开发环境:Google Colab
卷积 GAN - Celeba 生成人脸图像
挂载驱动器以访问 google drive 中的文件
# mount Drive to access data filesfrom google.colab import drivedrive.mount('./mount')
导入包 ```python import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import h5py import pandas, numpy, random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 标准的CUDA检查和设置步骤```python# 检查CUDA是否可用,如果可用,则设置默认的rensor类型为cuda# 使用CUDA需要在上方工具栏“代码执行程序-更改运行时类型-硬件加速器”改为GPUif torch.cuda.is_available():torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.cuda.FloatTensor)print("using cuda:", torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))passdevice = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")device
辅助函数
# 生成随机数据def generate_random_image(size):random_data = torch.rand(size) # 生成的数据符合0-1区间内的均匀分布return random_datadef generate_random_seed(size):random_data = torch.randn(size) # 生成的数据符合均值为0,方差为1的正态分布return random_data
# 将三维张量转换为一维张量(eg. 将大小为(218, 178, 3)的三维图像张量重塑成一个长度为218*178*3的一维张量)# modified from https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/720class View(nn.Module):def __init__(self, shape):super().__init__()self.shape = shape,def forward(self, x):return x.view(*self.shape)
# 将一个给定的numpy图像中裁剪为指定的长和宽,裁剪的区域位于输入图像的正中央def crop_centre(img, new_width, new_height):height, width, _ = img.shapestartx = width // 2 - new_width // 2 # 注意使用整数除法//starty = height // 2 - new_height // 2return img[ starty: starty + new_height, startx: startx + new_width, :]
数据集类
# 数据集类class CelebADataset(Dataset):def __init__(self, file):self.file_object = h5py.File(file, 'r')self.dataset = self.file_object['img_align_celeba']passdef __len__(self):return len(self.dataset)def __getitem__(self, index):if(index >= len(self.dataset)):raise IndexError()img = numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg'])# 将图像裁剪为128*128大小的正方形图像img = crop_centre(img, 128, 128)return torch.cuda.FloatTensor(img).permute(2, 0, 1).view(1, 3, 128, 128) / 255.0 # 使得结果范围在0-1# 最终返回一个四维张量的形式:(批次大小,通道数,高度,宽度)# 原本numpy数组的形式为(高度,宽度,通道数3)的三维张量,因此先用permute(2, 0, 1)将numpy数组重新排序为(通道数3,高度,宽度)# 再使用view(1, 3, 128, 128)增加一个额外的维度,代表批量大小,这里为1def plot_image(self, index):if(index >= len(self.dataset)):raise IndexError()img = numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg'])# 将图像裁剪为128*128大小的正方形图像img = crop_centre(img, 128, 128)plt.imshow(img, interpolation='nearest')passpass
# 创建数据集对象celeba_dataset = CelebADataset('mount/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/pytorch_gan/celeba_data/celeba_aligned_small.h5py')
# 检查数据集中的图像 & 检查图像是否正确被裁减celeba_dataset.plot_image(43) # 索引范围是0-19999
鉴别器网络
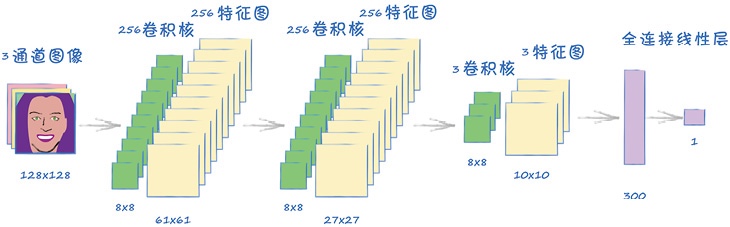
class Discriminator(nn.Module):def __init__(self):# 初始化pytorch父类super().__init__()# 定义神经网络层self.model = nn.Sequential(# 与其输入形状为 (1, 3, 128, 128)nn.Conv2d(3, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2), # 输入3通道彩色图像,应用256个卷积核,输出256个特征图,卷积核大小8*8,步长2,因此输出特征图大小为61*61nn.BatchNorm2d(256), # 对图层中的每个通道进行标准化nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2), # 输入256通道(256个特征图),应用256个卷积核,输出256个特征图,卷积核大小8*8,步长2,因此输出特征图大小为27*27nn.BatchNorm2d(256), # 对图层中的每个通道进行标准化nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),nn.Conv2d(256, 3, kernel_size=8, stride=2), # 输入256通道(256个特征图),应用3个卷积核,输出3个特征图,卷积核大小8*8,步长2,因此输出特征图大小为10*10nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),View(3*10*10), # 输入(1,3,10,10)的三维特征图,转换为含100个值的一维张量nn.Linear(3*10*10, 1), # 全连接层,将300个值所见到一个鉴别器的输出值nn.Sigmoid())# 创建损失函数self.loss_function = nn.BCELoss() # 二元交叉熵BCELoss()# 创建优化器,使用随机梯度下降self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001) # 使用Adam优化器# 计数器和进程记录self.counter = 0self.progress = []passdef forward(self, inputs):# 直接运行模型return self.model(inputs)def train(self, inputs, targets):# 计算网络的输出outputs = self.forward(inputs)# 计算损失值loss = self.loss_function(outputs, targets)# 每训练10次增加计数器self.counter += 1if(self.counter % 10 == 0):self.progress.append(loss.item())passif(self.counter % 10000 == 0):print("counter = ", self.counter)pass# 归零梯度,反向传播,并更新权重self.optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()self.optimiser.step()passdef plot_progress(self): # 打印训练过程df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16, 8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))passpass
测试鉴别器
%%time# 测试鉴别器能否鉴别真实数据和随机噪声# 训练鉴别器D = Discriminator()D.to(device) # 将模型移到cuda设备for image_data_tensor in celeba_dataset:# 真实数据D.train(image_data_tensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))# 生成数据D.train(generate_random_image((1, 3, 128, 128)), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0]))pass
# 绘制鉴别器的损失图D.plot_progress()
# 运行鉴别器,检查其能否区分真实图像和随机图像for i in range(4):image_data_tensor = celeba_dataset[random.randint(0, 20000)]print(D.forward(image_data_tensor).item())passfor i in range(4):print(D.forward(generate_random_image((1, 3, 128, 128))).item())pass
生成器网络
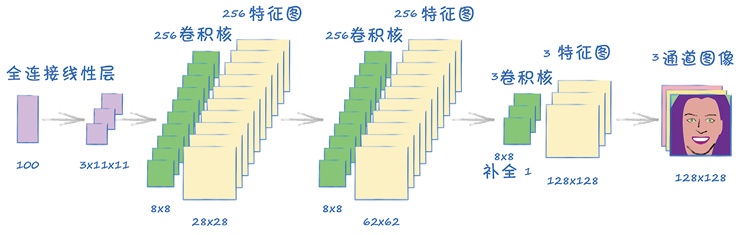
class Generator(nn.Module):def __init__(self):# 初始化pytorch父类super().__init__()# 定义神经网络层self.model = nn.Sequential(# 输入是一个一维数组(100个种子)nn.Linear(100, 3*11*11),nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),# 转换成四维View((1, 3, 11, 11)),nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2), # 转置卷积,256个卷积核nn.BatchNorm2d(256),nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),nn.BatchNorm2d(256),nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 3, kernel_size=8, stride=2, padding=1), # 因为输出要红绿蓝三通道,因此使用三个转置卷积核;padding用于从中间网格中去掉外围的方格nn.BatchNorm2d(3),nn.Sigmoid()# 输出为 (1, 3, 128, 128))# 不需要损失函数!!!# 创建优化器,使用随机梯度下降self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001) # 使用Adam优化器# 计数器和进程记录self.counter = 0self.progress = []passdef forward(self, inputs):# 直接运行模型return self.model(inputs)def train(self, D, inputs, targets):# 计算网络的输出g_outputs = self.forward(inputs)# 训练生成器需要鉴别器的损失值# 将生成器网络的输出输入到鉴别器d_outputs = D.forward(g_outputs)# 计算鉴别器的损失值loss = D.loss_function(d_outputs, targets)# 每训练10次增加计数器self.counter += 1if(self.counter % 10 == 0):self.progress.append(loss.item())pass# 鉴别器训练中不打印,这样可以通过真实的训练数据更准确地反应训练进度# 归零梯度,反向传播,并更新权重self.optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()self.optimiser.step()passdef plot_progress(self): # 打印训练过程df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16, 8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))passpass
检查生成器输出
# 检查生成器的输出大小,并确保运行没有错误G = Generator()# 将模型转存到CUDA设备G.to(device)output = G.forward(generate_random_seed(100))img = output.detach().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(128, 128, 3).cpu().numpy() # 用detach将输出图像与pytorch的计算图分离,存回CPU并转换成numpy数组# 上面permute(0,2,3,1)将numpy数组(批量大小,通道数3,高,宽)重新排序为(批量大小,高,宽,通道数3);view(128, 128, 3)则去掉了批量大小这一维度,将numpy转为三维张量(高,宽,通道数)plt.imshow(img, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')
训练GAN
%%time# 创建鉴别器和生成器D = Discriminator()D.to(device)G= Generator()G.to(device)epochs = 1for epoch in range(epochs):print("epoch = ", epoch + 1)# 训练鉴别器和生成器for image_data_tensor in celeba_dataset:# 第一步:用真实样本训练鉴别器D.train(image_data_tensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))# 第二步:用生成样本训练鉴别器# 使用detach()以避免计算生成器G中的梯度,节省计算成本D.train(G.forward(generate_random_seed(100)).detach(), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0]))# 第三步:训练生成器G.train(D, generate_random_seed(100), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))passpass
# 绘制鉴别器的损失图D.plot_progress()
# 绘制生成器的损失图G.plot_progress()# 实际上,鉴别器和生成器的二元交叉熵损失值最理想的情况是ln2=0.693
运行生成器
# 从训练好的生成器绘制一些输出# 在3行2列的网格中绘制生成图像(检查生成图像的多样性)f, axarr = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(16, 8))for i in range(2):for j in range(3):output = G.forward(generate_random_seed(100))img = output.detach().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(128, 128, 3).cpu().numpy()axarr[i, j].imshow(img, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')passpass
条件式 GAN - MNIST 生成指定数字图像
from google.colab import drive drive.mount(‘./mount’)
- 导入包```pythonimport torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom torch.utils.data import Datasetimport pandas, numpy, randomimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
数据类
class MnistDataset(Dataset): # 对于继承自Dataset的数据集,需要提供__len__()函数和__getitem__()函数def __init__(self, csv_file):self.data_df = pandas.read_csv(csv_file, header=None)passdef __len__(self): # 获取数据集大小(返回数据集中的项目总数)return len(self.data_df)def __getitem__(self, index): # 通过索引获取数据集中的项目# 目标图像(标签)label = self.data_df.iloc[index, 0]target = torch.zeros((10))target[label] = 1.0 # 转换为one-hot形式的标签向量# 图像数据,取值范围是0-255,标准化为0-1image_values = torch.FloatTensor(self.data_df.iloc[index, 1:].values) / 255.0# 返回标签、图像数据张量以及目标张量return label, image_values, targetdef plot_image(self, index): # 通过索引号,绘制对应编号的图img = self.data_df.iloc[index, 1:].values.reshape(28, 28)plt.title("label = " + str(self.data_df.iloc[index, 0]))plt.imshow(img, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')passpass
# 测试Dataset类是否可以正常工作# 加载数据mnist_dataset = MnistDataset('mount/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/pytorch_gan/mnist_data/mnist_train.csv')
# 检查数据包含图像mnist_dataset.plot_image(17)
生成随机数据的辅助函数
# 生成随机数据的函数def generate_random_image(size):random_data = torch.rand(size)return random_datadef generate_random_seed(size):random_data = torch.randn(size)return random_data# size here must only be an integerdef generate_random_one_hot(size):label_tensor = torch.zeros((size))random_idx = random.randint(0,size-1)label_tensor[random_idx] = 1.0return label_tensor
鉴别器类
class Discriminator(nn.Module):def __init__(self):# 初始化pytorch父类super().__init__()# 定义神经网络层self.model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(784+10, 200), # 输入:图像张量28*28=784 + 标签张量长度10nn.LeakyReLU(0.02),nn.LayerNorm(200),nn.Linear(200, 1),nn.Sigmoid())# 创建损失函数self.loss_function = nn.BCELoss()# 创建优化器,使用随机梯度下降self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001) # 改良4:使用Adam优化器# 计数器和进程记录self.counter = 0self.progress = []passdef forward(self, image_tensor, label_tensor): # 扩展forward()函数,使其同时接收图像张量和标签张量,并将它们拼接起来# 拼接种子和标签inputs = torch.cat((image_tensor, label_tensor))return self.model(inputs)def train(self, inputs, label_tensor, targets): # 扩展:接收标签张量# 计算网络的输出outputs = self.forward(inputs, label_tensor) # 同时接收图像张量和标签张量# 计算损失值loss = self.loss_function(outputs, targets)# 每训练10次增加计数器self.counter += 1if(self.counter % 10 == 0):self.progress.append(loss.item())passif(self.counter % 10000 == 0):print("counter = ", self.counter)pass# 归零梯度,反向传播,并更新权重self.optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()self.optimiser.step()passdef plot_progress(self): # 打印训练过程df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16, 8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))passpass
测试鉴别器
%%time# 测试鉴别器,确保其至少能将真实图像与随机噪声区分开# 训练鉴别器,奖励鉴别器将真实的训练数据判别为真,也就是输出1.0;将伪造的生成数据判别为假,也就是输出0.0D = Discriminator()for label, image_data_tensor, label_tensor in mnist_dataset:# 真实数据D.train(image_data_tensor, label_tensor, torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))# 生成数据D.train(generate_random_image(784), generate_random_one_hot(10), torch.FloatTensor([0.0]))pass
# 绘制训练过程中的损失值变化D.plot_progress()# 损失之下降并一直保持接近0的值,这正是我们希望达到的效果
# 随机选取一些训练集中的图像和随机噪声图像,分别作为输入来测试训练后的鉴别器for i in range(4):label, image_data_tensor, label_tensor = mnist_dataset[random.randint(0, 6000)]print(D.forward(image_data_tensor, label_tensor).item())passfor i in range(4):print(D.forward(generate_random_image(784), generate_random_one_hot(10)).item())pass
生成器类

条件式GAN架构:要让训练后的GAN生成器生成一个指定数字的图像,因此生成器和鉴别器的输入都在图像数据的基础上加入了类型标签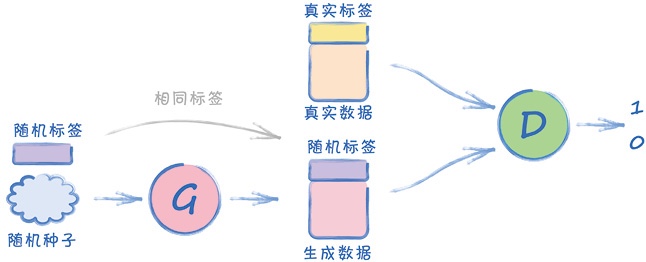
class Generator(nn.Module):def __init__(self):# 初始化pytorch父类super().__init__()# 定义神经网络层self.model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(100+10, 200),nn.LeakyReLU(0.02),nn.LayerNorm(200),nn.Linear(200, 784),nn.Sigmoid())# 不需要损失函数!!!# 创建优化器,使用随机梯度下降self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001)# 计数器和进程记录self.counter = 0self.progress = []passdef forward(self, seed_tensor, label_tensor):# 拼接种子和标签inputs = torch.cat((seed_tensor, label_tensor))return self.model(inputs)def train(self, D, inputs, label_tensor, targets):# 计算网络的输出g_outputs = self.forward(inputs, label_tensor)# 训练生成器需要鉴别器的损失值# 将生成器网络的输出输入到鉴别器d_outputs = D.forward(g_outputs, label_tensor)# 计算鉴别器的损失值loss = D.loss_function(d_outputs, targets)# 每训练10次增加计数器self.counter += 1if(self.counter % 10 == 0):self.progress.append(loss.item())pass# 鉴别器训练中不打印,这样可以通过真实的训练数据更准确地反应训练进度# 归零梯度,反向传播,并更新权重self.optimiser.zero_grad()loss.backward()self.optimiser.step()pass# 这个函数不应该放在类里把,应该单独拎出来,下面imshow那个G.forward,G是哪来的?def plot_images(self, label):label_tensor = torch.zeros((10))label_tensor[label] = 1.0# 在3行2列的网格中生成图像f, axarr = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(16, 8))for i in range(2):for j in range(3):axarr[i, j].imshow(G.forward(generate_random_seed(100), label_tensor).detach().cpu().numpy().reshape(28, 28), interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')passpasspassdef plot_progress(self): # 打印训练过程df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16, 8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))passpass
检查生成器输出
# 训练生成器前,先检查生成器输出格式是否正确G = Generator()output = G.forward(generate_random_seed(100), generate_random_one_hot(10))img = output.detach().numpy().reshape(28, 28)plt.imshow(img, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')
训练GAN
%%time# 训练GAN# 创建鉴别器和生成器D = Discriminator()G = Generator()epochs = 4# 训练鉴别器和生成器for epoch in range(epochs):print("epoch = ", epoch + 1)for label, image_data_tensor, label_tensor in mnist_dataset:# 第一步:用真实样本训练鉴别器D.train(image_data_tensor, label_tensor, torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))# 为鉴别器生成一个随机独热标签(用生成图像训练鉴别器时,对生成器和鉴别器输入同一标签张量)random_label = generate_random_one_hot(10)# 第二步:用生成样本训练鉴别器# 使用detach()以避免计算生成器G中的梯度,节省计算成本D.train(G.forward(generate_random_seed(100), random_label).detach(), random_label, torch.FloatTensor([0.0]))# 为生成器另外生成一个随机独热标签random_label = generate_random_one_hot(10)# 第三步:训练生成器(输入鉴别器对象和随机单值输入来训练生成器)G.train(D, generate_random_seed(100), random_label, torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))passpass
# 绘制鉴别器在训练中的损失值变化图D.plot_progress()# 损失值迅速下降到接近于0,并一直保持在很低的位置。训练期间,损失值偶尔发生跳跃。这说明生成器和鉴别器之间仍然没有取得平衡
# 绘制生成器训练过程中的损失值变化图G.plot_progress()# 损失值先是上升,表示在训练早期生成器落后于鉴别器。之后,损失值下降并保持在3左右。记住,与MSELoss不同,BCELoss没有1.0的上限
运行生成器
# 试验训练后的生成器会生成什么样的图像# 由于不同的随机种子应当生成不同的图像,所以绘制多幅输出图像并查看label = 9label_tensor = torch.zeros((10))label_tensor[label] = 1.0# 在3行2列的网格中生成图像f, axarr = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(16, 8))for i in range(2):for j in range(3):output = G.forward(generate_random_seed(100), label_tensor)img = output.detach().cpu().numpy().reshape(28, 28)axarr[i, j].imshow(img, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')passpass# 由图可知,生成的图像不是随机噪声,而是有某种形状# 但这些图像看起来都相同,这种现象称为“模式崩溃”
总结
- 训练 GAN 时的理想状态:生成器与鉴别器达到平衡,生成器已经学会了生成看起来足以以假乱真的数据,使得鉴别器无法区分真实数据与生成器生成的数据
训练 GAN 时的理想损失值:(即生成器和鉴别器达到平衡时的损失值)
- 均方误差 MSE Loss:0.25
- 即鉴别器无法从伪造数据中识别真实数据,就无法确定输出0.0还是1.0,索性就输出0.5,因此均方误差为
- 即鉴别器无法从伪造数据中识别真实数据,就无法确定输出0.0还是1.0,索性就输出0.5,因此均方误差为
- 二元交叉熵 BCE Loss:ln2 ≈ 0.693
- 均方误差 MSE Loss:0.25
GAN 不会学习记忆训练数据中的实例,GAN 学习的是训练数据中每个元素出现的可能性(即概率分布)
模式崩溃:
- eg. 使用 MNIST 数据集训练 GAN,希望生成所有 10 个数字,也就是说希望能学习到所有 10 个数字图像的概率分布
- 但,有可能训练出的GAN只会生成其中一种数字,也就是模式崩溃,即生成器只学会了一类图像的概率分布
梯度下降并不适合对抗博弈

