声明周期方法
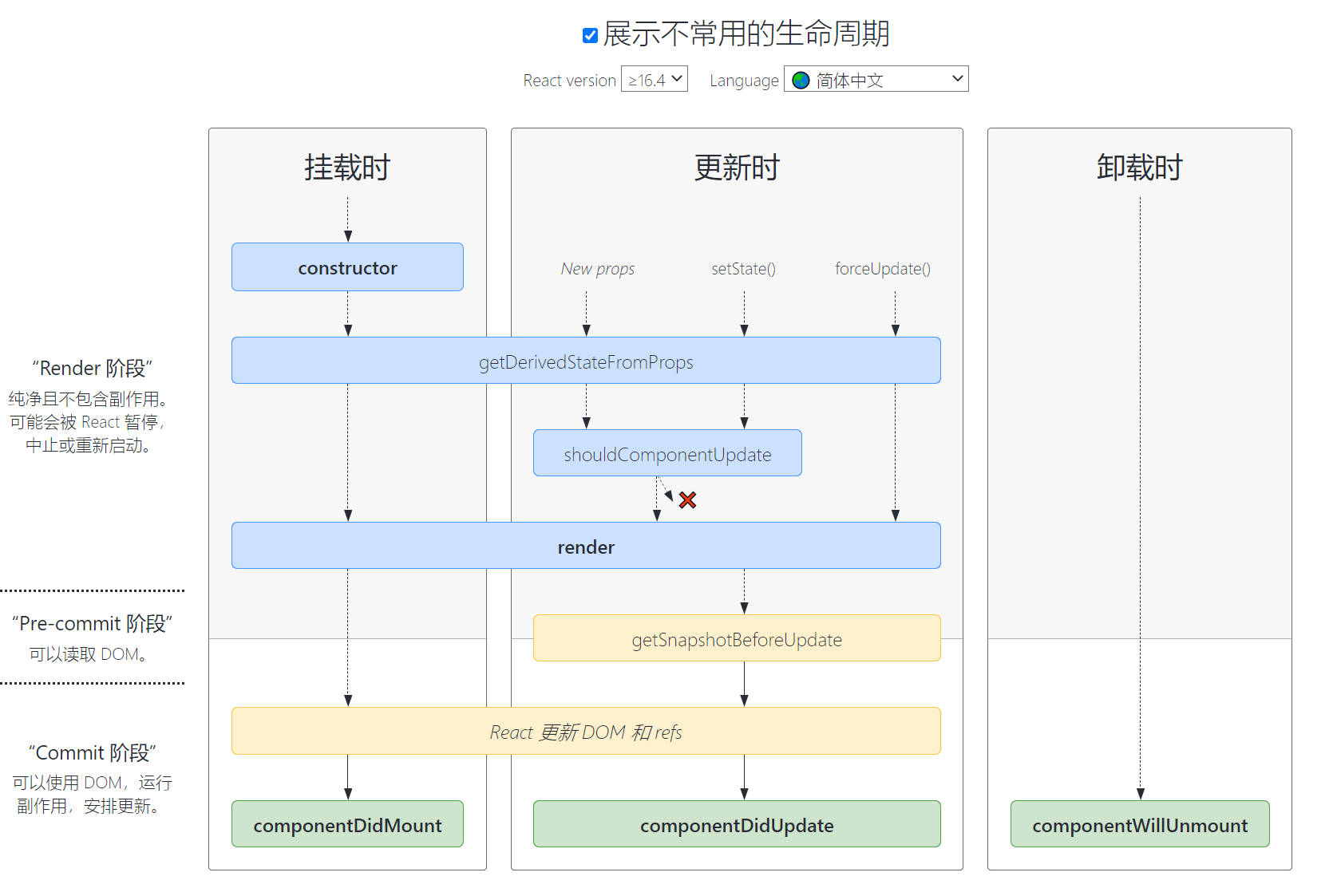
我们需要在react组件渲染的不同阶段,触发不同的事件逻辑,所以我们需要有生命周期方法.以下列举几个常用的生命周期函数: componentDidMount(): 组件已经渲染完毕.componentDidUpdate(): 组件更新后会被立即调用.componentWillUnmount(): 组件即将销毁.
不常用生命周期函数: static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state): render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用. 文档:shouldComponentUpdate(): 根据返回值,判断 React 组件的输出是否受当前 state 或 props 更改的影响.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState): 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用.
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {componentDidMount(){console.log('组件渲染完毕...');}componentWillUnMount(){console.log('组件即将销毁...');}render(){console.log('render...')return (<div className={'danger large'}><h2>倒计时</h2>{ /* className和class属性是一样的,而且必须是驼峰 */ }<span>{ new Date().toString() }</span></div>)}}// 通过调用React自身方法render可以得到当前组件的实例对象,并渲染到页面容器.ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />,document.getElementById('root'));
在 componentDidMount中声明当前时间:
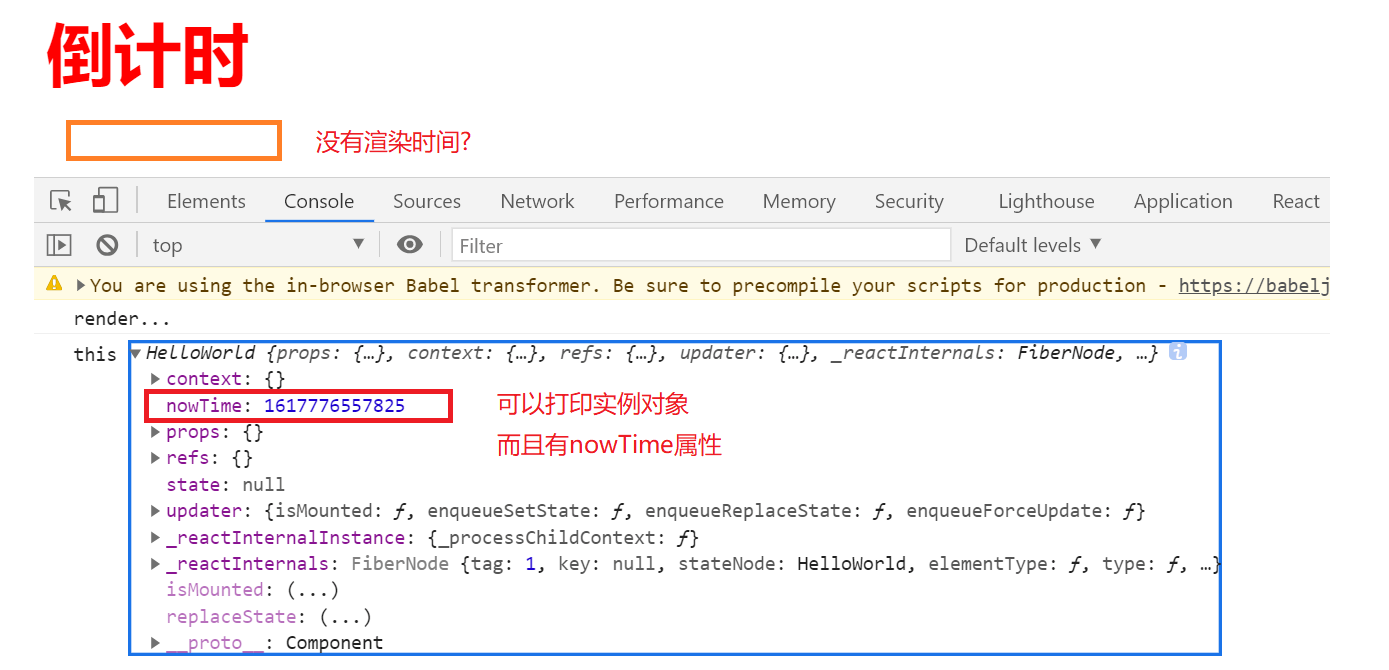
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {componentDidMount(){console.log('this',this);this.nowTime = new Date().getTime();}componentWillUnMount(){console.log('组件即将销毁...');}render(){console.log('render...')return (<div className={'danger large'}><h2>倒计时</h2>{ /* className和class属性是一样的,而且必须是驼峰 */ }<span>{ this.nowTime }</span></div>)}}// 通过调用React自身方法render可以得到当前组件的实例对象,并渲染到页面容器.ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />,document.getElementById('root'));
我们发现,可以打印出实例对象,存在nowTime属性,但是页面不渲染. 为什么?
因为render只在初始化的时候执行了一次,而nowTime是在componentDidMount生命周期函数中才添加的.
也就是说,如果我们想要得到页面渲染的结果:
- 在构造函数中优先创建
nowTime - 在
componentDidMount中修改nowTime的值
构造函数
- 在构造函数中优先创建
nowTime
我们可以对class添加构造函数 constructor() , 如果对es6 class部分不清楚的同学,需要回顾下相关知识点.
我们发现 constructor()中的 this 和 render() 中的this是一致的,指向 HelloWorld组件的实例对象.
注意: 构造函数中的super() 必须调用 , 文档 .
- 在
componentDidMount中修改nowTime的值
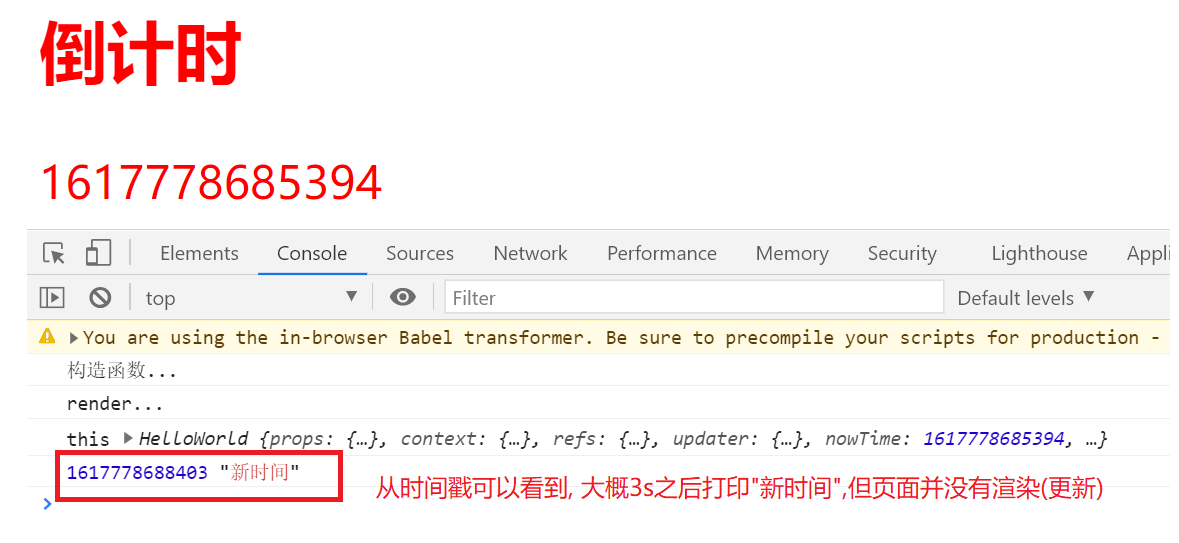
我们尝试在生命周期函数中,修改nowTime, 发现也打印修改后的内容,但页面并没有被渲染. 也就是说直接手动修改实例对象的属性,并不会触发**render() **执行 (这个和vue的双向数据绑定不同,react是没有双向数据绑定的).
那如何才能在数据被修改的时候,重新触发render()呢?
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {constructor(){// 如果写了构造函数,那么super必须写super();console.log('构造函数...');this.nowTime = new Date().getTime();}componentDidMount(){console.log('this',this);setTimeout(()=>{this.nowTime = '新时间';console.log(new Date().getTime(),this.nowTime)},3000)}componentWillUnMount(){console.log('组件即将销毁...');}render(){console.log('render...')return (<div className={'danger large'}><h2>倒计时</h2>{ /* className和class属性是一样的,而且必须是驼峰 */ }<span>{ this.nowTime }</span></div>)}}// 通过调用React自身方法render可以得到当前组件的实例对象,并渲染到页面容器.ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />,document.getElementById('root'));
state和setState()
创建响应式属性
state 是组件的属性 , 组件中的 state 包含了随时可能发生变化的数据。state 由用户自定义,它是一个普通 JavaScript 对象。
我们不能直接修改state本身,可以通过api **setState()** 方法来修改state.
利用setState在componentDidMount 中修改nowTime的值:
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {constructor(){// 如果写了构造函数,那么super必须写super();console.log('构造函数...');this.state = {nowTime: new Date().getTime()}}componentDidMount(){console.log('this',this);setTimeout(()=>{this.setState({nowTime: '新时间'})console.log(new Date().getTime(),this.state.nowTime)},3000)}componentWillUnMount(){console.log('组件即将销毁...');}render(){console.log('render...')return (<div className={'danger large'}><h2>倒计时</h2>{ /* className和class属性是一样的,而且必须是驼峰 */ }<span>{ this.state.nowTime }</span></div>)}}// 通过调用React自身方法render可以得到当前组件的实例对象,并渲染到页面容器.ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />,document.getElementById('root'));
页面得到更新,也就是说,state可以创建 响应式 对象,我们可以通过setState()来实现对数据的修改,同时触发render() 函数更新页面.
注意1: 不要直接修改 State
// 这样无法触发UI更新this.state.nowTime = 'xxx';//而应该使用this.setState({nowTime='xx'});
注意2: State 的更新可能是异步的
出于性能考虑,React 可能会把多个 [setState()](https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html#setstate) 调用合并成一个调用。所以你不要依赖他们的值来更新下一个状态。
// 这种事错误的this.setState({counter: this.state.counter + 1,});// 可以通过回调方法来获取到上一次更新后的state.// 回调方法接收两个参数,props下一章节再讨论this.setState((state,props) => ({counter: state.counter + 1}));
回调:
setState(updater, [callback])
setTimeout中调用setState()
componentDidMount(){console.log('组件挂载完毕...');// 1. 更新一次count ,检查setState()是否是异步的// 2. setState()会合并更新,某一次更新如果依赖于上一次的值,可能会有问题// 3. setState() 如果写到setTimeout/setInterval中,会变成同步函数.// 尝试修改nowTimesetTimeout(()=>{this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1 // 1})console.log('this.state.count_1',this.state.count);this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1 // 2})// 不能直接修改state的值,需要通过setState()this.setState({nowTime: new Date().toString()})// console.log('this.nowTime',this.state.nowTime);console.log('this.state.count_2',this.state.count); // 2?},3000)}
注意3: State 的更新会被合并
setState是对state进行了浅合并,只会修改相同的属性,保留其他属性.
constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {posts: [],comments: []};}componentDidMount() {fetchPosts().then(response => {this.setState({posts: response.posts});});fetchComments().then(response => {this.setState({comments: response.comments});});}
完整的声明周期函数
声明: 放到Ref课程之后讲解比较合适.
constructor(): 构造函数.render(): 渲染/更新.componentDidMount(): 组件已经渲染完毕.componentDidUpdate(): 组件更新后会被立即调用.componentWillUnmount(): 组件即将销毁.
不常用生命周期函数: static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state): render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用. 文档:shouldComponentUpdate(): 根据返回值,判断 React 组件的输出是否受当前 state 或 props 更改的影响.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState): 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用.
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {number: 1,};this.ulRef = React.createRef();console.log('constructor...');}static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {console.log("getDerivedStateFromProps...", this);return {age: 10,};}componentDidMount() {console.log("componentDidMount...");}componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {console.log("componentDidUpdate...", snapshot);}shouldComponentUpdate(){console.log('shouldComponentUpdate...',this.state.number)// 判断是否渲染UI// return (this.state.number%2==0)return true;}getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {console.log("getSnapshotBeforeUpdate...");return null;}incNumber() {this.setState((state) => ({number: ++state.number,age: ++state.age,}));}render() {console.log("render...", this);return (<div><ul ref={this.ulRef} onClick={() => this.incNumber()}>{Array(this.state.number).fill(null).map((item, index) => (<li key={index}>{index}__</li>))}</ul><p>age: {this.state.age}</p></div>);}}ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />, document.getElementById("root"));
了解:getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
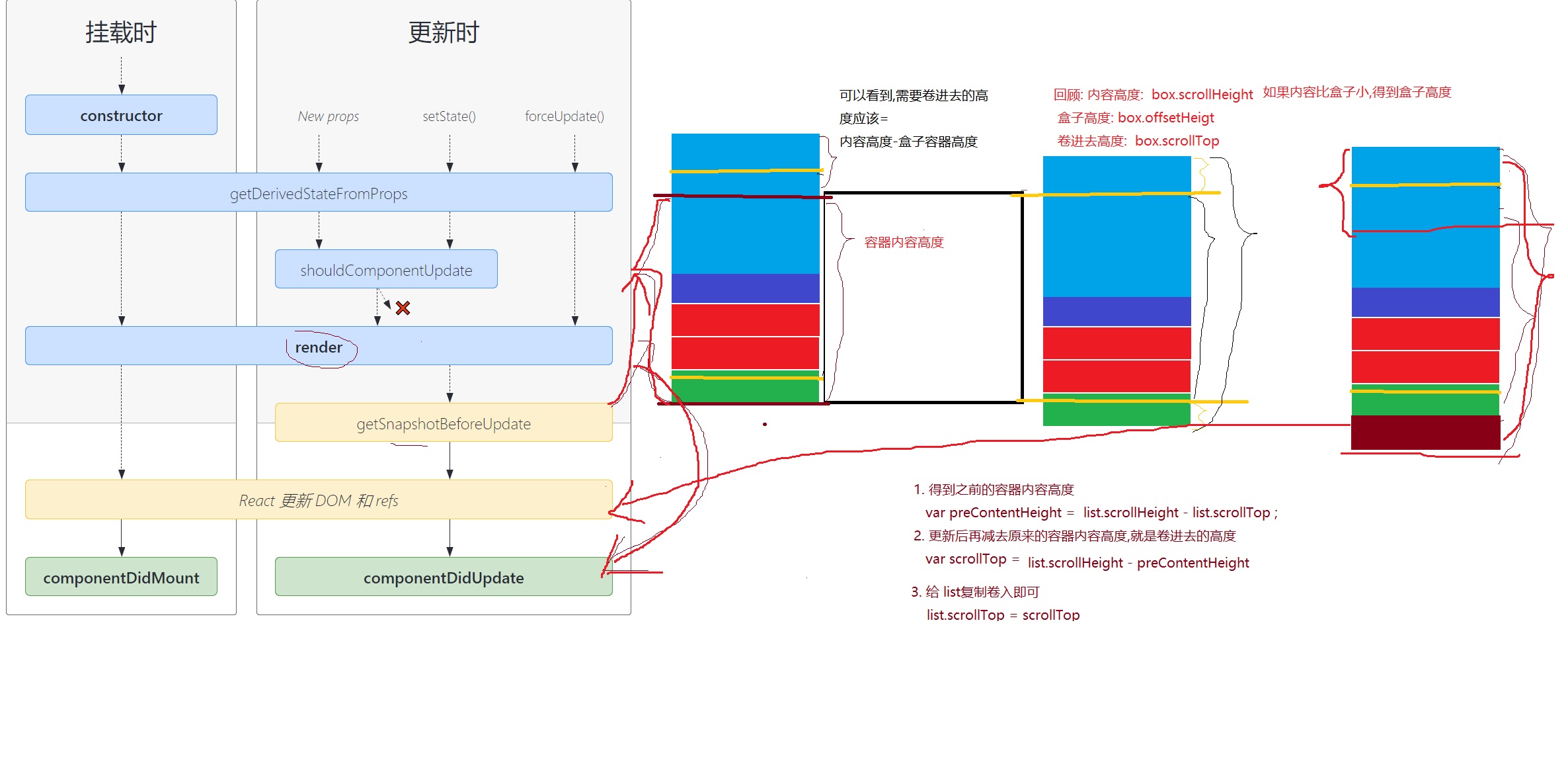
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。它使得组件能在发生更改之前从 DOM 中捕获一些信息(例如,滚动位置)。此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给componentDidUpdate()。
此用法并不常见,但它可能出现在 UI 处理中,如需要以特殊方式处理滚动位置的聊天线程等。
应返回 snapshot 的值(或null)。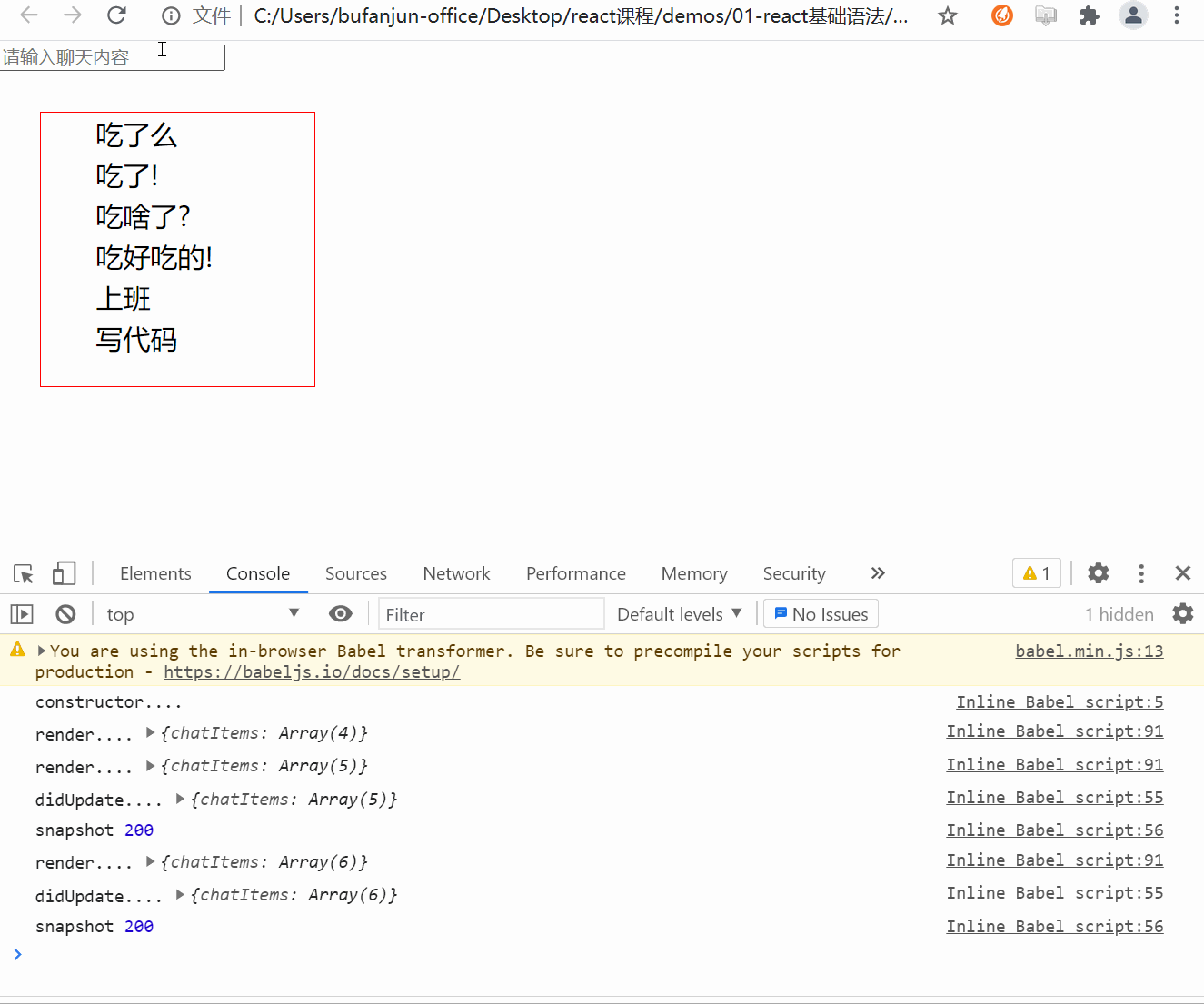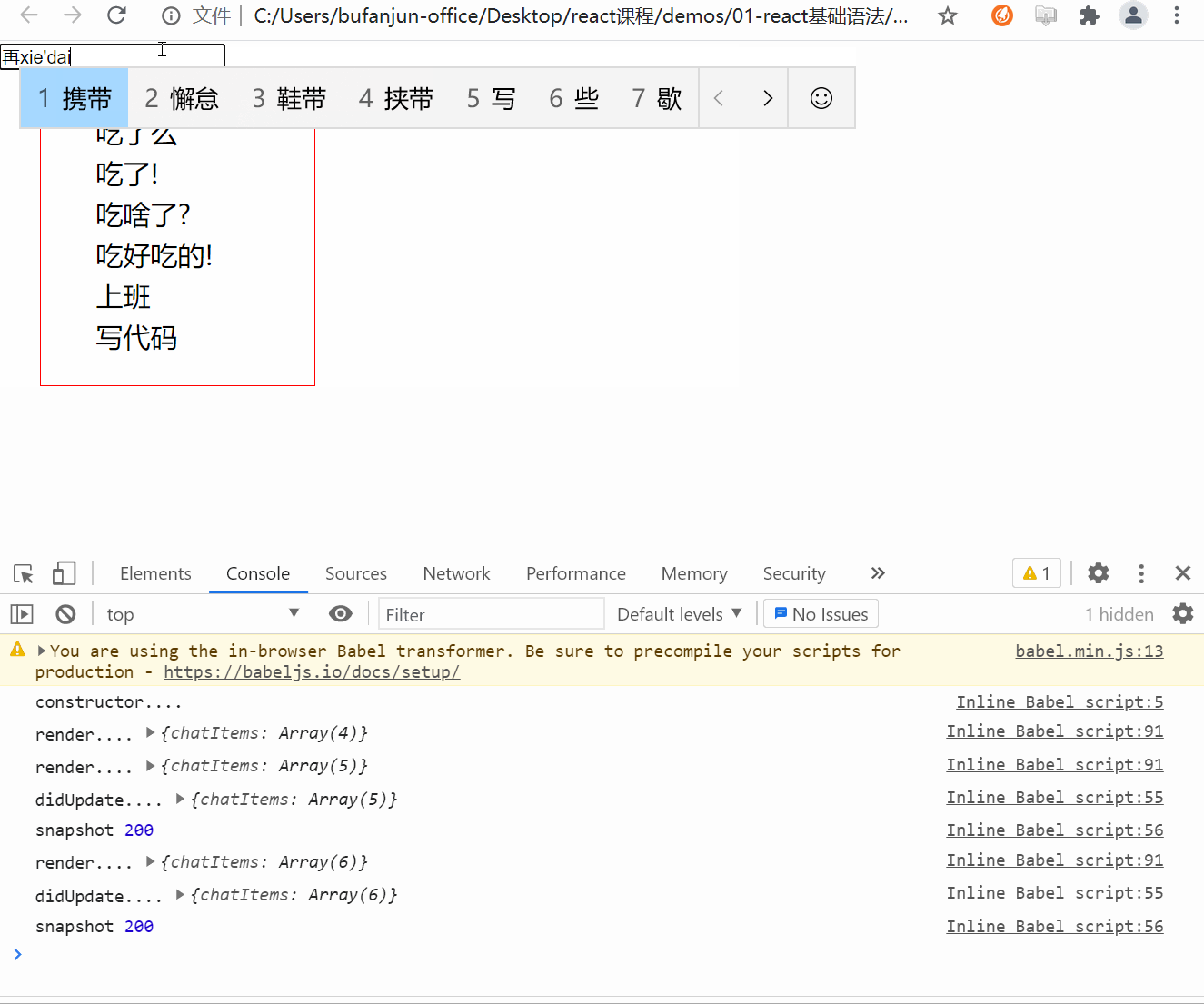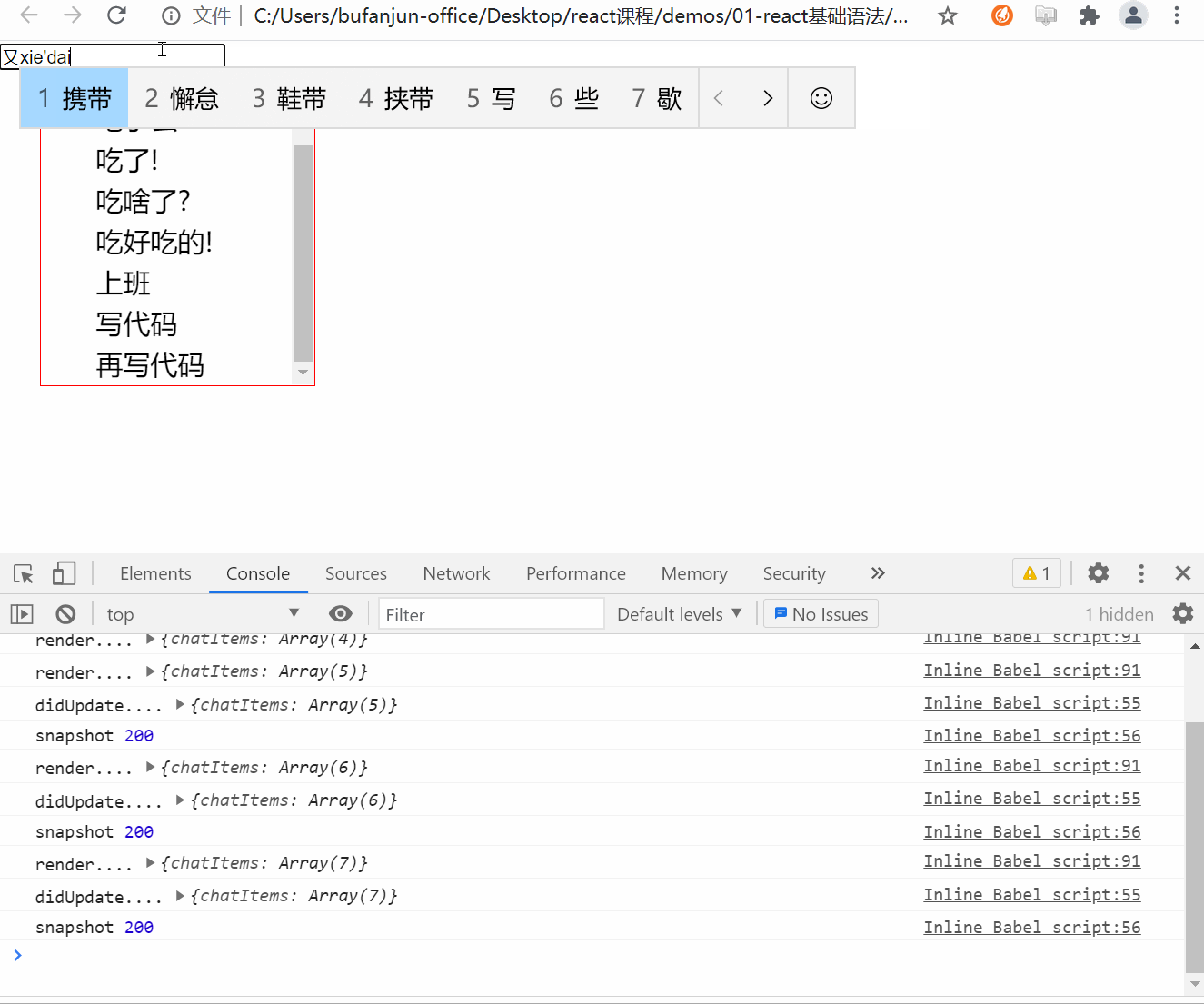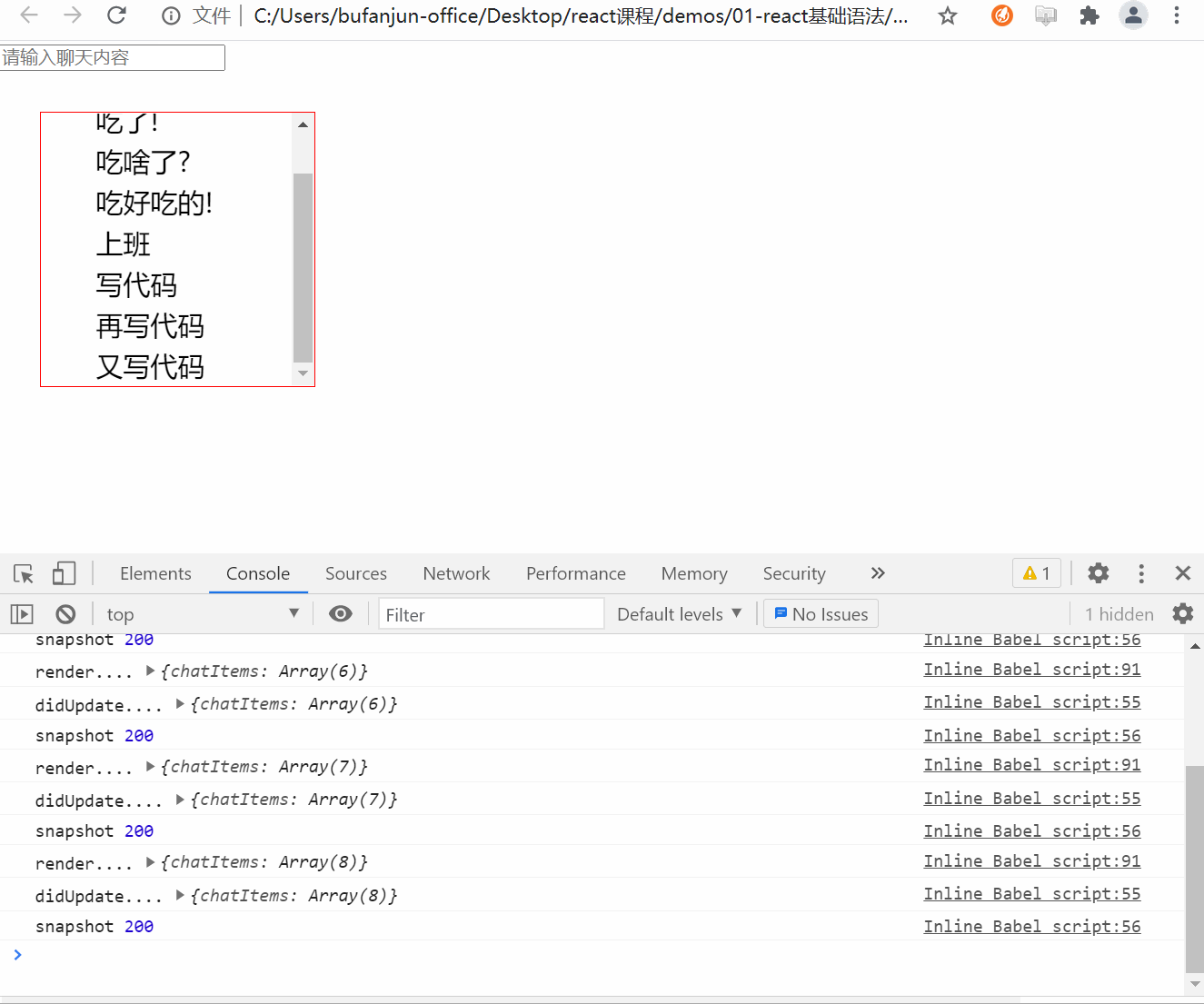
<style>*{margin: 0;padding: 0;}.ul-chat{width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;margin: 30px;overflow: auto;}.ul-chat>li{height: 30px;font-size: 20px;line-height: 30px;text-indent: 2em;}</style>class HelloWorld extends React.Component {constructor(props){super(props);console.log('constructor....');// 创建refthis.chatUlRef = React.createRef();this.state = {chatItems: [{id: 1,text: '吃了么'},{id: 2,text: '吃了!'},{id: 3,text: '吃啥了?'},{id: 4,text: '吃好吃的!'}]}// bindthis.handleKeyUp = this.handleKeyUp.bind(this);}componentDidMount(){}// 在state被更新后触发,而又没来得及更新到UI的时候// 这里可以获取到更新之前的UI状态,比如滚轮位置// prevState 上一次的state// 此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给 componentDidUpdate()。getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState){// 1. 得到之前容器的高度// 注意: 必须是等内容高度发生变化的时候再处理if(this.state.chatItems.length > prevState.chatItems.length){// 这里没来得及更新UI,所以得到的是上一次更新后的DOMvar chatUl = this.chatUlRef.current;// 之前的容器内容高度var preContentHeight = chatUl.scrollHeight - chatUl.scrollTop;return preContentHeight;}// 如果聊天列表高度没变化,则返回nullreturn null;}// snapshot 是通过getSnapshotBeforeUpdate声明周期函数返回的componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot){console.log('didUpdate....',this.state);console.log('snapshot',snapshot);// 2. 用更新后的最新高度 - 原来的内容高度 得到的就是需要被卷进去的高度if(snapshot){var chatUl = this.chatUlRef.current;// 计算需要被卷入的高度(多余的高度)var useScrollTop = chatUl.scrollHeight - snapshot;// 3. 赋值chatUl.scrollTop = useScrollTop;}}// 如果是输入了enter,需要把最新文本内容 更新到state.chatItemshandleKeyUp(e){// keyCode 可以获取键盘按键的 Ascii编码值var keyCode = e.keyCode;// 如果值== 13 说明是enter键if(keyCode == 13){// 获取input的value// 不能直接修改state的值,必须通过setState才能触发render()!!!// 所以如果state的某个值是对象类型,需要先克隆// [...xxx] 数组结构var chatItems = [...this.state.chatItems];chatItems.push({id: new Date().getTime(), // 时间戳肯定不同text: e.target.value})// 用setState更新this.setState({chatItems})// 更新后还原输入框e.target.value = '';}}render(){console.log('render....',this.state);var liItems = this.state.chatItems.map(item=>(<li key={item.id}>{item.text}</li>))return (<div><input type="text" onKeyUp={this.handleKeyUp} placeholder="请输入聊天内容" /><ul className="ul-chat" ref={this.chatUlRef}>{liItems}</ul></div>)}}// 使用react 相关api 渲染到容器ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />,document.getElementById('root'));