适用场景
- 数据通常不会有Update操作,适用于Time Based索引数据(生命周期管理),同时数据量比较大的场景。
- 引入Warm节点,低配置大容量的机器存放老数据,以降低部署成本。
两类数据节点不同硬件配置
Hot节点—用于数据写入
索引不断有新文档写入,Indexing对CPU和IO都有很高的要求,所以需要使用高配置的机器,存储性能也要好,一般使用SSD
Warm节点—用于保存只读索引,比较旧的数据
索引不存在新数据写入,也不存在大量的数据查询,通常使用大容量HDD
配置步骤
使用ShardFiltering 分为以下3步
标记节点Tagging
- 配置索引到Hot Node
- 配置索引到Warm节点
标记节点
需要通过”node.attr”来标记一个节点
节点的attribute可以是任何的key/valuenode.attr.{attribute}:{value}
可以通过elasticsearch.yml或者-E命令指定bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=hotnode -E cluster.name=robin -E path.data=/data/hot -E node.attr.node_type=hot
将数据路由到指定节点
index.routing.allocation是一个索引级的dynamic settingindex.routing.allocation.include.{attribute}//表示索引可以分配在包含多个值中其中一个的节点上index.routing.allocation.require.{attribute}//表示索引要分配在包含索引指定值的节点上(通常一般设置一个值)index.routing.allocation.exclude.{attribute}//表示索引只能分配在不包含所有指定值的节点上。
数据迁移至冷节点
可以通过API在后期进行数据迁移
方法1:手动迁移
方法2:通过shell脚本迁移 ```PUT myindex/_settings{"index.routing.allocation.require.node_type":"warm"}
!/bin/bash hot数据(保留7天)迁移到cold
Time=$(date -d “1 week ago” +”%Y.%m.%d”) Hostname=$(hostname) arr=(“orderstpprdinf” “order_stppayinf”) for var in ${arr[@]} do curl -H “Content-Type: application/json” -XPUT http://$Hostname:9200/$var$Time/_settings?pretty -d’ { “settings”: { “index.routing.allocation.require.hotwarm_type”: “cold” # 指定数据存放到冷数据节点 } }’ done
方法3:通过curator迁移,action
Remember, leave a key empty if there is no value. None will be a string,
not a Python “NoneType”
#
Also remember that all examples have ‘disable_action’ set to True. If you
want to use this action as a template, be sure to set this to False after
copying it.
actions: 1: action: allocation # 这里执行操作类型为删除索引 description: >- Apply shard allocation routing to ‘require’ ‘tag=cold’ for hot/cold node setup for logstash- indices older than 3 days, based on index_creation date. options: key: hotwarm_type # es节点中定义的属性 value: cold # 要更新的值,变为冷节点 allocation_type: require # alloction的类型 disable_action: false filters:
- filtertype: patternkind: prefix # 匹配前缀为 “order_” 的索引,还可以支持正则匹配等,详见官方文档value: order_- filtertype: age # 匹配时间source: name # 根据索引name来匹配,还可以根据字段等,详见官方文档direction: oldertimestring: "%Y-%m" # 用于匹配和提取索引或快照名称中的时间戳unit: months # 定义months,还有days,weeks等,总时间为unit * unit_countunit_count: 3
<a name="Wi6aG"></a>### Rack AwarenessES的节点可能分布在不通的机架- 当一个机架断电,可能会同时丢失几个节点- 如果一个索引相同的主分片和副本分片同时在这个机架上,就有可能导致数据的丢失- 通过rack awareness的机制,就可以尽可能避免将同一个索引的主副分片同时分配在一个机架的节点上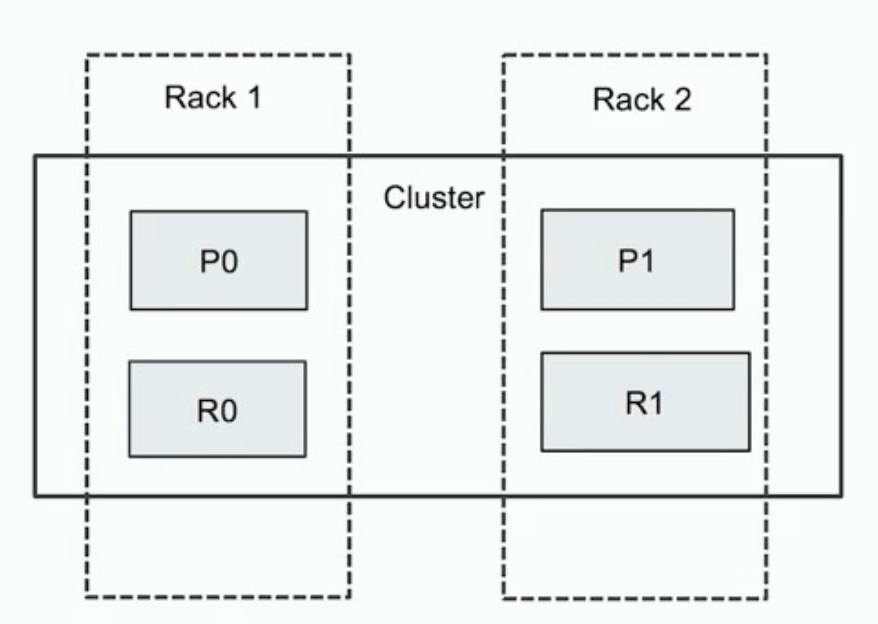<br />标记rack节点+配置集群
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node1 -E cluster.name=robin -E path.data=/data/node1 -E node.attr.rack_id=rack1
PUT _cluster/settings
{
“persistent”: {
“cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes”: “rack_id”
}
}
PUT test_index { “setting”:{ “number_of_shards”:2, “number_of_replicas”:1 } }
Forced Awareness
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node1 -E cluster.name=robin -E path.data=/data/node1 -E node.attr.rack_id=rack1
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node2 -E cluster.name=robin -E path.data=/data/node2 -E node.attr.rack_id=rack2
PUT _cluster/settings
{
“persistent”: {
“cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes”: “rack_id”,
“cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values”: “rack1,rack2”
}
}
```
Shard Filtering
- node.attr—标记节点
- index.routing.allocation—分配索引到节点 | 设置 | 分配索引到节点,节点的属性规则 | | —- | —- | | index.routing.allocation.include.{attr} | 至少包含一个值 | | index.routing.allocation.exclude.{attr} | 不能包含任何一个值 | | index.routing.allocation.require.{attr} | 所有值都需要包含 |

