给每个线程拷贝一个线程自己本地的变量副本,每个线程就直接操作自己的本地副本就ok了,然后就跟其他的线程就没有冲突了,避免多个线程并发的访问同一个共享的数据。重点就是用一个变量,同时多个线程操作的时候不让变量是共享。
源码剖析
设置值流程
public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null)map.set(this, value);elsecreateMap(t, value);}
- Thread t = Thread.currentThread();获取当前线程
- ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);获取Thread的ThreadLocalMap,这个map只能是自己线程内部可以使用。一个Thread可以放多个ThreadLocal
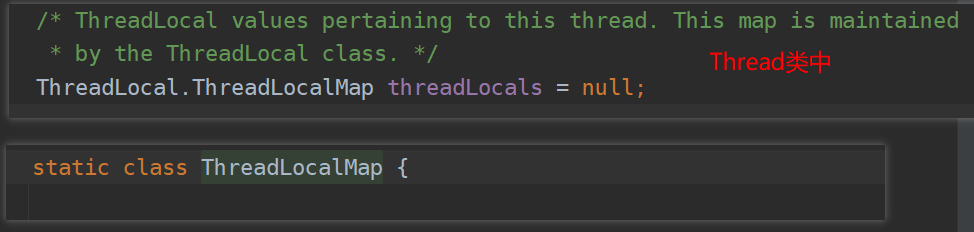
map != null;如果map不为空就可以直接set,没有map就得创建
map.set(this, value); key就是当前线程的ThreadLocal对象,value就是设置的值
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}if (k == null) {replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();}
获取值流程
public T get() {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null) {ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")T result = (T)e.value;return result;}}return setInitialValue();}
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();获取当前线程
- ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);拿到线程的ThreadLocalMap
- ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); 通过当前线程的ThreadLocal对象找到那个entry数组
- T result = (T)e.value;从entry数组中获取值,然后返回。

