1. 常用的包
1.1 包的名称和功能
- java.lang包:该包时Java语言的核心包, 并且该包中的所有内容由Java虚拟机自动导入
- java.util包:Java语言的工具包
- java.io包 : Java语言的输入输出包
- java.net包:Java语言中的网络包
- java.sql包:java语言的数据包
- ….
- java程序员在编程时可以使用大量类库,因此Java编程时需要记的很多,对编程的要求不是特别高。
1.2 Object类的概述
1.2.1 基本概念
- java.lang.object 类时Java 语言中类层次结构的根类,也就是 说 任何一个类都是该类的直接子类或间接子类。
- 如果定义一个Java类时没有使用extends关键字声明其父类,则其父类为Java.lang.Object~
- Object类定义了对象的基本行为,被子类默认继承
1.2.2 常用的方法
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| Object() | 使用无参方法构造对象 |
| public boolean equals(Object obj) | 用于判断调用对象是否与参数对象相等 该方法默认比较地址是否相等 |
| public int hashCode() | 默认用于获取对象的哈希码值(内存地址的编号) 若两个对象调用equals方法相等,则各自调用方法结果必须相同 若两个对象调用equals方法不相同,则各自调用方法的结果应该不相等 |
| public String toString() | 用于获取调用对象的字符串形式 该方法默认返回的字符串为:包名.类名@哈希码值的十六进制 为返回更有意义的数据,通常需要重写该方法 使用print或println打印引用或字符串拼接引用都会自动调用该方法。 |
| public final Class<?> getClass() | 用于返回调用对象执行时的class实例,反射机制使用 |
两个对象相等,hashcode一定相等
两个对象不等,hashcode不一定不等
hashcode相等,两个对象不一定相等
hashcode不等,两个对象一定不等
案例题目
编程实现Student类的封装,特征:学号(id) 和 姓名,要求提供打印所有特征的方法
编程实现StudentTest类,在main方法中使用有参方式构造两个Student类并打印特征
题目拓展**
如何实现以姓名为基准判断两个对象是否相等?以及学号且户名同时作为基准判断两个对象是否相等。
package com.lagou.task11;import java.util.Objects;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/7/19* @description*/public class Student extends Object {private int id;private String name;@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return id == student.id &&Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(id, name);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}public Student() {}public Student(int id, String name) {setId(id);setName(name);}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {if(id > 0)this.id = id;elseSystem.out.println("学号不合理哦!");}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}}
1.3 包装类
1.3.1 包装类的概念
通常情况下基本数据类型的变量不是对象,为了满足万物皆对象的理念就需要对基本数据的类型进行打包封装处理变成对象,而负责将这些变量声明为成员变量进行对象化处理的相关类,叫做包装类。
Person p = new Person();
int num = 8;
1.3.2 包装类的分类
| 包装类 | 对应的基本类型 |
|---|---|
| java.lang.Byte | byte |
| java.lang.Short | short |
| java.lang.Integer | int |
| java.lang.Long | long |
| java.lang.Float | float |
| java.lang.Double | double |
| java.lang.Boolean | boolean |
| java.lang.Character | char |
1.1.3 Integer类的概述
(1) 基本概念
java.lang.Integer类内部包装了一个int类型的变量作为成员变量,主要用于实现对int类型的包装并提供int类型到String类型类之间的转换等方法。
(2)常用的常量
| 常量类型和名称 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| public final static int MAX_VALUE | 表示int类型可以描述的最大值,即2^31-1 |
| public static final int MIN_VALUE | 表示int类型可以描述的最小值,即 -2^31 |
| public static final int SIZE | 表示int类型采用二进制补码形式的位数 |
| public static final int BYTES | 表示int类型所占的字节个数 |
| public static final Class |
表示int类型的Class实例 代表一种类型或者类型的名称 |
(2) 常用的方法
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| Integer(int value) | 根据参数指定的整数来构造对象(已过时) |
| Interger(String s) | 根据参数指定的字符串来构造对象(已过时) |
| int intValue() | 获取调用对象中的整数值并返回 |
| static Integer valueOf(int i) | 根据参数指定的整数值得到Integer类型对象 |
| boolean equals(Object obj) | 比较调用对象与指定的对象是否相等 |
| String toString() | 返回描述对象数值的字符串形式 |
| static int parseInt(String s) | 将字符串类型转化为int类型并返回 |
| static String toString(int i) | 获取参数指定整数的十进制字符串形式 |
| static String toBinaryString(int i) | 获取参数指定整数的二进制字符串形式 |
| static String toHexString(int i) | 获取参数指定整数的十六进制字符串形式 |
| static String toOctalString(int i) | 获取参数指定整数的八进制字符串形式 |
- @deprecated It is rarely appropriate to use this constructor. The static factory {@link #valueOf(int)} is generally a better choice, as it is* likely to yield significantly better space and time performance.
(3) 装箱和拆箱的概念
(4) 自动装箱池
在Integer类的内部提供了自动装箱的技术, [-128, 127 ]之间的整数已经装箱完毕, 当程序使用该范围内的整数时,无需装箱直接取用自动装箱池中的对象即**可。**jdk.internal.misc.VM 能够用来定义 low和high的值··
/*** Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between* -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.** The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache* may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.* During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property* may be set and saved in the private system properties in the* jdk.internal.misc.VM class.*/private static class IntegerCache {static final int low = -128;static final int high;static final Integer cache[];static {// high value may be configured by propertyint h = 127;String integerCacheHighPropValue =VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); //jvm调优if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {try {int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);i = Math.max(i, 127);// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUEh = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.}}high = h;cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];int j = low;for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)cache[k] = new Integer(j++);// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;}private IntegerCache() {}}
java.lang.NumberFormatException:数据格式异常
**
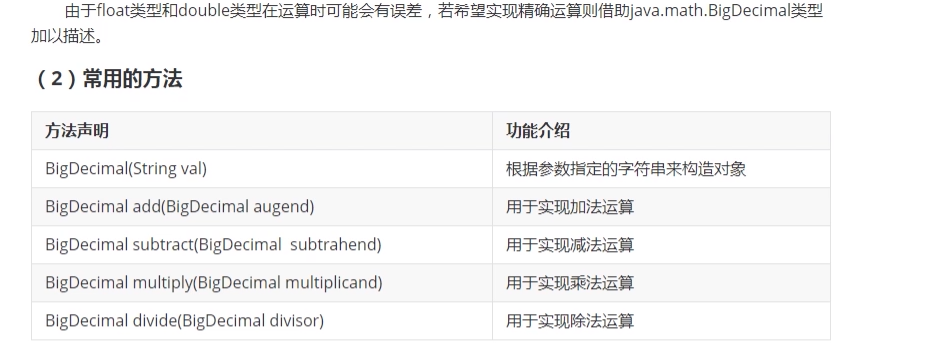
1.1.4 Double 类的概述

package com.lagou.task11;import java.util.function.DoubleBinaryOperator;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/7/25* @description*/public class DoubleTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 在Java5之前装箱拆箱的实现//Double db1 = new Double(3.14);Double db1 = Double.valueOf(3.14);System.out.println(db1.doubleValue());Double db2 = 3.14;double d2 = db2;double d3 = Double.parseDouble("13.88");System.out.println("db2对象的判断结果是:" + db2.isNaN()); //falseDouble db3 = Double.valueOf(0/0.0);System.out.println("db4对象的判断结果是:" + db3.isNaN()); //false}}
1.1.5 Boolean类的概述
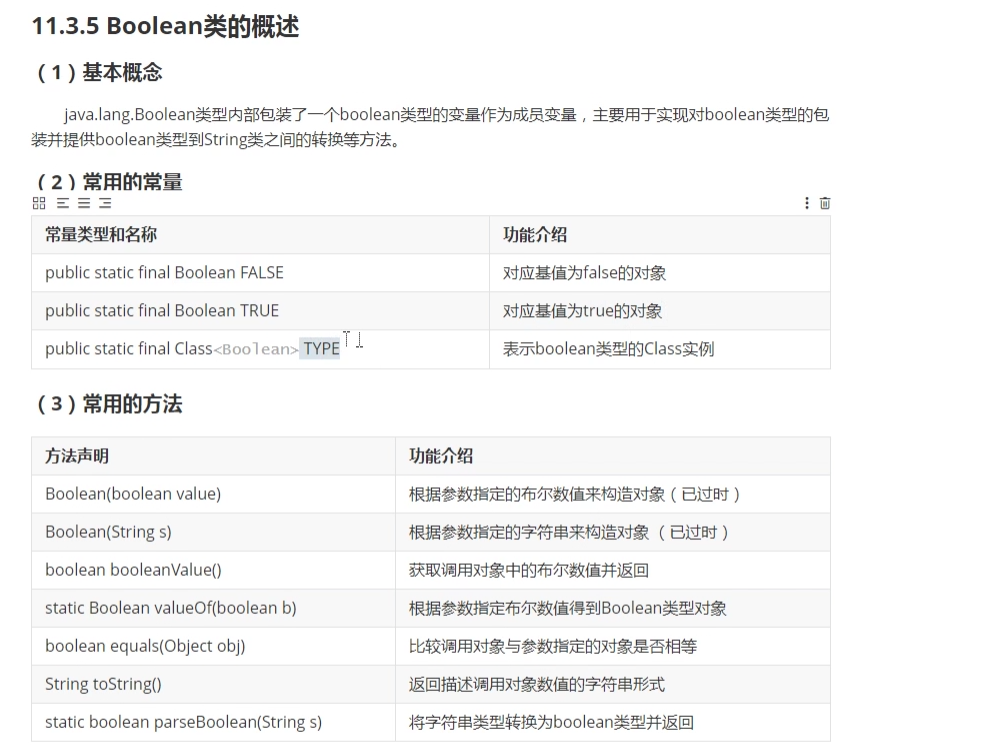
package com.lagou.task11;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/7/25* @description*/public class BooleanTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Boolean bl1 = new Boolean(false);System.out.println(bl1);boolean b2 = bl1.booleanValue();System.out.println("------------------------------");Boolean bl2 = true;boolean b3 = bl2;boolean b4 = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");System.out.println(b4);}}
1.1.6 Character 类的概述
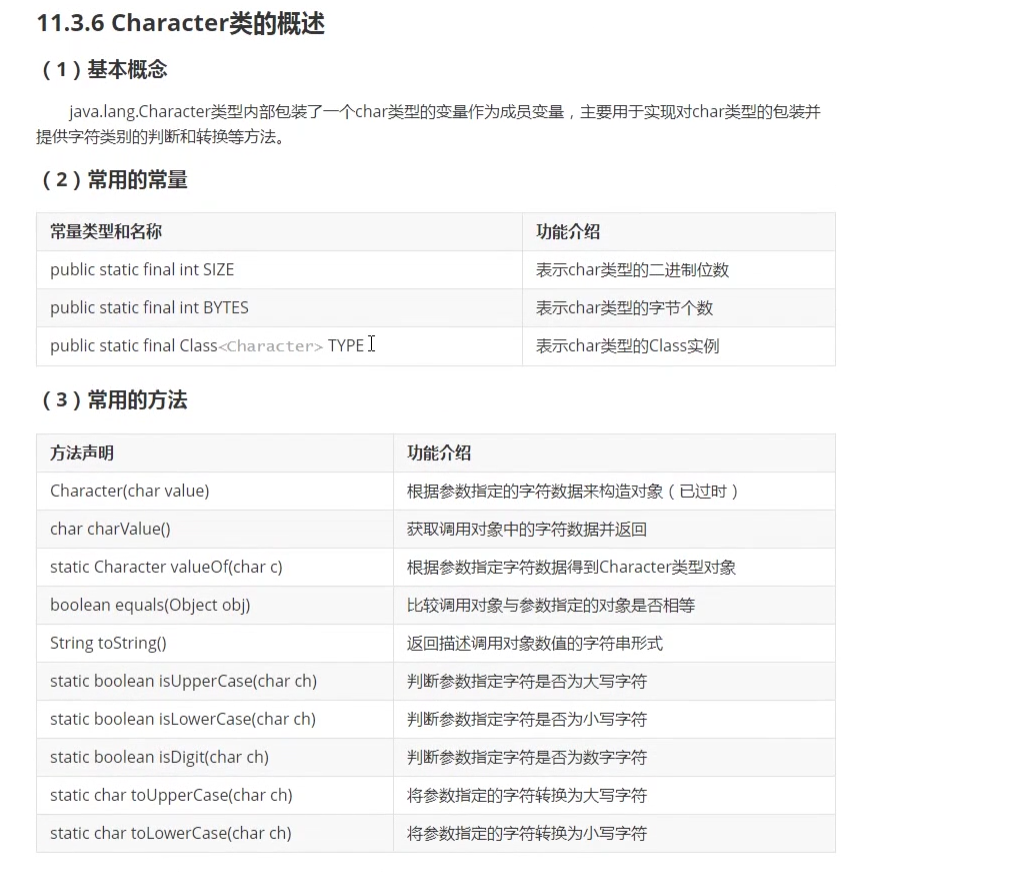
package com.lagou.task11;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/7/25* @description*/public class CharacterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//装箱Character ca1 = Character.valueOf('c');System.out.println("ca1 = " + ca1);//拆箱char c1 = ca1.charValue();System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);//自动装箱Character ca2 = 'b';char c2 = ca2;System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase(ca2));System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase(ca2));System.out.println(Character.isDigit(ca2));System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase(ca2));System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase(c2));}}
1.1.7 包装类(Wrapper)的使用总结
- 基本数据类型转换为对应包装类的方式
调用包装类的构造方法或静态方法即可。 valueOf()
- 获取包装类对象中基本数据类型变量数值的方式
调用包装类中xxxValue()方法即可
- 字符串转换为基本数据类型的方式
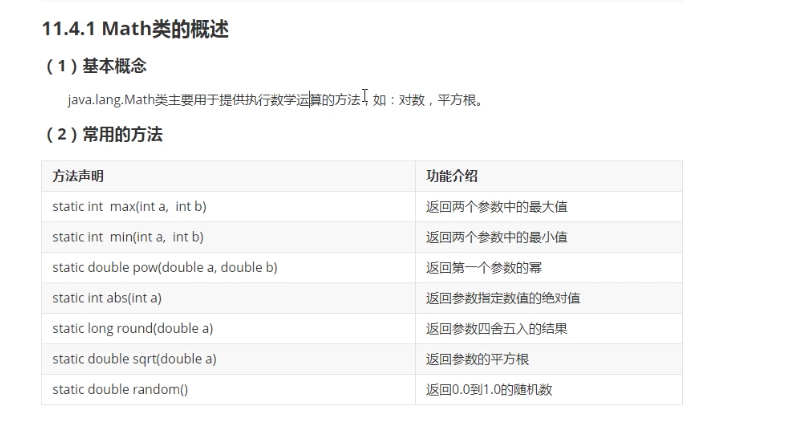
1.4 Math类-数学处理类
1.4.1 Math类的概述
1.4.2 BigDecimal类的概念
1.4.3 BigInteger类的概念
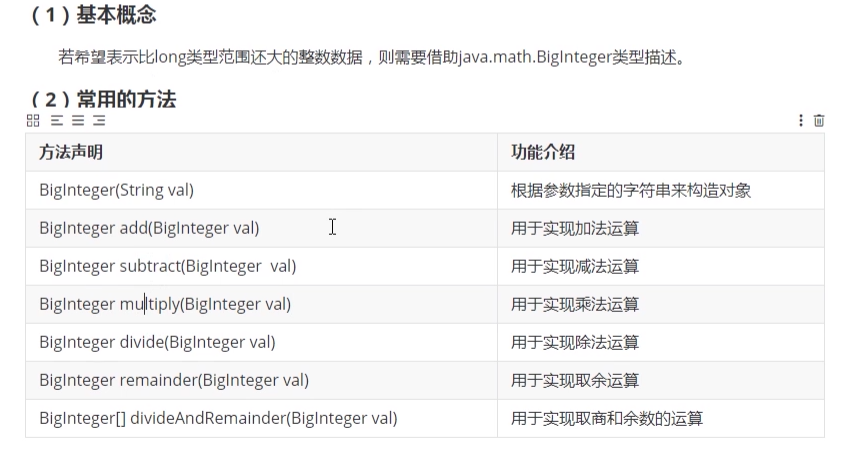
package com.lagou.task11;import java.math.BigInteger;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/7/25* @description*/public class BigIntegerTest {public static void main(String[] args) {BigInteger bi1 = new BigInteger("20");BigInteger bi2 = new BigInteger("8");System.out.println(bi1.add(bi2));System.out.println(bi1.subtract(bi2));System.out.println(bi1.multiply(bi2));System.out.println(bi1.divide(bi2));System.out.println(bi1.remainder(bi2));System.out.println("==================================");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bi1.divideAndRemainder(bi2)));}}
总结
- 常用的包(熟悉)
- java.lang、java.util、java.net、java.sql…
- Object类(重点)
- 概念
- equals()
- hashCode()
- toString()
- 重写
- 包装类(熟悉)
- 概念
- Integer
- Double
- Boolean
- Character
valueOf
- 常用的数学处理类(熟悉)
- Math类
- BigDecimal类
- BigInteger类