参考资料:
存储方式
数据结构的存储方式只有两种:顺序存储(数组)、链式存储(链表)。
| 名称 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 数组 | 连续存储、随机访问o(1) | 需要扩容、插入o(n)、删除o(n) |
| 链表 | 无需扩容、知道位置则插入删除o(1) | 不连续存储无法随机访问o(n) |
其他数据结构则是基于这两种存储方式的“上层建筑”:
| 名称 | 顺序存储 | 链式存储 |
|---|---|---|
| 队列 | 数组实现 | 链表实现 |
| 栈 | 数组实现 | 链表实现 |
| 图 | 邻接矩阵 | 邻接表 |
| 树 | 堆 | 链表实现 |
| 散列表 | 拉链法 | 线性探查法 |
线性表
api:初始化,判空,尾部插入,插入,删除,按值查找,按下标查找,获取长度
顺序表实现
class ListByArray {constructor() {this.length = 0;this.arr = [];}indexOf(target) {for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {if (this.arr[i] == target) return i;}return -1;}lastIndexOf(target) {for (let i = this.length - 1; i >= 0; i++) {if (this.arr[i] === target) return i;}return -1;}getLength() {return this.length;}getElement(position) {if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;return this.arr[position];}insert(position, element) {if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;for (let i = this.length; i > position; i--) {this.arr[i] = this.arr[i - 1];}this.arr[position] = element;this.length += 1;return this.arr;}delete(position) {if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;let currentItem = this.arr[position];for (let i = position + 1; i < this.length; i++) {this.arr[i - 1] = this.arr[i];}this.length -= 1;return currentItem;}append(element) {this.arr[this.length] = element;this.length += 1;return true;}}
链表实现(单链表)
参考链接:JavaScript数据结构——链表的实现与应用
单链表的结点结构: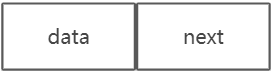
单链表根据有无头结点分为带头结点的单链表、不带头结点的单链表: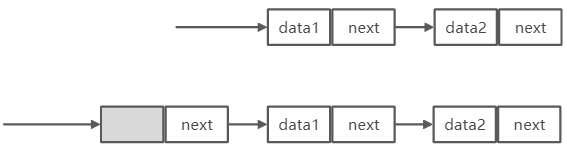
引入头结点的两个优点:1. 对头结点的操作如插入、删除操作与其它结点一致;
API:按索引查找、尾部插入、插入、删除、按值查找、判空
class Node { // 首先需要一个辅助类,用来描述链表中的节点constructor(val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;}}class LinkedList {constructor() {this.length = 0; // 长度this.head = null; // 头}getElement(position) {// 考虑所给索引是否超出范围,然后遍历即可,先实现这个,是其他的基础if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;let current = this.head;for (let i = 0; i < position; i++) {current = current.next;}return current;}append(element) {// 如果链表为空和不为空的情况let newNode = new Node(element);if (this.head === null) this.head = newNode;else {let lastNode = this.getElement(this.length - 1);lastNode.next = newNode;}this.length++;}isEmpty() {// 判断是否为空if (this.length == 0) return true;return false;}insert(position, element) {// 所给position不能超出边界值;再考虑是否插入的是首节点if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;let newNode = new Node(element);if (position === 0) {newNode.next = this.head;this.head = newNode;} else {let preNode = this.getElement(position - 1);newNode.next = preNode.next;preNode.next = newNode.next;}this.length++;return true;}remove(position) {// 是否超出范围;再考虑是否删除的首节点if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;if (position === 0) {this.head = this.head.next;} else {let preNode = this.getElement(position - 1);this.preNode.next = this.preNode.next.next;}this.length--;return true;}indexOf(element) {let current = this.head;for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {if (current.val == element) {return i;} else {current = current.next;}}return -1;}}
链表遍历
function traverse_iteration(head) {// 链表的迭代遍历1for (let p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {console.log(p.val);}}function traverse_iteration(head) {// 链表的迭代遍历2while(head){console.log(head.val);head = head.next;}function traverse_recurtion(head) {// 链表的递归遍历if (!head) {console.log(head.val);traverse_recurtion(head.next);}}
例题
寻找中间结点(快慢指针)
getMiddleNode() {let fast = this.head;let slow = this.head;while (fast && fast.next && fast.next.next) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
链表中是否含有环
hasCycle() {let fast = this.head;let slow = this.head;while (fast && fast.next && fast.next.next) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) {return true;}}return false;}
含有环返回环的起始位置
先让快慢指针相遇,再让其中一指针回到起点,两者再以相同速度前进,再次相遇即起始。
getCycleStart() {let fast = this.head;let slow = this.head;while (fast && fast.next && fast.next.next) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) break;}slow = this.head;while (slow && slow.next) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;if (slow == fast) return slow;}}
寻找链表倒数第k个元素
两个指针,让一指针先走K步,然后相同速度走,当快指针到头返回慢指针。
getLastK(k) {let fast = this.head;let slow = this.head;let i = 0;while (i < k && fast && fast.next) {i++;fast = fast.next;}if (i != k) return false;while (fast) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
循环单链表
将原来单链表末结点next原本的指向为null,改为指向头结点。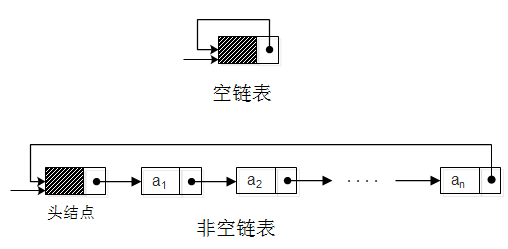
判空:
if(head === head.next)
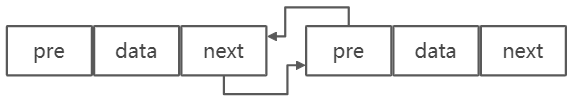
双链表
循环双链表
将双链表头结点前驱指针指向末结点,末结点后驱指针指向头结点。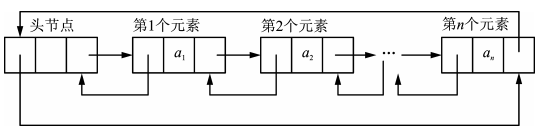
静态链表
即用顺序表来实现链表,即数组中保存着一个个结点对象,对象结构如下:
class Node {constructor(val) {this.val = val;this.next = null; // next指向为结点的下标}}
栈
api:栈顶添加元素append、返回栈顶元素top、弹出栈顶pop。
链表实现栈
class Node {constructor(val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;}}class StackByLink {constructor() {this.length = 0;this.tophead = null;}append(element) {let newNode = new Node(element);if (this.tophead == null) this.tophead = newNode;else {newNode.next = this.tophead;this.tophead = newNode;}this.length++;}pop() {if (this.length == 0) return false;let current = this.tophead;this.tophead = this.tophead.next;this.length --;return current;}top() {return this.tophead;}}
顺序表实现栈
class StackByArr {constructor() {this.length = 0;this.arr = [];}append(element) {this.arr[this.length++] = element;}pop() {if (this.length == 0) return false;let current = this.arr[this.length - 1];delete this.arr[this.length - 1];this.length--;return current;}top() {return this.arr[this.length - 1];}}
队列
链表实现队列
class QueueByLink {constructor() {this.length = 0;this.prehead = null;this.bachead = null;}isEmpty() {if (this.length === 0) return true;return false;}append(element) {let newNode = new Node(element);if (this.length === 0) {this.prehead = this.bachead = newNode;} else {this.bachead.next = newNode;this.bachead = newNode;}this.length++;}shift() {if (this.isEmpty()) return false;let current = this.prehead;this.prehead = this.prehead.next;this.length--;return current.val;}}
循环队列
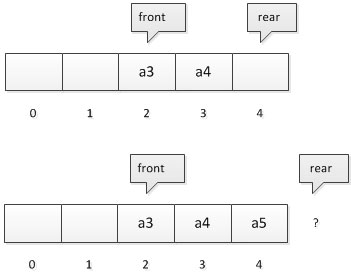
注意点:如何判断队空还是队满,因为此时都有front=rear。有两种方式处理:
- 增加一个标识flag:初始时为false,当指针front变动时,flag为false;当rear变动时,flag为true。当front=rear且flag=true时队列满,当front=rear且flag=false时队列空。
- 增加一个计数count:初始为0,当rear变动则count+1,front变动count-1但不小于0;当count=队列长度则队列满,count为0队列空。
- 少用一个元素空间并规定rear=front为队列空,rear下一位置若为front则队列满。
(在rear处添加元素后,rear指针往后移动一格,所以rear指针所指的元素值为空)
PS:先实现是否队空、队满。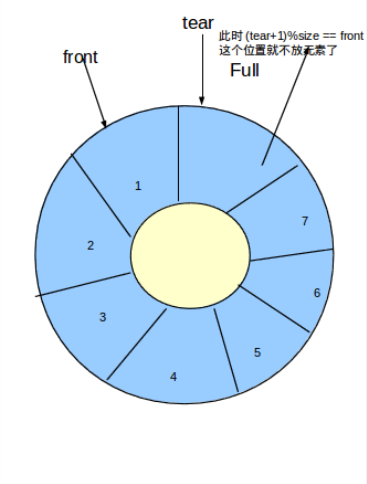
顺序表实现
class CircularQueue {constructor(MaxSize = 3) {this.MaxSize = MaxSize;this.front = 0;this.back = 0;this.flag = false;this.arr = [];}//判断是否为空队列isEmpty() {if (this.front == this.back && this.flag == false) return true;return false;}//判断队列是否已满isFull() {if (this.front == this.back && this.flag == true) return true;return false;}//返回队列元素个数queueNums() {let nums = null;if (this.back - this.front) nums = this.back - this.front;else nums = this.MaxSize - (this.front - this.back);return nums;}//返回队列头部元素top() {if (this.isEmpty()) return false;return this.arr[this.front];}//队尾插入元素append(element) {if (!this.isFull()) {this.arr[this.back] = element;this.flag = true;if (++this.back === this.MaxSize) {this.back = this.back % this.MaxSize;}return true;}return "队列已满";}//队头删除元素shift() {if (!this.isEmpty()) {let current = this.arr[this.front];this.arr[this.front] = null;this.flag = false;if (++this.front === this.MaxSize) {this.front = this.front % this.MaxSize;}return current}return "队列已空";}//根据值查找索引}
树
树的遍历
前序、中序、后续遍历;n叉树递归遍历
function tree_recurtion(root) {// “前序遍历”tree_recurtion(root.left);// “中序遍历”tree_recurtion(root.right);// “后序遍历”}function tree_recurtion_n(root) {// n叉树的递归遍历for (node of root) {tree_recurtion_n(node);}}
图示: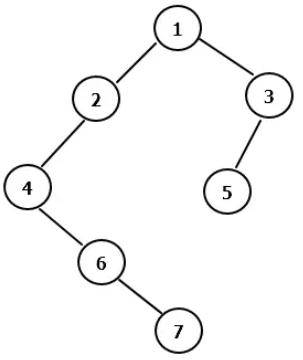
前序:1-2-4-6-7-3-5
中序:4-6-7-2-1-5-3
后序:7-6-4-2-5-3-1
两种遍历的递归写法等价:
function codec(res = [], root) { // code_1if(!root) res.push("#");else{res.push(root.val);codec(root.left);codec(root.right);}return res;}let res = []; // code_2function codec_2(root) {if (!root) res.push("#");else {res.push(root.val);codec(res, root.left);codec(res, root.right);}}
二叉树遍历的迭代写法:
层次遍历: [102] 二叉树的层序遍历
var levelOrder = function(root) { // 当前层、下一层if(!root)return [];let res = [];let cur_layer = [root]; // 初始层为根节点while(cur_layer.length){ // 当前层不为空时let next_layer = []; // 用于存储下一层结点let cur_vals = []; // 用于存储当前层的结果for(let i =0;i<cur_layer.length;i++){ // 遍历当前层的结点cur_vals.push(cur_layer[i].val); // 将当前层结果存储起来if(cur_layer[i].left){ // 若该节点左子树存在,则存入下一层next_layer.push(cur_layer[i].left);}if(cur_layer[i].right){ // 若该节点右子树存在,则存入下一层next_layer.push(cur_layer[i].right);}}if(cur_vals.length)res.push(cur_vals);cur_layer = next_layer; // 当前层遍历完毕, 将当前层替换为下一层}return res;};
结点结构
// 结点结构1function TreeNode(val, left, right) {this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)}// 结点结构2class TreeNode {constructor(val) {this.val = val;this.left = null;this.right = null;}}
二叉搜索树(BST)
定义:一个二叉树中,任意节点的值要大于等于左子树所有节点的值,且要小于等于右边子树的所有节点的值。
二叉树算法设计的总路线:把当前节点要做的事做好,其他的交给递归框架,不用当前节点操心。
特点:中序遍历得到有序数列。
BST遍历框架
function BST(root,target){if(target === root.val){// do something...}else if(target > root.val){BST(root.right, target)}else{BST(root.left, target)}}
例题
判断是否BST
可以通过辅助函数增长参数列表,借助参数传递信息。
var isValidBST = function (root) {// 验证是否是二叉搜索树function helper(root, min, max) {if (root === null) return true;if (root.val <= min || root.val >= max) return false;return (helper(root.left, min, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, max));}return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);};
判断是否有目标值
function isInBST(root, target) {// BST中是否有目标值,有则返回对应根,无则nullif (target === root.val) return root;if (target > root.val && root.right !== null)return isInBST(root.right, target);else if (target < root.val && root.left !== null)return isInBST(root.left, target);else return null;}
插入一个数
从大范围考虑时,左右子树需要变化,则写法1;从小范围考虑时,一直遍历找到需要变化的地方,则写法2。
// 写法1:var insertIntoBST = function (root, target) {// 若根节点不存在,则插入新节点if (root === null) return new TreeNode(target);if (root.val < target) {// 目标值插在根节点右边,则右子树需要变化root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, target);} else if (target < root.val) {// 目标值插在根节点右左边,则左子树需要变化root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, target);}return root;};// 写法2:var insertIntoBST = function (root, target) {function helper(root, target) {if (root === null) return new TreeNode(target);if (target < root.val && !!root.left) return helper(root.left, target);else if (target > root.val && !!root.right)return helper(root.right, target);else if (target < root.val && root.left === null)root.left = new TreeNode(target);else if (target > root.val && root.right === null)root.right = new TreeNode(target);return root;}if (root === null) return new TreeNode(target);helper(root, target);return root;};
删除一个数
function deleteBSTNode(root, target) {if (root == null) return null;if (root.val === target) {// 找到则删除if (root.left === null && root.right === null) return null;if (root.left == null) return root.right;if (root.right == null) return root.left;if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {// 左右子树都不为空,则用左子树最大的节点代替,或者使用右子树最小节点代替,然后删除对应节点var minNode = minInBST(root.right);root.val = minNode.val;root.right = deleteBSTNode(root.right, minNode.val);}} else if (root.val < target) {root.right = deleteBSTNode(root.right, target);} else if (target < root.val) {root.left = deleteBSTNode(root.left, target);}}
最小、最大的数
function minInBST(root) {// BST中最小的数if (root.left) return minInBST(root.left);return root;}function maxBST(root) {// BST中最大的数if (root.right) return maxBST(root.right);else return root;}
其它树
散列表(哈希表)
堆
参考资料:
堆可以用完全二叉树来表示。堆可分为两类,分别是最大堆和最小堆。对于最小堆,每个根结点值都小于等于其左右子节点;对于最大堆,每个根结点值都大于等于其左右子节点;这里以最大堆为例。
常常和优先队列
堆的表示
堆一般使用数组来表示: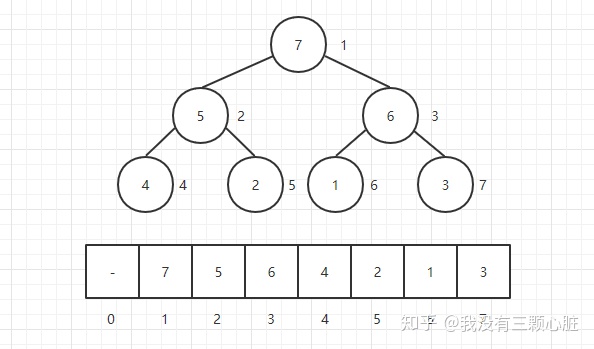
如图所示,设根节点下标为x,则左子节点下标=x2,右子节点下标=x2+1。根结点下标=孩子结点下标 / 2。
二叉堆的相关操作
以最大堆为例
// 插入元素、上浮操作(将大的数上浮到顶部)// 删除最大数、下沉操作(先将最大数[在堆顶]与最后一个元素交换,删除最后一个元素,然后将堆顶元素下沉到合适位置)
优先队列
优先队列包括最大优先队列、最小优先队列。而优先队列的底层数据结构就是堆,最大堆—>最大优先队列,最小堆—>最小优先队列。
优先队列的ADT:
// --- 优先队列主要操作 ---insert(key, data) // 元素入队操作,以key为排序依据,data为数据deleteQueueTop(key) // 删除堆顶元素(最小 / 最大)getQueueTop(key) // 返回堆顶元素// --- 优先队列辅助操作 ---第k最小/第k最大:返回优先队列中键值为第k个最小/最大的元素大小(size):返回优先队列中的元素个数堆排序(Heap Sort):基于键值的优先级将优先队列中的元素进行排序
具体实现:
参考:二叉堆实现优先级队列
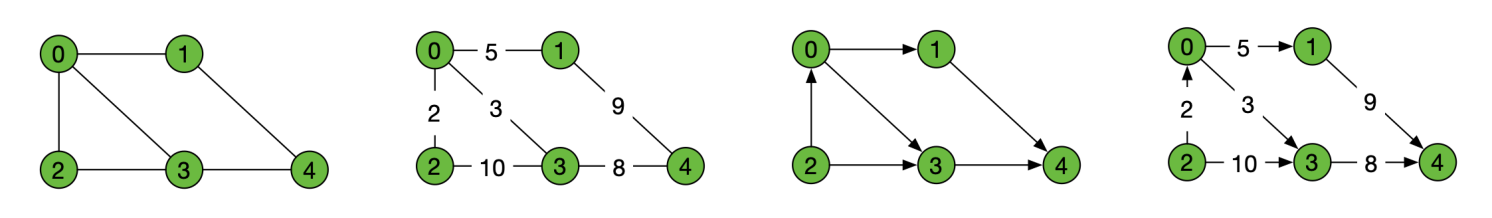
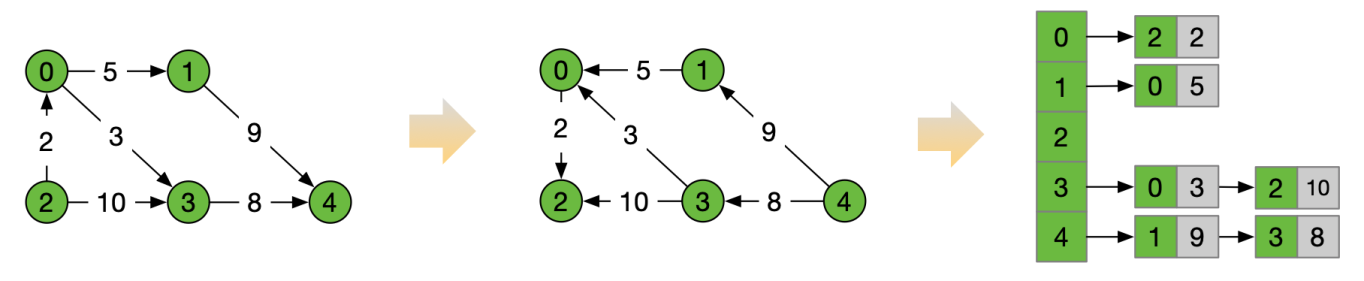
图
参考资料:
图的分类
图的表示方法
- 边列表

- 邻接矩阵
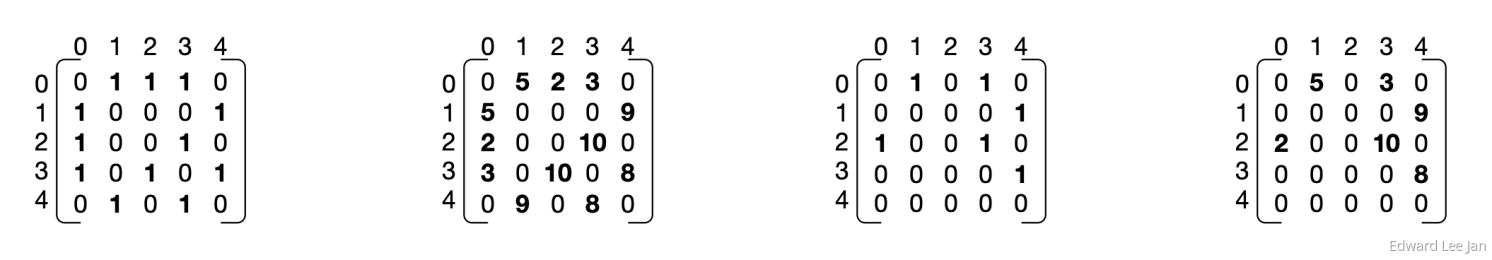
- 邻接表
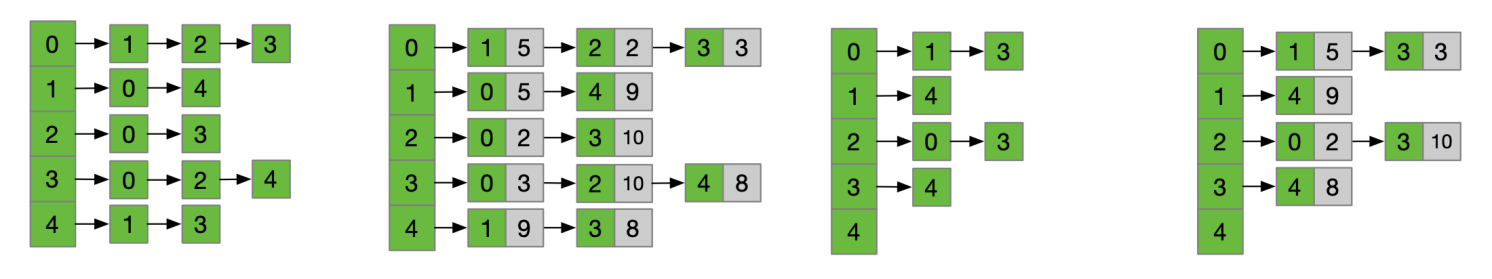
- 逆邻接表
图的实现
扩展
LRU算法
数据结构的构造为:哈希表+双向链表