基本介绍:
- 迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是常用的设计模式,属于行为型模式
- 如果集合元素是用不同的方式实现的,有数组还有Java的集合类或其他方式,当客户端要遍历这些集合元素的时候就要使用多种遍历方式,而且还会暴露元素的内部结构,可以考虑使用迭代器模式解决
- 迭代器模式提供一种遍历集合元素的统一接口,用一致的方法遍历集合元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示,即不暴露其内部的结构
迭代器模式类图: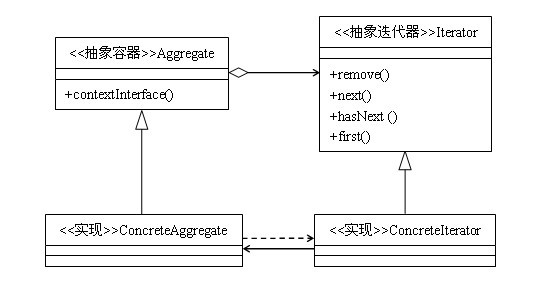
迭代器模式角色及职责:
- Iterator:迭代器接口,系统提供,含有
hasnext()next()remove()等方法 - ConcreteIterator:具体的迭代器类,管理迭代
- Aggregate:一个统一的聚合接口,将客户端和具体聚合解耦
- ConcreteAggregate:具体的聚合,持有对象集合,并提供一个方法,返回一个迭代器,该迭代器可以正确遍历集合
代码示例:
@Data@AllArgsConstructorpublic class Department {private String name;private String desc;}public class ComputerCollegeIterator implements Iterator<Department> {Department[] departments;/*** 遍历的位置*/int position = 0;public ComputerCollegeIterator(Department[] departments){this.departments = departments;}@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return position < departments.length && departments[position] != null;}@Overridepublic Department next() {Department department = departments[position];position++;return department;}/*** 删除的方法,默认空实现*/@Overridepublic void remove(){}}public interface College {public void addDepartment(String name, String desc);public Iterator createIterator();}public class ComputerCollege implements College {Department[] departments;/*** 保存当前数组的对象个数*/int numOfDepartment = 0;public ComputerCollege(){this.departments = new Department[5];}@Overridepublic void addDepartment(String name, String desc) {Department department = new Department(name, desc);departments[numOfDepartment] = department;numOfDepartment++;}@Overridepublic Iterator<Department> createIterator() {return new ComputerCollegeIterator(departments);}}public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {ComputerCollege computerCollege = new ComputerCollege();computerCollege.addDepartment("1号学院","1");computerCollege.addDepartment("2号学院","2");computerCollege.addDepartment("3号学院","3");Iterator<Department> iterator = computerCollege.createIterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){Department next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}}}
迭代器模式在JDK-ArrayList集合应用的源码分析:
- 内部类Itr充当具体实现迭代器Iterator的类,作为ArrayList内部类
- List就是充当了聚合接口,含有一个
iterator()的方法,返回一个迭代器对象 - ArrayList是实现聚合接List的子类,实现了
iterator() - Iterator接口由系统提供
- 迭代器模式解决了不同集合(ArrayList、LinkedList)统一遍历问题
迭代器模式的注意事项和细节
- 优点:
- 提供一个统一的方法遍历对象,客户不用再考虑聚合的类型,使用一种方法就可以遍历对象了
- 隐藏了聚合的内部结构,客户端要遍历聚合的时候只能取到迭代器,而不会知道聚合的具体组成
- 提供了一种设计思想,就是一个类应该只有一个引起变化的原因(单一责任原则)。在聚合类中,我们把迭代器分开,就是要把管理对象集合和遍历对象集合的责任分开,这样一来集合改变的话,只影响到聚合对象。而如果遍历方式变的话,只影响到了迭代器
- 当要展示一组相似对象,或者遍历一组相同对象时使用,适合使用迭代器模式
- 缺点:每个聚合对象都要一个迭代器,会生成多个迭代器,不好管理类

