扩展运算符与 rest 参数达成的效果真好相反
扩展运算符
把数组或者类数组展开成用逗号隔开的值
与解构赋值相结合
扩展运算符与 函数参数 的 解构赋值相结合
let arr = [1, 2, 3];function foo(a,b,c) {console.log(a, b, c);}foo(...arr) // 1 2 3
合并数组
ES5中的方法 Array.prototype.push.apply()
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3];let arr2 = [4, 5, 6];Array.prototype.push.apply(arr1, arr2);console.log('arr1: ', arr1);// arr1: (6) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
ES6中的做法 使用 扩展运算符
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3];let arr2 = [4, 5, 6];arr1.push(...arr2)console.log('es6 的 arr1: ', arr1);// es6 的 arr1: (6) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
拆分字符串
let str1 = 'imooc'let str2 = '学习es6语法'const arr1 = [...str1]const arr2 = [...str2]console.log('arr imooc', arr1)console.log('arr 学习', arr2);// arr imooc (5) ["i", "m", "o", "o", "c"]// arr 学习 (7) ["学", "习", "e", "s", "6", "语", "法"]
默认将字符串中的每个字符拆分,然后用逗号分隔成数组, 并且 兼容 数字,字母,汉字
rest 参数/ 剩余运算符
把逗号隔开的值组合成一个数组,
不定参数的求和
ES5 的方式
这里的 argument 代表的就是方法的形参,这是一个伪数组
function foo(x, y,z) {let sum = 0Array.prototype.forEach.call(arguments, function (item) {sum += item})return sum}console.log(foo(1, 2)); // 3console.log(foo(1, 2, 3)); // 6
ES6 处理 伪数组的方式
使用 Array.from() 的方式将 伪数组 转化成正常数组 ,然后遍历
function foo(x, y, z) {let sum = 0Array.from(arguments).forEach(item => {sum += item});return sum}console.log(foo(1, 2)); // 3console.log(foo(1, 2, 3)); // 6
ES6 的 rest参数方式, 处理求和
首先了解 rest参数具体是什么
function foo(...args) {console.log(args)}foo(1, 2, 3, 4);foo(11, 22, 33, 44);

由此可知,rest 参数,会自动将传入的参数转化成一个数组,由此求和就简单了很多
function foo(...args) {
let sum = 0
args.forEach(value => {
sum += value
});
return sum
}
console.log(foo(1, 2, 3, 4)); // 10
console.log(foo(11, 22, 33, 44)); // 110
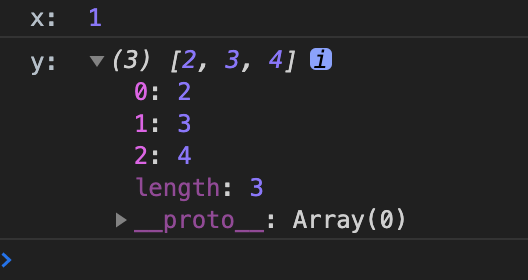
剩余运算符的应用
function foo(x, ...y) {
console.log('x: ', x);
console.log('y: ', y)
}
foo(1, 2, 3, 4);
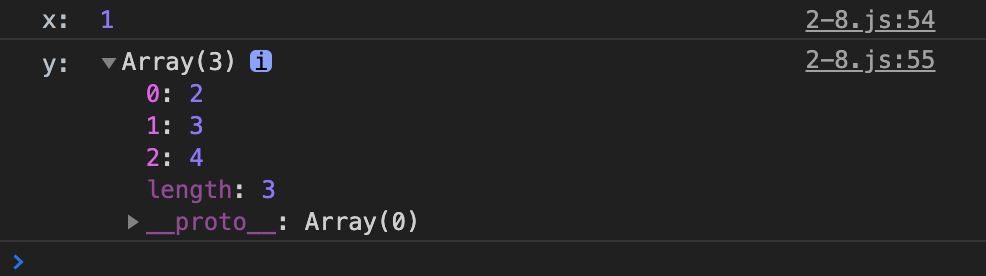
与解构赋值相结合
let [x, ...y] = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log('x: ', x);
console.log('y: ', y);