https://www.jianshu.com/p/b2e1fb9de714
适配
在不同尺寸的移动设备上, 页面相对性的达到合理的展示(自适应), 或者保持同一效果的等比缩放(看起来差不多)
适配的元素
- 字体
- 宽高
- 间距
-
适配的方法
百分比适配
- viewport 缩放适配
- DPR 缩放适配
- rem 适配
-
百分比适配
360手机站
拉钩H5页面 顶部底部, 职位列表 都是高度定死, 宽度100%自适应
高度固定, 宽度百分比, 在高度不能定死的状况下, 不是很好用, 一般都是配合其他是适配使用
当元素为奇数或者某个元素占比不均匀的时候, 不是很好算360顶部模拟<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no"/><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body *{-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0)}button, input{-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder{color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder{color: #f00;}.header {width: 100%;height: 48px;background: #23ac38;display: flex;justify-content: space-between;align-items: center;box-sizing: border-box;padding: 0 10px;}.logo img{width: 80px;}.list img{width: 20px;}</style></head><body><header class="header"><span class="logo"><img src="http://p2.qhmsg.com/t01ecc3b6b24e7bdbd8.png" alt=""></span><span class="list"><img src="http://p9.qhmsg.com/t010fa93a99715aad32.png" alt=""></span></header></body></html>
viewport 适配
把所有机型的
css像素设置成一致的 viewport 需要使用 js 动态设置, (不能直接把 device 的值设置为数值)
通过设置比例(初始比例以及缩放比例), 把宽度缩放成一致
缩放比 = css 像素 / 375<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no" /><meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0" id="view"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body * {-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)}button, input {-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #f00;}div {width: 75px;height: 100px;float: left;}div:nth-child(1) {background: #f00;}div:nth-child(2) {background: #ff0;}div:nth-child(3) {background: #f0f;}div:nth-child(4) {background: #0ff;}div:nth-child(5) {background: #0f0;}</style><script>; (function () {/* 获取 css 像素 (viewport没有缩放, initial-scale=1.0)*/var curWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidthvar curWidth = window.innerWidthvar curWidth = window.screen.width/* 以上三种方式都可以准确的获取到 html 的 width */var targetWidth = 375 // 目标值var scale = curWidth / targetWidthvar meta = document.getElementById('view')var content = 'initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scalemeta.content = content})()</script></head><body><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div></body></html>
但是这种肯定是有问题的
在ipad上, 宽度为768,pro为1024, 一张375的图片放上去 …DPR 适配
把 CSS 像素缩放成与设备像素一样大的尺寸
只有在 PC 端这两个值才是对应的1css像素 = 1物理像素iphone6的物理像素750 * 1334. 通过缩放, 将CSS像素的375 * 667缩放, 按照设计稿750切图.<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no" /><meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0" id="view"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body * {-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)}button, input {-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #f00;}div {width: 20%;height: 100px;float: left;}div:nth-child(1) {background: #f00;}div:nth-child(2) {background: #ff0;}div:nth-child(3) {background: #f0f;}div:nth-child(4) {background: #0ff;}div:nth-child(5) {background: #0f0;}</style><script>; (function () {/*要将 375 => 750 就是 375 / 0.5 dpr = 2375 / ? = 750 这个 ? 就是 dpr 的倒数*/var meta = document.querySelector('meta[name="viewport"]')var scale = 1 / window.devicePixelRatioif(!meta){ // 没有默认设置 viewport 的 meta, 创建meta = document.createElement('meta')meta.name = 'viewport'meta.content = 'width=device-width, initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scaledocument.head.appendChild(meta)} else { // 有默认设置 viewport 的 meta, 修改meta.setAttribute('content', 'width=device-width, initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scale)}})()</script></head><body><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div></body></html>
虽然一个
CSS像素对应了一个物理像素, 但是对于不同尺寸的设备, 依然不是一个好的解决方案, 需要rem进行配合rem 适配
把所有的设备分成相同的若干份, 再计算元素宽度所占的份数
em:当意义为font-size的时候,1em代表父元素的字体大小, 当作为其他单位(宽度高度)的时候, 代表自身字体大小chrome下有最小字体限制12px, 字体小于12px无法再变小rem: r root, 根元素的font-size将html的font-size设置为20px,1rem = 20px元素适配的宽度 = 元素所占的列数 * 一列的宽度
- 元素在设计稿里面的宽度
- 列数 (随便给的) 100
- 一列的宽度 = 屏幕宽度(css像素) / 列数
元素实际占的列数 = 设计稿里面的宽度 / 一列的宽度
var colWidth = 0var col = 100 // 假设 100 列// 计算 iPhone5 iPhone6里面一列的宽度colWidth = 375 / col // 3.75px 6colWidth = 320 / col // 3.20px 5// 一个 div 占 10 列var width = 10 * 3.75 // 37.5px 6var width = 10 * 3.20 // 32.0px 5// 一个 div 50pxdivCol = 50 / 3.75 // 13.333divCol = 50 / 3.20 // 15.625// 所以按照此方案, 50px 的 div, 在不同的设备里, 会占到不同的份数
屏幕已经被分成了若干份
那么width: 10rem;(写入 CSS 文件的代码)
元素适配的宽度 =>元素所占的列数 * 一列的宽
元素适配的宽度 =>width 10 * 1rem
元素所占的列数 =>10
一列的宽 =>1rem1rem=html的font-size
根据栅格系统的原理, 将屏幕分成若干份, 不同的屏幕被分成相同的份数, 所以一份的宽度会不一样
但是份数是一样的, 所以整体比例是一样的; (function (fs) {var html = document.documentElementvar width = html.clientWidth // css 像素html.style.fontSize = width / fs + 'px'// 分成 16 列, iPhone5 为例 320px 得到 1rem = 20px})(16)
这种方式并没有一个基准点, 只是按照屏幕的增大,
html的font-size在变大
我们希望增加一个基准点, 这个点就是iPhone6, 屏幕仍然分成16份
如果屏幕尺寸为375, 那么就html字体也是16px
如果屏幕小于375那font-size也会小于16px
反之, 大于16px
如下代码:; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {const html = doc.documentElementconst refreshDom = () => {const clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 16 * clientWidth / 375 + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
但是这样做有一个弊端, 当计算出了
rem值之后, 还要除以dpr, 才是真正应该写的值
而且很多是除不尽的, 跟着一大串小数, 虽然有less sass去做这些事情, 但是还是觉得美中不足rem 最终方案
; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {const html = doc.documentElementconst refreshDom = () => {const clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
只有一行代码不同
那么html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'又是什么意思呢 ?
基于iPhone6的尺寸, 将整个页面适配成7.5 rem.
所以, 只要设计稿是750px, 在切图的时候, 量出来出多少px, 直接将这个值除以100, 加上rem就ok
这个时候, 屏幕被分割成多少份这个概念已经不怎么明朗了, 说是7.5份吗? 好像不太对劲. 那就索性不管了.
如果设计图是640px, 那么整屏的宽度就是6.4rem, 只需要将参数修改一下就可以了.
但是上面的代码是用到了ES6的语法,ios9不是原生支持的, 直接在上面跑会出现很大的问题, 就相当于适配没有做一样.
所以改写吧:; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {var html = doc.documentElementfunction refreshDom(){var clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
这种方案总体来说没什么大问题了. 如果在设计稿上量出来长度为
50px, 那么实际写上去的长度应该是50 / 2 = 25px. 因为750的设计稿,375px就会占满屏幕. 或者是写.5rem.
字体也要用标注的字体大小除以2, 如标注28px, 实则应该写14px, 或者.28remhotcss
大佬写的号称移动端终极解决方案, 原理跟如上一样, 只是考虑的东西更多, 功能更强大.
去github上下载或者clone, 地址是:https://github.com/imochen/hotcss
需要做一点点小小的处理, 将第十四行左右的maxWidth = 540, 修改为设计稿的尺寸, 这个540是几年前写的, 相较现在来说有点小了.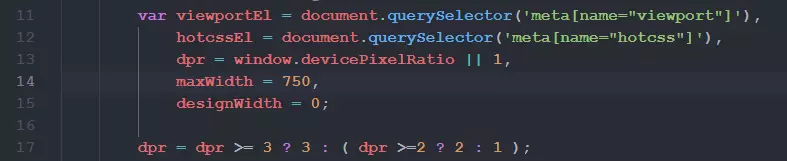
然后在页面中引入这个hotcss.js. 使用sass.
在写scss的地方引入px2rem的scss文件, 然后就可以在scss上愉快的写代码了.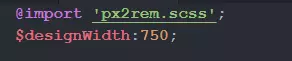
量出来多少(100px)就直接px2rem(100)vw, vh 适配
这俩单位就是为适配而生的
vw:viewport's width1vw=视口宽度的 1%vh:viewport's height1vh=视口高度的 1%vmax: 取vw,vh中的最大值vmin: 取vw,vh中的最小值
支持情况:ios >= 8; android >= 4.4
浏览器将任何屏幕都分成 100 份, 只要使用此单位, 就不会翻车两种方案
方案一: 通篇使用
vw@function vw($px){@return $px / 750 * 100vw;}
为方便切图, 写了一个如上函数
(scss), 以750为基准, 在任何屏幕上都可以看做是'750'
因为例如此函数传250进去, 会被转换成33.33333vw, 三个这样的大小将占满屏幕宽度, 在任何尺寸屏幕上的都是这样.
方案二: 通过vw设置根节点的字体大小, 页面尺寸依然使用rem
一个很暴力的方式, 还是以750为基准.375(css像素) / 750(设计稿宽度) * 100这是rem适配的原理所在
这个值最终是50, 这个值就是rem适配中,html的字体大小 .
那通过vw适配, 要达到rem同样的适配效果, 是不是应该让?vw = 50px?
所以50 / 3.75=13.333333333333334(15位小数)
然后:html {font-size: 13.333333333333334vw;}
然后,
rem适配需要的js代码可以删除了. 然后在任意尺寸的屏幕上也是可以横着走的.
整个屏幕7.5rem. 与rem适配的结果都是一样的
需要注意一些问题:css尺寸写rem, 比如1/4屏幕大小的div,width: 1.875rem;html的font-size会带来负面影响. 很多有文本属性(受font-size影响)的标签里面的内容会继承html的字体大小,13.33vw字体其实是非常大的, 所以不处理的话, 页面将会乱套.img的display属性默认是inline-block, 它会根据字体来对齐. 如果字体继承了html. 图片就会跑到一个匪夷所思的地方. 这个时候需要将img的包裹层的font-size做出相应的调整- 比较一劳永逸的方法, 在该设置的字体的地方设置字体大小, 然后最主要的是, 在
body里面, 将font-size设置为chrome最小字体12px, 阻止页面的元素去继承html的字体大小. 即现在html的字体大小只能影响rem这个单位.
移动端适配方案
适配
在不同尺寸的移动设备上, 页面相对性的达到合理的展示(自适应), 或者保持同一效果的等比缩放(看起来差不多)
适配的元素
- 字体
- 宽高
- 间距
-
适配的方法
百分比适配
- viewport 缩放适配
- DPR 缩放适配
- rem 适配
-
百分比适配
360手机站
拉钩H5页面 顶部底部, 职位列表 都是高度定死, 宽度100%自适应
高度固定, 宽度百分比, 在高度不能定死的状况下, 不是很好用, 一般都是配合其他是适配使用
当元素为奇数或者某个元素占比不均匀的时候, 不是很好算360顶部模拟<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no"/><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body *{-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0)}button, input{-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder{color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder{color: #f00;}.header {width: 100%;height: 48px;background: #23ac38;display: flex;justify-content: space-between;align-items: center;box-sizing: border-box;padding: 0 10px;}.logo img{width: 80px;}.list img{width: 20px;}</style></head><body><header class="header"><span class="logo"><img src="http://p2.qhmsg.com/t01ecc3b6b24e7bdbd8.png" alt=""></span><span class="list"><img src="http://p9.qhmsg.com/t010fa93a99715aad32.png" alt=""></span></header></body></html>
viewport 适配
把所有机型的
css像素设置成一致的 viewport 需要使用 js 动态设置, (不能直接把 device 的值设置为数值)
通过设置比例(初始比例以及缩放比例), 把宽度缩放成一致
缩放比 = css 像素 / 375<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no" /><meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0" id="view"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body * {-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)}button, input {-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #f00;}div {width: 75px;height: 100px;float: left;}div:nth-child(1) {background: #f00;}div:nth-child(2) {background: #ff0;}div:nth-child(3) {background: #f0f;}div:nth-child(4) {background: #0ff;}div:nth-child(5) {background: #0f0;}</style><script>; (function () {/* 获取 css 像素 (viewport没有缩放, initial-scale=1.0)*/var curWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidthvar curWidth = window.innerWidthvar curWidth = window.screen.width/* 以上三种方式都可以准确的获取到 html 的 width */var targetWidth = 375 // 目标值var scale = curWidth / targetWidthvar meta = document.getElementById('view')var content = 'initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scalemeta.content = content})()</script></head><body><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div></body></html>
但是这种肯定是有问题的
在ipad上, 宽度为768,pro为1024, 一张375的图片放上去 …DPR 适配
把 CSS 像素缩放成与设备像素一样大的尺寸
只有在 PC 端这两个值才是对应的1css像素 = 1物理像素iphone6的物理像素750 * 1334. 通过缩放, 将CSS像素的375 * 667缩放, 按照设计稿750切图.<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no,email=no" /><meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0" id="view"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>body {font-family: helvetica;margin: 0;}body * {-webkit-user-select: none;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;}a, button, input {-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)}button, input {-webkit-appearance: none;border-radius: 0;}input::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #000;}input:focus::-webkit-input-placeholder {color: #f00;}div {width: 20%;height: 100px;float: left;}div:nth-child(1) {background: #f00;}div:nth-child(2) {background: #ff0;}div:nth-child(3) {background: #f0f;}div:nth-child(4) {background: #0ff;}div:nth-child(5) {background: #0f0;}</style><script>; (function () {/*要将 375 => 750 就是 375 / 0.5 dpr = 2375 / ? = 750 这个 ? 就是 dpr 的倒数*/var meta = document.querySelector('meta[name="viewport"]')var scale = 1 / window.devicePixelRatioif(!meta){ // 没有默认设置 viewport 的 meta, 创建meta = document.createElement('meta')meta.name = 'viewport'meta.content = 'width=device-width, initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scaledocument.head.appendChild(meta)} else { // 有默认设置 viewport 的 meta, 修改meta.setAttribute('content', 'width=device-width, initial-scale=' + scale + ', user-scalable=no, maximum-scalable=' + scale + ', minimum-scalable=' + scale)}})()</script></head><body><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div></body></html>
虽然一个
CSS像素对应了一个物理像素, 但是对于不同尺寸的设备, 依然不是一个好的解决方案, 需要rem进行配合rem 适配
把所有的设备分成相同的若干份, 再计算元素宽度所占的份数
em:当意义为font-size的时候,1em代表父元素的字体大小, 当作为其他单位(宽度高度)的时候, 代表自身字体大小chrome下有最小字体限制12px, 字体小于12px无法再变小rem: r root, 根元素的font-size将html的font-size设置为20px,1rem = 20px元素适配的宽度 = 元素所占的列数 * 一列的宽度
- 元素在设计稿里面的宽度
- 列数 (随便给的) 100
- 一列的宽度 = 屏幕宽度(css像素) / 列数
元素实际占的列数 = 设计稿里面的宽度 / 一列的宽度
var colWidth = 0var col = 100 // 假设 100 列// 计算 iPhone5 iPhone6里面一列的宽度colWidth = 375 / col // 3.75px 6colWidth = 320 / col // 3.20px 5// 一个 div 占 10 列var width = 10 * 3.75 // 37.5px 6var width = 10 * 3.20 // 32.0px 5// 一个 div 50pxdivCol = 50 / 3.75 // 13.333divCol = 50 / 3.20 // 15.625// 所以按照此方案, 50px 的 div, 在不同的设备里, 会占到不同的份数
屏幕已经被分成了若干份
那么width: 10rem;(写入 CSS 文件的代码)
元素适配的宽度 =>元素所占的列数 * 一列的宽
元素适配的宽度 =>width 10 * 1rem
元素所占的列数 =>10
一列的宽 =>1rem1rem=html的font-size
根据栅格系统的原理, 将屏幕分成若干份, 不同的屏幕被分成相同的份数, 所以一份的宽度会不一样
但是份数是一样的, 所以整体比例是一样的; (function (fs) {var html = document.documentElementvar width = html.clientWidth // css 像素html.style.fontSize = width / fs + 'px'// 分成 16 列, iPhone5 为例 320px 得到 1rem = 20px})(16)
这种方式并没有一个基准点, 只是按照屏幕的增大,
html的font-size在变大
我们希望增加一个基准点, 这个点就是iPhone6, 屏幕仍然分成16份
如果屏幕尺寸为375, 那么就html字体也是16px
如果屏幕小于375那font-size也会小于16px
反之, 大于16px
如下代码:; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {const html = doc.documentElementconst refreshDom = () => {const clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 16 * clientWidth / 375 + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
但是这样做有一个弊端, 当计算出了
rem值之后, 还要除以dpr, 才是真正应该写的值
而且很多是除不尽的, 跟着一大串小数, 虽然有less sass去做这些事情, 但是还是觉得美中不足rem 最终方案
; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {const html = doc.documentElementconst refreshDom = () => {const clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
只有一行代码不同
那么html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'又是什么意思呢 ?
基于iPhone6的尺寸, 将整个页面适配成7.5 rem.
所以, 只要设计稿是750px, 在切图的时候, 量出来出多少px, 直接将这个值除以100, 加上rem就ok
这个时候, 屏幕被分割成多少份这个概念已经不怎么明朗了, 说是7.5份吗? 好像不太对劲. 那就索性不管了.
如果设计图是640px, 那么整屏的宽度就是6.4rem, 只需要将参数修改一下就可以了.
但是上面的代码是用到了ES6的语法,ios9不是原生支持的, 直接在上面跑会出现很大的问题, 就相当于适配没有做一样.
所以改写吧:; (function (doc, win, designWidth) {var html = doc.documentElementfunction refreshDom(){var clientWidth = html.clientWidthif(clientWidth >= designWidth){html.style.fontSize = "100px"}else{html.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / designWidth) + 'px'}}doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', refreshDom)})(document, window, 750)
这种方案总体来说没什么大问题了. 如果在设计稿上量出来长度为
50px, 那么实际写上去的长度应该是50 / 2 = 25px. 因为750的设计稿,375px就会占满屏幕. 或者是写.5rem.
字体也要用标注的字体大小除以2, 如标注28px, 实则应该写14px, 或者.28remhotcss
大佬写的号称移动端终极解决方案, 原理跟如上一样, 只是考虑的东西更多, 功能更强大.
去github上下载或者clone, 地址是:https://github.com/imochen/hotcss
需要做一点点小小的处理, 将第十四行左右的maxWidth = 540, 修改为设计稿的尺寸, 这个540是几年前写的, 相较现在来说有点小了.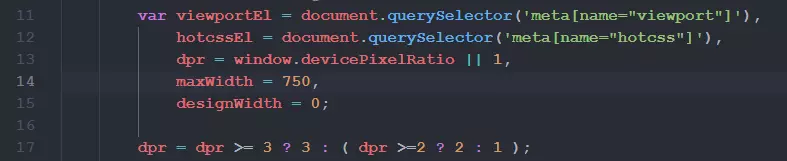
然后在页面中引入这个hotcss.js. 使用sass.
在写scss的地方引入px2rem的scss文件, 然后就可以在scss上愉快的写代码了.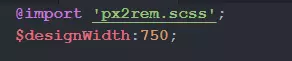
量出来多少(100px)就直接px2rem(100)vw, vh 适配
这俩单位就是为适配而生的
vw:viewport's width1vw=视口宽度的 1%vh:viewport's height1vh=视口高度的 1%vmax: 取vw,vh中的最大值vmin: 取vw,vh中的最小值
支持情况:ios >= 8; android >= 4.4
浏览器将任何屏幕都分成 100 份, 只要使用此单位, 就不会翻车两种方案
方案一: 通篇使用
vw@function vw($px){@return $px / 750 * 100vw;}
为方便切图, 写了一个如上函数
(scss), 以750为基准, 在任何屏幕上都可以看做是'750'
因为例如此函数传250进去, 会被转换成33.33333vw, 三个这样的大小将占满屏幕宽度, 在任何尺寸屏幕上的都是这样.
方案二: 通过vw设置根节点的字体大小, 页面尺寸依然使用rem
一个很暴力的方式, 还是以750为基准.375(css像素) / 750(设计稿宽度) * 100这是rem适配的原理所在
这个值最终是50, 这个值就是rem适配中,html的字体大小 .
那通过vw适配, 要达到rem同样的适配效果, 是不是应该让?vw = 50px?
所以50 / 3.75=13.333333333333334(15位小数)
然后:html {font-size: 13.333333333333334vw;}
然后,
rem适配需要的js代码可以删除了. 然后在任意尺寸的屏幕上也是可以横着走的.
整个屏幕7.5rem. 与rem适配的结果都是一样的
需要注意一些问题:css尺寸写rem, 比如1/4屏幕大小的div,width: 1.875rem;html的font-size会带来负面影响. 很多有文本属性(受font-size影响)的标签里面的内容会继承html的字体大小,13.33vw字体其实是非常大的, 所以不处理的话, 页面将会乱套.img的display属性默认是inline-block, 它会根据字体来对齐. 如果字体继承了html. 图片就会跑到一个匪夷所思的地方. 这个时候需要将img的包裹层的font-size做出相应的调整- 比较一劳永逸的方法, 在该设置的字体的地方设置字体大小, 然后最主要的是, 在
body里面, 将font-size设置为chrome最小字体12px, 阻止页面的元素去继承html的字体大小. 即现在html的字体大小只能影响rem这个单位.
这些问题逐一解决之后, 这也是一个很好的方案.

