案例一:使用 Flume 监听文件内容变动,将新增加的内容输出到控制台。 案例二:使用 Flume 监听指定目录,将目录下新增加的文件存储到 HDFS。 案例三:使用 Avro 将本服务器收集到的日志数据发送到另外一台服务器。
案例一
环境: 需先开启HDFS
需求: 监听文件内容变动,将新增加的内容输出到控制台。
实现: 主要使用 Exec Source 配合 tail 命令实现。
配置
/root/flume/examples目录下新建配置文件 exec-memory-logger.properties,其内容如下:
vi exec-memory-logger.properties#指定agent的sources,sinks,channelsa1.sources = s1a1.sinks = k1a1.channels = c1#配置sources属性 #监听文件为/tmp/log.txta1.sources.s1.type = execa1.sources.s1.command = tail -F /tmp/log.txta1.sources.s1.shell = /bin/bash -c#将sources与channels进行绑定a1.sources.s1.channels = c1#配置sinka1.sinks.k1.type = logger#将sinks与channels进行绑定a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1#配置channel类型a1.channels.c1.type = memory
启动
flume-ng agent \--conf conf \--conf-file /root/flume/examples/exec-memory-logger.properties \--name a1 \-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
测试
echo "hello world " >> /tmp/log.txt
案例二
需求: 监听指定目录,将目录下新增加的文件存储到 HDFS。
实现:使用 Spooling Directory Source 和 HDFS Sink。
配置
/root/flume/examples目录下新建配置文件 spooling-memory-hdfs.properties ,内容如下
vi spooling-memory-hdfs.properties#指定agent的sources,sinks,channelsa1.sources = s1a1.sinks = k1a1.channels = c1#配置sources属性a1.sources.s1.type =spooldir#监听目录a1.sources.s1.spoolDir =/tmp/logsa1.sources.s1.basenameHeader = truea1.sources.s1.basenameHeaderKey = fileName#将sources与channels进行绑定a1.sources.s1.channels =c1#配置sinka1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs# 上传到hdfs的路径a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /root/flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H/a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = %{fileName}#生成的文件类型,默认是Sequencefile,可用DataStream,则为普通文本a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStreama1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true#将sinks与channels进行绑定a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1#配置channel类型a1.channels.c1.type = memory
启动
flume-ng agent \--conf conf \--conf-file /root/flume/examples/spooling-memory-hdfs.properties \--name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
注:如出现
即/tmp/logs 为一个文件,而不是目录,删除文件,并新建为目录即可。mkdir /tmp/logs
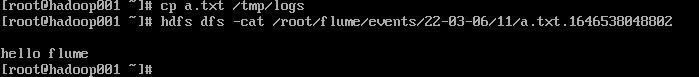
测试
案例三
需求: 将本服务器收集到的数据发送到另外一台服务器。
实现:使用 avro sources 和 avro Sink 实现。
配置日志收集Flume
/root/flume/examples目录下新建配置 netcat-memory-avro.properties,监听文件内容变化,然后将新的文件内容通过 avro sink 发送到 hadoop002 这台服务器的 8888 端口:
vi /root/flume/examples/netcat-memory-avro.properties#指定agent的sources,sinks,channelsa1.sources = s1a1.sinks = k1a1.channels = c1#配置sources属性a1.sources.s1.type = execa1.sources.s1.command = tail -F /tmp/log.txta1.sources.s1.shell = /bin/bash -ca1.sources.s1.channels = c1#配置sinka1.sinks.k1.type = avroa1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop002a1.sinks.k1.port = 8888a1.sinks.k1.batch-size = 1a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1#配置channel类型a1.channels.c1.type = memorya1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
配置日志聚合Flume
/root/flume/examples目录下新建配置 avro-memory-logger.properties
使用 avro source 监听 hadoop002 服务器的 8888 端口,将获取到内容输出到控制台:
vi /root/flume/examples/avro-memory-logger.properties#指定agent的sources,sinks,channelsa2.sources = s2a2.sinks = k2a2.channels = c2#配置sources属性a2.sources.s2.type = avroa2.sources.s2.bind = hadoop002a2.sources.s2.port = 8888#将sources与channels进行绑定a2.sources.s2.channels = c2#配置sinka2.sinks.k2.type = logger#将sinks与channels进行绑定a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2#配置channel类型a2.channels.c2.type = memorya2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
启动
flume-ng agent \--conf conf \--conf-file /root/flume/examples/avro-memory-logger.properties \--name a2 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
flume-ng agent \--conf conf \--conf-file /root/flume/examples/netcat-memory-avro.properties \--name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
测试
向监听文件添加内容
验证结果:
总结
通过flume简单三个案例的配置使用,进而接触到flume中的知识,了解flume的配置和架构。