线程间通信的模型有两种:共享内存和消息传递
线程间的通信具体步骤:(涉及上中下部)
- 创建资源类,在资源类中船舰属性和操作方法
- 在资源类操作方法:判断、操作、通知
- 创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法
- 防止虚拟唤醒问题
2.1 synchronized案例
操作线程的时候,等待线程使用wait()
通知另外的线程操作用notify()、notifyAll()
假设有两个线程,该线程在执行过程中,判断值(不是该值等待,让其他线程抢),操作值,通知另外一个线程的调度
通过使用两个线程对0这个值操作,一个线程加1,一个线程减1,交替实现多次
//第一步 创建资源类,定义属性和操作方法class Share {//初始值private int number = 0;//+1的方法public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {//第二步 判断 干活 通知if(number != 0) { //判断number值是否是0,如果不是0,等待this.wait(); //在哪里睡,就在哪里醒}//如果number值是0,就+1操作number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);//通知其他线程this.notifyAll();}//-1的方法public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {//判断if(number != 1) {this.wait();}//干活number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);//通知其他线程this.notifyAll();}}public class ThreadDemo1 {//第三步 创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法public static void main(String[] args) {Share share = new Share();//创建线程new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.incr(); //+1} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"AA").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.decr(); //-1} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"BB").start();}}
代码截图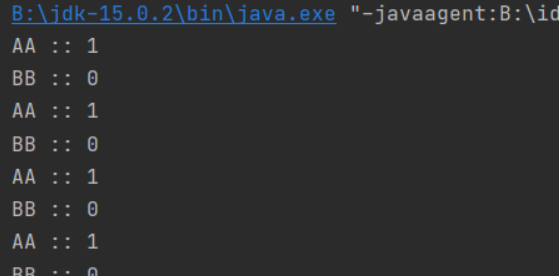
如果使用多个线程,添加额外两个线程,且操作要依次执行
new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.incr(); //+1} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"CC").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.decr(); //-1} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"DD").start();
执行结果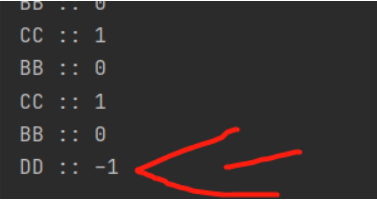
主要是虚拟唤醒导致:如果一个线程执行完毕后,通知其他线程,该线程又进入等待睡眠,可能会因为某些原因被唤醒后,if结构的语句就不会判断了,一直往下执行,所以需要将if换成while结构,每次都判断。因为wait在哪里睡眠就在哪里被唤醒,结果被某个异常唤醒了后回不去了,if结构不会在判断了,需要更改为while
while(number != 0) { //判断number值是否是0,如果不是0,等待this.wait(); //在哪里睡,就在哪里醒}
实现中断和虚假唤醒是可能的,需要将其while方法用在循环中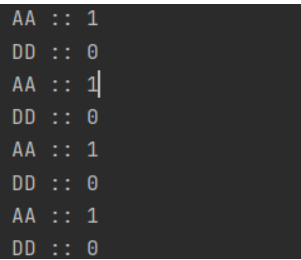
2.2 Lock案例
使用lock先要创建锁的对象以及通知的对象
放置在资源类中
//创建Lockprivate Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
上锁lock.lock();
解锁lock.unlock();
以下都为condition类:
唤醒所有等待的线程signalAll(),带上类名condition.signalAll();
唤醒一个等待线程signal(),带上类名,condition.signal();
造成当前线程在接到信号或者被中断之前一直处于等待状态await(),带上类名,condition.await();
同样是上面的案例题目换成lock
比如一个加1操作
//+1public void incr() throws InterruptedException {//上锁lock.lock();try {//判断while (number != 0) {condition.await();}//干活number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);//通知condition.signalAll();}finally {//解锁lock.unlock();}}
具体完整的代码示列
一般调用资源类的方法,先调用,在idea中使用快捷键抛出异常
//第一步 创建资源类,定义属性和操作方法class Share {private int number = 0;//创建Lockprivate Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();//+1public void incr() throws InterruptedException {//上锁lock.lock();try {//判断while (number != 0) {condition.await();}//干活number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);//通知condition.signalAll();}finally {//解锁lock.unlock();}}//-1public void decr() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {while(number != 1) {condition.await();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);condition.signalAll();}finally {lock.unlock();}}}public class ThreadDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Share share = new Share();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.incr();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"AA").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.decr();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"BB").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.incr();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"CC").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {try {share.decr();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},"DD").start();}}

