原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43168010/article/details/97613895
之前工作中发现有同事在使用线程池的时候经常搞混淆ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolExecutor,座椅在这里想写一片博客来讲讲这两个线程池的区别以及使用
ThreadPoolExecutor
这个类是JDK中的线程池类,继承自Executor, Executor 顾名思义是专门用来处理多线程相关的一个接口,所有县城相关的类都实现了这个接口,里面有一个execute()方法,用来执行线程,线程池主要提供一个线程队列,队列中保存着所有等待状态的线程。避免了创建与销毁的额外开销,提高了响应的速度。相关的继承实现类图如下。
一、线程池接口:ExecutorService为线程池接口,提供了线程池生命周期方法,继承自Executor接口,ThreadPoolExecutor为线程池实现类,提供了线程池的维护操作等相关方法,继承自AbstractExecutorService,AbstractExecutorService实现了ExecutorService接口。
二、线程池的体系结构:
java.util.concurrent.Executor 负责线程的使用和调度的根接口
|—ExecutorService 子接口: 线程池的主要接口
|—ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的实现类
|—ScheduledExceutorService 子接口: 负责线程的调度
|—ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor : 继承ThreadPoolExecutor,实现了ScheduledExecutorService
三、工具类 : Executors
Executors为线程迟工具类,相当于一个工厂类,用来创建合适的线程池,返回ExecutorService类型的线程池。有人如下方法。
ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool() : 创建固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() : 缓存线程池,线程池的数量不固定,可以根据需求自动的更改数量。
ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() : 创建单个线程池。 线程池中只有一个线程
ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool() : 创建固定大小的线程,可以延迟或定时的执行任务
其中AbstractExecutorService是他的抽象父类,继承自ExecutorService,ExecutorService 接口扩展Executor接口,增加了生命周期方法。
实际应用中我一般都比较喜欢使用Exectuors工厂类来创建线程池,里面有五个方法,分别创建不同的线程池,如上,创建一个制定大小的线程池,Exectuors工厂实际上就是调用的ExectuorPoolService的构造方法,传入默认参数。
public class Executors {/*** Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads* operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most* {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks.* If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,* they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.* If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution* prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to* execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist* until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}.** @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool* @return the newly created thread pool* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0}*/public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());}/*** Creates a thread pool that maintains enough threads to support* the given parallelism level, and may use multiple queues to* reduce contention. The parallelism level corresponds to the* maximum number of threads actively engaged in, or available to* engage in, task processing. The actual number of threads may* grow and shrink dynamically. A work-stealing pool makes no* guarantees about the order in which submitted tasks are* executed.** @param parallelism the targeted parallelism level* @return the newly created thread pool* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parallelism <= 0}* @since 1.8*/public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) {return new ForkJoinPool(parallelism,ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,null, true);}
当然,我们也可以直接new ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法来创建线程池,传入需要的参数。
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
这个类则是spring包下的,是sring为我们提供的线程池类,这里重点讲解这个类的用法,可以使用基于xml配置的方式创建
<!-- spring线程池 --><bean id="taskExecutor" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor"><!-- 核心线程数 --><property name="corePoolSize" value="10"/><!-- 最大线程数 --><property name="maxPoolSize" value="200"/><!-- 队列最大长度 >=mainExecutor.maxSize --><property name="queueCapacity" value="10"/><!-- 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间 --><property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="20"/><!-- 线程池对拒绝任务(无线程可用)的处理策略 --><property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"><bean class="java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$CallerRunsPolicy"/></property></bean>
然后通过自动注入的方式注入线程池,
@Resource(name="taskExecutor")ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor;// 或者可以直接@Autowried@AutoWiredThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor
或者是通过配置类的方式配置线程池,然后注入。
@Configurationpublic class ExecturConfig {@Bean("taskExector")public Executor taskExector() {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();int i = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();//获取到服务器的cpu内核executor.setCorePoolSize(5);//核心池大小executor.setMaxPoolSize(100);//最大线程数executor.setQueueCapacity(1000);//队列程度executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(1000);//线程空闲时间executor.setThreadNamePrefix("tsak-asyn");//线程前缀名称executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());//配置拒绝策略return executor;}
上面注解中已经注释了参数的详解,这里重点讲解一下spring线程池的拒绝策略和处理流程。
拒绝策略
rejectedExectutionHandler参数字段用于配置绝策略,常用拒绝策略如下
AbortPolicy:用于被拒绝任务的处理程序,它将抛出RejectedExecutionException
CallerRunsPolicy:用于被拒绝任务的处理程序,它直接在execute方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务。
DiscardOldestPolicy:用于被拒绝任务的处理程序,它放弃最旧的未处理请求,然后重试execute。
DiscardPolicy:用于被拒绝任务的处理程序,默认情况下它将丢弃被拒绝的任务。
处理流程
1.查看核心线程池是否已满,不满就创建一条线程执行任务,否则执行第二步。
2.查看任务队列是否已满,不满就将任务存储在任务队列中,否则执行第三步。
3.查看线程池是否已满,即就是是否达到最大线程池数,不满就创建一条线程执行任务,否则就按照策略处理无法执行的任务。
流程图如下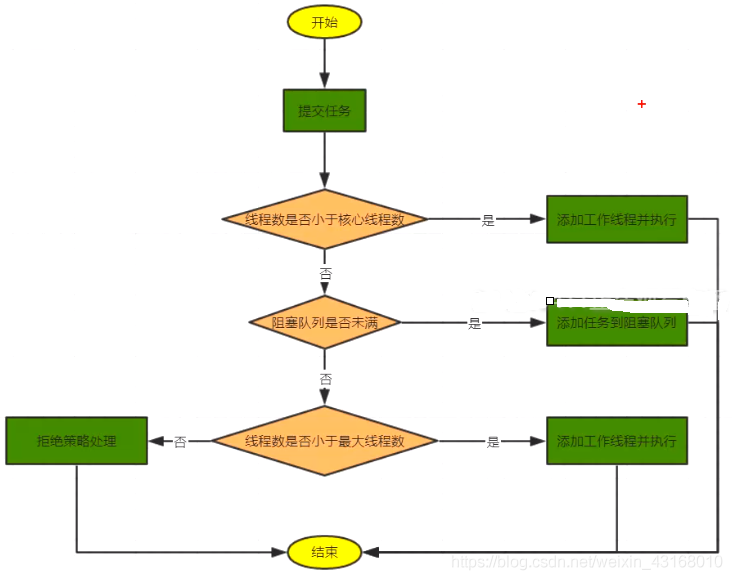
总结:本篇文章主要讲了一下JDK线程池和spring线程池这两个线程池,具体实际业务则和平时使用一样。

