(localMap[i][j]==0){// 当前点还没走过localMap[i][j]=2; // 先假定该点是可以走通的,如果走不通,则回溯// 下-->左-->上-->右if(findWay(localMap,i+1,j)){return true;}else if(findWay(localMap,i,j+1)){return true;}else if(findWay(localMap,i-1,j)){return true;}else if(findWay(localMap,i-1,j-1)){return true;}else{localMap[i][j]=3;return false;}}else { // 当不是0时,表明已经走过不能在走,或者时墙走不通return false;}}}}
6. 八皇后问题
Math.abs(n-i)==Math.abs(resArray[n]-resArray[i]) 判断第n个皇后是否和第i个皇后在同一斜线。按照正方向来计算,对角线置为的长和高相等
resArray[i]==resArray[n] 判读第n个是否和前面所有的皇后在同一列
package com.atguigu.Recursion;import java.util.Arrays;public class Queue8Demo {// 定义一个max表示有多少个皇后int max = 8;// 定义一个数组,保存位置的结果int[] resArray= new int[];public static void main(String[] args) {}// 编写一个方法,放置第n个皇后private void check(int n){if(n==max){ // 放第9个皇后,不需要print();return;}// 依次放入皇后,并判断是否冲突for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {// 先把当前皇后放到该行的第1列resArray[n]=i;// 判断第n个皇后到i列时,是否冲突if(isConflict(n)){//如果不冲突,放第n+1个皇后check(n+1);}// 如果冲突,就执行i++,即移动当前皇后到后一个位置}}// 查看当我们放置第N个皇后,就去检测该皇后是否和之前已摆放的皇后冲突private boolean isConflict(int n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 1. resArray[i]==resArray[n] 判读第n个是否和前面所有的皇后在同一列// 2. Math.abs(n-i)==Math.abs(resArray[n]-resArray[i]) 判断第n个皇后是否和第i个皇后在同一斜线。按照正方向来计算,对角线置为的长和高相等if(resArray[i]==resArray[n]||Math.abs(n-i)==Math.abs(resArray[n]-resArray[i])){return false;}}return true;}// 写一个方法可以把结果打印出来private void print() {for (int i = 0; i < resArray.length; i++) {System.out.printf("第%d行摆放的皇后位置是:%d \n",i,resArray[i]);}}}