
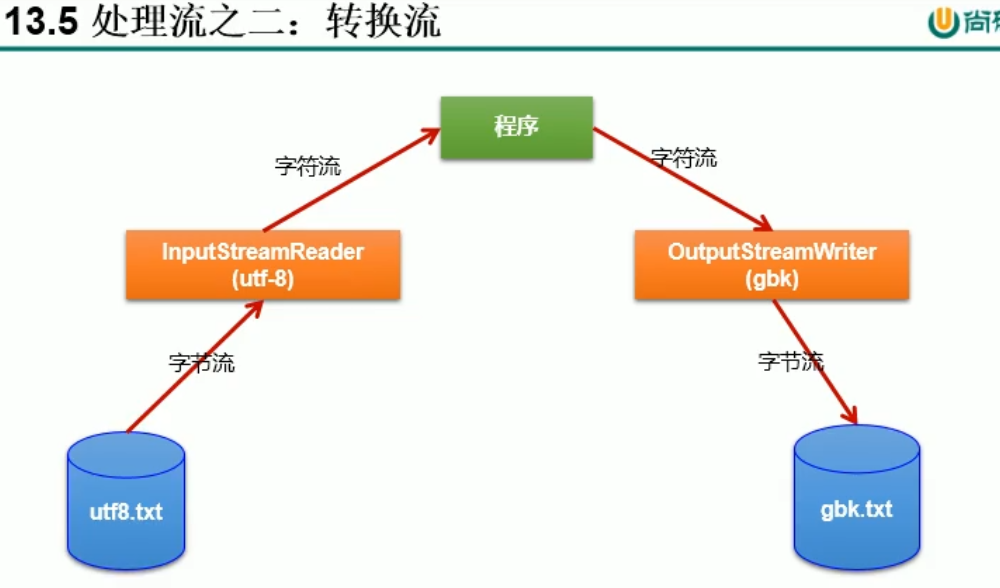




- 处理就之二:转换流的使用
1.转换流:属于字符流
InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
OutputStreamWrite: 将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
2.作用:提供字节流与字符流之间的转换
3.解码:字节、字节数组 —->字符数组、字符串
编码:字符数组、字符串 —->字节、字节数组
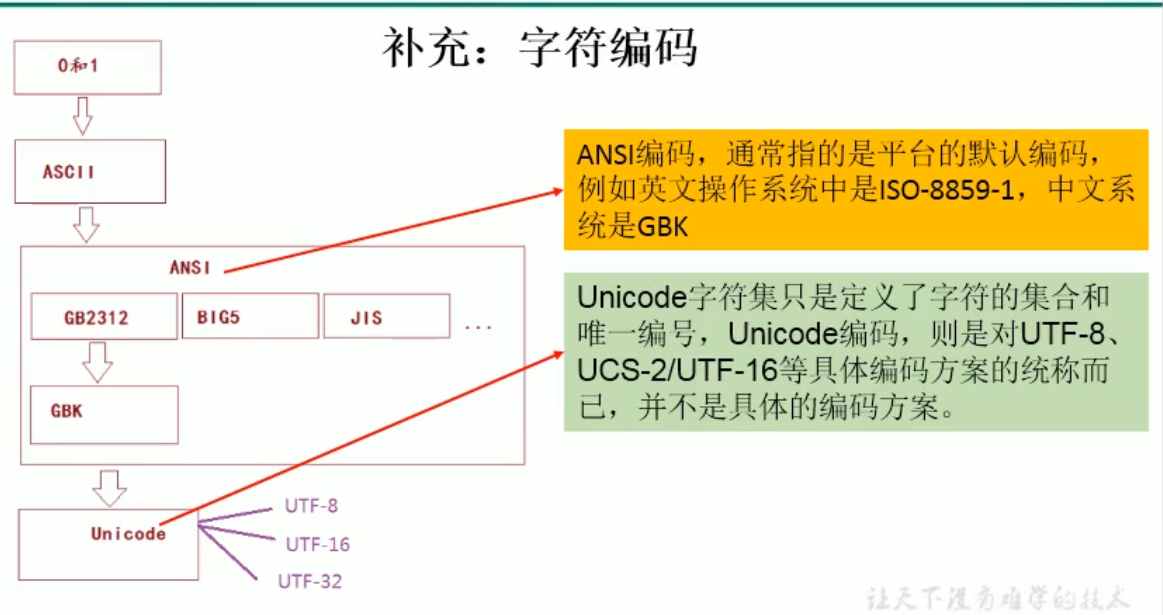
* 4.字符集 ```java package com.atguigu.java1;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
- 处理就之二:转换流的使用 *
- 1.转换流:属于字符流
- InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
- OutputStreamWrite: 将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流 *
- 2.作用:提供字节流与字符流之间的转换 *
- 3.解码:字节、字节数组 —->字符数组、字符串
- 编码:字符数组、字符串 —->字节、字节数组 *
- 4.字符集
- @author Dxkstart
@create 2021-05-30 16:05 */ public class InputStreamReaderTest {
/ InputStreamReader的使用,实现字节的输入流到字符的输入流的转换 / @Test public void test1(){
InputStreamReader isr = null;//自定义字符集try {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Hello1.txt");
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集
//参数2,指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件保存时使用的字符集isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");char[] buff = new char[20];int len;while ((len = isr.read(buff)) != -1){String str = new String(buff,0,len);System.out.println(str);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if(isr != null) {isr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
/*综合使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter*/@Testpublic void test2(){InputStreamReader isr = null;OutputStreamWriter osw = null;try {//1.造文件、造流File file1 = new File("Hello1.txt");File file2 = new File("Hello1_gbk.txt");FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");//读写过程char[] buff = new char[20];int len;while((len = isr.read(buff)) != -1){osw.write(buff,0,len);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if(isr != null) {isr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if(osw != null) {osw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
```

