什么是表达式:An expressions is a syntactic entity whose evaluation either produces a value or fails to terminate, in which case the expression is undefined.
evaluate a single value, object, method, or namespace
Single Value
int x = 100;x++;++x;
Object
(new Form()).ShowDialog();
Method
// Console.WriteLine 就是方法Action myActino = new Action(Console.WriteLine);
Namespace
// System.Windows.Forms 名称空间访问表达式System.Windows.Forms.Form myForm = new Form();
各类表达式概览

C# 语言中表达式的分类
- A value. Every value has an associated type.
回顾上一节讲的操作符,并讲解由这些操作符组成的表达式所返回的类型。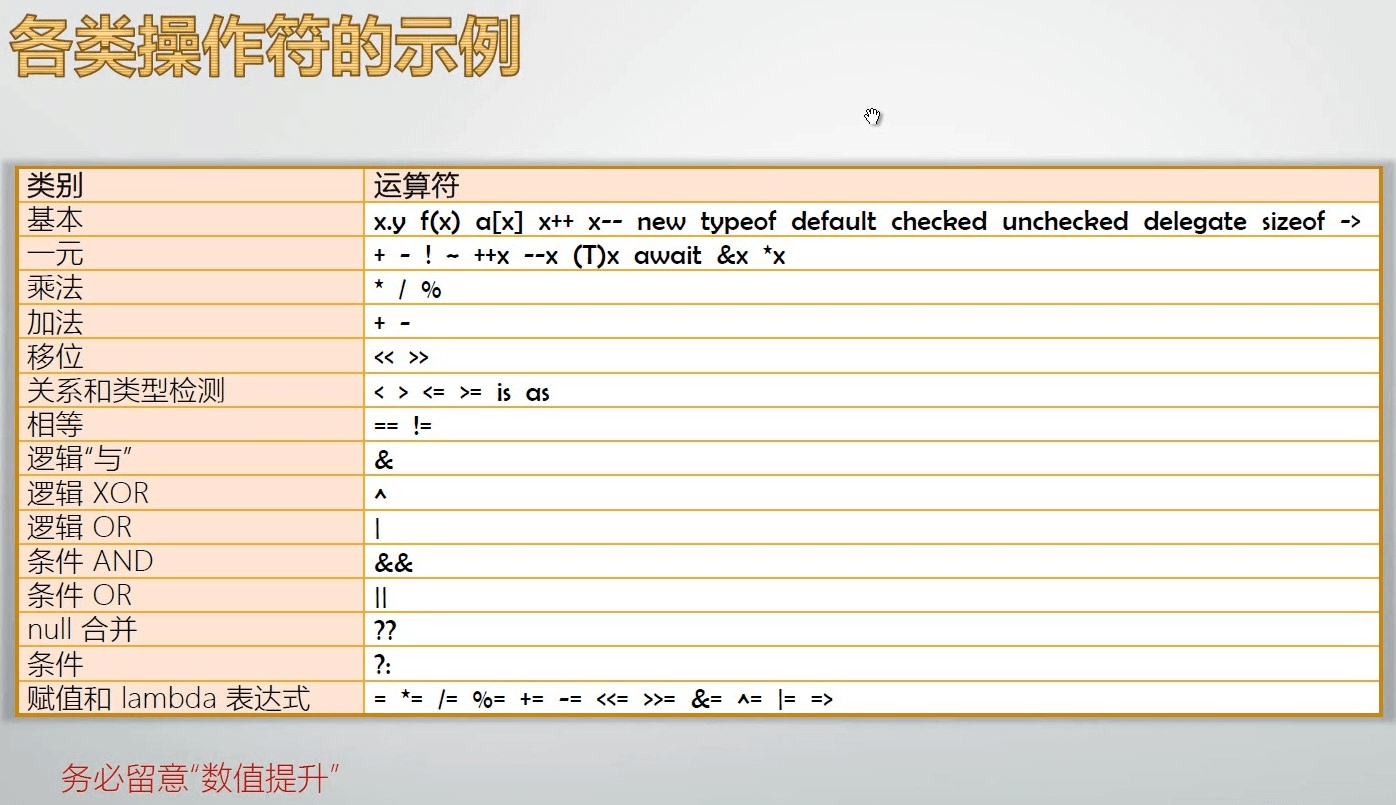
:::info
条件操作符?:总会返回精度高的那个类型:如此处尽管返回的值为2,但是它的数据类型为double
:::
var x = 5>3?2:3.0;Console.WriteLine(x.GetType().FullName);// System.Double
A variable. Every variable has an associated type.
int x = 100;int y;y = x;
A namespace.
System.Windows.Forms.Form myForm = new Form();
A type.
var t = typeof(Int32);
A method group
Console.WriteLine,这是一组方法(19 种重载),重载决策决定具体调用那种方法。A null literal.
null 值也是一个值。Form myForm = null;
A property access.
- An event access. ```csharp static void Main(string[] args) { var myForm = new Form(); // 访问属性 myForm.Text = “Hello”; // 访问事件 myForm.Load += MyForm_Load; myForm.ShowDialog(); }
private static void MyForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { var form = sender as Form; if (form == null) { return; }
form.Text = "New Title";
}
- An indexer access.```csharpvar intList = new List<int>() {1, 2, 3 };var x = intList[2];
- Nothing.对返回值为 void 方法的调用
复合表达式的求值
C#语言定义文档里面未明确定义复合表达式,但确实常用。
注意操作符的优先级和同优先级操作符的运算方向(除了赋值操作符,基本都是从左向右)。
参考C#语言定义文档
第七章专门讲表达式。
对于初学者,仅作参考,不必深究 —— 毕竟我们是在学习语言、不是去实现这门语言。
语句的定义
广义:
狭义:
实例讲解高级语言与低级语言的差异
C 版本
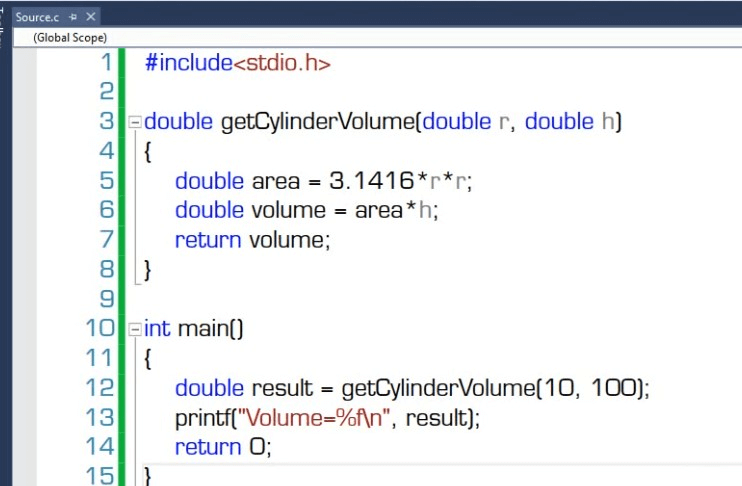


C# 版本
C# 看汇编输出
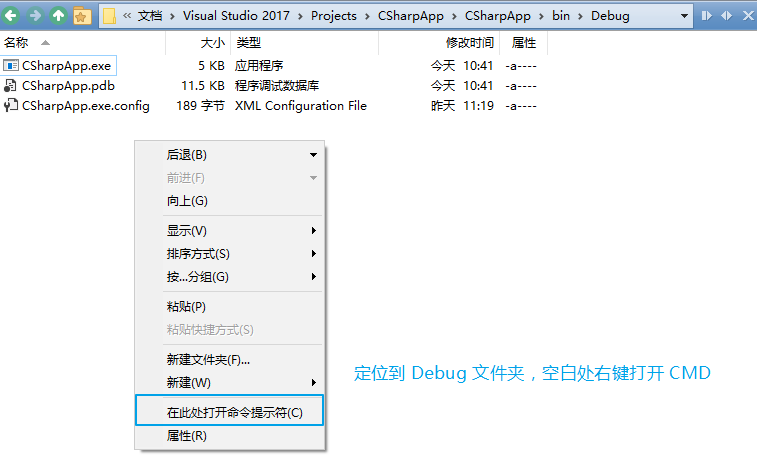
- 找到编译的 Application
- 在电脑里面搜索找到 Developer Command Prompt
- 输入 ildasm 命令
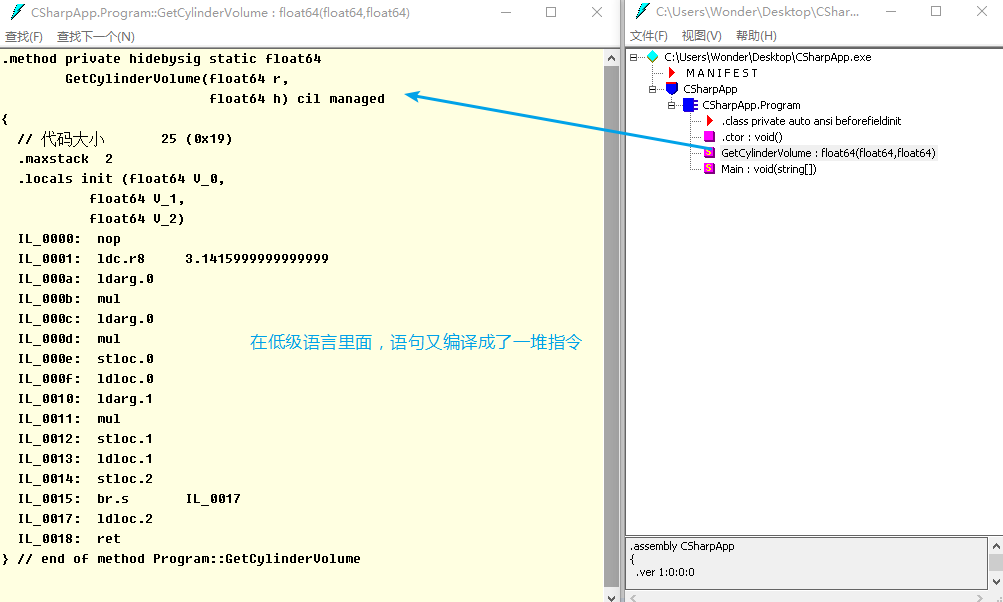
- 用 ildasm 工具打开第 1 步找到的 Application

- 双击具体方法,查看编译结果
PS:现在推荐使用 dotPeek 进行反编译。
实例演示控制流(flow of control)
static void Main(string[] args){string input = Console.ReadLine();try{double score = double.Parse(input);if (score >= 60){Console.WriteLine("Pass!");}else{Console.WriteLine("Failed!");}}catch{Console.WriteLine("Not a number!");}}
程序没变,控制流变了。 
语句详解

嵌入式语句
声明语句
讲解了局部变量声明与局部常量声明,详情参见C#语言定义文档。
表达式语句

expression-statement 用于计算所给定的表达式。由此表达式计算出来的值(如果有)被丢弃。
static void Main(string[] args){// Add 产生的 7.0,如果前面没有拿变量接收它,值被丢弃了。Add(3.0, 4.0);}static double Add(double a,double b){return a + b;}
Single Responsibility 单一职责原则:一个方法尽量只做一件事情。
下面 x+y 这种语句在 C 语言里面是允许的,在 C# 里面不允许。
int x = 100;int y = 200;x+y;
块语句

- 块语句无论什么时候都被编译器当做一条语句来看待
- 编译器认为块语句是一条完整的语句(即块语句最后不用加
;号)
Code Snippet Ctrl + }:跳转至该花括号对应的花括号处。
变量的作用域:块之内声明的变量,作用域仅在块内。
static void Main(string[] args){int x = 100;{Console.WriteLine(x);int y = 200;Console.WriteLine(y);}// Error CS0103 当前上下文中不存在名称“y”Console.WriteLine(y);}
选择(判断、分支)语句

if 语句
 :::tips
假如这里增加多条语句,只会执行一句语句。
:::
编程规范推荐即使只有一条语句,也建议使用块语句。
:::info
Code Snippet:自动跳转到块中
:::
:::tips
假如这里增加多条语句,只会执行一句语句。
:::
编程规范推荐即使只有一条语句,也建议使用块语句。
:::info
Code Snippet:自动跳转到块中
:::

程序员经常修缮前人代码以满足新需求,但因为需求变化(需要实现新逻辑) + 业务逻辑复杂(不敢修改旧代码),导致写出来的代码很臃肿,还很容易陷入思维定式。
无论多长的if else,它都是一条语句。之所以能有**else if{}这种结构,也是因为if{}**是一条语句。
switch 语句

int score = 101;switch (score/10){case 10:if (score==100){goto case 8;}else{goto default;}// 只有单独的标签才能连起来写。case 8:case 9:// 一旦有了具体的 section,就必需配套 break。Console.WriteLine("A");break;...default:break;}
:::info Code Snippet:自动补全枚举的所有情况 :::
- Ctrl + L 剪切一整行

try 语句

可以通过 MSDN 查方法相应的异常。
如 Int32.Parse 方法 (String) 就有以下异常。
- 应该把释放系统资源的语句写在 finally block 里面
- 有时候也在 finally block 里面写 log
throw 将异常抛给调用者。
throw 关键字的语法比较灵活。
try{...}catch(OverflowException){throw;}
迭代(循环)语句
- while 语句按不同条件执行一个嵌入语句零次或多次
- do 语句按不同条件执行一个嵌入语句一次或多次
- for 语句计算一个初始化表达式序列,然后,当某个条件为真时,重复执行相关的嵌入语句并计算一个迭代表达式序列
- foreach 语句用于枚举一个集合的元素,并对该集合中的每个元素执行一次相关的嵌入语句
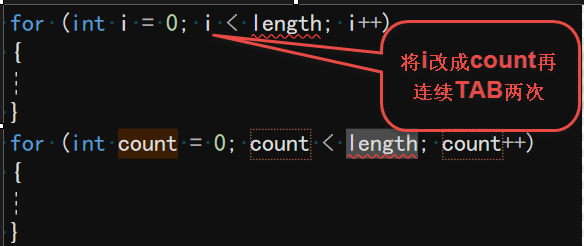
for 循环圆括号里面的的三部分都是 opt 可选的(两个分号不能省略),由此可以组成许多平时用不到的奇葩结构。 :::info Code Snipet:for+tab+tab->更改变量+tab+tab :::
//死循环for(;;){}
遍历和迭代器
Array 实现了 IEnumerable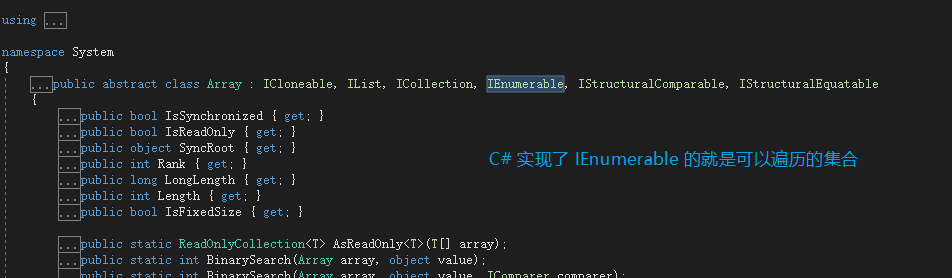


集合遍历的底层原理和迭代器,foreach 语句就是对集合遍历的简记法。
static void Main(string[] args){var intArray = new int[] { 1, 3, 5 ,7};IEnumerator enumerator = intArray.GetEnumerator();while (enumerator.MoveNext()){Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);}var intList = new List<int>() { 2, 4, 6, 8 };IEnumerator enumerator2 = intList.GetEnumerator();while (enumerator2.MoveNext()){Console.WriteLine(enumerator2.Current);}}
跳转语句
- continue 语句将开始直接封闭它的 while、do、for 或 foreach 语句的一次新迭代
- break 语句将退出直接封闭它的 switch、while、do、for 或 foreach 语句
- goto 语句将控制转到由标签标记的语句
- goto 语句基本被淘汰
- goto 语句基本被淘汰
- throw 语句将引发一个异常
- throw 语句语法比较灵活,它后面可以什么都不跟
- throw 语句语法比较灵活,它后面可以什么都不跟
- return 语句会将控制返回到出现 return 语句的函数的当前调用方
- 提前 return 原则
- 方法的每个分支里面都需要有 return
- 提前 return 原则
尽早return 原则
通过提前 return 可以让代码阅读者立刻就鉴别出来程序将在什么情况下 return,同时减少 if else 嵌套,写出更优雅的代码。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Greeting("Mr.Duan");}static void Greeting(string name){if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name)){// 通过尽早 return 可以让代码阅读者立刻就鉴别出来// name 参数在什么情况下是有问题的return;}Console.WriteLine("Hello, {0}", name);}}