初心 & 目标
很早就想通过阅读源码向大神学习了,但由于拖延一直未能开始,这次算是莽一波不再挑来挑去直接开读。
选择 Westwind.ApplicationConfiguration 的原因有三:最近在用,好奇某些问题它是如何解决的,代码量小。
预设目标:
项目结构
Class Structure
This library consists of the main AppConfiguration class plus provider logic. Providers are based on a IConfigurationProvider interface with a ConfigurationProviderBase class providing base functionality.
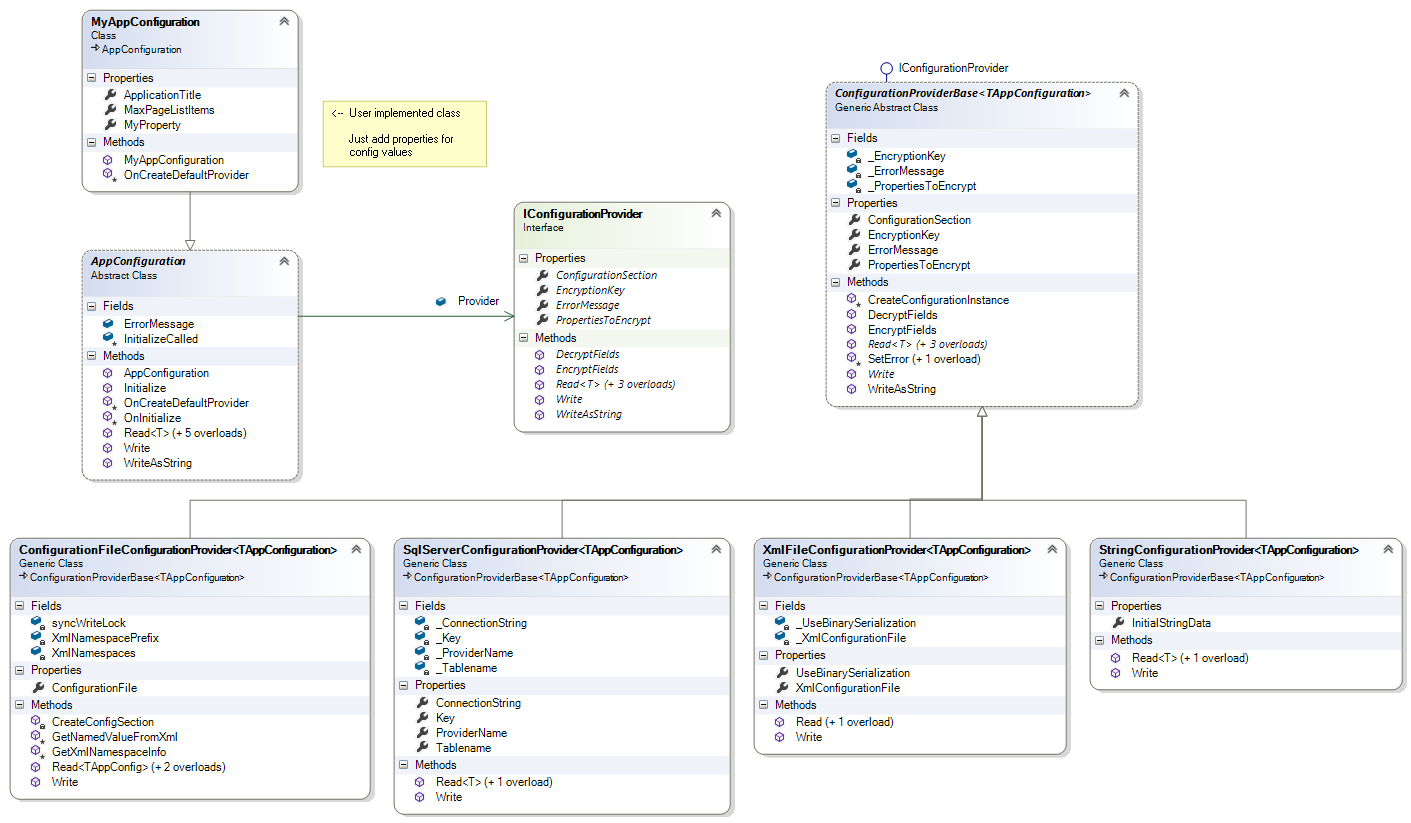
解决方案
有亮点的代码片段
加密 & 解密
源码内完整的加密流程是:
- 传入对象及该对象需加密的属性(或字段)名
- 通过反射获取属性(或字段)值
- 将值转换为字符串(仅支持加密能转换为字符串的属性值)
- Triple DES 加密字符串
下面展示 Encryption.cs 中用于 Triple DES 加密的代码片段:
/// <summary>/// Encrypts a string using Triple DES encryption with a two way encryption key./// String is returned as Base64 encoded value rather than binary./// </summary>/// <param name="inputString"></param>/// <param name="encryptionKey"></param>/// <returns></returns>public static string EncryptString(string inputString, string encryptionKey){return Convert.ToBase64String(EncryptBytes(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(inputString), encryptionKey));}/// <summary>/// Replace this value with some unique key of your own/// Best set this in your App start up in a Static constructor/// </summary>public static string Key = "0a1f131c";/// <summary>/// Encodes a stream of bytes using DES encryption with a pass key. Lowest level method that/// handles all work./// </summary>/// <param name="inputString"></param>/// <param name="encryptionKey"></param>/// <returns></returns>public static byte[] EncryptBytes(byte[] inputString, string encryptionKey){if (encryptionKey == null) encryptionKey = Key;var des = new TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider();var hashmd5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();des.Key = hashmd5.ComputeHash(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(encryptionKey));des.Mode = CipherMode.ECB;ICryptoTransform transform = des.CreateEncryptor();byte[] buffer = inputString;return transform.TransformFinalBlock(buffer,0,buffer.Length);}
解密:
/// <summary>/// Decrypts a string using DES encryption and a pass key that was used for/// encryption./// <seealso>Class wwEncrypt</seealso>/// </summary>/// <param name="decryptString"></param>/// <param name="encryptionKey"></param>/// <returns>String</returns>public static string DecryptString(string decryptString, string encryptionKey){try{return Encoding.ASCII.GetString(DecryptBytes(Convert.FromBase64String(decryptString), encryptionKey));}catch{// Probably not encodedreturn string.Empty;}}/// <summary>/// Decrypts a Byte array from DES with an Encryption Key./// </summary>/// <param name="decryptBuffer"></param>/// <param name="encryptionKey"></param>/// <returns></returns>public static byte[] DecryptBytes(byte[] decryptBuffer, string encryptionKey){if (decryptBuffer == null || decryptBuffer.Length == 0) return null;if (encryptionKey == null) encryptionKey = Key;var des = new TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider();var hashmd5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();des.Key = hashmd5.ComputeHash(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(encryptionKey));des.Mode = CipherMode.ECB;// 创建解密器对象ICryptoTransform transform = des.CreateDecryptor();return transform.TransformFinalBlock(decryptBuffer, 0, decryptBuffer.Length);}
通过反射实现的对象复制
源码:
public const BindingFlags MemberAccess =BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic |BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.IgnoreCase;/// <summary>/// Copies the content of one object to another. The target object 'pulls' properties of the first./// </summary>/// <param name="source"></param>/// <param name="target"></param>/// <param name="excludedProperties"></param>public static void CopyObjectData(object source, Object target, string excludedProperties){CopyObjectData(source, target,excludedProperties, MemberAccess);}/// <summary>/// Copies the data of one object to another. The target object 'pulls' properties of the first./// This any matching properties are written to the target.////// The object copy is a shallow copy only. Any nested types will be copied as/// whole values rather than individual property assignments (ie. via assignment)/// </summary>/// <param name="source">The source object to copy from</param>/// <param name="target">The object to copy to</param>/// <param name="excludedProperties">A comma delimited list of properties that should not be copied</param>/// <param name="memberAccess">Reflection binding access</param>public static void CopyObjectData(object source, object target, string excludedProperties, BindingFlags memberAccess){string[] excluded = null;if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(excludedProperties)){excluded = excludedProperties.Split(new[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);}MemberInfo[] miTarget = target.GetType().GetMembers(memberAccess);foreach (MemberInfo field in miTarget){string name = field.Name;// Skip over any property exceptionsif (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(excludedProperties) && excluded.Contains(name))continue;if (field.MemberType == MemberTypes.Field){FieldInfo sourceField = source.GetType().GetField(name);if (sourceField == null) continue;object sourceValue = sourceField.GetValue(source);((FieldInfo)field).SetValue(target, sourceValue);}else if (field.MemberType == MemberTypes.Property){PropertyInfo piSource = source.GetType().GetProperty(name, memberAccess);if (piSource == null) continue;PropertyInfo piTarget = field as PropertyInfo;if (piTarget != null && piTarget.CanWrite && piSource.CanRead){object sourceValue = piSource.GetValue(source, null);piTarget.SetValue(target, sourceValue, null);}}}}
调用时传入无需复制的属性或字段名(通过 , 分隔):
DataUtils.CopyObjectData(newConfig, config, "Provider,ErrorMessage");
ReflectionUtils.cs 里面还有很多关于反射的应用。
常见类型与字符串间的转换
ConfigurationFileConfigurationProvider.cs 里面的 TypedValueToString 和 StringToTypedValue 方法实现了各种常见类型与 string 间的互相转换(并且考虑了 CultureInfo):
/// <summary>/// Converts a type to string if possible. This method supports an optional culture generically on any value./// It calls the ToString() method on common types and uses a type converter on all other objects/// if available/// </summary>/// <param name="rawValue">The Value or Object to convert to a string</param>/// <param name="culture">Culture for numeric and DateTime values</param>/// <param name="unsupportedReturn">Return string for unsupported types</param>/// <returns>string</returns>private static string TypedValueToString(object rawValue, CultureInfo culture = null, string unsupportedReturn = null){if (rawValue == null) return string.Empty;if (culture == null) culture = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture;Type valueType = rawValue.GetType();string returnValue;if (valueType == typeof(string)){returnValue = rawValue as string;}else if (valueType == typeof(int) || valueType == typeof(decimal) ||valueType == typeof(double) || valueType == typeof(float) || valueType == typeof(Single)){returnValue = string.Format(culture.NumberFormat, "{0}", rawValue);}else if (valueType == typeof(DateTime)){returnValue = string.Format(culture.DateTimeFormat, "{0}", rawValue);}else if (valueType == typeof(bool) || valueType == typeof(Byte) || valueType.IsEnum){returnValue = rawValue.ToString();}else if (valueType == typeof(byte[])){returnValue = Convert.ToBase64String(rawValue as byte[]);}else if (valueType == typeof(Guid?)){if (rawValue == null){returnValue = string.Empty;}else{return rawValue.ToString();}}else if (rawValue is IList){return "ILIST_TYPE";}else{// Any type that supports a type converterTypeConverter converter = TypeDescriptor.GetConverter(valueType);if (converter != null && converter.CanConvertTo(typeof(string)) && converter.CanConvertFrom(typeof(string))){returnValue = converter.ConvertToString(null, culture, rawValue);}else{// Last resort - just call ToString() on unknown typereturnValue = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(unsupportedReturn) ? unsupportedReturn : rawValue.ToString();}}return returnValue;}/// <summary>/// Turns a string into a typed value generically./// Explicitly assigns common types and falls back/// on using type converters for unhandled types./// <seealso>Class ReflectionUtils</seealso>/// </summary>/// <param name="sourceString"> The string to convert from </param>/// <param name="targetType"> The type to convert to </param>/// <param name="culture"> Culture used for numeric and datetime values. </param>/// <returns>object. Throws exception if it cannot be converted.</returns>private static object StringToTypedValue(string sourceString, Type targetType, CultureInfo culture = null){object result = null;bool isEmpty = string.IsNullOrEmpty(sourceString);if (culture == null) culture = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture;if (targetType == typeof(string)){result = sourceString;}else if (targetType == typeof(Int32) || targetType == typeof(int)){result = isEmpty ? 0 : Int32.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(Int64)){result = isEmpty ? (Int64)0 : Int64.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(Int16)){result = isEmpty ? (Int16)0 : Int16.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(decimal)){result = isEmpty ? 0M : decimal.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(DateTime)){result = isEmpty ? DateTime.MinValue : Convert.ToDateTime(sourceString, culture.DateTimeFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(byte)){result = isEmpty ? 0 : Convert.ToByte(sourceString);}else if (targetType == typeof(double)){result = isEmpty ? 0F : Double.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(Single)){result = isEmpty ? 0F : Single.Parse(sourceString, NumberStyles.Any, culture.NumberFormat);}else if (targetType == typeof(bool)){if (!isEmpty &&sourceString.ToLower() == "true" || sourceString.ToLower() == "on" || sourceString == "1"){result = true;}else{result = false;}}else if (targetType == typeof(Guid)){result = isEmpty ? Guid.Empty : new Guid(sourceString);}else if (targetType.IsEnum){result = Enum.Parse(targetType, sourceString);}else if (targetType == typeof(byte[])){result = Convert.FromBase64String(sourceString);}else if (targetType.Name.StartsWith("Nullable`")){if (sourceString.ToLower() == "null" || sourceString == string.Empty){result = null;}else{targetType = Nullable.GetUnderlyingType(targetType);result = StringToTypedValue(sourceString, targetType);}}else{// Check for TypeConverters or FromString static methodTypeConverter converter = TypeDescriptor.GetConverter(targetType);if (converter != null && converter.CanConvertFrom(typeof(string))){result = converter.ConvertFromString(null, culture, sourceString);}else{// Try to invoke a static FromString method if it existstry{var mi = targetType.GetMethod("FromString");if (mi != null){return mi.Invoke(null, new object[] { sourceString });}}catch{// ignore error and assume not supported}Debug.Assert(false, $"Type Conversion not handled in StringToTypedValue for {targetType.Name} {sourceString}");//throw (new InvalidCastException(Resources.StringToTypedValueValueTypeConversionFailed + targetType.Name));}}return result;}
实现跨项目引用同一配置
看 Westwind.ApplicationConfiguration 的介绍时就很好奇它是如何实现的多个项目可以引用同一个配置,而且在任意项目中都可以更新配置。
看了源码后才意识到是我想太多了,其实并不复杂,核心就在于 —— 保证不同项目能对同一个配置实体进行读写。
Westwind.ApplicationConfiguration 支持多个类型的配置实体,它们大致分为三类:
- 文件类,其本质就是一个 XML 或 Json 文件
- 数据库类,其本质就是数据库中的一张表
- .NET config 类,根据项目类型不同,其本质就是一个 Web.config 或 App.config 文件
文件类
这是最简单的:
- 使用属性存储配置文件路径,保证读写的都是同一文件
- 读取配置对应 Open FileStream
- 写入配置对应 Write FileStream
数据库类
- 使用属性存储数据库连接字符串和表名,保证读写的都是同一张表
- 配置表只有两列,一列存配置名,一列存配置序列化后的字符串
CREATE TABLE [{Tablename}] ( [id] [int] , [ConfigData] [ntext] )
- 读取配置对应
SELECT - 写入配置对应
UPDATE
.NET config 类
首先要有个认知 —— .NET config 文件本质上是一个 XML 文件。
- 当指定了配置文件路径时底层逻辑和 文件类 相似
- 未指定配置文件路径时:
- 文件路径使用
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.SetupInformation.ConfigurationFile,保证读写同一文件 - 读取配置对应
XmlDocument.Load - 写入配置对应
XmlDocument.Save
- 文件路径使用
注:读写过程中还经常使用 ConfigurationManager.RefreshSection 来刷新配置的命名节,以保证配置的时效性。
编码技巧
方法返回值优先选择表征执行状态的值
很多方法既要返回执行结果又要返回执行状态(例如执行是否成功和状态代码等),对于这类方法推荐优先选择表征执行状态的值作为方法的返回值。
例如将对象序列化为字符串的 SerializeObject 方法执行后会有两个返回值,一是序列化是否成功(bool),二是序列化后得到的字符串(string)。在这种情况下有两种选择:
- 方法返回 string,序列化是否成功通过 out 传出
- 方法返回 bool,序列化字符串通过 out 传出
两种选择哪个更好,我们只需看看调用 SerializeObject 的代码便能理解:
// 方案 1public static string SerializeObjectToString(object instance){var xmlResultString = SerializeObject(instance, out bool serializeSuccess);if (!serializeSuccess) return null;return xmlResultString;}// 方案 2public static string SerializeObjectToString(object instance){if (!SerializeObject(instance, out string xmlResultString)) return null;return xmlResultString;}
不难看出,对于即返回执行结果又返回执行状态的方法,因为调用方在调用它们时大概率会优先关心执行状态,在确定执行状态后才会去使用具体的执行结果,所以从调用方的角度来看方案 2 的 SerializeObject 用起来更顺手,代码也更简洁。

