Set
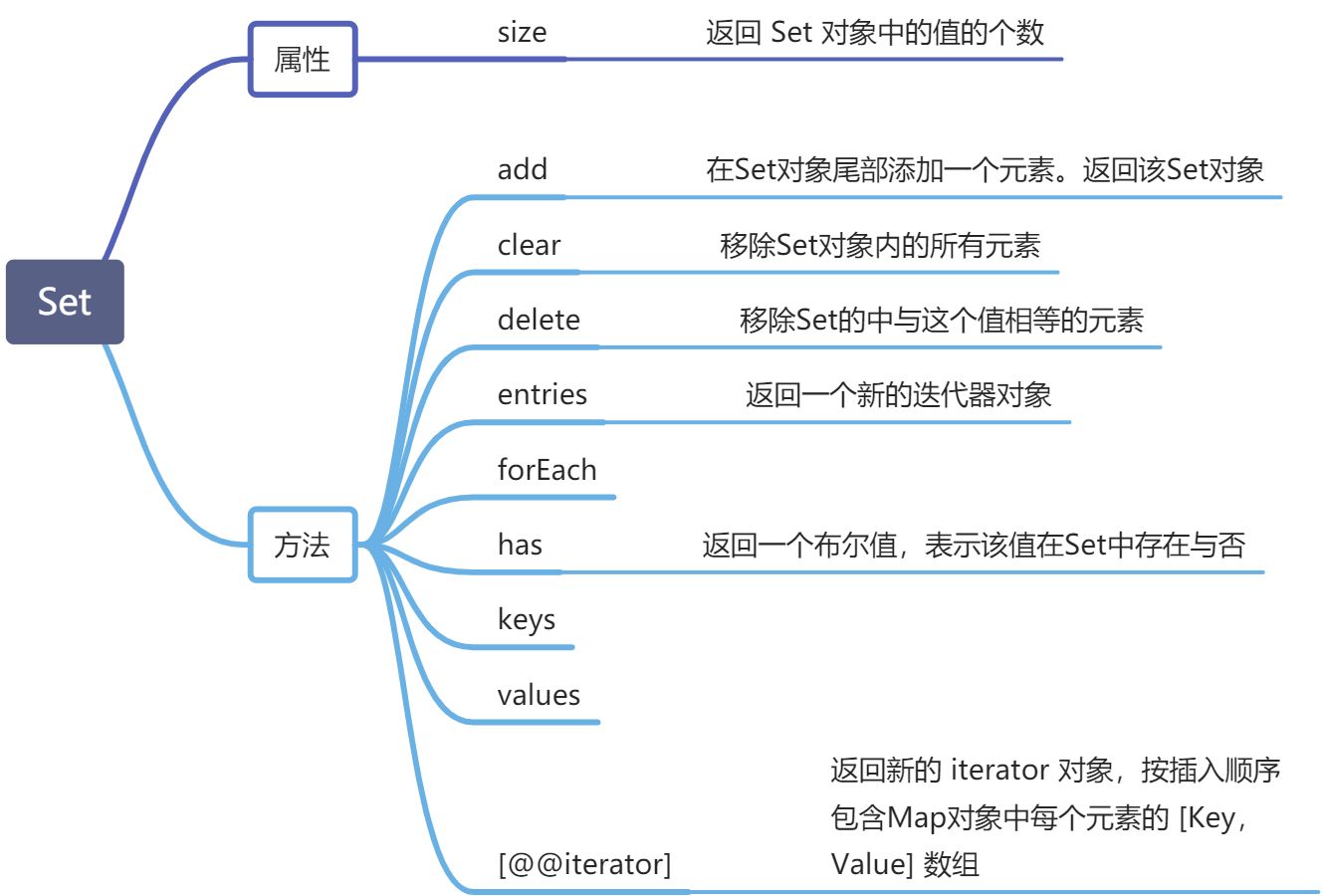 > Set是ES6新的数据结构,类似数组,但成员的值是唯一的,没有重复的值。
> Set是ES6新的数据结构,类似数组,但成员的值是唯一的,没有重复的值。
Set 常用方法 遍历 应用场景 WeakSet 用法
{// 向Set中加入值的时候不会发生类型转换,所以5和”5”是两个不同的值,// Set内部判断两个值是否相等,使用的是 ===,这就意味着这两个对象总是不相等。// 唯一列外的是NaN本身(精确相等运算符认为NaN不等于自身)let list = new Set();list.add(5);list.add(7);console.log("size", list.size); // size 2}{let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];let list = new Set(arr);console.log("size", list.size); // size 5}{// 唯一的let list = new Set();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(1);console.log("list", list); // list Set { 1, 2 }// 去重// 数组let arr = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2];let list2 = new Set(arr);console.log("unique", list2); // unique Set { 1, 2, 3 }// 对象数组const objArrays = [{ id: 1 },{ id: 1 },{ id: 2 },{ id: 1 },{ id: 5 },{ id: 7 },{ id: 9 },];const idSet = new Set();console.log(objArrays.filter((item) => {const existingId = idSet.has(item.id);idSet.add(item.id);return !existingId;}));// [ { id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 5 }, { id: 7 }, { id: 9 } ]}{let arr = ["add", "delete", "clear", "has"];let list = new Set(arr);console.log("has", list.has("add")); // has trueconsole.log("delete", list.delete("add"), list); // delete true Set { 'delete', 'clear', 'has' }list.clear();console.log("list", list); // list Set { }}{let arr = ["add", "delete", "clear", "has"];let list = new Set(arr);for (let value of list) {console.log("value--", value);// value-- add// value-- delete// value-- clear// value-- has}for (let key of list.keys()) {console.log("key", key);// key add// key delete// key clear// key has}for (let value of list.values()) {console.log("value", value);// value add// value delete// value clear// value has}for (let [key, value] of list.entries()) {console.log("entries", key, value);// entries add add// entries delete delete// entries clear clear// entries has has}list.forEach(function (item) {console.log(item);// add// delete// clear// has});}{/*1、WeakSet 成员只能够是对象2、作为 WeakSet 成员的对象都是弱引用,即垃圾回收机制不考虑 WeakSet 对该对象的引用,也就是说,如果其他对象都不再引用该对象,那么垃圾回收机制会自动回收该对象所占用的内存,不考虑该对象还存在与WeakSet之中。这个特点意味着,无法引用WeakSet的成员,因此WeakSet是不可遍历的。3、使用WeakSet存储对象实例的好处是,由于是对对象实例的引用,不会被计入内存回收机制,所以删除实例的时候,不用考虑weaket,也不会出现内存泄漏。*/let weakList = new WeakSet();let arg = {};weakList.add(arg);weakList.add(2); // Invalid value used in weak setconsole.log("weakList", weakList); // weakList WeakSet {}// weakList.forEach((item) => {// console.log(item);// });// weakList.forEach is not a function}
Map
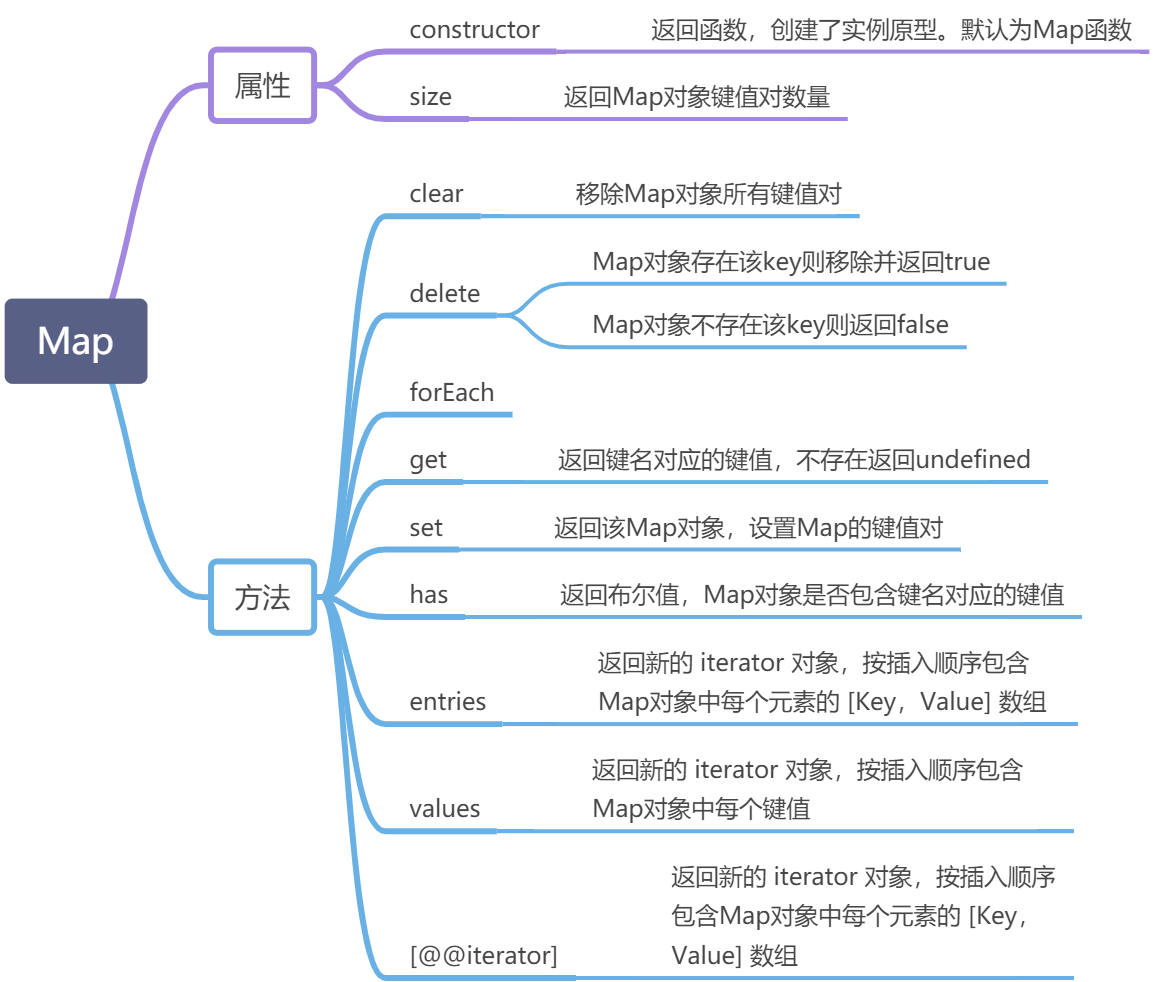
{let map = new Map();let arr = ["123"];map.set(arr, 456);console.log("map", map, map.get(arr));// map Map { [ '123' ] => 456 } 456}{let map = new Map([["a", 123], ["b", 456]]);console.log("map args", map); // map args Map { 'a' => 123, 'b' => 456 }console.log("size", map.size); // size 2console.log("delete", map.delete("a"), map); // delete true Map { 'b' => 456 }console.log("clear", map.clear(), map); // clear undefined Map { }}{let weakmap = new WeakMap();let o = {};weakmap.set(o, 123);console.log(weakmap.get(o)); // 123}// 数据结构// Map与Array的对比// Set与Array的对比{// 数据结构横向对比,增,查,改,删let map = new Map();let array = [];// 增map.set("t", 1);array.push({ t: 1 });console.log("map-array", map, array); // map-array Map { 't' => 1 } [ { t: 1 } ]// 查let map_exist = map.has("t");let array_exist = array.find(item => item.t);console.log("map-array", map_exist, array_exist); // map-array true { t: 1 }// 改map.set("t", 2);array.forEach(item => (item.t ? (item.t = 2) : ""));console.log("map-array-modify", map, array); // map-array-modify Map { 't' => 2 } [ { t: 2 } ]// 删map.delete("t");let index = array.findIndex(item => item.t);array.splice(index, 1);console.log("map-array-empty", map, array); // map-array-empty Map { } []}{// set和array的对比let set = new Set();let array = [];// 增set.add({ t: 1 });array.push({ t: 1 });console.log("set-array", set, array); // set-array Set { { t: 1 } } [ { t: 1 } ]// 查let set_exist = set.has({ t: 1 });let array_exist = array.find(item => item.t);console.log("set_exist", set_exist, array_exist); // set_exist false { t: 1 }// 改set.forEach(item => (item.t ? (item.t = 2) : ""));array.forEach(item => (item.t ? (item.t = 2) : ""));console.log("set_array-modify", set, array); // set_array-modify Set { { t: 2 } } [ { t: 2 } ]// 删set.forEach(item => (item.t ? set.delete(item) : ""));let index = array.findIndex(item => item.t);array.splice(index, 1);console.log("set-array-empty", set, array); // set-array-empty Set { } []}{// map,set,objet对比let item = { t: 1 };let map = new Map();let set = new Set();let obj = {};// 增map.set("t", 1);set.add(item);obj["t"] = 1;console.log("map-set-obj", obj, map, set); // map-set-obj { t: 1 } Map { 't' => 1 } Set { { t: 1 } }// 查console.log({map_exist: map.has("t"),set_exist: set.has(item),obj_exist: "t" in obj}); // { map_exist: true, set_exist: true, obj_exist: true }// 改map.set("t", 2);item.t = 2;obj["t"] = 2;console.log("map-set-obj-modify", obj, map, set); // map-set-obj-modify { t: 2 } Map { 't' => 2 } Set { { t: 2 } }// 删map.delete("t");set.delete(item);delete obj["t"];console.log("map-set-obj-empty", obj, map, set); // map-set-obj-empty {} Map { } Set { }}

