- 1. IO流的概念
- 2. 基本分类
- 3. 体系结构
- 4. 相关流的详解
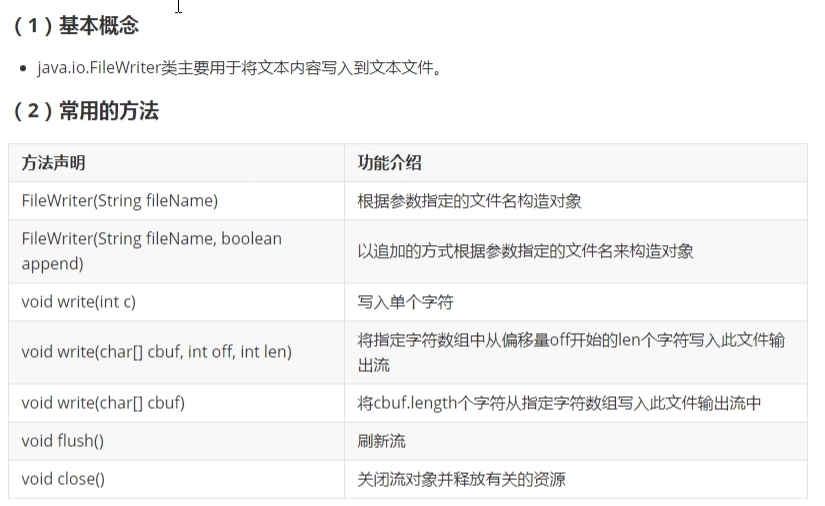
- 1. FileWriter类(重点)
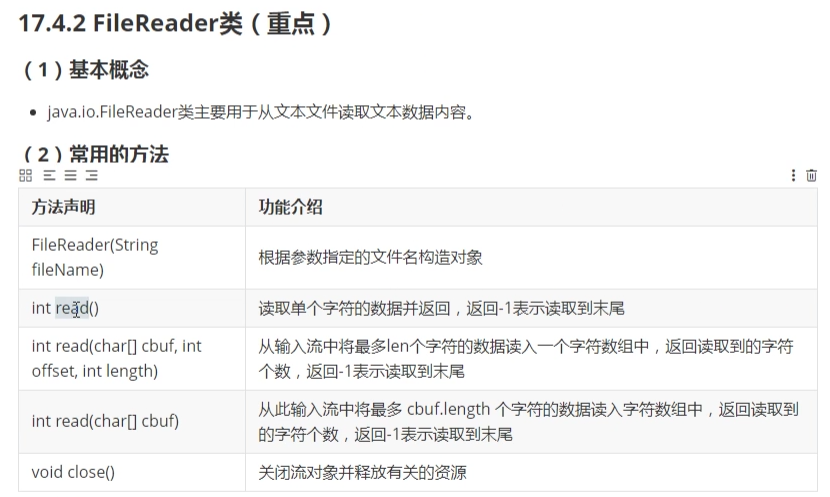
- 2. FileReader类(重点)
- 3. FileOutputStream类(重点)
- 4. FileInputStream类(重点)
- 5. BufferedOutputStream类(重点)
- 6. BufferedInputStream类(重点)
- 7. BufferedWriter类 (重点)
- 8. BufferedReader类 (重点)
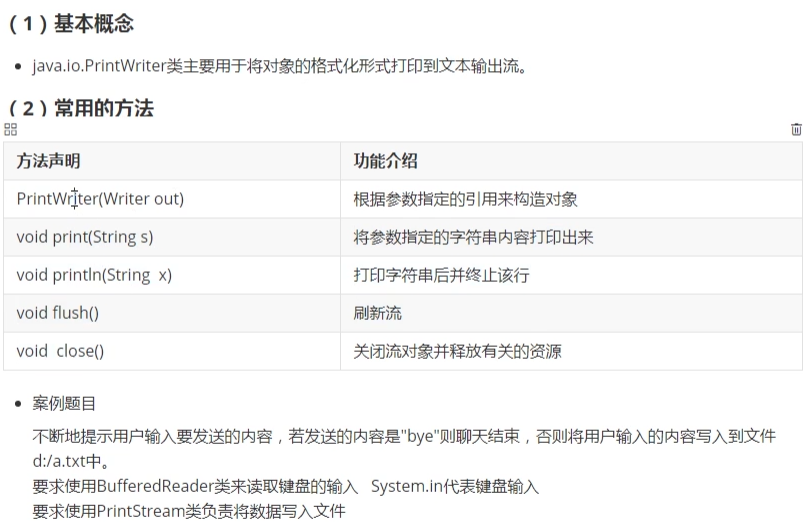
- 9. PrintStream类
- 10. PrintWriter类
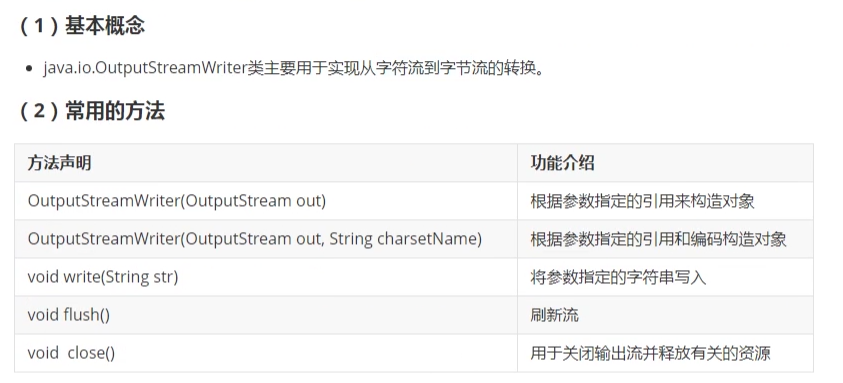
- 11. OutputStreamWriter类
- 12. InputStreamReader类
- 13. 字符编码
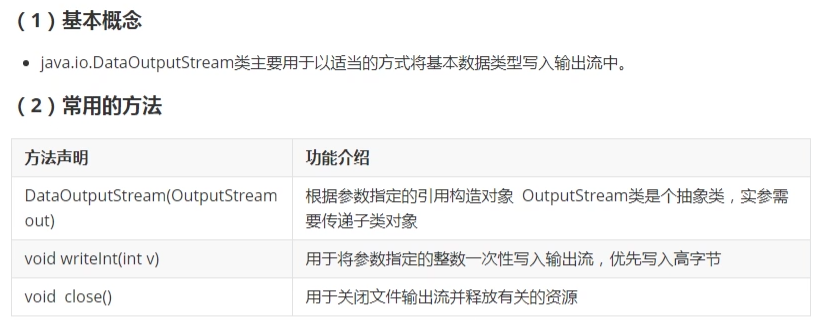
- 14. DataOutPutStream类(了解)
- 15. DataInputStream类(了解)
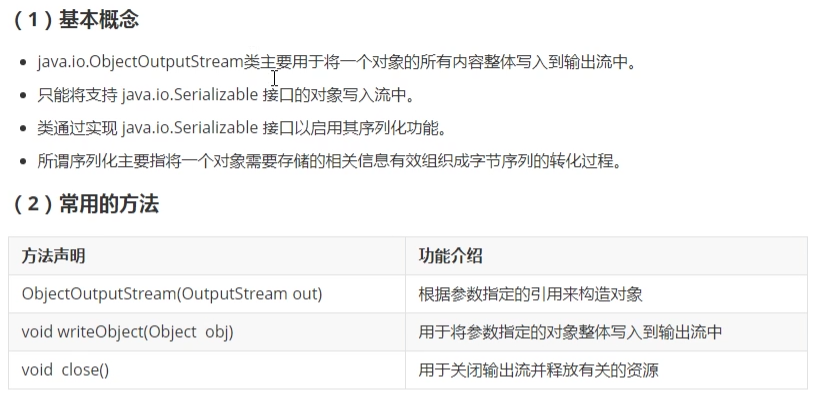
- 16. ObjectOutputStream类(重点)
- 17. ObjectInputStream类(重点)
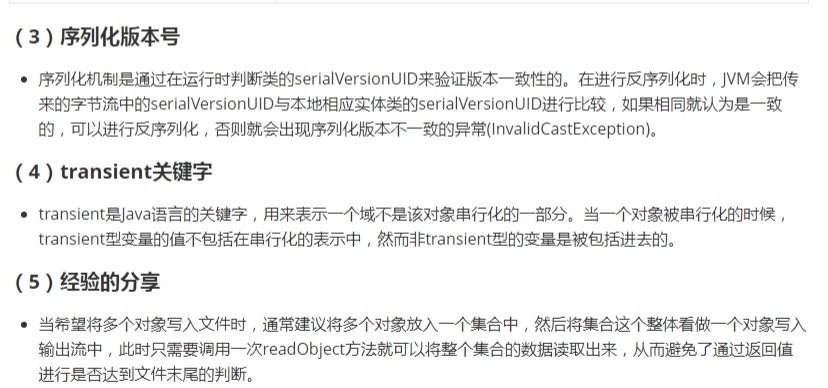
- 18. RandomAccessFile类
- 本任务总结
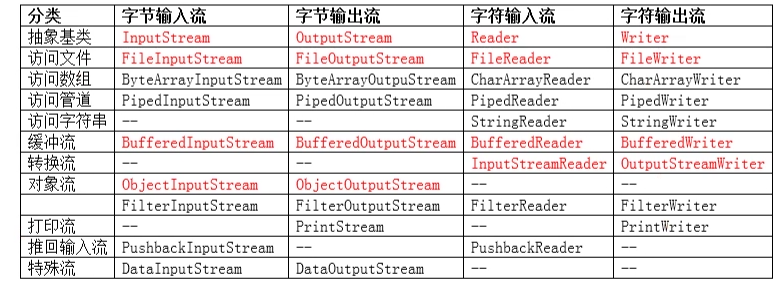
1. IO流的概念
2. 基本分类

- 字节流
- 字符流(2个字节)
- 字节流可以读写任意类型的文件
- 字符流只能读取文本文件
- 汉字一般占两个字节,半个汉字?
- 输入流
- 输出流 -> 站在程序的角度看
- 输入流读文件到程序内存
- 输出流写文件到文件中
- 节点流
- 处理流
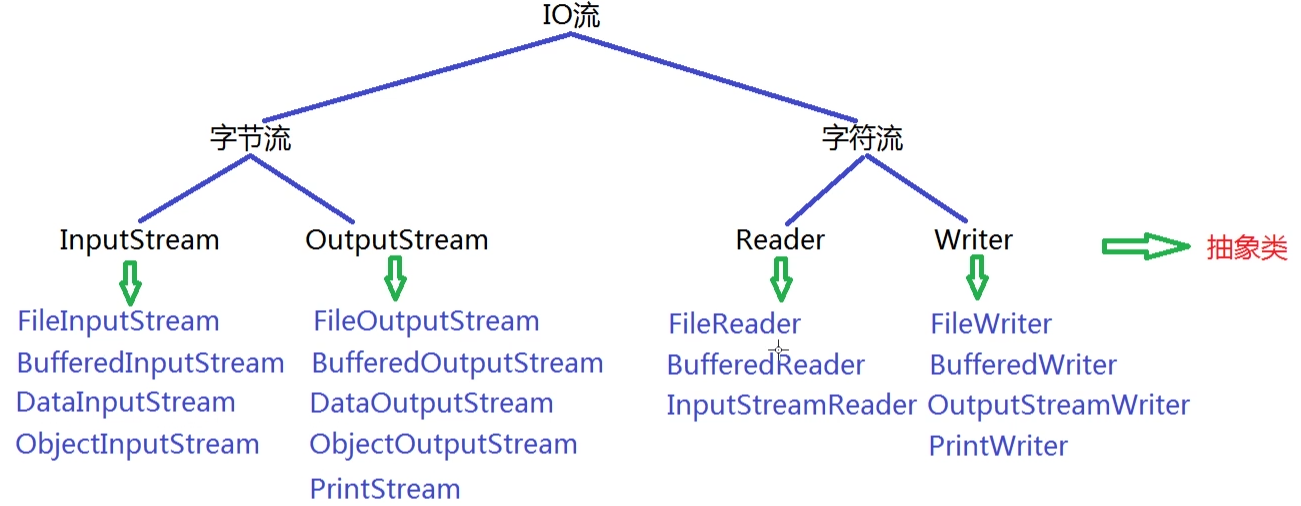
3. 体系结构
4. 相关流的详解
1. FileWriter类(重点)
(1) 基本概念和基本使用
package com.lagou.task17;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/8/12* @description*/public class FileWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {FileWriter fw = null;// 选中代码后可以使用 ctrl+alt+t来生成异常的捕获代码等try {//构造FileWriter类型的对象与f:/a.txt文件关联// 若文件不存在, 该流会自动创建新的文件//若文件存在则会清空文件中的原有内容//fw = new FileWriter("f:/a.txt");// 以追加的方式创建对象去关联文件// 若文件不存在则自动创建新的文件,若文件存在则保留原有数据内容fw = new FileWriter("f:/a.txt", true);//2. 通过流对象写入数据fw.write('a');System.out.println("写入文件成功 !");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//3. 关闭流对象并释放相关的资源if(null != fw) {try {fw.close(); //close自带flush方法功能} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
(2)FileWriter类的方法使用
package com.lagou.task17;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author 西风月* @date 2020/8/12* @description*/public class FileWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {FileWriter fw = null;// 选中代码后可以使用 ctrl+alt+t来生成异常的捕获代码等try {//构造FileWriter类型的对象与f:/a.txt文件关联// 若文件不存在, 该流会自动创建新的文件//若文件存在则会清空文件中的原有内容fw = new FileWriter("f:/a.txt");// 以追加的方式创建对象去关联文件// 若文件不存在则自动创建新的文件,若文件存在则保留原有数据内容//fw = new FileWriter("f:/a.txt", true);//2. 通过流对象写入数据fw.write('a');//准备字符数组char[] cArr = new char[] {'a','b','c','d','g'};//将字符数组的部分写入fw.write(cArr, 1,3);//将整个数组写入fw.write(cArr);//刷新六fw.flush();System.out.println("写入文件成功 !");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//3. 关闭流对象并释放相关的资源if(null != fw) {try {fw.close(); //close自带flush方法功能} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
2. FileReader类(重点)
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/12
* @description
*/
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1. 构造FileReader类的对象与f:/a.txt文件相关联
fr = new FileReader("f:/a.txt");
/*//2. 读取文件内容并打印
int res = 0;
while((res = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println("读取到的单个字符是" + (char)res);
}
//int res = fr.read();*/
//准备一个字符数组来保存读取到的数据内容
char[] cArr = new char[5];
//期望读满字符数组中的一部分空间,也就是放入3字符放入到数组cArr中下标1开始的位置
/*int res = fr.read(cArr, 1, 3);
System.out.println("实际读取到的个数是" + res);
for (char cv: cArr) {
System.out.println("读取到的单个字符是:" + (char)cv);
}*/
int res = fr.read(cArr);
System.out.println("实际读取到的个数是" + res);
for (char cv: cArr) {
System.out.println("读取到的单个字符是:" + (char)cv);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.关闭流对象并释放有关的资源
if(null != fr) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
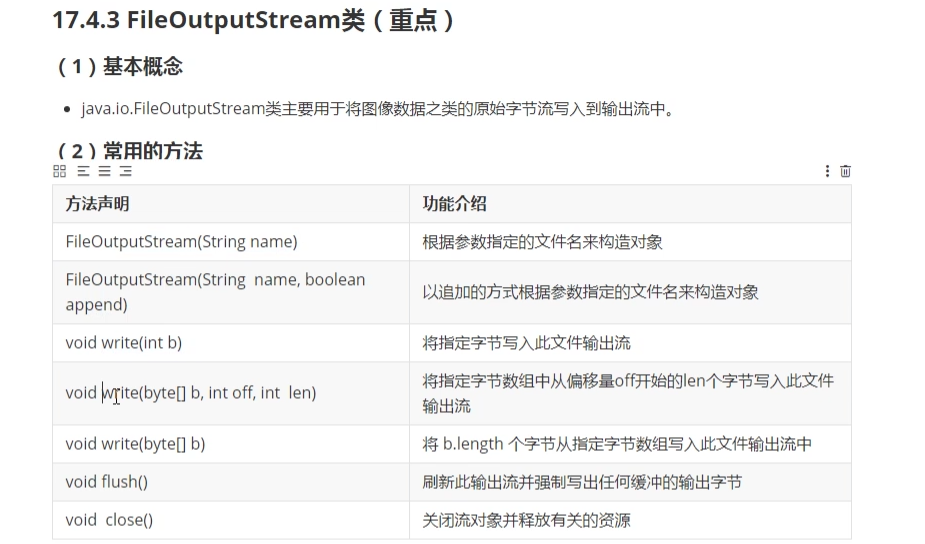
3. FileOutputStream类(重点)
4. FileInputStream类(重点)

- 二进制文件拷贝与文本文件拷贝 ```java package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException;
/**
- @author 西风月
- @date 2020/8/12
- @description
*/
public class FilesCharCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
} }FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { //1. 创建FileReader类型的对象与f:/a.txt管理 fr = new FileReader("f:/testPicture.jpg"); //fr = new FileReader("f:/a.txt"); //2. 创建FileWriter类型的对象与f:/b.txt管理 fw = new FileWriter("f:/test.jpg"); //fw = new FileWriter("f:/1.txt"); //3. 不断的从输入流中读取数据内容并写入到输出流中 int res = 0; System.out.println("正在玩命得拷贝!"); //拷贝图片文件失败! while((res = fr.read()) != -1) { fw.write(res); } System.out.println("拷贝文件成功"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4. 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 if(null != fw) { try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(null != fr) { try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 拷贝文件方式的比较
```java
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/12
* @description
*/
public class FileByteCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1. 创建FileInputStream类型的对象 f:/testPicture.jpg的文件关联
//fis = new FileInputStream("f:/testPicture.jpg");
fis = new FileInputStream("f:/day2.wmv");
//2. 创建FileOutputStream类型的对象与f:/test1.jpg文件关联
fos = new FileOutputStream("f:/day2-new.wmv");
//3. 不断的从输入流中读取数据并写入到输出流中
System.out.println("正在玩命得拷贝中...");
//方式一:以单个字节为单位进行拷贝时, 也就是每次读取一个字节后再写入一个字节
//缺点: 文件稍大时, 效率很低, 耗时感人
/*int res = 0;
while((res = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(res);
}*/
//方式二: 准备一个和文件大小一样的缓冲区, 一次性将所有的内容取出到缓冲区然后一次性写入进去
//缺点:当文件过大时,资源受限的问题,无法申请跟文件大小一样大的缓冲区,超时实际的物理内存大小.
/*int length = fis.available();
System.out.println("获取到的文件大小是:" + length);
byte[] bArr = new byte[length];
int res = fis.read(bArr);
System.out.println("实际读取到的文件大小是:" + res);
fos.write(bArr);*/
//方式三: 准备一个相对适当的缓冲区,分多次将文件拷贝直到完成
byte[] bArr = new byte[1024];
int res = 0;
while((res = fis.read(bArr)) != -1) { //read返回值是实际读取的字节大小
fos.write(bArr, 0, res);
}
System.out.println("拷贝文件成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源
if(null != fos) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != fis) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
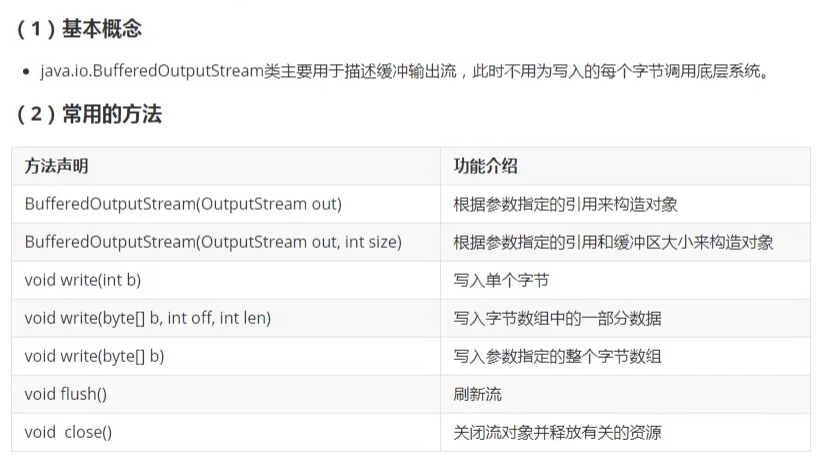
5. BufferedOutputStream类(重点)
6. BufferedInputStream类(重点)
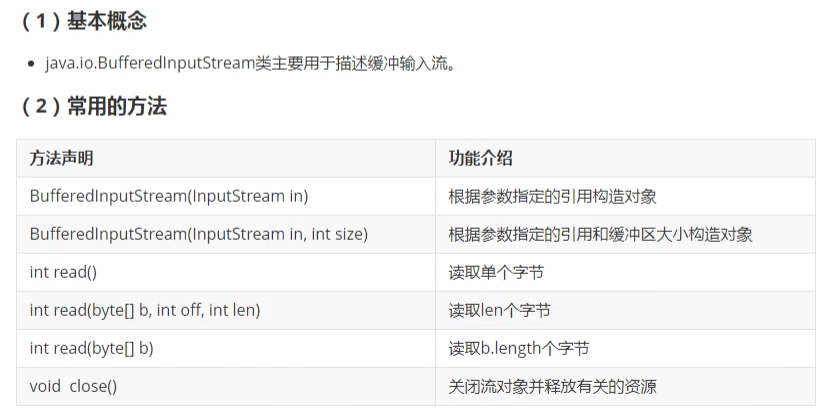
8096 byte
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class BufferedByteCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long g1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前系统时间距离1970-1-1 0:0:0:0的毫秒数
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1. 创建BufferedInputStream类型的对象与文件相关联
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("f:/day2.wmv"));
//2. 创建BufferedOutputStream类型的对象与文件相关联
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/day2_20200816.wmv"));
//3. 不断的从输入流读取并写入到输出流
System.out.println("正在玩命的拷贝中.....");
byte[] bArr = new byte[1024];
int res = 0;
while((res=bis.read(bArr)) != -1) {
bos.write(bArr, 0, res);
}
System.out.println("拷贝文件成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭相关资源
if (null != bos) {
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (null != bis) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long g2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前系统时间距离1970-1-1 0:0:0:0的毫秒数
System.out.println("使用缓冲区拷贝视频文件消耗的时间:" + (g2-g1)); //612
}
}
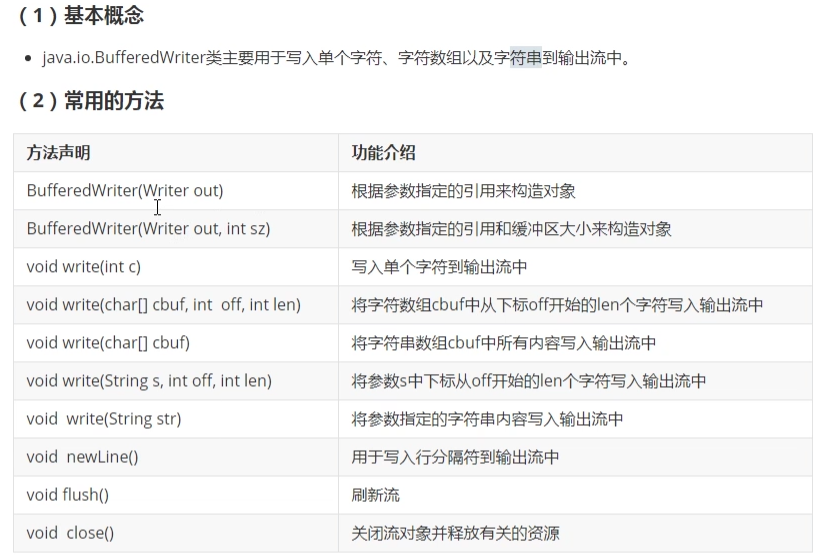
7. BufferedWriter类 (重点)
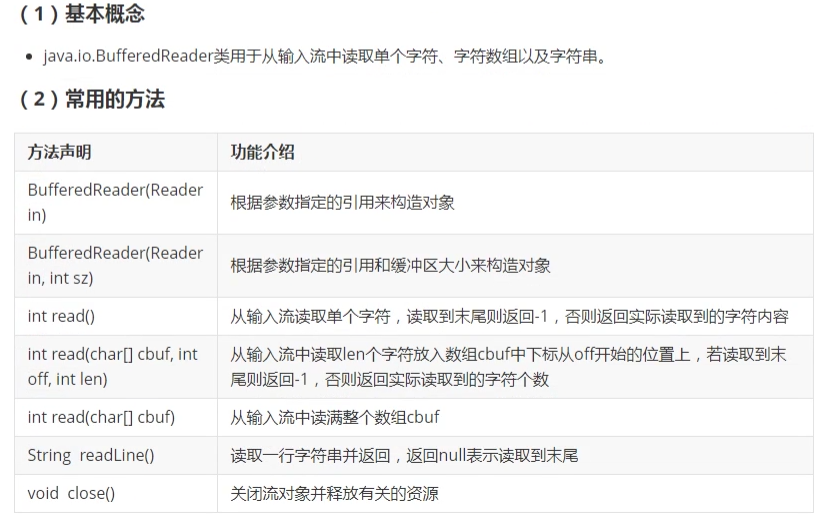
8. BufferedReader类 (重点)
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class BufferedCharCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//1. 创建BufferReader类型的对象与文本文件关联
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("f:/a.txt"));
//2. 创建BufferWriter类型的对象与文本文件关联
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("f:/new_a.txt"));
//3. 从输入流读取对象并写入到输出流中
String str = null;
System.out.println("正在玩命的拷贝中....");
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine(); //当前系统的行分割符/r/n
}
System.out.println("拷贝文件成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭流对象并释放相关的资源
if(null != bw) {
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != br) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
9. PrintStream类
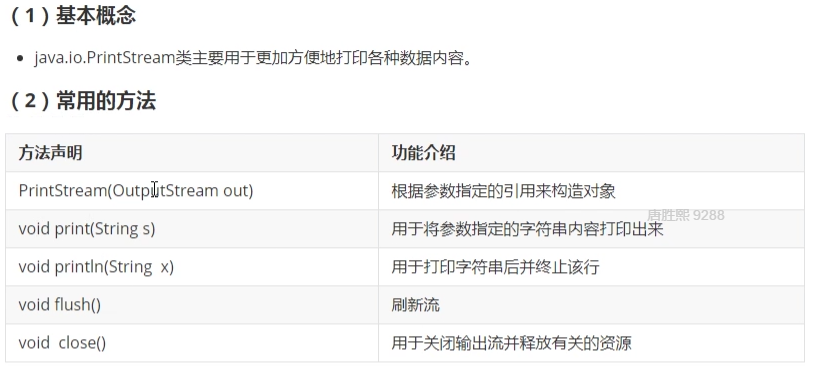
System.out.println();
public static final PrintStream out
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class PrintStreamChatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//ps = System.out;
ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt", true));
//声明一个布尔类型的变量作为发送方的代表
boolean flag = true;
while(true) {
//1. 提示用户要输入的聊天内容并使用变量记录
System.out.print("请" + (flag ? "张三" : "李四") + "输入要发送的聊天内容:");
//由手册可知:构造方法需要Reader类的对象,但其是抽象类,故实参只能传递子类,字符流
//由手册可知,System.in表示的是键盘输入,而且是InputStream类型 字节流
//2. 判断用户输入的内容是否是"bye",若是则聊天结束
String str = br.readLine();
if ("bye".equalsIgnoreCase(str)) {
System.out.println("聊天结束!");
break;
}
//3. 不是"bye"则将输入写入f:/a.txt
//获取当前系统时间并调整格式
Date d1 = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
ps.println(sdf.format(d1) + (flag? "张三说 " : "李四说 ")+ str);
flag = !flag;
}
ps.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭流对象
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
10. PrintWriter类
11. OutputStreamWriter类
12. InputStreamReader类
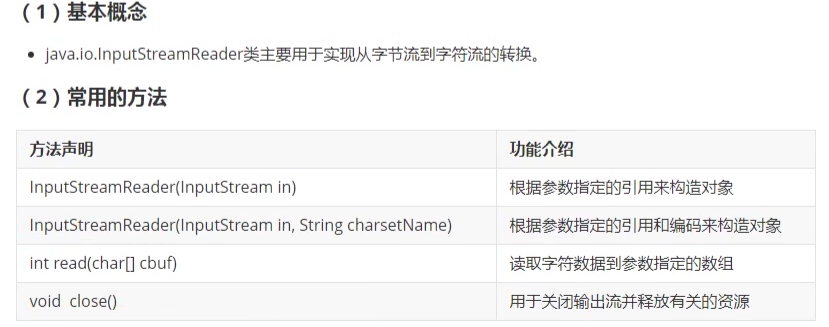
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class PrintStreamChatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//ps = System.out;
ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt", true));
//PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
//声明一个布尔类型的变量作为发送方的代表
boolean flag = true;
while(true) {
//1. 提示用户要输入的聊天内容并使用变量记录
System.out.print("请" + (flag ? "张三" : "李四") + "输入要发送的聊天内容:");
//由手册可知:构造方法需要Reader类的对象,但其是抽象类,故实参只能传递子类,字符流
//由手册可知,System.in表示的是键盘输入,而且是InputStream类型 字节流
//2. 判断用户输入的内容是否是"bye",若是则聊天结束
String str = br.readLine();
if ("bye".equalsIgnoreCase(str)) {
System.out.println("聊天结束!");
break;
}
//3. 不是"bye"则将输入写入f:/a.txt
//获取当前系统时间并调整格式
Date d1 = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
ps.println(sdf.format(d1) + (flag? "张三说 " : "李四说 ")+ str);
//printWriter.println(sdf.format(d1) + (flag? "张三说 " : "李四说 ")+ str);
//printWriter.flush();
flag = !flag;
}
ps.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭流对象
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
13. 字符编码

15. DataInputStream类(了解)

package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class DataOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
try {
//1. 创建DataOutputStream类型的对象与文件关联
dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt"));
//2. 准备一个整数并写入输入流
int num = 66;
//66: 0000 0000 .... 0100 0010 ==> ( B)
//dos.write(num); //java.io.EOFException
dos.writeInt(num); //写入4个字节
System.out.println("写入数据成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3. 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源
if (dos != null) {
try {
dos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class DataInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("f:/a.txt"));
int i = dis.readInt(); //java.io.EOFException 读取四个字节
//int i = dis.read();
System.out.println("读取到的整数值:" + i);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (dis != null) {
try {
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
16. ObjectOutputStream类(重点)
17. ObjectInputStream类(重点)
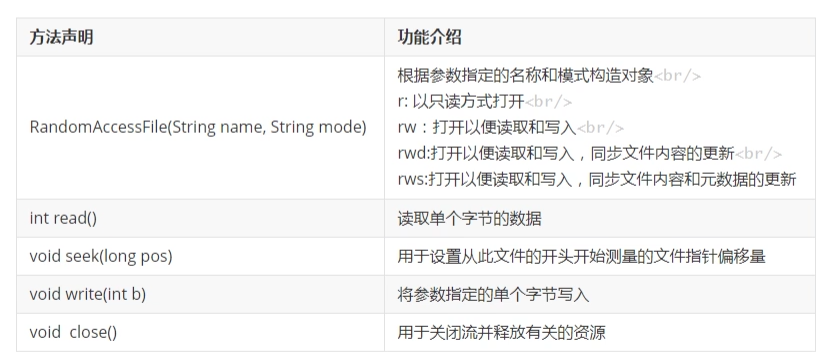
18. RandomAccessFile类
(1) 基本概念
(2) 常用的方法
package com.lagou.task17;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/16
* @description
*/
public class RandomAccessFileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile("f:/a.txt", "rw");
//设置距离文件开头的偏移量, 从文件开头位置向后偏移3个字节 abcdabcdg
raf.seek(1);
int res = raf.read();
System.out.println("读取到的单个字符是:" + (char)res);
res = raf.read();
System.out.println("读取到的单个字符是:" + (char)res);
raf.write('2'); //执行该行代码后覆盖了字符'd'
System.out.println("写入成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(null != raf) {
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
本任务总结
- IO流(重点)
概念、分类、体系结构图、相关类的详解等。