Spring的ioc容器功能非常强大,负责Spring的Bean的创建和管理等功能。而Spring 的bean是整个Spring应用中很重要的一部分,了解Spring Bean的生命周期对我们了解整个spring框架会有很大的帮助。
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext是Spring两种很重要的容器,前者提供了最基本的依赖注入的支持,而后者在继承前者的基础进行了功能的拓展,例如增加了事件传播,资源访问和国际化的消息访问等功能。
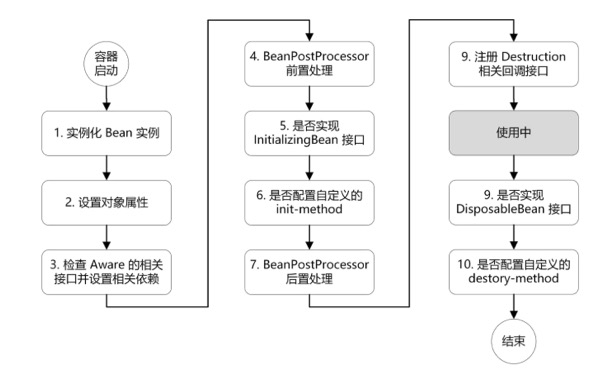
ApplicationContext容器中,Bean的生命周期流程如上图所示,流程大致如下:
1.首先容器启动后,会对scope为singleton且非懒加载的bean进行实例化,
2.按照Bean定义信息配置信息,注入所有的属性,
在org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#prepareBeanFactory开始设置一些BeanFactory上下文的一些特征,可以设置BeanFactory上下文回调
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization里面调用方法invokeAwareInterfaces,invokeAwareInterfaces方法里面会执行一堆Aware接口
如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,会回调该接口的setBeanName()方法,可以知道这个Bean的name属性,
如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,会回调该接口的setBeanFactory()方法,传入该Bean的BeanFactory,这样该Bean就获得了自己所在的BeanFactory,
如果Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,会回调该接口的setApplicationContext()方法,传入该Bean的ApplicationContext,这样该Bean就获得了自己所在的ApplicationContext,
等等,还有很多Aware…
6.如果有Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,则会回调该接口的postProcessBeforeInitialzation()方法,
7.如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,则会回调该接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法,
8.如果Bean配置了init-method方法,则会执行init-method配置的方法,
9.如果有Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,则会回调该接口的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,
10.经过流程9之后,就可以正式使用该Bean了,对于scope为singleton的Bean,Spring的ioc容器中会缓存一份该bean的实例,而对于scope为prototype的Bean,每次被调用都会new一个新的对象,期生命周期就交给调用方管理了,不再是Spring容器进行管理了
11.容器关闭后,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,则会回调该接口的destroy()方法,
12.如果Bean配置了destroy-method方法,则会执行destroy-method配置的方法,至此,整个Bean的生命周期结束.
ApplicationContext Bean生命周期
Bean 的生命周期概括起来就是 4 个阶段:
1. 实例化(Instantiation)
2. 属性赋值(Populate)
3. 初始化(Initialization)
4. 销毁(Destruction)
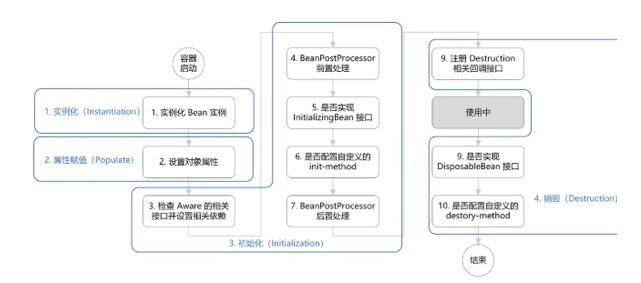
1. 实例化:第 1 步,实例化一个 bean 对象;
2. 属性赋值:第 2 步,为 bean 设置相关属性和依赖;
3. 初始化:第 3~7 步,步骤较多,其中第 5、6 步为初始化操作,第 3、4 步为在初始化前执行,第 7 步在初始化后执行,该阶段结束,才能被用户使用;
4. 销毁:第 8~10步,第8步不是真正意义上的销毁(还没使用呢),而是先在使用前注册了销毁的相关调用接口,为了后面第9、10步真正销毁 bean 时再执行相应的方法。
1.doCreateBean()
在 doCreateBean() 方法中能看到依次执行了这 4 个阶段
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.javaprotected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {// 1. 实例化BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;if (instanceWrapper == null) {instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);}Object exposedObject = bean;try {// 2. 属性赋值populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);// 3. 初始化exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);}// 4. 销毁-注册回调接口try {registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);}return exposedObject;}
initializeBean
源码
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.javaprotected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {// 3. 检查 Aware 相关接口并设置相关依赖if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);return null;}, getAccessControlContext());}else {invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);}// 4. BeanPostProcessor 前置处理Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}// 5. 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法// 6. 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行try {invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException((mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);}// 7. BeanPostProceesor 后置处理if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}return wrappedBean;}
自定义扩展点
可以在bean初始化完成,所有属性设置完成后执行特定逻辑,例如对自动装配对属性进行验证等等。
InitializingBean 是 Spring 为 bean 初始化提供的扩展点。
InitializingBean接口 的定义如下:
public interface InitializingBean {void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;}
在 afterPropertiesSet() 方法写初始化逻辑。
destroy
// DisposableBeanAdapter.javapublic void destroy() {// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {try {if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();return null;}, this.acc);}else {((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();}}}// 10. 若配置自定义的 detory-method 方法,则执行if (this.destroyMethod != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);}else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);if (methodToInvoke != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke));}}}

