一、目标
(1)了解Mycat提供的读写分离功能。
(2)了解MySQL数据库的主从架构。
(3)构建以Mycat为中间件的读写分离数据库集群。
二、分析
1. 规划节点
使用Mycat作为数据库中间件服务构建读写分离的数据库集群,节点规划
| IP | 主机名 | 节点 |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.200.30 | mycat | Mycat中间件服务节点 |
| 192.168.200.40 | db1 | MariaDB数据库集群主节点 |
| 192.168.200.50 | db2 | MariaDB数据库集群从节点 |
2. 基础准备
使用CentOS 7.2系统,flavor使用2vCPU/4G内存/50G硬盘,创建3台虚拟机进行实验。
其中2台虚拟机db1和db2部署MariaDB数据库服务,搭建主从数据库集群;一台作为主节点,负责写入数据库信息;另一台作为从节点,负责读取数据库信息。
使用一台虚拟机部署Mycat数据库中间件服务,将用户提交的读写操作识别分发给相应的数据库节点。这样将用户的访问操作、数据库的读与写操作分给3台主机,只有数据库集群的主节点接收增、删、改SQL语句,从节点接收查询语句,分担了主节点的查询压力。
Yum源使用提供的gpmall-repo文件夹作为本地源,Mycat组件使用提供的Mycat-server-1.6-RELEASE-20161028204710-linux.tar.gz压缩包安装。
三、实施
1. 基础环境配置
(1)修改主机名
使用hostnamectl命令修改3台主机的主机名。
Mycat节点修改主机名命令:
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname mycat[root@localhost ~]# su[root@mycat ~]#
db1节点修改主机名命令:
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname db1[root@localhost ~]# su[root@db1 ~]#
db2节点修改主机名命令:
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname db2[root@localhost ~]# su[root@db2 ~]#
(2)编辑hosts文件
3台集群虚拟机的/etc/hosts文件配置部分:
[root@mycat ~]# cat /etc/hosts127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6192.168.200.30 mycat192.168.200.40 db1192.168.200.50 db2
(3)配置Yum安装源
数据库集群需要安装MariaDB数据库服务,需要给集群虚拟机配置Yum安装源文件,使用提供的gpmall-repo文件上传至3个虚拟机的/opt目录下,设置本地Yum源。
首先将3个节点/etc/yum.repo.d目录下的文件移动到/media下,命令如下:
[root@mycat ~]# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/* /media/
3台集群虚拟机的Yum安装源文件配置部分:
# 创建文件夹[root@mycat ~]# mkdir /opt/gpmall-repo# 挂载光驱[root@mycat ~]# mount -o loop /dev/cdrom /opt/gpmall-repo# 配置yum源[root@mycat ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo[mariadb]name=mariadbbaseurl=file:///opt/gpmall-repogpgcheck=0enabled=1# 加载及清理[root@mycat ~]# yum clean all[root@mycat ~]# yum repolist
(4)安装JDK环境
部署Mycat中间件服务需要先部署JDK 1.7或以上版本的JDK软件环境,这里部署JDK 1.8版本。
Mycat节点安装Java环境:
[root@mycat ~]# yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel[root@mycat ~]# java -versionopenjdk version "1.8.0_65"OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_65-b17)OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.65-b01, mixed mode)
(5)关闭防火墙(全部节点)
[root@mycat ~]# iptables -F[root@mycat ~]# iptables -X[root@mycat ~]# iptables -Z[root@mycat ~]# iptables-save# Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Wed Sep 15 18:31:02 2021*filter:INPUT ACCEPT [4:264]:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]:OUTPUT ACCEPT [3:292]COMMIT# Completed on Wed Sep 15 18:31:02 2021[root@mycat ~]# systemctl status firewallld● firewallld.serviceLoaded: not-found (Reason: No such file or directory)Active: inactive (dead)
2. 部署MariaDB主从数据库集群服务
(1)安装MariaDB服务
通过YUM命令在db1和db2虚拟机节点上安装MariaDB服务,命令如下:
[root@db1 ~]# yum install -y mariadb mariadb-server[root@db2 ~]# yum install -y mariadb mariadb-server
2个节点启动MariaDB服务,并设置MariaDB服务为开机自启。
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl start mariadb[root@db1 ~]# systemctl enable mariadbCreated symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.[root@db2 ~]# systemctl start mariadb[root@db2 ~]# systemctl enable mariadbCreated symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
(2)初始化MariaDB数据库
在db1和db2虚拟机节点上初始化MariaDB数据库,并设置MariaDB数据库root访问用户的密码为123456。
[root@db1 ~]# mysql_secure_installation/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation:行379: find_mysql_client: 未找到命令NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDBSERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the currentpassword for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, andyou haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,so you should just press enter here.Enter current password for root (enter for none): # 默认按回车OK, successfully used password, moving on...Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDBroot user without the proper authorisation.Set root password? [Y/n] yNew password: # 输入数据库root密码123456Re-enter new password: # 重复输入密码123456Password updated successfully!Reloading privilege tables..... Success!By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyoneto log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created forthem. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installationgo a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into aproduction environment.Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y... Success!Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. Thisensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n... skipping.By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone canaccess. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removedbefore moving into a production environment.Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y- Dropping test database...... Success!- Removing privileges on test database...... Success!Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so farwill take effect immediately.Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y... Success!Cleaning up...All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDBinstallation should now be secure.Thanks for using MariaDB!
(3)配置数据库集群主节点
编辑主节点db1虚拟机的数据库配置文件my.cnf,在配置文件my.cnf中增添下面的内容:
[root@db1 ~]# vim /etc/my.cnflog_bin = mysql-binbinlog_ignore_db = mysqlserver_id = 40# 以下是配置文件内容[mysqld]log_bin = mysql-bin # 记录操作日志binlog_ignore_db = mysql # 不同步MySQL系统数据库server_id = 40 # 数据库集群中的每个节点id都要不同,一般使用IP地址的最后段的数字,例如192.168.200.40,server_id就写40datadir=/var/lib/mysqlsocket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security riskssymbolic-links=0[mysqld_safe]log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.logpid-file=/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid
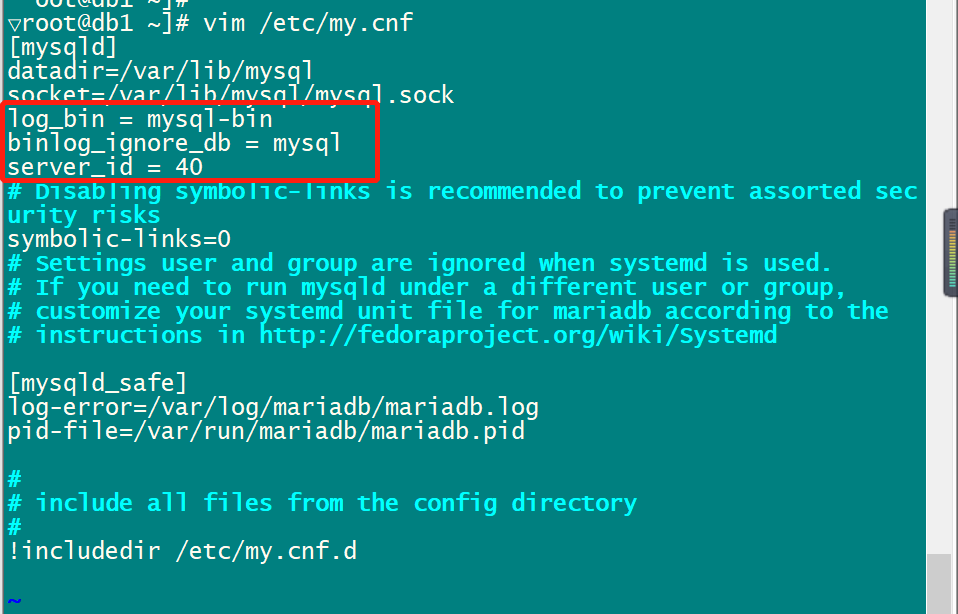
编辑完成配置文件my.cnf后,重启MariaDB服务。
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
(4)开放主节点的数据库权限
在主节点db1虚拟机上使用mysql命令登录MariaDB数据库,授权在任何客户端机器上可以以root用户登录到数据库。
[root@db1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.Your MariaDB connection id is 2Server version: 5.5.44-MariaDB-log MariaDB ServerCopyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by "123456";Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]>
在主节点db1数据库上创建一个user用户让从节点db2连接,并赋予从节点同步主节点数据库的权限,命令如下:
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by "123456";
(5)配置从节点db2同步主节点db1
在从节点db2虚拟机上使用mysql命令登录MariaDB数据库,配置从节点连接主节点的连接信息。master_host为主节点主机名db1,master_user为在步骤(4)中创建的用户user,命令如下:
[root@db2 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.Your MariaDB connection id is 9Server version: 5.5.44-MariaDB MariaDB ServerCopyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='db1',master_user='user',master_password='123456';Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]>
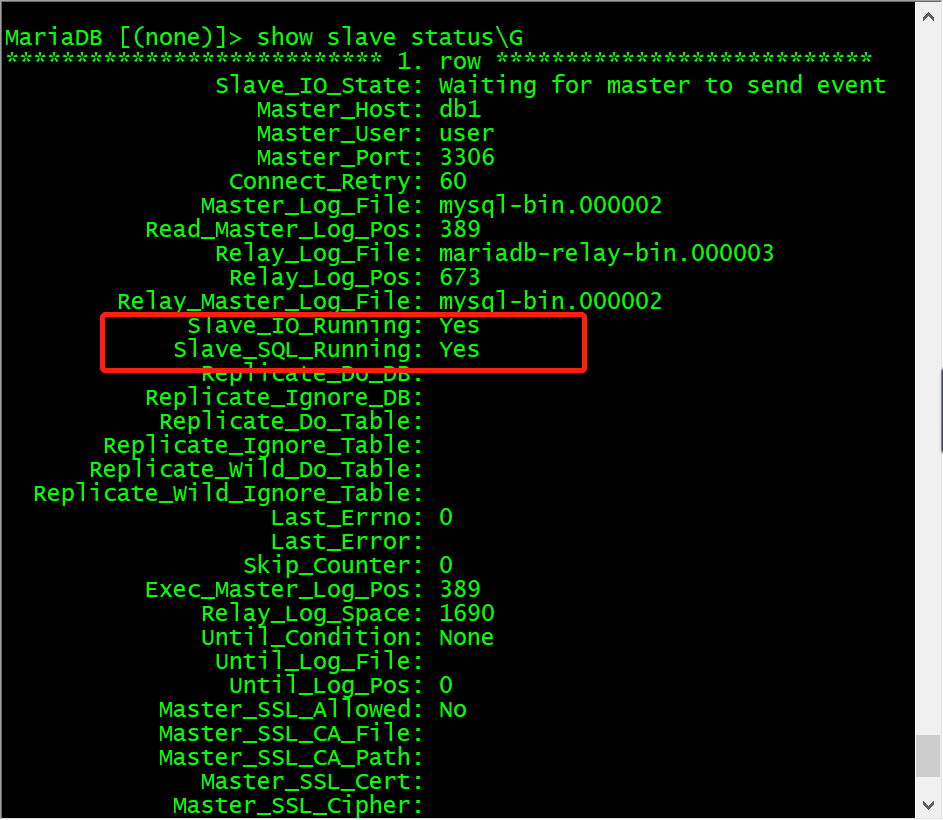
配置完毕主从数据库之间的连接信息之后,开启从节点服务。使用show slave status\G; 命令并查看从节点服务状态,如果Slave_IO_Running和Slave_SQL_Running的状态都为YES,则从节点服务开启成功。
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G*************************** 1. row ***************************Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send eventMaster_Host: db1Master_User: userMaster_Port: 3306Connect_Retry: 60Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002Read_Master_Log_Pos: 389Relay_Log_File: mariadb-relay-bin.000003Relay_Log_Pos: 673Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002Slave_IO_Running: YesSlave_SQL_Running: YesReplicate_Do_DB:Replicate_Ignore_DB:Replicate_Do_Table:Replicate_Ignore_Table:Replicate_Wild_Do_Table:Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table:Last_Errno: 0Last_Error:Skip_Counter: 0Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 389Relay_Log_Space: 1690Until_Condition: NoneUntil_Log_File:Until_Log_Pos: 0Master_SSL_Allowed: NoMaster_SSL_CA_File:Master_SSL_CA_Path:Master_SSL_Cert:Master_SSL_Cipher:Master_SSL_Key:Seconds_Behind_Master: 0Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: NoLast_IO_Errno: 0Last_IO_Error:Last_SQL_Errno: 0Last_SQL_Error:Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids:Master_Server_Id: 401 row in set (0.00 sec)
(6)验证主从数据库的同步功能
先在主节点db1的数据库中创建库test,并在库test中创建表company,插入表数据。创建完成后,查看表company数据,如下所示:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database test;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]> use testDatabase changedMariaDB [test]> create table company(id int not null primary key,name varchar(50),addr varchar(255));Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)MariaDB [test]> insert into company values(1,"facebook","usa");Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)MariaDB [test]> select * from company;+----+----------+------+| id | name | addr |+----+----------+------+| 1 | facebook | usa |+----+----------+------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
这时从节点db2的数据库就会同步主节点数据库创建的test库,可以在从节点查询test数据库与表company,如果可以查询到信息,就能验证主从数据库集群功能在正常运行。查询结果如下所示:
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;+--------------------+| Database |+--------------------+| information_schema || mysql || performance_schema || test |+--------------------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]> select * from test.company;+----+----------+------+| id | name | addr |+----+----------+------+| 1 | facebook | usa |+----+----------+------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3. 部署Mycat读写分离中间件服务
(1)安装Mycat服务
将Mycat服务的二进制软件包Mycat-server-1.6-RELEASE-20161028204710-linux.tar.gz上传到Mycat虚拟机的/root目录下,并将软件包解压到/use/local目录中。赋予解压后的Mycat目录权限。
[root@mycat ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfgMycat-server-1.6-RELEASE-20161028204710-linux.tar.gz[root@mycat ~]# tar -zxvf Mycat-server-1.6-RELEASE-20161028204710-linux.tar.gz -C /usr/local/[root@mycat ~]# chown -R 777 /usr/local/mycat/
在/etc/profile系统变量文件中添加Mycat服务的系统变量,并生效变量。
[root@mycat ~]# echo export MYCAT_HOME=/usr/local/mycat/ >> /etc/profile[root@mycat ~]# source /etc/profile
(2)编辑Mycat的逻辑库配置文件
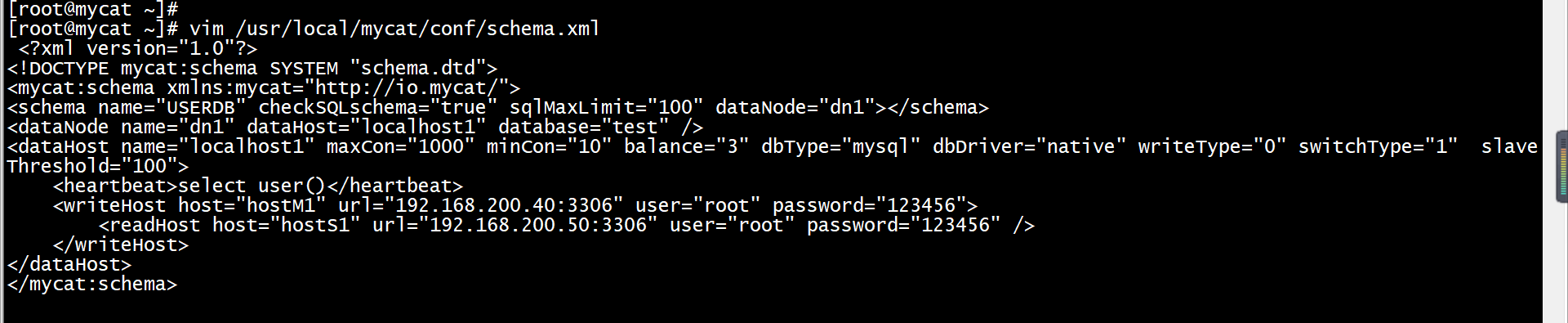
配置Mycat服务读写分离的schema.xml配置文件在/usr/local/mycat/conf/目录下,可以在文件中定义一个逻辑库,使用户可以通过Mycat服务管理该逻辑库对应的MariaDB数据库。在这里定义一个逻辑库schema,name为USERDB;该逻辑库USERDB对应数据库database为test(在部署主从数据库时已安装);设置数据库写入节点为主节点db1;设置数据库读取节点为从节点db2。(可以直接删除原来schema.xml的内容,替换为如下。)
注意:IP需要修改成实际的IP地址。
[root@mycat ~]# vim /usr/local/mycat/conf/schema.xml<?xml version="1.0"?><!DOCTYPE mycat:schema SYSTEM "schema.dtd"><mycat:schema xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/"><schema name="USERDB" checkSQLschema="true" sqlMaxLimit="100" dataNode="dn1"></schema><dataNode name="dn1" dataHost="localhost1" database="test" /><dataHost name="localhost1" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="3" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native" writeType="0" switchType="1" slaveThreshold="100"><heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat><writeHost host="hostM1" url="192.168.200.40:3306" user="root" password="123456"><readHost host="hostS1" url="192.168.200.50:3306" user="root" password="123456" /></writeHost></dataHost></mycat:schema>
代码说明:
⚪sqlMaxLimit:配置默认查询数量。
⚪database:为真实数据库名。
⚪ balance=”0”:不开启读写分离机制,所有读操作都发送到当前可用的writeHost上。
⚪balance=”1”:全部的readHost与stand by writeHost参与select语句的负载均衡,简单来说,当双主双从模式(M1->S1,M2->S2,并且M1与M2互为主备),正常情况下,M2、S1、S2都参与select语句的负载均衡。
⚪ balance=”2”:所有读操作都随机的在writeHost、readhost上分发。
⚪ balance=”3”:所有读请求随机地分发到wiriterHost对应的readhost执行,writerHost不负担读压力,注意balance=3只在1.4及其以后版本有,1.3版本没有。
⚪ writeType=”0”:所有写操作发送到配置的第一个writeHost,第一个挂了需要切换到还生存的第二个writeHost,重新启动后已切换后的为准,切换记录在配置文件dnindex.properties中。
⚪ writeType=”1”:所有写操作都随机的发送到配置的writeHost。
(3)修改配置文件权限
修改schema.xml的用户权限,命令如下:
[root@mycat ~]# chown root:root /usr/local/mycat/conf/schema.xml
(4)编辑mycat的访问用户
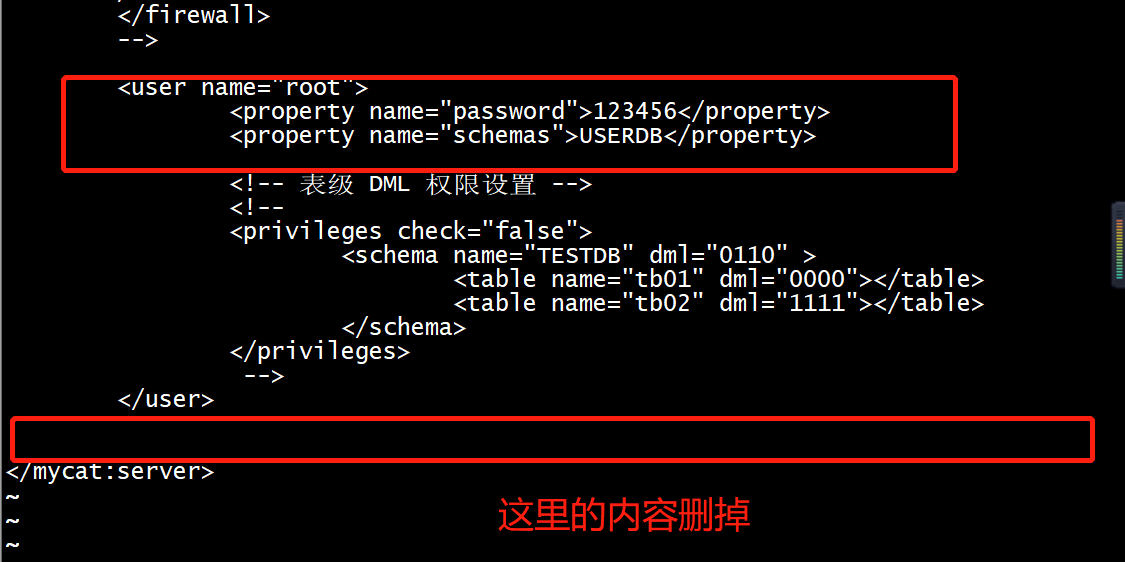
修改/usr/local/mycat/conf/目录下的server.xml文件,修改root用户的访问密码与数据库,密码设置为123456,访问Mycat的逻辑库为USERDB,命令如下:
[root@mycat ~]# vim /usr/local/mycat/conf/server.xml<user name="root"><property name="password">123456</property><property name="schemas">USERDB</property></user>
然后删除如下几行:
<user name="user"><property name="password">user</property><property name="schemas">TESTDB</property><property name="readOnly">true</property></user>
(5)启动Mycat服务
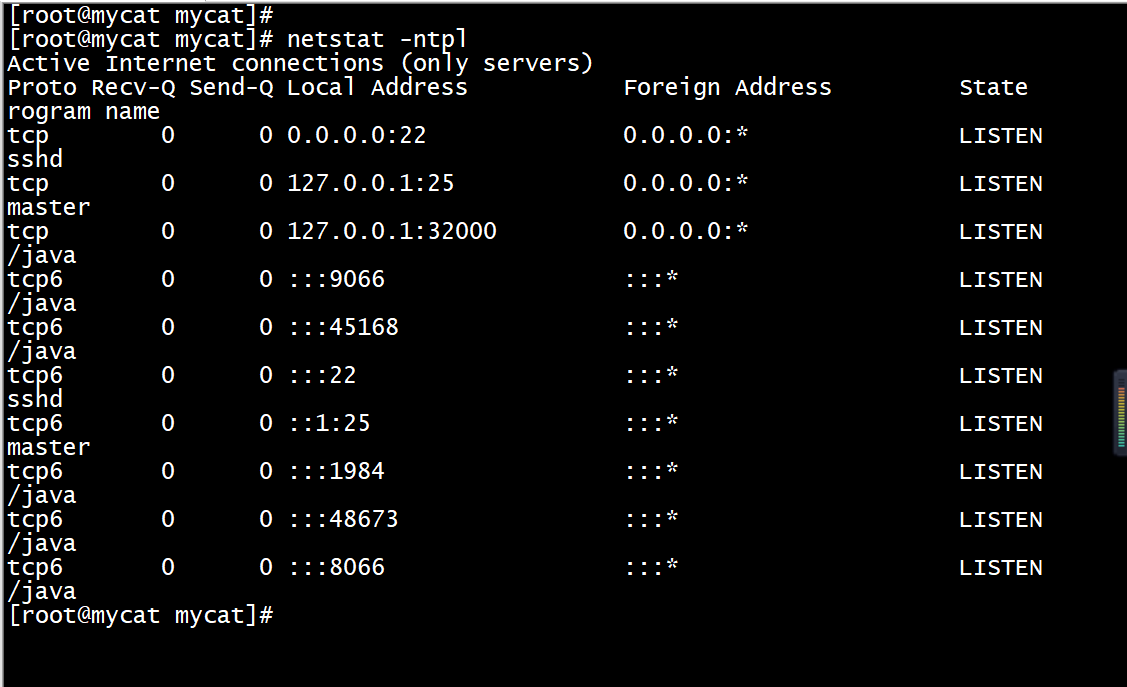
通过命令启动Mycat数据库中间件服务,启动后使用netstat -ntpl命令查看虚拟机端口开放情况,如果有开放8066和9066端口,则表示Mycat服务开启成功。端口查询情况如下图所示。
[root@mycat ~]# /bin/bash /usr/local/mycat/bin/mycat startStarting Mycat-server...[root@mycat mycat]# netstat -ntplActive Internet connections (only servers)Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program nametcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1091/sshdtcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1420/mastertcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:32000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13689/javatcp6 0 0 :::9066 :::* LISTEN 13689/javatcp6 0 0 :::45168 :::* LISTEN 13689/javatcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1091/sshdtcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1420/mastertcp6 0 0 :::1984 :::* LISTEN 13689/javatcp6 0 0 :::48673 :::* LISTEN 13689/javatcp6 0 0 :::8066 :::* LISTEN 13689/java
4. 验证数据库集群服务读写分离功能
上传压缩包gpmall-repo
# 安装依赖[root@mycat ~]# yum install -y unzip# 解压[root@mycat ~]# unzip gpmall-repo.zip# 移动到/mnt下[root@mycat ~]# mv gpmall-repo /mnt/# 因为我之前挂载的路径冲突,所以我需要修改一下yum路径[root@mycat ~]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo[mariadb]name=mariadbbaseurl=file:///mnt/gpmall-repogpgcheck=0enabled=1[root@mycat ~]# yum clean all[root@mycat ~]# yum repolist
(1)用Mycat服务查询数据库信息
先在Mycat虚拟机上使用Yum安装mariadb-client服务。
[root@mycat ~]# yum install -y MariaDB-client
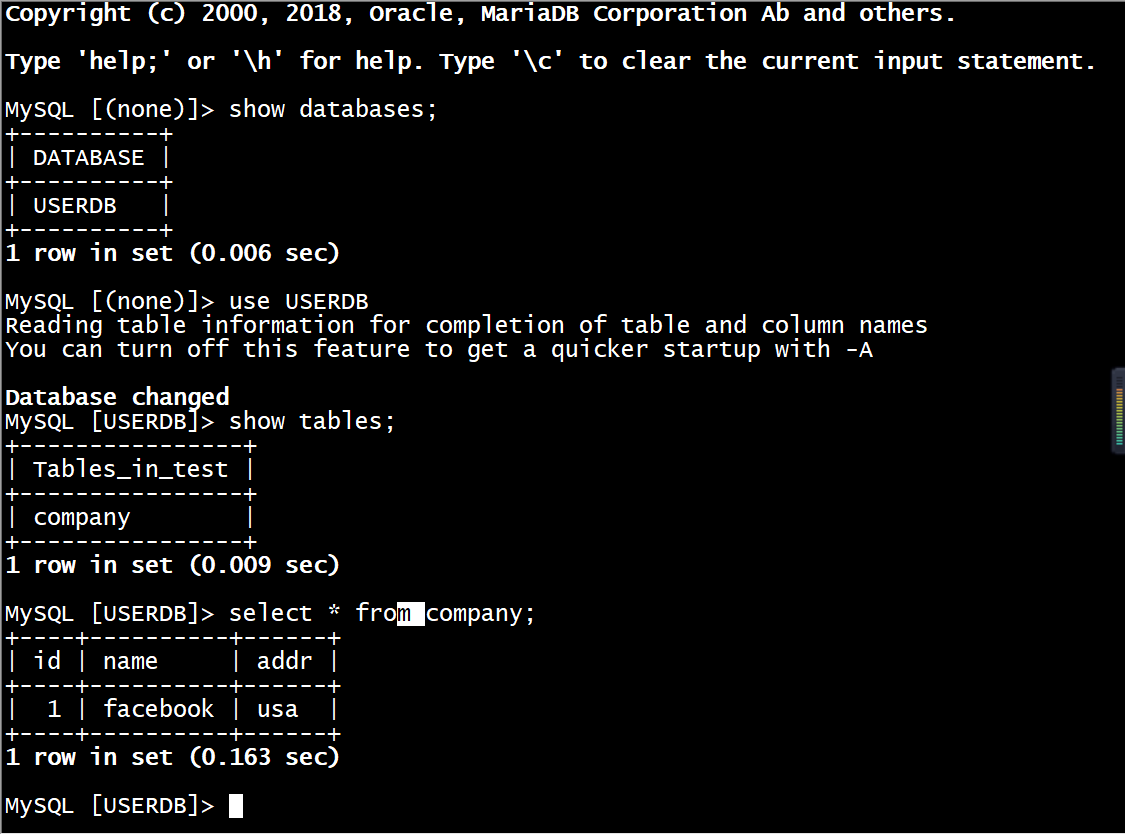
在Mycat虚拟机上使用mysql命令查看Mycat服务的逻辑库USERDB,因为Mycat的逻辑库USERDB对应数据库test(在部署主从数据库时已安装),所以可以查看库中已经创建的表company。命令如下。
[root@mycat ~]# mysql -h127.0.0.1 -P8066 -uroot -p123456MySQL [(none)]> show databases;MySQL [(none)]> use USERDBReading table information for completion of table and column namesYou can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -ADatabase changedMySQL [USERDB]> show tables;MySQL [USERDB]> select * from company;
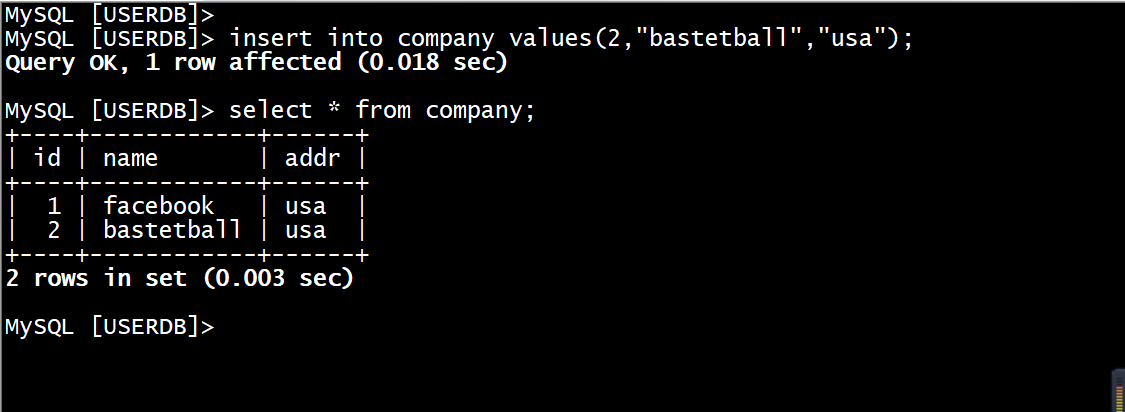
(2)用Mycat服务添加表数据
在Mycat虚拟机上使用mysql命令对表company添加一条数据(2,”basketball”,”usa”),添加完毕后查看表信息。命令如下。
MySQL [USERDB]> insert into company values(2,"bastetball","usa");MySQL [USERDB]> select * from company;
(3)验证Mycat服务对数据库读写操作分离
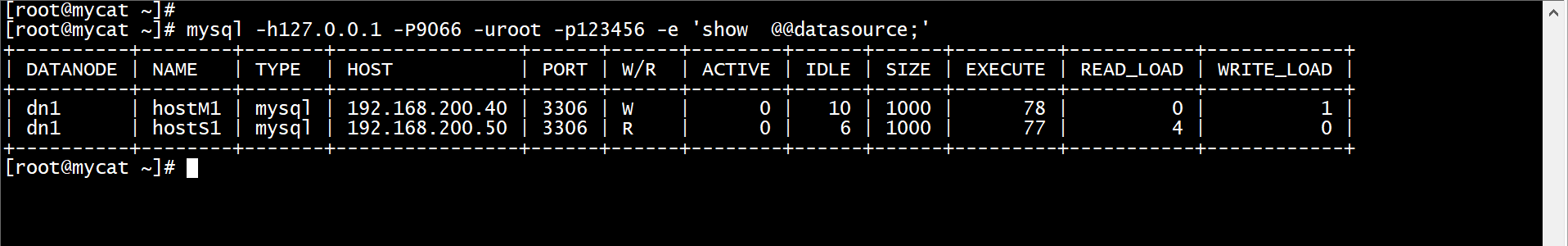
在Mycat虚拟机节点使用mysql命令,通过9066端口查询对数据库读写操作的分离信息。可以看到所有的写入操作WRITE_LOAD数都在db1主数据库节点上,所有的读取操作READ_LOAD数都在db2主数据库节点上。由此可见,数据库读写操作已经分离到db1和db2节点上了。命令如下。
[root@mycat ~]# mysql -h127.0.0.1 -P9066 -uroot -p123456 -e 'show @@datasource;'
至此,Mycat读写分离数据库案例完成。