二叉树节点结构
class Node<V>{V value;Node* left;Node* right;}
:::info 遍历方式:
- 递归遍历
- 非递归遍历
遍历的顺序:
- 先序
- 中序
- 后序 ::: 二叉树实际上是一种特殊的没有环的链表
遍历方式-递归
递归序
void f(Node* head){//1 第一次访问if(head==nullptr)return ;//1f(head->left);//2 第二次访问//2f(head->right);//3 第三次访问//3}
按递归序遍历:1,2,4,4,4,2,5,5,5,2,1,3,6,6,6,3,7,7,7,3,1
:::tips
遍历时,可以回到自己三次!在这期间可以干点什么,也可以不干;
:::
:::info
在递归序的基础上,可以提出
- 先序
- 中序
- 后序
:::
先序遍历
:::tips 先序遍历:对于所有子树,都是先处理(打印)头节点,在处理左子树的节点,在处理右子树 ::: 1,2,4,5,3,6,7 :::tips 递归序中第一次到达该节点时打印(操作),剩下到达该节点时什么也不做,此时即为先序遍历 :::void preOrder(Node* head){if(head==nullptr)return;cout<<head->value;preOrder(head->left);preOrder(head->right);}
中序遍历
:::info 对于任意一个子树,先打印左子树,在打印头节点,在打印右子树 ::: 4,2,5,1,6,3,7 :::tips 递归序中第二次来到该节点时才打印,剩下什么也不做 ::: ```cpp void inOrder(Node* head){ if(head==nullptr){
} inOrder(head->left); cout<return
value; inOrder(head->right);
}
<a name="xCWCd"></a>## 后序遍历:::info对于任意一个子树,先打印左子树,在打印右子树,在打印头::::::tips在递归序中第三次来到该节点才打印,第一次第二次不处理:::```cppvoid posOrder(Node* head){if(head==nullptr)return;posOrder(head->left);posOrder(head->right);cout<<head->value;}
非递归遍历
先序遍历
:::info
任何递归函数都可以改成非递归函数!
都是系统帮助压栈
:::
需要准备一个栈
先序遍历:
1,2,4,5,3,6,7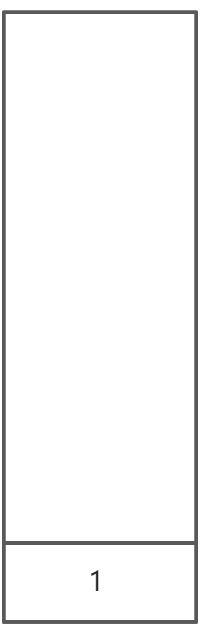 :::tips
:::tips
- 每次在栈中弹出一个节点,记作cur
- 打印or处理cur
- 先把cur的右子节点压栈,再把cur左子节点压入如果有的话
repeat :::
void preOrder(Node* head){if(head!=nullptr){stack<Node> s;Node cur;s.push(*head);while(!s.empty()){cur=s.pop();cout<<cur.value<<endl;if(cur.right!=nullptr){s.push(*(cur.right));}if(cur.left!=nullptr){s.push(*(cur.left));}}}}
若是先序遍历想要按照头右左的顺序遍历呢?
-
后序遍历
 :::info
:::info 先弹出cur,放入收集栈
- 对于cur的子节点,先压左再压右(头右左的递归遍历顺序)
- repeat
这样将收集栈逆序弹出,顺序就是左右头的递归顺序,因此是后续遍历 :::
void posOrder(Node* head){if(head!=nullptr){stack<Node> s1;stack<Node> s2Node cur;s.push(*head);while(!s1.empty()){cur=s1.pop();s2.push(cur);if(cur.left!=nullptr){s.push(*(cur.left));}if(cur.right!=nullptr){s.push(*(cur.right));}}while(!s2.empty()){cout<<(s2.pop()).value<<endl;}}}
中序遍历
:::info 中序遍历:左-头-右
先将子树的左边界压入栈中
- 依次弹出,弹出时打印or操作,并将弹出节点的右子树做相同的操作(左边界压栈)
repeat :::
void preOrder(Node* head){if(head!=nullptr){stack<Node*> s;while(!s.empty()||head!=nullptr){if(head!=nullptr){s.push(head);\\压栈在单边head=head->left;}else{head=s.pop();cout<<head->value;head=head->right;\\不用在这里把right压栈}}}}
:::info 所有的数都是可以被左边界分解的
左边界放到栈里:头—>左的顺序,那么弹出的顺序必然是左—>头;
- 弹出时对右边界做同样的操作。意味着对于右树后做先左再头的打印;
-
二叉树的宽度优先遍历
:::info 二叉树的先序遍历就是其深度优先遍历
宽度优先遍历?
队列:先进先出 :::
先把头节点放入队列中
- 弹出节点并打印
- 先放入弹出节点的左子节点,再放入右子节点
repeat
void BFS(Node* head) {if (head == nullptr) {return;}queue<Node*> q;q.push(head);while (!q.empty()) {Node* cur = q.front();q.pop();cout << cur->_value << endl;if (cur->_left != nullptr) {q.push(cur->_left);}if (cur->_right != nullptr) {q.push(cur->_right);}}}
Example
:::info 求一个二叉树的最大宽度?
知道每个节点所在那一层?
统计每一层的节点个数 :::
void BFS_n(Node* head) {//代码有问题,C++中unordered_map未匹配if (head == nullptr) {return;}queue<Node*> q;q.push(head);int currentLevelNodes=0;int curLevel=1;int maxNum=-1;unordered_map<Node*,int> levelMap;levelMap.insert(head,1);while (!q.empty()) {Node* cur = q.front();int curNodelevel=levelMap.find(cur);if(curNodeLevel==curLevel){currentLevelNodes++;}else{maxNum=max(currentLevelNodes,max);curLevel++;currentLevelNodes=1;}q.pop();if (cur->_left != nullptr) {levelMap.insert(cur->left,curLevel+1);q.push(cur->_left);}if (cur->_right != nullptr) {levelMap.insert(cur->right,curLevel+1)q.push(cur->_right);}}}

