1. 基本概念
2. 线程的概念
3. 线程的创建(重中之重)
1. Thread类的概念

-
2. 创建方式

自定义类继承Thread类并重写run方法
自定义类实现Runable接口并重写run方法
run方法
- 要看是否继承Runnable接口
- start方法:Java虚拟机会自动调用该线程的run方法
4. 执行流程
 ```java
public Thread() {
this(null, null, “Thread-“ + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
```java
public Thread() {
this(null, null, “Thread-“ + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { this(group, target, name, stackSize, null, true); }
this.target = null;
public void run() { if (target != null) { target.run(); } }
```javapublic Thread() {this(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);}public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize) {this(group, target, name, stackSize, null, true);}this.target = null;public void run() {if (target != null) {target.run();}}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/22
* @description
*/
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 使用无参方式格构造Thread类型的对象
//由源码可知,Thread中的target是Null
Thread t1 = new Thread();
//2. 调用run方法进程测试
//由于target==null,跳过run方法的方法体
t1.run();
//3. 打印一句话
System.out.println("call run() over!");
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class SubRunnableRun implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("run()方法中:" + i);
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class SubRunnableRunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建自定义类型的对象, 实现Runnable接口类对象
SubRunnableRun srr = new SubRunnableRun();
//2. 使用该对象作为Thread类型对象的参数
// 由源码可知: 经过构造方法的调用之后,Thread类中成员变量target的值为srr
Thread t1 = new Thread(srr);
//3. 使用Thread类型的对象调用start()
//若使用Runnable引用构造了线程对象,调用该方法(run)时最终接口中的版本
t1.start(); //target不为空则执行target.run()
for(int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("-----------------main()方法中:" + i);
}
}
}
5. 方式的比较

import com.lagou.task10.StaticOuter;
/**
- @author 西风月
- @date 2020/8/23
@description */ public class ThreadAnonymousTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类的语法格式: 父类/接口 引用变量名 = new 父类/接口() {方法的重写}; //1. 使用继承加匿名内部类的方式创建并启动线程 /*Thread t1 = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("张三说: 在吗?"); } }; t1.start();*/ new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("张三说: 在吗?"); } }.start(); //2. 使用实现接口加匿名内部类的方式创建并启动线程 /*Runnable ra = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("美女说: 不在"); } }; Thread t2 = new Thread(ra); t2.start();*/ /*new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("美女说: 不在"); } }).start();*/ //Java8开始支持Lambda表达式: (形参列表)->{方法体} /*Runnable ra = ()->{System.out.println("美女说: 不在");}; new Thread(ra).start();*/ new Thread(()->{System.out.println("美女说: 不在");}).start();
}
}
<a name="JOlic"></a>
# 4. 线程的生命周期(熟悉)
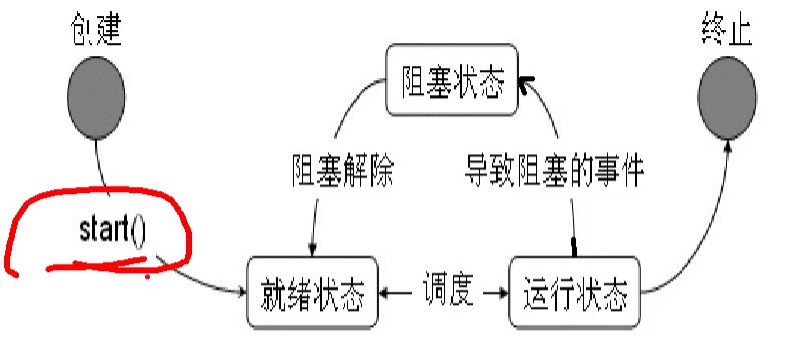``
- 创建--start()-->就绪--线程调度器-->运行-时间执行完成->阻塞状态 --> 终止

<a name="97mq0"></a>
# 5. 线程的编号和名称(熟悉)
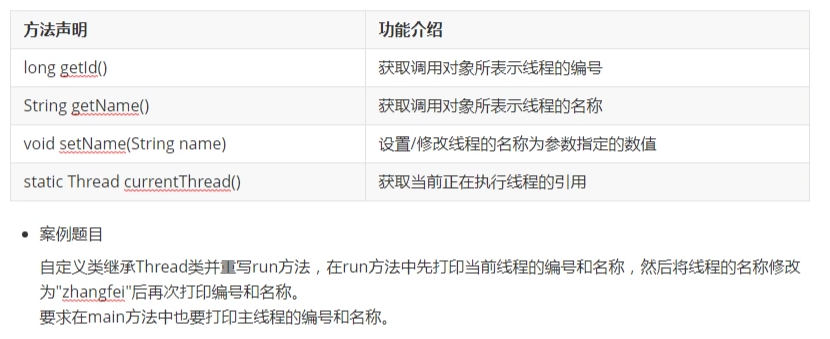
- getId(): 获取线程的编号
- getName():获取线程的名称
- setName(String name):设置:修改线程的名称
- static Thread currentThread(): 获取正在执行的线程引用
```java
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class ThreadIdNameTest extends Thread {
public ThreadIdNameTest(String str) {
super(str); //表示调用父类的构造方法
setName("zhangfei");
System.out.println("修改后子线程的编号是:" + getId() + ", 线程名称是:" + getName());
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("子线程的编号是:" + getId() + ", 线程名称是:" + getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadIdNameTest tint = new ThreadIdNameTest("guanyu");
tint.start();
System.out.println("主线程的编号是:" + currentThread().getId() + ", 线程名称是:" + currentThread().getName()); //获取当前正在执行的线程的引用
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class RunnableIdNameTest implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("子线程的ID:" + t1.getId() + ", 子线程名:" + t1.getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RunnableIdNameTest rint = new RunnableIdNameTest();
new Thread(rint, "zhangfei").start();
Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("Main线程的ID:" + t1.getId() + ", Main线程名:" + t1.getName());
}
}
6. 常用的方法(重点)


package com.lagou.task18;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class ThreadSleepTest extends Thread {
//声明一个boolean类型的变量作为循环开关
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
//每个一秒获取一次系统时间, 模拟时钟的效果
while(flag) {
//获取当前系统时间并调整格式打印
//LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
Date d1 = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(d1));
//睡眠
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); // InterruptedException 子类中重写的方法不能抛出更大的异常 Thread.run()未抛出异常
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSleepTest tst = new ThreadSleepTest();
tst.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待....");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//停止子线程, 过时, 不建议使用
//tst.stop();
tst.flag = false;
System.out.println("主线程结束等待.");
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class ThreadPriorityTest extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("子线程优先级是:" + getPriority()); //5 10
//优先级越高的线程不一定就先执行
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程中:i=" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPriorityTest tpt = new ThreadPriorityTest();
//设置子线程的优先级
tpt.setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);
tpt.start();
Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread();
//System.out.println("主线程的优先级是:" + t1.getPriority()); //5
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("----------------主线程中:i=" + i);
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class ThreadJoinTest extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//模拟倒数十个数的效果
System.out.println("倒计时开始!");
for(int i = 10; i > 0; i --) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("新年快乐!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadJoinTest tjt = new ThreadJoinTest();
tjt.start();
//主线程开始等待
System.out.println("主线程开始等待.....");
try {
//表示当前正在执行的线程对象等待调用线程对象, 也就是主线程等待子线程终止
//tjt.join();
tjt.join(5000); //最多等待5秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//System.out.println("终于等到你, 还好没有放弃!");
System.out.println("可惜不是你, 陪我到最后!");
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class MySubThread extends Thread {
boolean flag;
public MySubThread(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if(flag) {
for(int i = 1; i < 100; i += 2) {
System.out.println("子线程1中 i = " + i );
}
} else {
for(int i = 2; i < 100; i += 2) {
System.out.println("=============子线程2中 i = " + i );
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySubThread mst1 = new MySubThread(false);
MySubThread mst2 = new MySubThread(true);
mst1.start();
mst2.start();
System.out.println("主线程等待开始!");
try {
mst1.join();
mst2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("主线程等待结束!");
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class MySubRunnableThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for(int i = 1; i < 100; i +=2 ) System.out.println("子线程1中: i = " +i);});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for(int i = 2; i < 100; i +=2 ) System.out.println("=====子线程2中: i = " +i);});
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程等待开始!");
try {
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("主线程等待结束!");
}
}
7. 线程同步机制(重点)
1. 基本概念

package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class AccountRunnableTest implements Runnable {
private int balance;
public AccountRunnableTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountRunnableTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountRunnableTest art = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
Thread t1 = new Thread(art);
Thread t2 = new Thread(art);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + art.getBalance());
}
}
2. 解决方案
3. 实现方式

package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class AccountRunnableTest implements Runnable {
private int balance;
private Demo dm = new Demo();
public AccountRunnableTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountRunnableTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
synchronized (this) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200 ) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountRunnableTest art = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
Thread t1 = new Thread(art);
Thread t2 = new Thread(art);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
//t2.start(); //也就是等待线程一取款结束后再启动线程二
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + art.getBalance());
}
}
class Demo {}
4. 静态方法的锁定
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/24
* @description
*/
public class AccountThreadTest extends Thread {
private int balance;
private static Demo dm = new Demo();
public AccountThreadTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountThreadTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
synchronized (dm) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200 ) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountThreadTest t1 = new AccountThreadTest(888);
t1.start();
AccountThreadTest t2 = new AccountThreadTest(888);
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
//t2.start(); //也就是等待线程一取款结束后再启动线程二
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + t1.getBalance());
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class AccountRunnableTest implements Runnable {
private int balance;
private Demo dm = new Demo();
public AccountRunnableTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountRunnableTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public synchronized void run() { //将整个方法的所有代码加锁
//synchronized (this) { //由源码可知, 最终由account对象来调用run() 方法, 因此当前正在调用的对象就是account, 即this
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
//synchronized (dm) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200 ) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
//}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountRunnableTest art = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
//AccountRunnableTest art2 = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
Thread t1 = new Thread(art);
Thread t2 = new Thread(art);
//Thread t2 = new Thread(art2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
//t2.start(); //也就是等待线程一取款结束后再启动线程二
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + art.getBalance());
}
}
class Demo {}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/24
* @description
*/
public class AccountThreadTest extends Thread {
private int balance;
private static Demo dm = new Demo();
public AccountThreadTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountThreadTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public /*synchronized*/ void run() {
/*System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
//synchronized (dm) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200 ) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
//}*/
test();
}
public /*synchronized*/ static void test() { //静态方法加synchronized等价于 类名.class
synchronized (AccountThreadTest.class) { //表示该类型对应的class对象, 由于类型是固定的, 那么class对象也是唯一的
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
//synchronized (dm) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = 1000;// getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if (tmp >= 200) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
//setBalance(tmp);
//}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountThreadTest t1 = new AccountThreadTest(888);
t1.start();
AccountThreadTest t2 = new AccountThreadTest(888);
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
//t2.start(); //也就是等待线程一取款结束后再启动线程二
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + t1.getBalance());
}
}
5. 注意事项

6. 线程安全类和不安全类

7. 死锁的概念

- 尽量减少同步的资源, 减少同步代码块的嵌套结构的使用。
8. 使用Lock(锁)实现线程同步
8.1 基本概念
8.2 常用的方法

package com.lagou.task18;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/23
* @description
*/
public class AccountRunnableTest implements Runnable {
private int balance;
private Demo dm = new Demo();
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public AccountRunnableTest(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public AccountRunnableTest() {
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public /*synchronized*/ void run() { //将整个方法的所有代码加锁
//开始加锁
lock.lock();
//synchronized (this) { //由源码可知, 最终由account对象来调用run() 方法, 因此当前正在调用的对象就是account, 即this
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已启动 ");
//synchronized() 要求必须是同一个对象
//synchronized (new Demo()) { //锁不住
//synchronized (dm) {
//1. 模拟从后台查询账户余额的过程
int tmp = getBalance();
//2. 模拟取款200RMB的过程
if(tmp >= 200 ) {
System.out.println("正在出钞, 请稍后...");
tmp -= 200;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请取走您的钞票 ");
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足! 请核对您的账户余额");
}
//3. 将最新的余额写入变量
setBalance(tmp);
//}
lock.unlock(); //实现解锁
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountRunnableTest art = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
//AccountRunnableTest art2 = new AccountRunnableTest(888);
Thread t1 = new Thread(art);
Thread t2 = new Thread(art);
//Thread t2 = new Thread(art2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始等待......");
try {
t1.join();
//t2.start(); //也就是等待线程一取款结束后再启动线程二
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("最终的账户余额:" + art.getBalance());
}
}
class Demo {}
8.3 与synchronized方式的比较

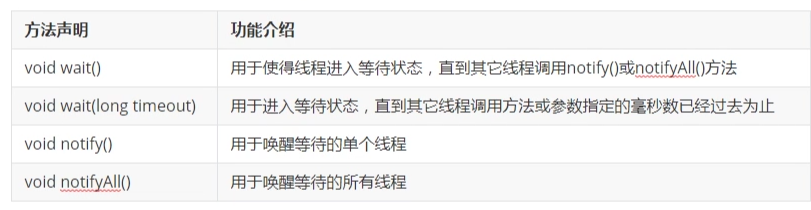
9. Object类中常用的方法
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/24
* @description
*/
public class ThreadObjectTest implements Runnable {
private int step = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
//每当由一个线程进来后先大喊一声, 调用notify方法
notify();
if(step <= 100) {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "中:step = " + step);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
step++;
try {
//当前线程进入阻塞状态后,自动释放对象锁
// 必须在锁定的代码中调用,//当前线程打印完一个整数后,为了防止继续打印下一个数据,则调用wait方法
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadObjectTest tot = new ThreadObjectTest();
Thread t1 = new Thread(tot);
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(tot);
t2.start();
}
}
4. 生产者消费者模型(重点)

package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
* 编程实现一个仓库类
*/
public class StoreHouse {
private int cnt = 0; //用于记录产品的数量
public synchronized void produceProduct() {
notify();
if(cnt < 10) {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在生产" + (cnt + 1) + "个产品...");
cnt++;
} else {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void consumerProduct() {
notify();
if(cnt > 0) {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在消费" + cnt + "个产品...");
cnt--;
} else {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
*/
public class StoreHouseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StoreHouse storeHouse = new StoreHouse();
ProducerThread t1 = new ProducerThread(storeHouse);
ConsumerThread t2 = new ConsumerThread(storeHouse);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
*/
public class ConsumerThread extends Thread {
//声明一个仓库类型的引用作为成员变量, 是为了能调用仓库类中的生产放法 合成复用原则
private StoreHouse storeHouse;
public ConsumerThread(StoreHouse storeHouse) {
this.storeHouse = storeHouse;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
storeHouse.consumerProduct();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package com.lagou.task18;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
*/
public class ProducerThread extends Thread {
//声明一个仓库类型的引用作为成员变量, 是为了能调用仓库类中的生产放法 合成复用原则
private StoreHouse storeHouse;
public ProducerThread(StoreHouse storeHouse) {
this.storeHouse = storeHouse;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
storeHouse.produceProduct();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
线程池的概念(熟悉)
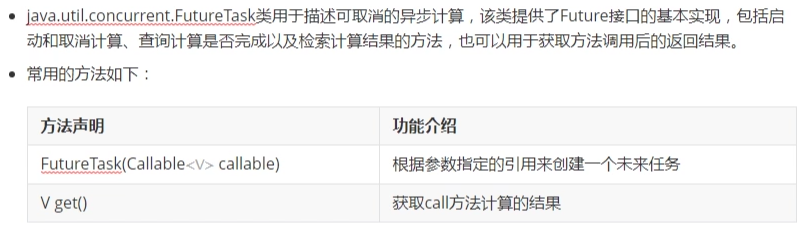
(1) 实现Callable接口
(2) FutureTask类
package com.lagou.task18;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
*/
public class ThreadCallableTest implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
// 计算1-10000之间的累加和, 并打印返回
int sum=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("计算所得累计和:" + sum);
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadCallableTest tct = new ThreadCallableTest();
FutureTask ft = new FutureTask(tct);
Thread t1 = new Thread(ft);
t1.start();
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = ft.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程处理方式的返回值是:" + obj);
}
}
(3) 线程池的由来
(4) 概念和原理

(5) 相关类和方法

package com.lagou.task18;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author 西风月
* @date 2020/8/25
* @description
*/
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//2. 向线程池中布置任务
executorService.submit(new ThreadCallableTest());
executorService.submit(new ProducerThread(new StoreHouse()));
executorService.submit(new ConsumerThread(new StoreHouse()));
//3. 关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}








