一:为什么要学多线程
- 应付面试 :多线程几乎是面试中必问的题,所以掌握一定的基础知识是必须的。
- 了解并发编程:实际工作中很少写多线程的代码,这部分代码一般都被人封装起来了,在业务中使用多线程的机会也不是很多(看具体项目),虽然代码中很少会自己去创建线程,但是实际环境中每行代码却都是并行执行的,同一时刻大量请求同一个接口,并发可能会产生一些问题,所以也需要掌握一定的并发知识
二:进程与线程
1. 进程
进程是资源(CPU、内存等)分配的基本单位,它是程序执行时的一个实例。程序运行时系统就会创建一个进程,并为它分配资源,然后把该进程放入进程就绪队列,进程调度器选中它的时候就会为它分配CPU时间,程序开始真正运行。2. 线程
线程是一条执行路径,是程序执行时的最小单位,它是进程的一个执行流,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,一个进程可以由很多个线程组成,线程间共享进程的所有资源,每个线程有自己的堆栈和局部变量。线程由CPU独立调度执行,在多CPU环境下就允许多个线程同时运行。同样多线程也可以实现并发操作,每个请求分配一个线程来处理。
一个正在运行的软件(如迅雷)就是一个进程,一个进程可以同时运行多个任务( 迅雷软件可以同时下载多个文件,每个下载任务就是一个线程), 可以简单的认为进程是线程的集合。
线程是一条可以执行的路径。
- 对于单核CPU而言:多线程就是一个CPU在来回的切换,在交替执行。
对于多核CPU而言:多线程就是同时有多条执行路径在同时(并行)执行,每个核执行一个线程,多个核就有可能是一块同时执行的。
3. 进程与线程的关系
一个程序就是一个进程,而一个程序中的多个任务则被称为线程。进程是表示资源分配的基本单位,又是调度运行的基本单位。,亦即执行处理机调度的基本单位。 进程和线程的关系:
一个线程只能属于一个进程,而一个进程可以有多个线程,但至少有一个线程。线程是操作系统可识别的最小执行和调度单位。
- 资源分配给进程,同一进程的所有线程共享该进程的所有资源。同一进程中的多个线程共享代码段(代码和常量),数据段(全局变量和静态变量),扩展段(堆存储)。但是每个线程拥有自己的栈段,栈段又叫运行时段,用来存放所有局部变量和临时变量,即每个线程都有自己的堆栈和局部变量。
- 处理机分给线程,即真正在处理机上运行的是线程。
- 线程在执行过程中,需要协作同步。不同进程的线程间要利用消息通信的办法实现同步。
如果把上课的过程比作进程,把老师比作CPU,那么可以把每个学生比作每个线程,所有学生共享这个教室(也就是所有线程共享进程的资源),上课时学生A向老师提出问题,老师对A进行解答,此时可能会有学生B对老师的解答不懂会提出B的疑问(注意:此时可能老师还没有对A同学的问题解答完毕),此时老师又向学生B解惑,解释完之后又继续回答学生A的问题,同一时刻老师只能向一个学生回答问题(即:当多个线程在运行时,同一个CPU在某一个时刻只能服务于一个线程,可能一个线程分配一点时间,时间到了就轮到其它线程执行了,这样多个线程在来回的切换)
4. 为什么要使用多线程
多线程可以提高程序的效率。
实际生活案例:村长要求喜洋洋在一个小时内打100桶水,可以喜洋洋一个小时只能打25桶水,如果这样就需要4个小时才能完成任务,为了在一个小时能够完成,喜洋洋就请美洋洋、懒洋洋、沸洋洋,来帮忙,这样4只羊同时干活,在一小时内完成了任务。原本用4个小时完成的任务现在只需要1个小时就完成了,如果把每只羊看做一个线程,多只羊即多线程可以提高程序的效率。
5. 多线程应用场景
- 一般线程之间比较独立,互不影响
-
三:多线程的实现方式
1. 顺序编程
顺序编程:程序从上往下的同步执行,即如果第一行代码执行没有结束,第二行代码就只能等待第一行执行结束后才能结束。 ```java public class Main { // 顺序编程 吃喝示例:当吃饭吃不完的时候,是不能喝酒的,只能吃完晚才能喝酒 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 先吃饭再喝酒eat();drink();
}
private static void eat() throws Exception {
System.out.println("开始吃饭?...\t" + new Date());Thread.sleep(5000);System.out.println("结束吃饭?...\t" + new Date());
}
private static void drink() throws Exception {
System.out.println("开始喝酒?️...\t" + new Date());Thread.sleep(5000);System.out.println("结束喝酒?...\t" + new Date());
} }
<br /><a name="qmNMh"></a>#### 2. 并发编程**并发编程:多个任务可以同时做,常用与任务之间比较独立,互不影响。**<br />**线程上下文切换:**<br />同一个时刻一个CPU只能做一件事情,即同一时刻只能一个线程中的部分代码,假如有两个线程,Thread-0和Thread-1,刚开始CPU说Thread-0你先执行,给你3毫秒时间,Thread-0执行了3毫秒时间,但是没有执行完,此时CPU会暂停Thread-0执行并记录Thread-0执行到哪行代码了,当时的变量的值是多少,然后CPU说Thread-1你可以执行了,给你2毫秒的时间,Thread-1执行了2毫秒也没执行完,此时CPU会暂停Thread-1执行并记录Thread-1执行到哪行代码了,当时的变量的值是多少,此时CPU又说Thread-0又该你,这次我给你5毫秒时间,去执行吧,此时CPU就找出上次Thread-0线程执行到哪行代码了,当时的变量值是多少,然后接着上次继续执行,结果用了2毫秒就Thread-0就执行完了,就终止了,然后CPU说Thread-1又轮到你,这次给你4毫秒,同样CPU也会先找出上次Thread-1线程执行到哪行代码了,当时的变量值是多少,然后接着上次继续开始执行,结果Thread-1在4毫秒内也执行结束了,Thread-1也结束了终止了。CPU在来回改变线程的执行机会称之为线程上下文切换。```javapublic class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 一边吃饭一边喝酒new EatThread().start();new DrinkThread().start();}}class EatThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("开始吃饭?...\t" + new Date());try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("结束吃饭?...\t" + new Date());}}class DrinkThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("开始喝酒?️...\t" + new Date());try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("结束喝酒?...\t" + new Date());}}
并发编程,一边吃饭一边喝酒总共用时5秒,比顺序编程更快,因为并发编程可以同时运行,而不必等前面的代码运行完之后才允许后面的代码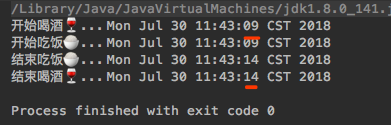
本示例主要启动3个线程,一个主线程main thread、一个吃饭线程(Thread-0)和一个喝酒线程(Thread-1),共三个线程, 三个线程并发切换着执行。main线程很快执行完,吃饭线程和喝酒线程会继续执行,直到所有线程(非守护线程)执行完毕,整个程序才会结束,main线程结束并不意味着整个程序结束。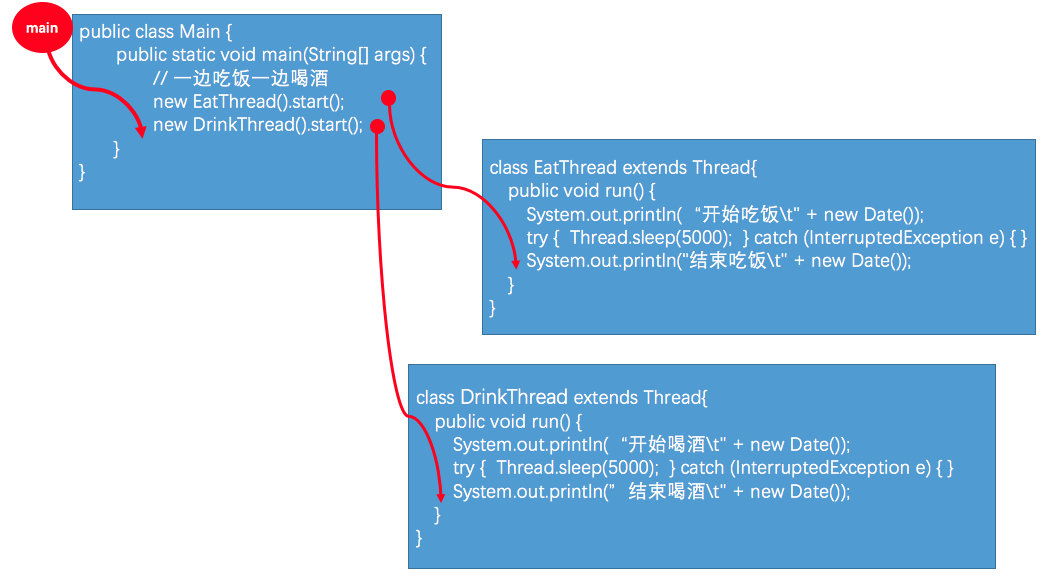
- 顺序:代码从上而下按照固定的顺序执行,只有上一件事情执行完毕,才能执行下一件事。就像物理电路中的串行,假如有十件事情,一个人来完成,这个人必须先做第一件事情,然后再做第二件事情,最后做第十件事情,按照顺序做。
- 并行:多个操作同时处理,他们之间是并行的。假如十件事情,两个人来完成,每个人在某个时间点各自做各自的事情,互不影响
- 并发:将一个操作分割成多个部分执行并且允许无序处理,假如有十件事情,如果有一个人在做,这个人可能做一会这个不想做了,再去做别的,做着做着可能也不想做了,又去干其它事情了,看他心情想干哪个就干哪个,最终把十件事情都做完。如果有两个人在做,他们俩先分一下,比如张三做4件,李四做6件,他们各做自己的,在做自己的事情过程中可以随意的切换到别的事情,不一定要把某件事情干完再去干其它事情,有可能一件事做了N次才做完。
通常一台电脑只有一个cpu,多个线程属于并发执行,如果有多个cpu,多线程并发执行有可能变成并行执行。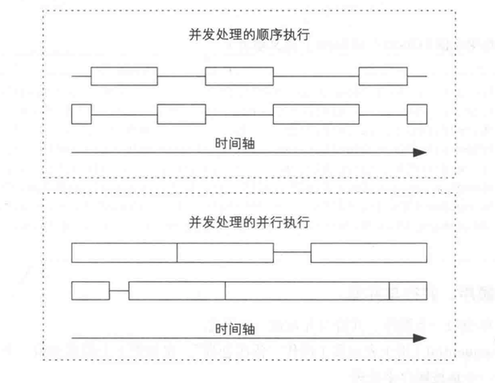
3. 多线程创建方式
- 继承 Thread
- 实现 Runable
- 实现 Callable
①:继成java.lang.Thread, 重写run()方法
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyThread().start();}}class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}
Thread类
package java.lang;public class Thread implements Runnable {// 构造方法public Thread(Runnable target);public Thread(Runnable target, String name);public synchronized void start();}
Runnable 接口
package java.lang;@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Runnable {pubic abstract void run();}
②:实现java.lang.Runnable接口,重写run()方法,然后使用Thread类来包装
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 将Runnable实现类作为Thread的构造参数传递到Thread类中,然后启动Thread类MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();new Thread(runnable).start();}}class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}
可以看到两种方式都是围绕着Thread和Runnable,继承Thread类把run()写到类中,实现Runnable接口是把run()方法写到接口中然后再用Thread类来包装, 两种方式最终都是调用Thread类的start()方法来启动线程的。
两种方式在本质上没有明显的区别,在外观上有很大的区别,第一种方式是继承Thread类,因Java是单继承,如果一个类继承了Thread类,那么就没办法继承其它的类了,在继承上有一点受制,有一点不灵活,第二种方式就是为了解决第一种方式的单继承不灵活的问题,所以平常使用就使用第二种方式
其它变体写法:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 匿名内部类new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}).start();// 尾部代码块, 是对匿名内部类形式的语法糖new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}.start();// Runnable是函数式接口,所以可以使用Lamda表达式形式Runnable runnable = () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId());};new Thread(runnable).start();}}
③:实现Callable接口,重写call()方法,然后包装成java.util.concurrent.FutureTask, 再然后包装成Thread
Callable:有返回值的线程,能取消线程,可以判断线程是否执行完毕
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 将Callable包装成FutureTask,FutureTask也是一种RunnableMyCallable callable = new MyCallable();FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(callable);new Thread(futureTask).start();// get方法会阻塞调用的线程Integer sum = futureTask.get();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "=" + sum);}}class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "\t" + new Date() + " \tstarting...");int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i <= 100000; i++) {sum += i;}Thread.sleep(5000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "\t" + new Date() + " \tover...");return sum;}}
Callable 也是一种函数式接口
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Callable<V> {V call() throws Exception;}
FutureTask
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {// 构造函数public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable);// 取消线程public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);// 判断线程public boolean isDone();// 获取线程执行结果public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;}
RunnableFuture
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {void run();}
三种方式比较:
- Thread: 继承方式, 不建议使用, 因为Java是单继承的,继承了Thread就没办法继承其它类了,不够灵活
- Runnable: 实现接口,比Thread类更加灵活,没有单继承的限制
- Callable: Thread和Runnable都是重写的run()方法并且没有返回值,Callable是重写的call()方法并且有返回值并可以借助FutureTask类来判断线程是否已经执行完毕或者取消线程执行
- 当线程不需要返回值时使用Runnable,需要返回值时就使用Callable,一般情况下不直接把线程体代码放到Thread类中,一般通过Thread类来启动线程
- Thread类是实现Runnable,Callable封装成FutureTask,FutureTask实现RunnableFuture,RunnableFuture继承Runnable,所以Callable也算是一种Runnable,所以三种实现方式本质上都是Runnable实现
四:线程的状态
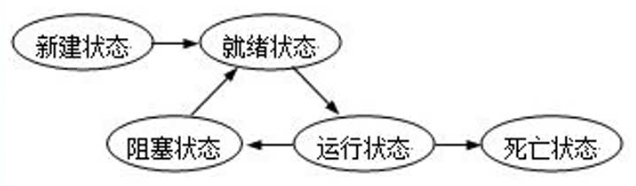
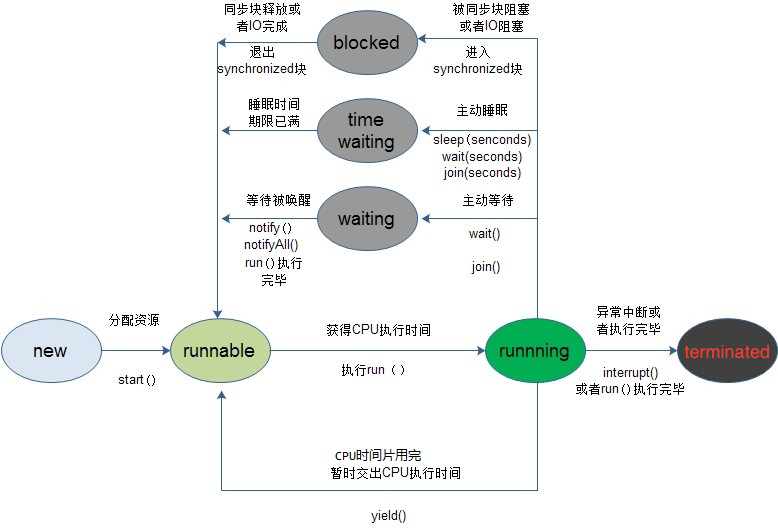
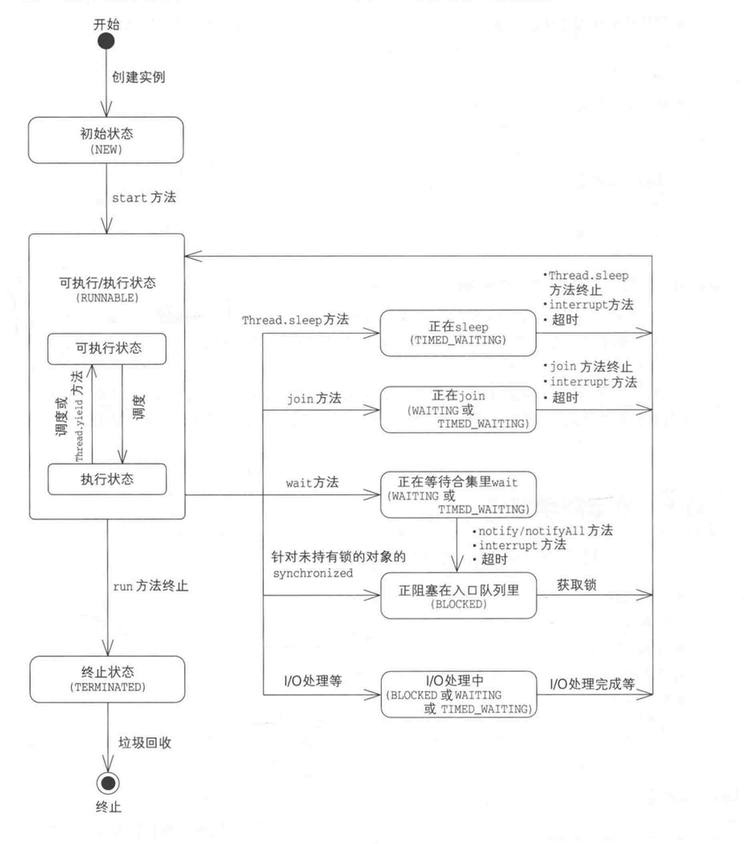
- 创建(new)状态: 准备好了一个多线程的对象,即执行了new Thread(); 创建完成后就需要为线程分配内存
- 就绪(runnable)状态: 调用了start()方法, 等待CPU进行调度
- 运行(running)状态: 执行run()方法
- 阻塞(blocked)状态: 暂时停止执行线程,将线程挂起(sleep()、wait()、join()、没有获取到锁都会使线程阻塞), 可能将资源交给其它线程使用
- 死亡(terminated)状态: 线程销毁(正常执行完毕、发生异常或者被打断interrupt()都会导致线程终止)
五:Thread常用方法
Thread
public class Thread implements Runnable {// 线程名字private volatile String name;// 线程优先级(1~10)private int priority;// 守护线程private boolean daemon = false;// 线程idprivate long tid;// 线程组private ThreadGroup group;// 预定义3个优先级public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;// 构造函数public Thread();public Thread(String name);public Thread(Runnable target);public Thread(Runnable target, String name);// 线程组public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target);// 返回当前正在执行线程对象的引用public static native Thread currentThread();// 启动一个新线程public synchronized void start();// 线程的方法体,和启动线程没毛关系public void run();// 让线程睡眠一会,由活跃状态改为挂起状态public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException;// 打断线程 中断线程 用于停止线程// 调用该方法时并不需要获取Thread实例的锁。无论何时,任何线程都可以调用其它线程的interruptf方法public void interrupt();public boolean isInterrupted()// 线程是否处于活动状态public final native boolean isAlive();// 交出CPU的使用权,从运行状态改为挂起状态public static native void yield();public final void join() throws InterruptedExceptionpublic final synchronized void join(long millis)public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException// 设置线程优先级public final void setPriority(int newPriority);// 设置是否守护线程public final void setDaemon(boolean on);// 线程idpublic long getId() { return this.tid; }// 线程状态public enum State {// new 创建NEW,// runnable 就绪RUNNABLE,// blocked 阻塞BLOCKED,// waiting 等待WAITING,// timed_waitingTIMED_WAITING,// terminated 结束TERMINATED;}}
public static void main(String[] args) {// main方法就是一个主线程// 获取当前正在运行的线程Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();// 线程名字String name = thread.getName();// 线程idlong id = thread.getId();// 线程优先级int priority = thread.getPriority();// 是否存活boolean alive = thread.isAlive();// 是否守护线程boolean daemon = thread.isDaemon();// Thread[name=main, id=1 ,priority=5 ,alive=true ,daemon=false]System.out.println("Thread[name=" + name + ", id=" + id + " ,priority=" + priority + " ,alive=" + alive + " ,daemon=" + daemon + "]");}
0. Thread.currentThread()
public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();// 线程名称String name = thread.getName();// 线程idlong id = thread.getId();// 线程已经启动且尚未终止// 线程处于正在运行或准备开始运行的状态,就认为线程是“存活”的boolean alive = thread.isAlive();// 线程优先级int priority = thread.getPriority();// 是否守护线程boolean daemon = thread.isDaemon();// Thread[name=main,id=1,alive=true,priority=5,daemon=false]System.out.println("Thread[name=" + name + ",id=" + id + ",alive=" + alive + ",priority=" + priority + ",daemon=" + daemon + "]");}
1. start() 与 run()
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {new Thread(()-> {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}}, "Thread-A").start();new Thread(()-> {for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + j);try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}}, "Thread-B").start();}
start(): 启动一个线程,线程之间是没有顺序的,是按CPU分配的时间片来回切换的。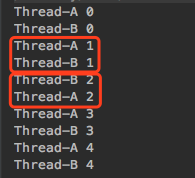
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {new Thread(()-> {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}}, "Thread-A").run();new Thread(()-> {for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + j);try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}}, "Thread-B").run();}
注意:执行结果都是main主线程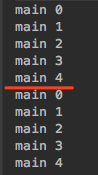
run(): 调用线程的run方法,就是普通的方法调用,虽然将代码封装到两个线程体中,可以看到线程中打印的线程名字都是main主线程,run()方法用于封装线程的代码,具体要启动一个线程来运行线程体中的代码(run()方法)还是通过start()方法来实现,调用run()方法就是一种顺序编程不是并发编程。
有些面试官经常问一些启动一个线程是用start()方法还是run()方法,为了面试而面试。
2. sleep() 与 interrupt()
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;public void interrupt();
sleep(long millis): 睡眠指定时间,程序暂停运行,睡眠期间会让出CPU的执行权,去执行其它线程,同时CPU也会监视睡眠的时间,一旦睡眠时间到就会立刻执行(因为睡眠过程中仍然保留着锁,有锁只要睡眠时间到就能立刻执行)。
- sleep(): 睡眠指定时间,即让程序暂停指定时间运行,时间到了会继续执行代码,如果时间未到就要醒需要使用interrupt()来随时唤醒
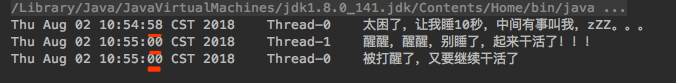
interrupt(): 唤醒正在睡眠的程序,调用interrupt()方法,会使得sleep()方法抛出InterruptedException异常,当sleep()方法抛出异常就中断了sleep的方法,从而让程序继续运行下去 ```java public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread thread0 = new Thread(()-> {
try {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t太困了,让我睡10秒,中间有事叫我,zZZ。。。");Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t被叫醒了,又要继续干活了");}
}); thread0.start();
// 这里睡眠只是为了保证先让上面的那个线程先执行 Thread.sleep(2000);
new Thread(()-> {
System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t醒醒,醒醒,别睡了,起来干活了!!!");// 无需获取锁就可以调用interruptthread0.interrupt();
}).start(); }
<a name="ihHoD"></a>#### 3. wait() 与 notify()wait、notify和notifyAll方法是Object类的final native方法。所以这些方法不能被子类重写,Object类是所有类的超类,因此在程序中可以通过this或者super来调用this.wait(), super.wait()- wait(): 导致线程进入等待阻塞状态,会一直等待直到它被其他线程通过notify()或者notifyAll唤醒。该方法只能在同步方法中调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。wait(long timeout): 时间到了自动执行,类似于sleep(long millis)- notify(): 该方法只能在同步方法或同步块内部调用, 随机选择一个(注意:只会通知一个)在该对象上调用wait方法的线程,解除其阻塞状态- notifyAll(): 唤醒所有的wait对象注意:- Object.wait()和Object.notify()和Object.notifyall()必须写在synchronized方法内部或者synchronized块内部- 让哪个对象等待wait就去通知notify哪个对象,不要让A对象等待,结果却去通知B对象,要操作同一个对象Object```javapublic class Object {public final void wait() throws InterruptedException;public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException;public final native void notify();public final native void notifyAll();}
WaitNotifyTest
public class WaitNotifyTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {WaitNotifyTest waitNotifyTest = new WaitNotifyTest();new Thread(() -> {try {waitNotifyTest.printFile();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {waitNotifyTest.printFile();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t睡觉1秒中,目的是让上面的线程先执行,即先执行wait()");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}waitNotifyTest.notifyPrint();}).start();}private synchronized void printFile() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t等待打印文件...");this.wait();System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t打印结束。。。");}private synchronized void notifyPrint() {this.notify();System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t通知完成...");}}
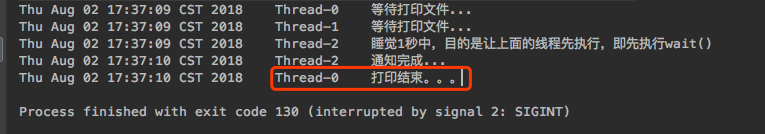
wait():让程序暂停执行,相当于让当前,线程进入当前实例的等待队列,这个队列属于该实例对象,所以调用notify也必须使用该对象来调用,不能使用别的对象来调用。调用wait和notify必须使用同一个对象来调用。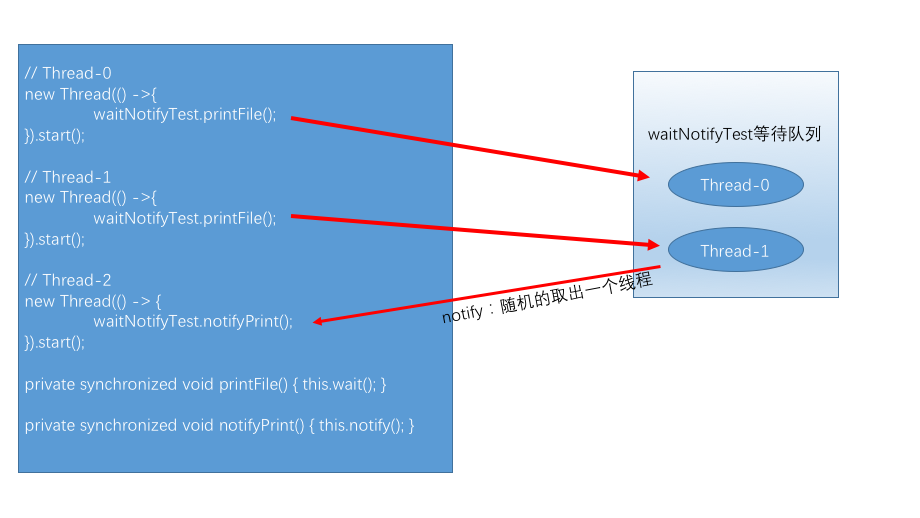
this.notifyAll();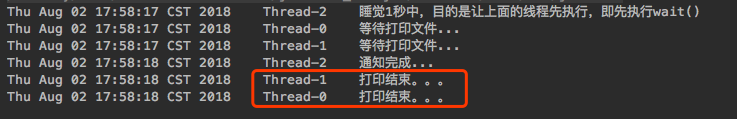
4. sleep() 与 wait()
① Thread.sleep(long millis): 睡眠时不会释放锁
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Object lock = new Object();new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}}}).start();Thread.sleep(1000);new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);}}}).start();}
因main方法中Thread.sleep(1000)所以上面的线程Thread-0先被执行,当循环第一次时就会Thread.sleep(1000)睡眠,因为sleep并不会释放锁,所以Thread-1得不到执行的机会,所以直到Thread-0执行完毕释放锁对象lock,Thread-1才能拿到锁,然后执行Thread-1;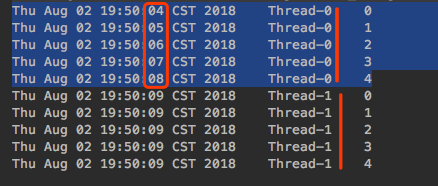
5. wait() 与 interrupt()
wait(): 方法的作用是释放锁,加入到等待队列,当调用interrupt()方法后,线程必须先获取到锁后,然后才抛出异常InterruptedException。注意: 在获取锁之前是不会抛出异常的,只有在获取锁之后才会抛异常
所有能抛出InterruptedException的方法都可以通过interrupt()来取消的
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;public final void wait() throws InterruptedException;public final void join() throws InterruptedException;public void interrupt();
notify()和interrupt()
从让正在wait的线程重新运行这一点来说,notify方法和intterrupt方法的作用有些类似,但仍有以下不同之处:
- notify/notifyAll是java.lang.Object类的方法,唤醒的是该实例的等待队列中的线程,而不能直接指定某个具体的线程。notify/notifyAll唤醒的线程会继续执行wait的下一条语句,另外执行notify/notifyAll时线程必须要获取实例的锁
- interrupte方法是java.lang.Thread类的方法,可以直接指定线程并唤醒,当被interrupt的线程处于sleep或者wait中时会抛出InterruptedException异常。执行interrupt()并不需要获取取消线程的锁。
总之notify/notifyAll和interrupt的区别在于是否能直接让某个指定的线程唤醒、执行唤醒是否需要锁、方法属于的类不同
6. interrupt()
有人也许认为“当调用interrupt方法时,调用对象的线程就会InterruptedException异常”, 其实这是一种误解,实际上interrupt方法只是改变了线程的“中断状态”而已,所谓中断状态是一个boolean值,表示线程是否被中断的状态。 ```java public class Thread implements Runnable { public void interrupt() {
中断状态 = true;
}
// 检查中断状态 public boolean isInterrupted();
// 检查中断状态并清除当前线程的中断状态 public static boolean interrupted() {
// 伪代码boolean isInterrupted = isInterrupted();中断状态 = false;
} }
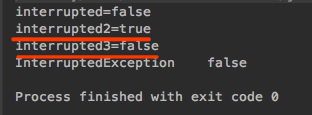
假设Thread-0执行了sleep、wait、join中的一个方法而停止运行,在Thread-1中调用了interrupt方法,此时线程Thread-0的确会抛出InterruptedException异常,但这其实是sleep、wait、join中的方法内部会对线程的“中断状态”进行检查,如果中断状态为true,就会抛出InterruptedException异常。假如某个线程的中断状态为true,但线程体中却没有调用或者没有判断线程中断状态的值,那么线程则不会抛出InterruptedException异常。isInterrupted() 检查中断状态<br />若指定线程处于中断状态则返回true,若指定线程为非中断状态,则反回false, isInterrupted() 只是获取中断状态的值,并不会改变中断状态的值。interrupted()<br />检查中断状态并清除当前线程的中断状态。如当前线程处于中断状态返回true,若当前线程处于非中断状态则返回false, 并清除中断状态(将中断状态设置为false), 只有这个方法才可以清除中断状态,Thread.interrupted的操作对象是当前线程,所以该方法并不能用于清除其它线程的中断状态。interrupt()与interrupted()- interrupt():打断线程,将中断状态修改为true- interrupted(): 不打断线程,获取线程的中断状态,并将中断状态设置为false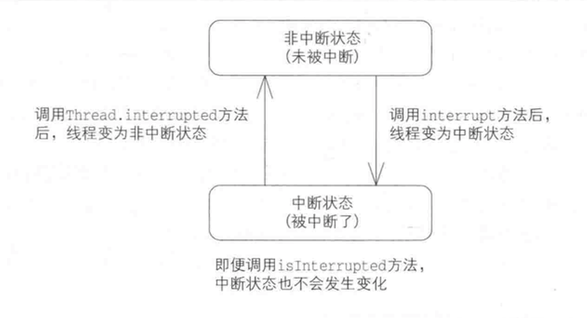```javapublic class InterrupptTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(new MyRunnable());thread.start();boolean interrupted = thread.isInterrupted();// interrupted=falseSystem.out.println("interrupted=" + interrupted);thread.interrupt();boolean interrupted2 = thread.isInterrupted();// interrupted2=trueSystem.out.println("interrupted2=" + interrupted2);boolean interrupted3 = Thread.interrupted();// interrupted3=falseSystem.out.println("interrupted3=" + interrupted3);}}class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (this) {try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// InterruptedException falseSystem.out.println("InterruptedException\t" + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());}}}}
① object.wait(long timeout): 会释放锁
public class SleepWaitTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {SleepWaitTest object = new SleepWaitTest();new Thread(() -> {synchronized (object) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t等待打印文件...");try {object.wait(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t打印结束。。。");}}).start();// 先上面的线程先执行Thread.sleep(1000);new Thread(() -> {synchronized (object) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);}}}).start();}}
因main方法中有Thread.sleep(1000)所以上面的线程Thread-0肯定会被先执行,当Thread-0被执行时就拿到了object对象锁,然后进入wait(5000)5秒钟等待,此时wait释放了锁,然后Thread-1就拿到了锁就执行线程体,Thread-1执行完后就释放了锁,当等待5秒后Thread-0就能再次获取object锁,这样就继续执行后面的代码。wait方法是释放锁的,如果wait方法不释放锁那么Thread-1是拿不到锁也就没有执行的机会的,事实是Thread-1得到了执行,所以说wait方法会释放锁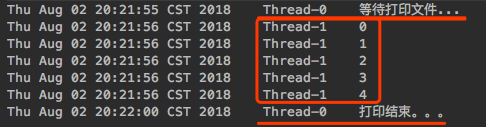
② sleep与wait的区别
- sleep在Thread类中,wait在Object类中
- sleep不会释放锁,wait会释放锁
- sleep使用interrupt()来唤醒,wait需要notify或者notifyAll来通知
7. join()
让当前线程加入父线程,加入后父线程会一直wait,直到子线程执行完毕后父线程才能执行。当我们调用某个线程的这个方法时,这个方法会挂起调用线程,直到被调用线程结束执行,调用线程才会继续执行。
将某个线程加入到当前线程中来,一般某个线程和当前线程依赖关系比较强,必须先等待某个线程执行完毕才能执行当前线程。一般在run()方法内使用
join() 方法:
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {join(0);}public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException {long base = System.currentTimeMillis();long now = 0;if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}if (millis == 0) {// 循环检查线程的状态是否还活着,如果死了就结束了,如果活着继续等到死while (isAlive()) {wait(0);}} else {while (isAlive()) {long delay = millis - now;if (delay <= 0) {break;}wait(delay);now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;}}}public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("nanosecond timeout value out of range");}if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {millis++;}join(millis);}
JoinTest
public class JoinTest {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new ParentRunnable()).start();}}class ParentRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {// 线程处于new状态Thread childThread = new Thread(new ChildRunable());// 线程处于runnable就绪状态childThread.start();try {// 当调用join时,parent会等待child执行完毕后再继续运行// 将某个线程加入到当前线程childThread.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "父线程 running");}}}class ChildRunable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(new Date() + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "子线程 running");}}}
程序进入主线程,运行Parent对应的线程,Parent的线程代码分两段,一段是启动一个子线程,一段是Parent线程的线程体代码,首先会将Child线程加入到Parent线程,join()方法会调用join(0)方法(join()方法是普通方法并没有加锁,join(0)会加锁),join(0)会执行while(isAlive()) { wait(0);} 循环判断线程是否处于活动状态,如果是继续wait(0)知道isAlive=false结束掉join(0), 从而结束掉join(), 最后回到Parent线程体中继续执行其它代码。
在Parent调用child.join()后,child子线程正常运行,Parent父线程会等待child子线程结束后再继续运行。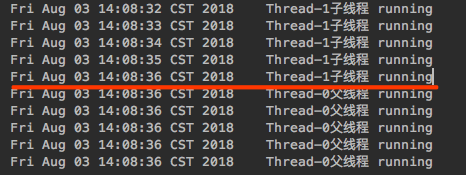
- join() 和 join(long millis, int nanos) 最后都调用了 join(long millis)。
- join(long millis, int nanos)和join(long millis)方法 都是synchronized。
- join() 调用了join(0),从源码可以看到join(0)不断检查当前线程是否处于Active状态。
- join() 和 sleep() 一样,都可以被中断(被中断时,会抛出 InterrupptedException 异常);不同的是,join() 内部调用了wait(),会出让锁,而 sleep() 会一直保持锁。
8. yield()
交出CPU的执行时间,不会释放锁,让线程进入就绪状态,等待重新获取CPU执行时间,yield就像一个好人似的,当CPU轮到它了,它却说我先不急,先给其他线程执行吧, 此方法很少被使用到; ```java /**- A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield
- its current use of a processor. The scheduler is free to ignore this
- hint. *
Yield is a heuristic attempt to improve relative progression
- between threads that would otherwise over-utilise a CPU. Its use
- should be combined with detailed profiling and benchmarking to
- ensure that it actually has the desired effect. *
It is rarely appropriate to use this method. It may be useful
- for debugging or testing purposes, where it may help to reproduce
- bugs due to race conditions. It may also be useful when designing
- concurrency control constructs such as the ones in the
- {@link java.util.concurrent.locks} package. */ public static native void yield();
```javapublic static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new Runnable() {int sum = 0;@Overridepublic void run() {long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 99999; i++) {sum += 1;// 去掉该行执行用2毫秒,加上271毫秒Thread.yield();}long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("用时:"+ (endTime - beginTime) + " 毫秒!");}}).start();}
sleep(long millis) 与 yeid()
- sleep(long millis): 需要指定具体睡眠的时间,不会释放锁,睡眠期间CPU会执行其它线程,睡眠时间到会立刻执行
- yeid(): 交出CPU的执行权,不会释放锁,和sleep不同的时当再次获取到CPU的执行,不能确定是什么时候,而sleep是能确定什么时候再次执行。两者的区别就是sleep后再次执行的时间能确定,而yeid是不能确定的
yield会把CPU的执行权交出去,所以可以用yield来控制线程的执行速度,当一个线程执行的比较快,此时想让它执行的稍微慢一些可以使用该方法,想让线程变慢可以使用sleep和wait,但是这两个方法都需要指定具体时间,而yield不需要指定具体时间,让CPU决定什么时候能再次被执行,当放弃到下次再次被执行的中间时间就是间歇等待的时间
9. setDaemon(boolean on)
线程分两种:
用户线程:如果主线程main停止掉,不会影响用户线程,用户线程可以继续运行。
- 守护线程:如果主线程死亡,守护线程如果没有执行完毕也要跟着一块死(就像皇上死了,带刀侍卫也要一块死),GC垃圾回收线程就是守护线程
```java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread() {
}; thread.start();@Overridepublic void run() {IntStream.range(0, 5).forEach(i -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\ti=" + i);});}
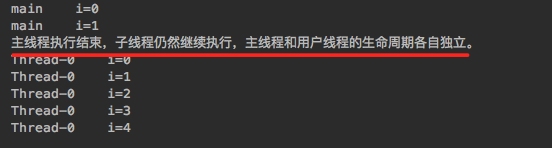
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\ti=" + i);}System.out.println("主线程执行结束,子线程仍然继续执行,主线程和用户线程的生命周期各自独立。");
}
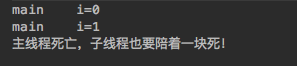
```javapublic static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {IntStream.range(0, 5).forEach(i -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\ti=" + i);});}};thread.setDaemon(true);thread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\ti=" + i);}System.out.println("主线程死亡,子线程也要陪着一块死!");}
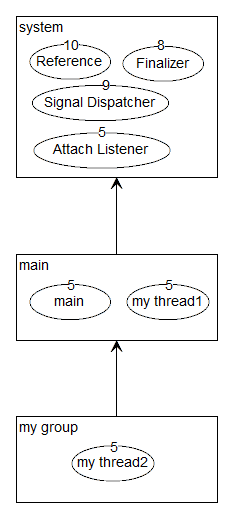
六 线程组
可以对线程分组,分组后可以统一管理某个组下的所有线程,例如统一中断所有线程
public class ThreadGroup implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {private final ThreadGroup parent;String name;int maxPriority;Thread threads[];private ThreadGroup() {this.name = "system";this.maxPriority = Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;this.parent = null;}public ThreadGroup(String name) {this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);}public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);}// 返回此线程组中活动线程的估计数。public int activeGroupCount();// 中断此线程组中的所有线程。public final void interrupt();}
public static void main(String[] args) {String mainThreadGroupName = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName();System.out.println(mainThreadGroupName);// 如果一个线程没有指定线程组,默认为当前线程所在的线程组new Thread(() -> { }, "my thread1").start();ThreadGroup myGroup = new ThreadGroup("MyGroup");myGroup.setMaxPriority(5);Runnable runnable = () -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}ThreadGroup threadGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();String groupName = threadGroup.getName();ThreadGroup parentGroup = threadGroup.getParent();String parentGroupName = parentGroup.getName();ThreadGroup grandpaThreadGroup = parentGroup.getParent();String grandpaThreadGroupName = grandpaThreadGroup.getName();int maxPriority = threadGroup.getMaxPriority();int activeCount = myGroup.activeCount();// system <- main <- MyGroup(1) <- my thread2System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0} <- {1} <- {2}({3}) <- {4}",grandpaThreadGroupName,parentGroupName,groupName,activeCount,Thread.currentThread().getName()));};new Thread(myGroup, runnable, "my thread2").start();}
线程组与线程组之间是有父子关系的,自定义线程组的父线程组是main线程组,main线程组的父线程组是system线程组。