什么是Vue:
Vuex是一个用来管理组件之间通信的插件,它是一个专为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式,它解决了多组件之间同一状态的共享问题,它能够更好地在组件外部管理状态。
Vuex相当于是Vue的一个集中式的存储仓库
- 它储存的数据就是状态
- 存储仓库:本地存储cookie数据库
开发中大型应用时使用 集中式数据管理,一处修改,多处使用
安装
- yarn
$ yarn add vuex@next -save
手动在 src 目录下新建 store 文件夹 在该文件夹内创建 index.ts
使用
1.初始化store下index.ts中的内容
// todo 1、 引入资源import { createStore } from "vuex";// todo 2、 创建一个store实例const store = createStore({modules:{ // 用于数据分块...各种类数据块}})// todo 3、 导出storeexport default store
2.在mian.ts中激活挂载到当前项目到Vue实例当中去
todo 1、导入storeimport store from './store'todo 2、 使用use方法来激活store这个单例createApp(App).use(store).mount('#app')
3.在组件中使用Vuex
// 在vuex中引出useStoreimport {useStore} from 'vuex'export default defineComponent({setup(){const store = useStore() // 在setup中通过useStore得到一个store实例console.log(store) // 此时你可以打印看看这个实例,数据块在该实例的state中通过计算属性方法得到store中的数据const n = computed(() => store.state.数据块类名.数据)const add = () => {// 通过store实例中的dispatch方法来激活actionsstore.dispatch({type: '数据库名/actions中的方法名',payload:xxx})}return {n,add,}}})
Composition API
要访问setup钩子中的store,需要调用 useStore 函数,等效 this.$store与使用OptionAPI在组件内进行检索
import { useStore } from 'vuex'export default {setup () {const store = useStore();}}
为了访问状态和获取方法,需要创建 computed 引用以保留反应性。
const n = computed(() => store.state.count)
访问actions需要使用 dispatch
store.dispatch({type: '数据库名/actions中的方法名',payload:xxx})
核心内容
State、Getters、Mutations、Actions、Modules
State 状态 数据 Getters 几乎不实用。。。 Actions 动作 mutations 修改数据 Modules 用于数据分块
vue2 中 Vuex3 的使用
Vue2 使用vuex3 vue3 使用vuex4
安装
$ yarn add vuex@3
基础搭建
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store// 引入vueimport Vue from 'vue';// 引入vueximport Vuex from 'vuex';// 使用vuex插件Vue.use(Vuex);// 准备 actions 用于响应组件中的动作const actions = {}// 准备 mutations 用于操作数据(state)const mutations = {}// 准备 state 用于存储const state = {}// 创建并导出 storeexport default new Vuex.Store({actions,mutations,state,});
import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'// 引入我们创建的storeimport store from './store';Vue.config.productionTip = false;new Vue({render: h => h(App),// vue配置项中添加 store 项store, // 此时vm身上会有一个 $store 属性}).$mount('#app')
简单的计数案例
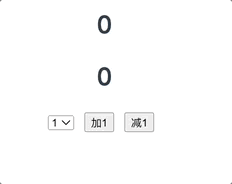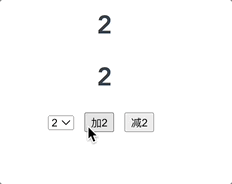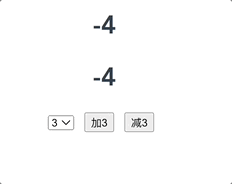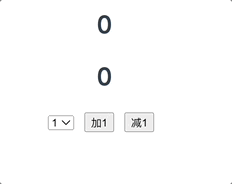
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的storeimport Vue from 'vue';// 引入vueximport Vuex from 'vuex';// 使用vuex插件Vue.use(Vuex);// 准备 actions 用于响应组件中的动作const actions = {increment: function (context, payload) {console.log('increment', context, payload);context.commit('INCREMENT', payload);},subtract: function (context, payload) {context.commit('SUBTRACT', payload);}}// 准备 mutations 用于操作数据(state)const mutations = {INCREMENT: function (state, payload) {console.log('INCREMENT', state, payload);state.count += payload;},SUBTRACT: function (state, payload) {state.count -= payload;}}// 准备 state 用于存储const state = {count: 0,}// 创建并导出 storeexport default new Vuex.Store({actions,mutations,state,});// ------------------src/main.js------------------------------------// main.js 中使用 storeimport Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'// 引入我们创建的storeimport store from './store';console.log(store);Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({render: h => h(App),// vue配置项中添加 store 项store, // 此时vm身上会有一个 $store 属性}).$mount('#app')
<template><div><h1>{{ count }}</h1><h1>{{ $store.state.count }}</h1><select v-model.number="n"><option value="1">1</option><option value="2">2</option><option value="3">3</option></select><button @click="increment">加{{ n }}</button><button @click="subtract">减{{ n }}</button></div></template><script>export default {data() {return {n: 1,};},computed: {count() {return this.$store.state.count;},},methods: {increment() {this.$store.dispatch("increment", this.n);// this.$store.commit("INCREMENT", this.n);},subtract() {this.$store.dispatch("subtract", this.n);},},};</script><style></style>
组件中读取vuex中的数据:$store.state.count
组件中修改vuex中的数据:$store.dispatch('actions中的方法名', 数据) 或者 $store.commit('mutations中的方法名', 数据)
tips:若没有网络请求或者其他业务逻辑,组件中也可以直接越过actions,即不写
dispatch,直接使用commit
核心 - getters(冷门)
- 概念:当state中的数据需要经过加工后再使用时,可以使用getters加工。
- 在
store.js中追加getters配置项 ```javascript … const getters = { tenfoldCount(state) {
} }return state.count * 10;
export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state,
getters, // 配置我们创建的getters
});
3. 组件中读取数据:`$store.getters.tenfoldCount`<a name="zyseV"></a>### vuex中的四个map方法的使用使用时都需要在组件中导入```javascriptimport { mapState, mapGetters, mapActions, mapMutations } from "vuex";
mapState
用于帮助我们映射 state 中的数据为计数属性
computed:{// 借助 mapState 生成计算属性:count、info(对象写法,使用时直接使用key值)...mapState({ count: "count", info: "info" }),// 借助 mapState 生成计算属性:count、info(数组写法)...mapState(['count', 'info']),}
mapGetters
用于帮助我们映射 getters 中的数据为计算属性
computed: {// 借助 mapGetters 生成计算属性:tenfoldCount(对象写法)..mapGetters([tenfoldCount: "tenfoldCount"]),// 借助 mapGetters 生成计算属性:tenfoldCount(数组写法)...mapGetters(["tenfoldCount"]),},
mapActions
用于帮助我们生产与 actions 对话的方法,即:包含 $store.dispatch(xxx) 的函数
methods: {// 生成 increment、subtract(对象写法)...mapActions({ increment: "increment", subtract: "subtract" }),// 生成 increment、subtract(数组写法)...mapActions(["increment", "subtract"]),},// 在模板中使用时候进行传递参数,否则默认传递Event事件对象。<button @click="increment(n)">加{{ n }}</button><button @click="subtract(n)">减{{ n }}</button>
mapMutations
用于帮助我们生成与 mutations 对话的方法,即:包含 $store.commit(xxx) 的函数
methods: {// 生成 INCREMENT、SUBTRACT(对象写法)...mapMutations({ INCREMENT: "INCREMENT", SUBTRACT: "SUBTRACT" }),// 生成 INCREMENT、SUBTRACT(数组写法)...mapMutations(["INCREMENT", "SUBTRACT"]),},// 在模板中使用时候进行传递参数,否则默认传递Event事件对象。<button @click="INCREMENT(n)">加{{ n }}</button><button @click="SUBTRACT(n)">减{{ n }}</button>
tips:mapActions 与 mapMutations 使用时,若需要传递参数,需要在模板绑定事件时传递好参数,否则默认参数为 Event事件对象。
模块化+命名空间
目的:让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
const moduleA = {state: () => ({ ... }),mutations: { ... },actions: { ... },getters: { ... }}const moduleB = {state: () => ({ ... }),mutations: { ... },actions: { ... }}const store = new Vuex.Store({modules: {moduleA,moduleB}})
开启命名空间后,组件中读取 state 数据:
// 方法一:自己直接读取this.$store.state.moduleA.stateName;// 方法二:借助mapState读取...mapState('moduleA', ['stateName1', 'stateName2']);
开启命名空间后,组件中读取 getters 数据:
// 方法一:自己直接读取this.$store.getters['moduleA/stateName1'];// 方法二:借用mapGetters读取...mapGetters('moduleA', ['getterName1', 'getterName2']);
开启命名空间后,组件中调用 dispatch :
// 方法一:自己直接调用this.$store.dispatch('moduleA/dispatchName', data);// 方法二:借助mapActions调用...mapActions('moudleA', ['dispatchName1', 'dispatchName2']);
开启命名空间后,组件中调用 commit :
// 方法一:自己直接调用this.$store.commit('moduleA/MutationsName', data);// 方法二:借助mapMutations调用...mapMutations('moduleA', ['MutationsName1', 'MutationsName2'])

