1.1 集合的概述

- 变量 -> 数组
- 对象 -> 对象数组
1.2 Collection集合(重点)
1. 基本概念
2. 常用方法
- Ctrl+F12 搜索类中的方法内容
- ctrl + N 查找类并打开类的源码 ```java package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List;
/**
- @author 西风月
- @date 2020/7/29
@description */ public class CollectionTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 准备一个Collection 集合//Collection c1 = new Collection(); //接口不能实例化,不能创建对象Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); //接口类型的引用指向实现类的对象,实现多台System.out.println("集合中的元素有:" + c1) ; //自动调用toString()方法,默认打印格式[元素值1, ...]System.out.println("=============================================================================");//2. 向集合中添加单元素System.out.println(c1.add("One"));System.out.println("集合中的元素有:" + c1) ; //自动调用toString()方法,默认打印格式[元素值1, ...]System.out.println(c1.add(Integer.valueOf(2)));System.out.println("集合中的元素有:" + c1) ; //自动调用toString()方法,默认打印格式[元素值1, ...]//打印集合元素就是调用每个集合中对象, 调用toString()方法System.out.println(c1.add(new Person("liubei", 39)));System.out.println("集合中的元素有:" + c1) ; //自动调用toString()方法,默认打印格式[元素值1, ...]System.out.println("=============================================================================");Collection c2 = new ArrayList();c2.add("three"); //常量池c2.add(4); //自动装箱机制System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);//将c2中的元素依次添加到集合c1中System.out.println(c1.addAll(c2)); //c1 = [One, 2, Person{name='liubei', age=29}, three, 4]//c1.add(c2); //[One, 2, Person{name='liubei', age=29}, [three, 4]]System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);System.out.println("=============================================================================");//-判断集合中是否包含参数指定的单个元素System.out.println(c1.contains(new String("one")));System.out.println(c1.contains(new String("One")));System.out.println(c1.contains(Integer.valueOf(4)));System.out.println(c1.contains(Integer.valueOf(3)));//contains方法原理是调用 Objects.equals(o, e), 而该方法额equals方法的工作原理, 其中 o代表contains方法的形式参数,e代表集合中的每个元素./* public static boolean equals(Object a, Object b) {return (a == b) || (a != null && a.equals(b)); //(1) 地址相同 (2) 非空且调用equals方法相等}*/System.out.println(c1.contains(new Person("liubei", 39))); //false ? 必须重写Person后的equals方法System.out.println("=============================================================================");//[One, 2, Person{name='liubei', age=29}, three, 4]System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);//判断集合中是否包含参数指定的所有元素Collection c3 = new ArrayList();c3.add(4);c3.add(2);System.out.println("c3 = " + c3);System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c3)); //true//笔试考点System.out.println("c2 = " + c2); //[three, 4]System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c2));System.out.println(c1.contains(c2));System.out.println("=============================================================================");//6.计算两个集合的交集,并保留到当前对象System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);System.out.println("c3 = " + c3);System.out.println(c2.retainAll(c2)); //false 当前集合元素未发生改变System.out.println(c2);System.out.println(c2.retainAll(c3)); //true 当前集合的元素发生改变System.out.println(c2);System.out.println(c3);System.out.println("=============================================================================");//实现集合中元素的删除 remove还是调用Objects.remove方法System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);System.out.println(c1.remove(1)); //falseSystem.out.println("c1 = " + c1);System.out.println(c1.remove("One"));System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);System.out.println(c1.remove(new Person("liubei", 39)));System.out.println("c1 =" + c1) ;System.out.println("c3 = " + c3);System.out.println(c1.removeAll(c3));System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);//笔试考点System.out.println(c1.remove(c3));System.out.println("=============================================================================");//实现集合中其他方法的测试System.out.println(c1.size());System.out.println(c1.isEmpty());c1.clear();System.out.println(c1.size());System.out.println(c1.isEmpty());Collection c4 = new ArrayList();c4.add(1);c4.add(2);Collection c5 = new ArrayList();c5.add(1);c5.add(2);c5.add(3);System.out.println(c4.equals(c5));System.out.println("=============================================================================");//实现集合和数组类型的转换 通常认为: 集合是用于取代数组的结构Object[] objects = c5.toArray();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));Collection objects1 = Arrays.asList(objects);System.out.println("集合中的元素:" + objects1);
} }
<a name="Q5tpR"></a># 1.3 Iterator接口(重点)```javapublic String toString() {Iterator<E> it = iterator();if (! it.hasNext())return "[]";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append('[');for (;;) {E e = it.next();sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);if (! it.hasNext())return sb.append(']').toString();sb.append(',').append(' ');}}
package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/29
* @description
*/
public class CollectionPrintTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 准备一个Collection集合放入元素并打印
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("One");
c1.add(2);
c1.add(new Person("zhangfei", 30));
//遍历方式1:自动调用toString方法 Stringl类型的整体
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);
//2.使用迭代器来遍历集合中的所有元素
Iterator iterator = c1.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
Iterator iterator1 = c1.iterator();
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder();
sb1.append("[");
while(iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator1.next();
//当获取的元素是最后一个元素是,则拼接加‘]’ 否则 ‘, ’
if (iterator1.hasNext()) {
sb1.append(obj).append(", ");
} else {
sb1.append(obj).append("]");
}
}
System.out.println(sb1);
}
}
1.4 for each循环(重点)

package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/29
* @description
*/
public class CollectionPrintTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 准备一个Collection集合放入元素并打印
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("One");
c1.add(2);
c1.add(new Person("zhangfei", 30));
//遍历方式1:自动调用toString方法 Stringl类型的整体
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);
//2.使用迭代器来遍历集合中的所有元素
Iterator iterator = c1.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
Iterator iterator1 = c1.iterator();
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder();
sb1.append("[");
while(iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator1.next();
//当获取的元素是最后一个元素是,则拼接加‘]’ 否则 ‘, ’
if (iterator1.hasNext()) {
sb1.append(obj).append(", ");
} else {
sb1.append(obj).append("]");
}
}
System.out.println(sb1);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
iterator1 = c1.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator1.next();
if("One".equals(obj)) {
iterator1.remove();
//c1.remove(obj); //ConcurrentModificationException 并发修改异常
}
}
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println("==========================================");
c1.add("New");
//使用for-each结构实现集合和数组的遍历, 代码简单更灵活
for(Object obj : c1) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
int[] arr = new int[] {23, 17, 15, 12, 25};
for(int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
- 添加断点:
- Alt+Shift+F9
- 下一步点: Step Over
- F8
- 进入自定义代码 Step Into
- F7
- 强制进入Java源码 ALT+SHIFT+f7
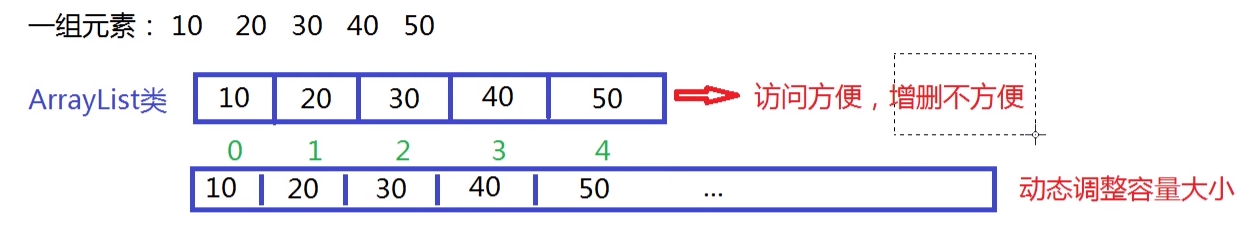
1.5 List集合(重中之重)
ArrayList
- 区别:动态数组进行数据管理
- 特点:访问方便,增删不方便
- ArrayList的扩容原理
- 原始长度 的 1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return minCapacity; } return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0) ? newCapacity : hugeCapacity(minCapacity); }
- 原始长度 的 1.5倍
package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/30
* @description
*/
public class ListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 声明一个List接口引用指向ArrayList对象
//由源码可知,当new对象时并没有申请数组内存空间
List lt1 = new ArrayList();
//由源码可知,当调用add方法添加元素时会给数组申请长度为10的一维数组,扩容原理是:原始长度*1.5倍
lt1.add("New");
System.out.println("lt1 = " + lt1);
}
}
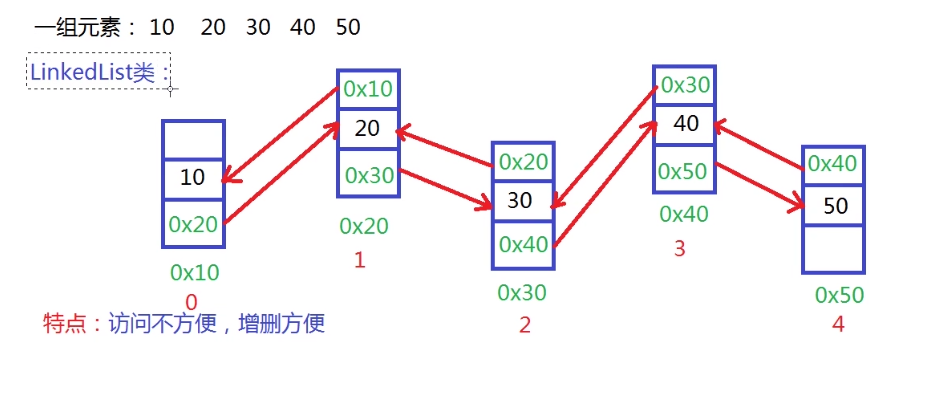
LinkedList 双向链表
- 底层采用双向链表的数据结构
- 特点: 内存空间不连续, 访问不方便, 增删方便
- 节点概念
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/30
* @description
*/
public class ListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 声明一个List接口引用指向ArrayList对象
//由源码可知,当new对象时并没有申请数组内存空间
List lt1 = new ArrayList();
//由源码可知,当调用add方法添加元素时会给数组申请长度为10的一维数组,扩容原理是:原始长度*1.5倍
lt1.add("New");
System.out.println("lt1 = " + lt1);
System.out.println("=======================================================");;
//2. 声明一个List接口的引用指向LinkedList类型的对象,形成了多态
List lt2 = new LinkedList();
lt2.add("New1");
System.out.println(lt2);
}
}
栈类 Stack
package com.lagou.task14;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/30
* @description
*/
public class ListMethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 准备一个List集合并打印
List lt1 = new LinkedList();
System.out.println(lt1);
//2. 向集合中添加元素并打印
lt1.add(0, "New");
System.out.println(lt1);
lt1.add(1, 3);
System.out.println(lt1);
lt1.add(1, "two");
System.out.println(lt1);
//3. 根据参数指定的下标来获取元素
String str1 = (String) lt1.get(0);
System.out.println(str1);
//注意:获取元素并进行强制类型转换时一定要慎重,因为容易发生类型转换异常. CLassCaseException
int str2 = (int) lt1.get(2);
System.out.println(str2);
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder();
sb1.append("[");
for(int i = 0; i < lt1.size(); i++) {
//System.out.println(o);
Object obj = lt1.get(i);
if(lt1.size() - 1 == i) {
sb1.append(obj).append("]");
} else{
sb1.append(obj).append(", ");
}
}
System.out.println(sb1);
//5. 查找指定元素出现的索引位置
System.out.println("One第一次出现的索引位置为:" + lt1.indexOf("One"));
System.out.println("New第一次出现的索引位置为:" + lt1.indexOf("new"));
lt1.add("One");
System.out.println(lt1);
System.out.println("One反向查找出现的位置:" + lt1.lastIndexOf("One"));
System.out.println(lt1.set(0, "One"));
System.out.println(lt1);
System.out.println(lt1.set(3, "4"));
System.out.println(lt1);
System.out.println("=======================================================");
//使用remove方法将集合中所有元素删除
//for(int i =0; i < lt1.size(); /*i++*/) {
//for(int i = lt1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// while(lt1.size() > 0) {
// //System.out.println(lt1.remove(i)); 删除元素后, 后面的元素补位
// System.out.println(lt1.remove(0));
// }
System.out.println(lt1);
//表示获取当前集合中下标为[0,3)的子集合,子集合和当前集合共有一块内存空间。
System.out.println(lt1.subList(0, 3));
lt1.subList(0,3).remove(1);
System.out.println(lt1);
}
}
- 栈的使用案例题详解
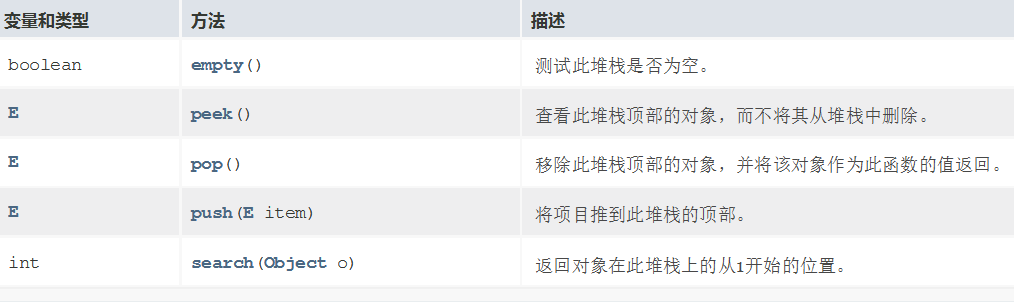
package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/7/30
* @description
*/
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.准备一个Stack栈类型的对象
Stack s1 = new Stack();
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
Stack s2 = new Stack();
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2);
System.out.println("=====================================");
//2. 入栈
for(int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.println("入栈的元素:" + s1.push(i * 11));
System.out.println("栈中的元素有:" + s1);
}
//3. 查看栈顶元素并打印
System.out.println("获取到的栈顶元素是:" + s1.peek());
//4.出栈
while(s1.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("出栈的元素为:" + s2.push(s1.pop()));
}
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
while(s2.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("s2 的出栈元素:" + s2.pop());
}
}
}
1.6 Quene集合

- 队列
- 先进先出
- offer 入队
- poll 出对 ```java package com.lagou.task14;
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue;
/**
- @author 西风月
- @date 2020/7/30
@description */ public class QueneTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先准备一个Quene集合并打印 Queue queue = new LinkedList(); System.out.println("队列中的元素有:" + queue); System.out.println("==========================================="); for(int i = 1; i < 6; i++) { System.out.println(queue.offer(i*11)); System.out.println("队列中的元素有:" + queue); } System.out.println(queue.peek()); while(queue.size() > 0) { System.out.println("出队的元素时:" + queue.poll()); }} }
```
总结
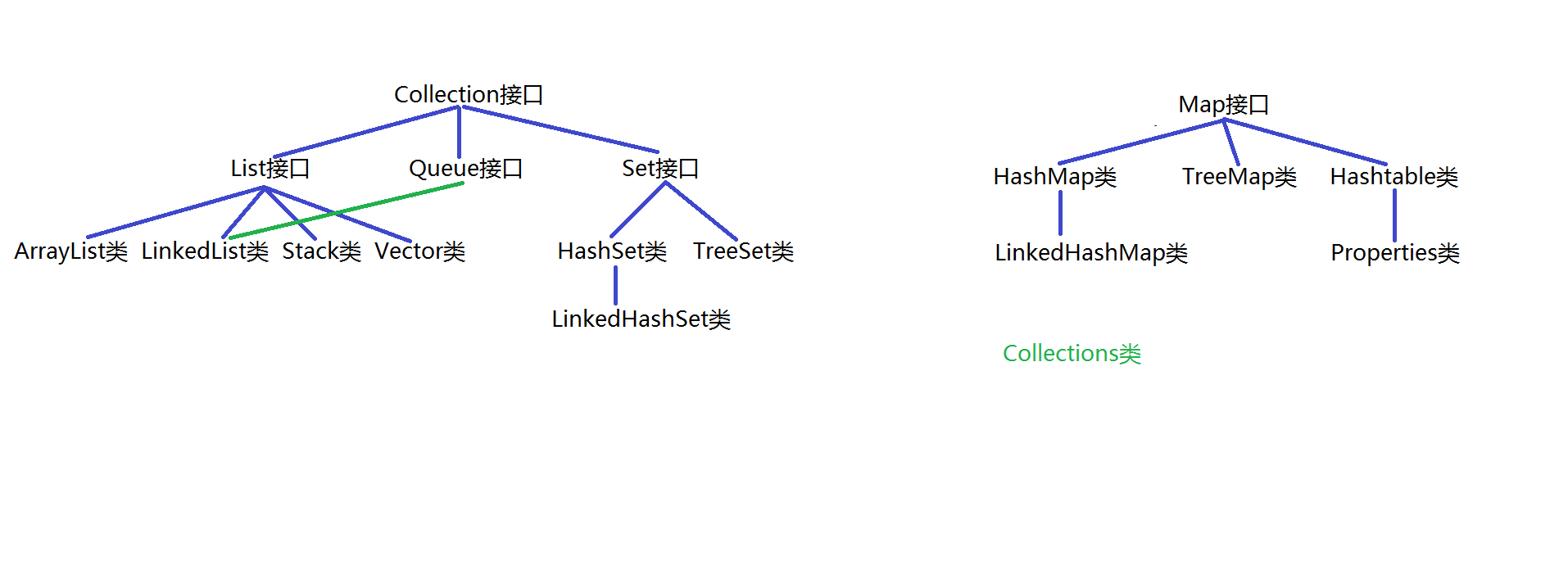
- 集合的概述
- 集合的由来、两张图
- Collection集合
- 常用的方法
- Iterator接口
- 概念、遍历集合
- for each
- 是Java5中新增的内容, 是迭代器的jj简化版
- List 集合
- 概念、常用方法、常用实现类
- Queue集合
- 概念,常用实现类,常用方法



