权限管理
权限管理:包括身份认证和授权两部分。对于需要访问控制的资源,用户首先经过身份认证,认证成功后具有某一资源访问权限才能访问。
认证
身份认证,就是判断一个用户是否为合法的用户,最常用的认证方式通过核对用户输入的用户名和密码,看是否和系统存储的用户名和密码一致,以此来判断用户的身份是否合法。常见的认证方式有:
- 手机短信验证
- 三方授权认证
- 刷脸认证等
- 微信扫码登录等
- ……….
授权
控制谁能访问哪些资源。用户(主体)身份认证通过后,需要分配权限才能访问系统的资源,对于某些资源如果没有分配权限是不能访问的。可以理解为:主体(subject)对系统资源(resource)有什么权限(Permission)
资源(Resource)
如网站页面、目录、菜单、按钮等
权限(Permission)
一个主体能访问哪些资源
相关专业术语
subject
访问系统的用户,主体可以是用户,也可以是一台设备比如路由器、服务器、程序等,进行认证的都称为主体。
principle
身份信息,是主体(subject)证明自己身份的标识,标识必须有唯一性。如手机号、邮箱地址、指纹、密钥等。一个主体可以有多个身份信息,但必须有一个主身份(Primary Principal)
Credential
凭证信息,只有主体自己才知道的安全信息,如密码,私钥等。
权限管理流程
我们需要实现如下流程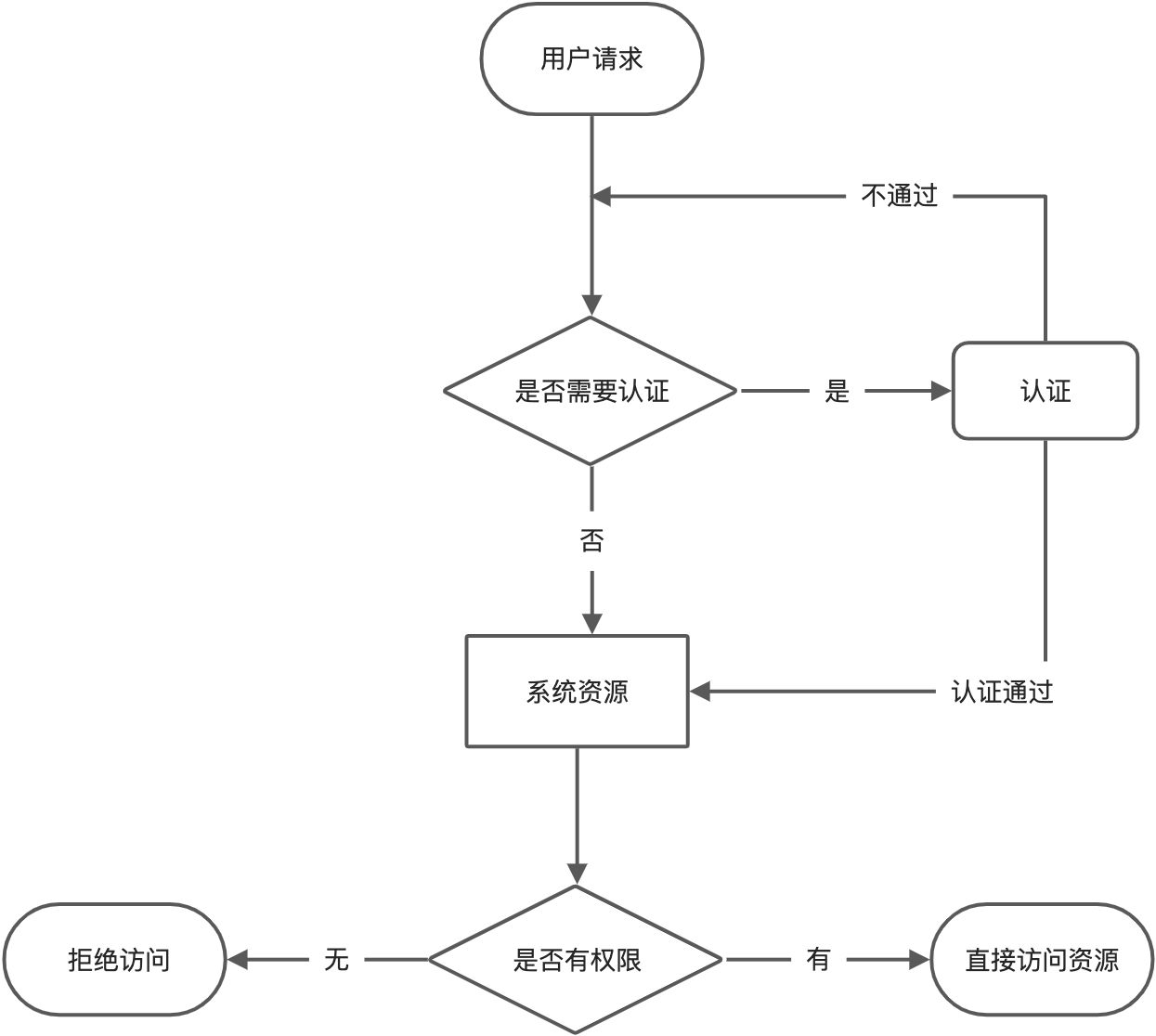
解决方案
怎么实现上图中的流程呢?行业常见的解决方案有2种:
- 使用Filter或SpringMVC的拦截器自己实现上面流程。
- 使用框架比如Shiro、Springsecurity等。
我们主要讲解Shiro的使用。
表的设计
在讲Shiro之前,我们先看怎么设计表结构。
常见的有2种方式
用户直接跟资源挂钩
设计成3张表:用户表(sys_usr)、资源表(sys_resource)、用户资源表(sys_user_resource)。
用户表(sys_usr)
| id | user_name | password |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 888888 |
| 3 | 王二 | 666666 |
资源表(sys_resource)
| id | resource_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 用户模块-查询 |
| 2 | 用户模块-删除 |
| 3 | 商品模块-查询 |
| 4 | 商品模块-删除 |
用户资源表(sys_user_resource)。
| user_id | resource_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
表示用户id为1的用户也就是张三有:用户模块-查询、用户模块-删除权限。用户id为2的用户也就是李四有:用户模块-查询、用户模块-删除、商品模块-查询权限。
这种设计有很大的弊端:假设新增一个用户叫赵四,赵四和李四的的权限是一样的。这就会在sys_user_resource表里面添加3条记录。如果用户很多,就会产生很多冗余的数据。
Role-based Access Control (以角色为基础的访问控制)
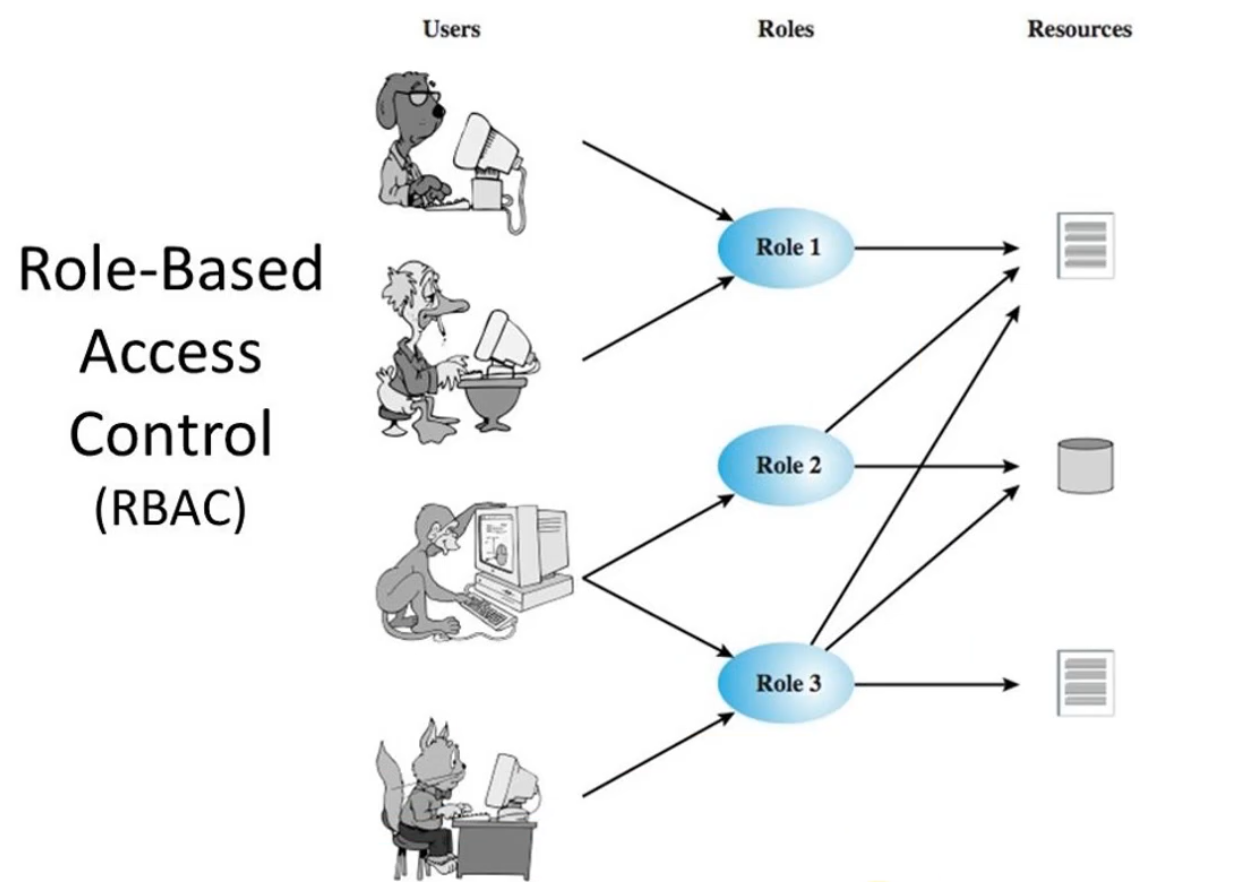
用户跟角色挂钩、角色跟资源挂钩,不同的用户有不同的角色,不同的角色有不同的访问资源的权限。
设计5张表:用户表(sys_usr)、角色表(sys_role)、资源表(sys_resource)
用户角色表(sys_user_role)、角色资源表(sys_role_resource)。
用户表(sys_usr)
| id | user_name | password |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 888888 |
| 3 | 王二 | 666666 |
资源表(sys_resource)
| id | resource_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 用户模块-查询 |
| 2 | 用户模块-删除 |
| 3 | 商品模块-查询 |
| 4 | 商品模块-删除 |
角色表(sys_role)
| id | role |
|---|---|
| 1 | 董事长 |
| 2 | 总经理 |
| 3 | 普通员工 |
角色资源表(sys_role_resource)
| role_id | resource_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
用户角色表(sys_user_role)
| user_id | role_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
由于角色的增加是有限的,新增角色表的同时,更新一下角色对应的资源表即可,当新增用户的时候,在用户角色表新增对应的角色即可,至于角色对应多少个资源权限,我们不需要关系。
推荐使用这种方式设计表结构。
Shiro
Shiro是Apache推出的安全管理框架,比SpringSecurity更加简单易用。
使用文档:https://shiro.apache.org/reference.html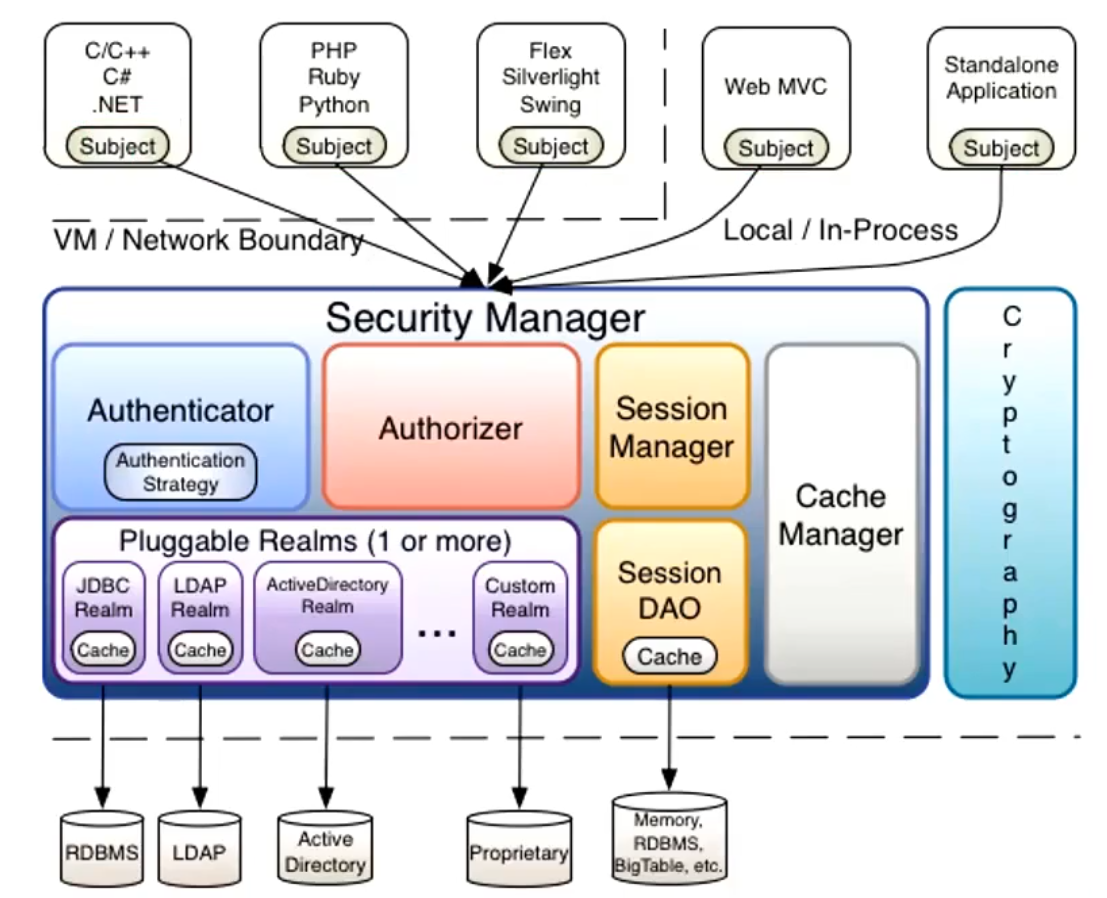
核心角色
- SecurityManager:安全管理器,是 Shiro 架构的核心,充当一种“伞形”对象,协调其内部各个组件
- Subject:主体,比如用户
- Realm:相当于数据源,可以获取主体(subject)的权限信息,主体的权限信息、用户名等信息存储在Realm
- Authenticator:认证器,从Realm里获取subject相关信息,对subject进行认证看一下是否为合法用户。
流程:当用户进行认证的时候,会找到SecurityManager,SecurityManager找到Authenticator,Authenticator去Realm里面读取用户数据,进行认证,后面有详细流程。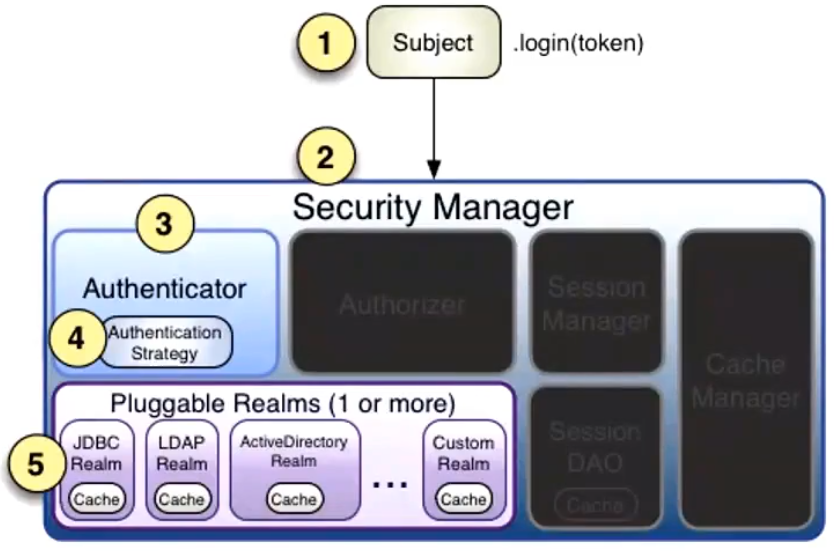
Authorizer:授权器,从Realm里面获取subject相关信息,对subject进行授权验证,看一下subject有没有对某一个资源有操作的权限。
流程:当用户进行授权的时候,会找到SecurityManager,SecurityManager找到Authorizer,Authorizer去Realm里面读取用户数据,进行授权。<br />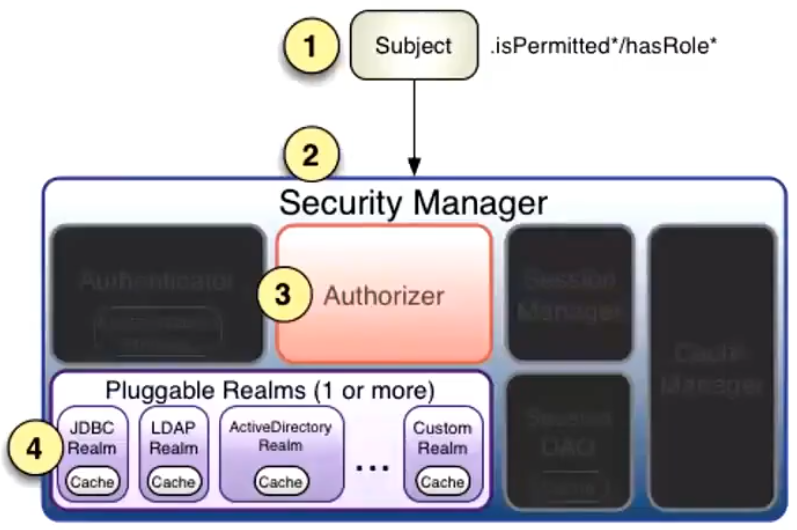
基本使用
/*创建安全管理器*/DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();/*设置Realm,从配置文件里面读取Realm,Realm有很多种,我们真实的项目肯定是要从数据库里面读取数据,来放到Realm上*/securityManager.setRealm(new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini"));SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();String userName = "lisi";String passWord = "123456";UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName,passWord);try {/*先传递一个简单的UsernamePasswordToken类型的AuthenticationToken*/subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated());//用户是否认证成功/*能来到这里说明上面认证没有问题,判断用户有没有某个权限*/Boolean isUserListPer = subject.isPermitted("user:list");/*判断用户是否有某个角色*/Boolean isAdminRole = subject.hasRole("admin");System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated());System.out.println(isAdminRole);subject.logout(); //退出登录,代表该用户没有认证,此时查用户的权限、角色就查不到了System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated());System.out.println(subject.hasRole("admin"));}catch (UnknownAccountException e){ //账号不存在System.out.println("账号不存在");}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){ //密码不正确System.out.println("密码不正确");}catch (AuthenticationException e){ //认证失败System.out.println("认证失败");}
Reaalm数据先从最简单的ini文件里面读取,shiro.ini文件数据如下
# =============================================================================# Tutorial INI configuration## Usernames/passwords are based on the classic Mel Brooks' film "Spaceballs" :)# =============================================================================# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------# Users and their (optional) assigned roles# username = password, role1, role2, ..., roleN# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------[users]root = 123456, adminlisi = 123456, guestzhangsan = 123456,guest# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------# Roles with assigned permissions# roleName = perm1, perm2, ..., permN# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------[roles]admin = *guest = user:list,user:update
上面是最基本的使用过程,以后用户的的数据,比如用户名、密码、角色、权限是要从数据库里面读取的。这时Realm的数据来源就不能像上面的ini文件了,我们需要从数据库里面读取。
Shiro提供给我们很多Realm的实现类,如下图所示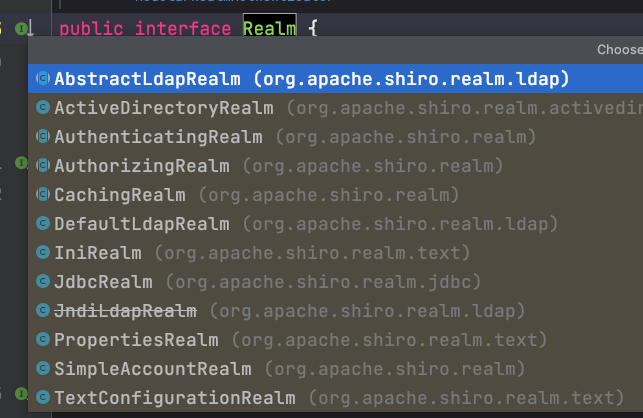
其中JdbcRealm就是从数据库里面读取数据创建Realm的,但遗憾的是该类型Realm要有固定的表结构,如下表名需要是users,用户的密码字段需要是password
public class JdbcRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {//TODO - complete JavaDoc/*--------------------------------------------| C O N S T A N T S |============================================*//*** The default query used to retrieve account data for the user.*/protected static final String DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY = "select password from users where username = ?";/*** The default query used to retrieve account data for the user when {@link #saltStyle} is COLUMN.*/protected static final String DEFAULT_SALTED_AUTHENTICATION_QUERY = "select password, password_salt from users where username = ?";/*** The default query used to retrieve the roles that apply to a user.*/protected static final String DEFAULT_USER_ROLES_QUERY = "select role_name from user_roles where username = ?";/*** The default query used to retrieve permissions that apply to a particular role.*/protected static final String DEFAULT_PERMISSIONS_QUERY = "select permission from roles_permissions where role_name = ?";private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JdbcRealm.class);//.....}
自定义Realm
为了自定义查询数据的方案,我们需要自定义Realm。
自定义类继承AuthorizingRealm 因为上面JdbcRealm也继承该类并且同时包含认证和授权。
import lombok.Data;import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {/*** 当用户subject需要进行权限、角色等判断时,就会调用该方法比如:subject.isPermitted("user:list")、subject.hasRole("admin");* 开发者需要在此方法里面根据用户名查询用户的权限、角色信息* @param principals* @return 返回用户的权限、角色信息*/@Overrideprotected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {// String userName = principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();//根据用户名到数据库里面查询用户的角色以及权限信息SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole("admin");simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:list");return simpleAuthorizationInfo;}/*** 当主体(subject)进行认证的时候调用 subject.login(token);* 开发者需要在这里根据用户标识(如用户名)到数据库查询用户的相关信息* @param token:为subject.login(token)传进来的token* @return 返回用户的具体信息如用户名、密码* @throws AuthenticationException*/@Overrideprotected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {String userName = String.valueOf(token.getPrincipal()); //获取用户名String password = String.valueOf(token.getPrincipal()); //获取密码//根据用户名到数据库查找用户相关信息,这 里做个假数据User user = new User();user.setUserName("lishi");user.setPasWord("123456");if (user == null) return null; //返回null内部会自己抛出UnknownAccountException异常// if (user == null){// throw new UnknownAccountException();// }// if (!password.equals(user.getPasWord())){ //这个我们不需要自己判断,内部会自行判断// throw new IncorrectCredentialsException();// }//返回用户具体信息,传入数据库中查询到的用户名和密码,Realm内部会根据传来的token和数据库传来的用户名、密码进行对比return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUserName(),user.getPasWord(),getName());}}@Dataclass User{private String userName;private String pasWord;}
外界使用
/*创建安全管理器*/DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();/*自定义Realm*/securityManager.setRealm(new CustomRealm());SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();String userName = "lisi";String passWord = "123456";UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName,passWord);try {/*先传递一个简单的UsernamePasswordToken类型的AuthenticationToken*/subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);//到这里说明认证已经通过System.out.println("subject 是否有user:list权限 " + subject.isPermitted("user:list"));System.out.println("subject 是否有admin角色 " + subject.hasRole("admin"));}catch (UnknownAccountException e){ //账号不存在System.out.println("账号不存在");}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){ //密码不正确System.out.println("密码不正确");}catch (AuthenticationException e){ //认证失败System.out.println("认证失败");}
认证流程
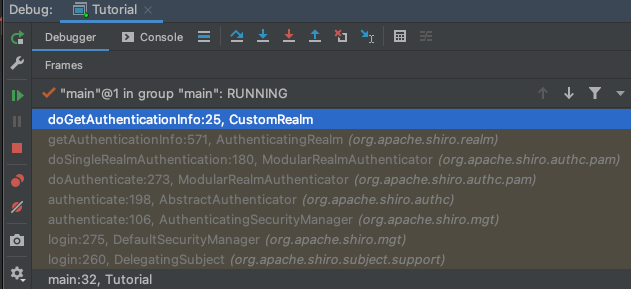
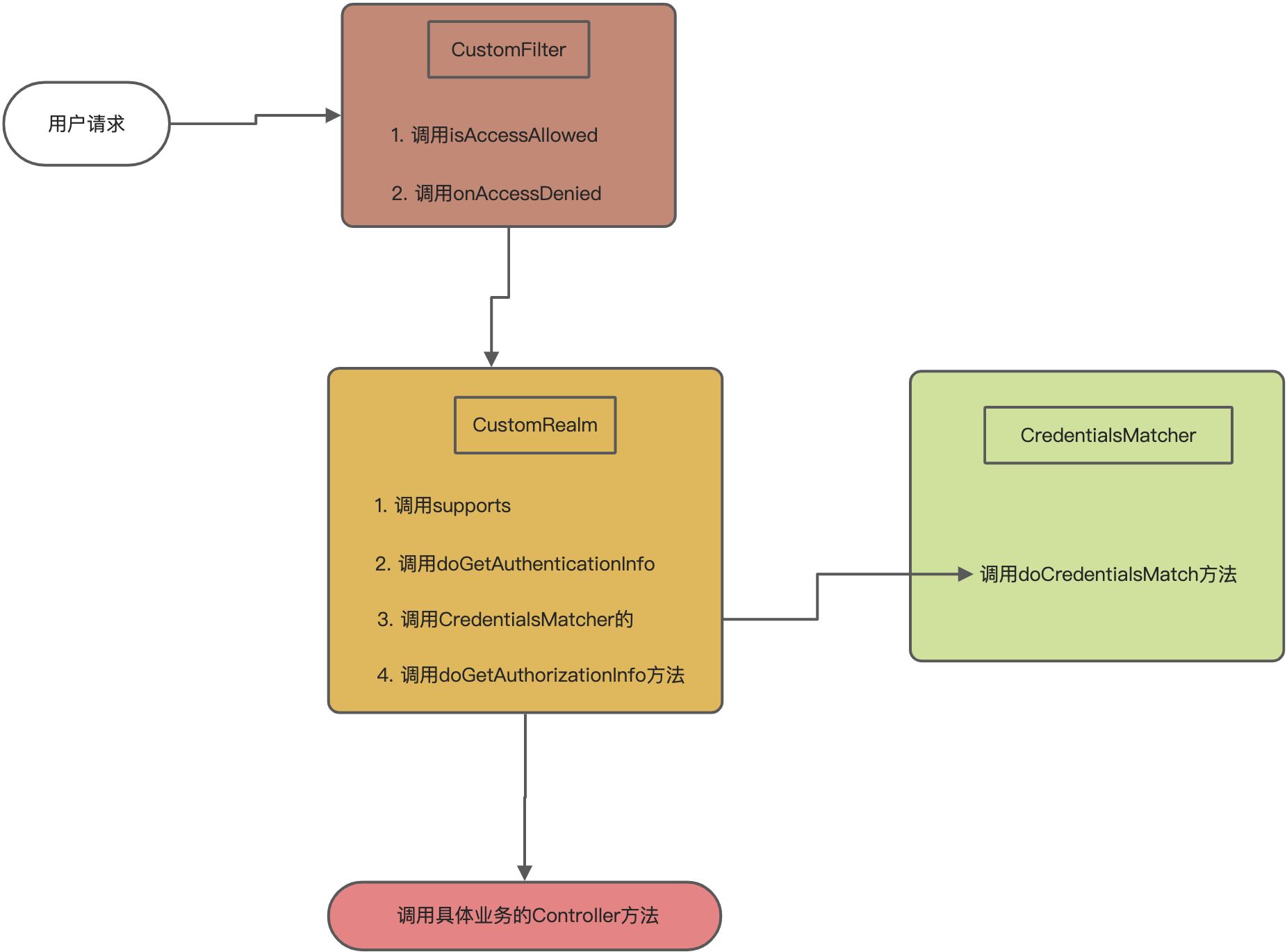
当用户调用subject.login()后,SecurityManager会找到认证器Authenticator,Authenticator会找到我们自定义的CustomRealm,就会调用CustomRealm里面的如下方法
/*** 当主体(subject)进行认证的时候调用 subject.login(token);* 开发者需要在这里根据用户标识(如用户名)到数据库查询用户的相关信息* @param token:为subject.login(token)传进来的token* @return 返回用户的具体信息* @throws AuthenticationException*/@Overrideprotected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {}
调用完上面的方法后会返回AuthenticationInfo。如果AuthenticationInfo没有值说明用户名没有就会报UnknownAccountException异常,如果有值就会调用Realm里面的assertCredentialsMatch方法
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);if (info == null) {//otherwise not cached, perform the lookup:info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);if (token != null && info != null) {cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);}} else {log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);}if (info != null) { //注意如果有值就会来到这里assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);} else {log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);}return info;}
�assertCredentialsMatch的方法内部是这样的
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();if (cm != null) {if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);}} else {throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");}}
也就是会调用CredentialsMatcher里面的doCredentialsMatch方法来判断密码是否正确,下面接口实现类就是专门负责匹配密码是否正确的。
public interface CredentialsMatcher {/*** Returns {@code true} if the provided token credentials match the stored account credentials,* {@code false} otherwise.** @param token the {@code AuthenticationToken} submitted during the authentication attempt* @param info the {@code AuthenticationInfo} stored in the system.* @return {@code true} if the provided token credentials match the stored account credentials,* {@code false} otherwise.*/boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info);//token为用户subject.login(token)传过来的,info为doGetAuthenticationInfo方法中我们返回的}
�不同的实现类有不同的密码匹配方式。为了满足项目中的需求我们通常也自定义CredentialsMatcher类自己实现密码匹配规则。
�
授权流程
当用户调用subject.isPermitted()或者 subject.hasRole()等权限、角色等方法时,SecurityManager会找到授权器Authorizer,Authorizer找到我们自定义的CustomRealm,调用CustomRealm的如下方法
/*** 当用户subject需要进行权限、角色等判断时,就会调用该方法比如:subject.isPermitted("user:list")、subject.hasRole("admin");* 开发者需要在此方法里面根据用户名查询用户的权限、角色信息* @param principals* @return 返回用户的权限、角色信息*/@Overrideprotected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {// String userName = principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();//根据用户名到数据库里面查询用户的角色以及权限信息SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole("admin");simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:list");return simpleAuthorizationInfo;}
根据返回的AuthorizationInfo信息判断权限、角色是否正确。
SpringBoot集成Shiro
场景:用户通过用户名密码登录后,服务端会返回客户端一个token,后续的请求中携带token放在请求头中,服务端验证token是否为合法的token。
依赖配置
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId><artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId><version>1.7.0</version></dependency>
日志这里使用logback
<dependency><groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId><artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId><version>1.2.3</version></dependency>
运行直接报如下错误
No bean of type 'org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm' found.
自定义CustomRealm
新建自定义CustomRealm类继承AuthorizingRealm
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {public CustomRealm() {super(new CustomMatcher()); //校验密码时,使用我们自定义的CredentialsMatcher去验证密码是否正确}@Overridepublic boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {return token instanceof Token;}/*** 授权*/@Overrideprotected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {// 拿到tokenString token = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();//根据token或者用户ID到数据库查找用户的角色、权限信息,也可以提前把用户信息缓存起来// 添加角色info.addRole("xxx");// 添加权限info.addStringPermission("resource.getPermission()");return info;}/*** 认证:基于token的方案,能来到这里说明是合法的用户,已经登录过了并且token是有效的,直接保证该方法能认证通过即可*/@Overrideprotected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {Token tk = (Token) token;return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(tk.getPrincipal(),tk.getCredentials(),getName());}}
Shiro配置文件
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.servlet.Filter;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;@Configurationpublic class ShiroCfg {@Beanpublic Realm realm() {return new CustomRealm();}/*** 在这里设置管理器、并且告诉Shiro如何进行拦截、拦截哪些URL、每个URL需要经过哪些Filter进行处理* @param realm* @return*/@Beanpublic ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(Realm realm) {ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();// 设置管理器,在web项目里面直接这样配置即可DefaultWebSecurityManager mgr = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(realm);bean.setSecurityManager(mgr);// 添加我们自定义的FilterMap<String, Filter> filters = new HashMap<>();//添加自定义Filter并给Filter起个别名filters.put("customFilterxxx", new CustomFilter());//添加了一个Filter,Filter的名称为customFilterxxx。类似于anon对应的Filter为org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.AnonymousFilter//设置自定义Filterbean.setFilters(filters);// 配置拦截的路径对应的FilterMap<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();//使用LinkedHashMap有顺序性,先加入的优先级最高//登录接口不需要拦截filterMap.put("/xx/login", "anon");//使用匿名Filter进行过滤,不需要登录也能访问//swagger接口文档不需要拦截filterMap.put("/swagger*/**", "anon");filterMap.put("/v2/api-docs/**", "anon");//测试接不需要拦截filterMap.put("/test/**", "anon");// 如果Filter里面发生异常就会来到我们自定义的ErrorController,这里面的URL也不应该被拦截filterMap.put("/error/filter", "anon");//所有其它的路径使用我们自定义的Filter拦截filterMap.put("/**", "customFilterxxx");bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);return bean;}/*** 解决:发现只要方法上面加@RequiresPermissions注解后,很多接口都报404问题,加下面代码解决此问题*/@Beanpublic DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator proxyCreator() {DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator proxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator();proxyCreator.setUsePrefix(true);return proxyCreator;}}
Shiro提供了如下Filter供我们使用,Filter Name可以理解Filter的别名。
自定义CredentialsMatcher
�自定义CredentialsMatcher来自己校验密码规则
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.CredentialsMatcher;public class CustomMatcher implements CredentialsMatcher {/*** @return true代表校验通过,直接返回true即可,因为我们是基于token的没有密码的概念*/@Overridepublic boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {return true;}}
自定义token
public class Token implements AuthenticationToken {private final String token;public Token(String accessToken) {this.token = accessToken;}@Overridepublic Object getPrincipal() {return token;}@Overridepublic Object getCredentials() {return token;}}
自定义Filter
import com.lff.dr.common.util.Strings;import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;import org.apache.shiro.web.filter.AccessControlFilter;import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;/*** 自定义Filter验证用户是否合法*/public class CustomFilter extends AccessControlFilter {public static final String TOKEN_HEADER = "Token";/**可以在这个方法里面初步判断是否允许请求通过* @return true会进入下一个链式调用(过滤器、拦截器、控制器),false就进入下面的onAccessDenied方法,交给shiro处理*/@Overrideprotected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse resp, Object o) throws Exception {return false;}/*** 上面的isAccessAllowed方法返回false,就会来到这里* @return true会进入下一个链式调用(过滤器、拦截器、控制器),false就不会进入*/@Overrideprotected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse resp) throws Exception {// 获得请求HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;// 获得tokenString token = request.getHeader("Token");// token为空if (Strings.isEmpty(token)) {throw new RuntimeException("token为空");}// 查找用户if (user == null) {throw new RuntimeException("token过期等");}// 鉴权,进入Realm,触发Realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo和doGetAuthorizationInfo方法,到数据库加载用户的角色、权限信息SecurityUtils.getSubject().login(new Token(token));// getSubject(req, resp).login(new Token(token));return true;}}
如果Filter里面有异常,比如CustomFilter里面抛出异常,Tomcat内部就会报500错误给客户端,我们的异常拦截器就会拦截不到这样的异常处理。下面是异常处理的示例代码,@RestControllerAdvice这样的注解只能拦截到Controller出现的异常。
@RestControllerAdvice@Slf4jpublic class CommonExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)public JsonVO handleThrowable(Throwable t) {}}
�为了能够拦截到Filter里面的异常,我们单独搞一个ErrorFilter,所有的请求先来到这个ErrorFilter,ErrorFilter处理完之后再把请求传递到其它Filter(如:我们的CustomFilter)。如果其中某一个Filter发生异常,我们再转发给Controller(单独搞一个ErrorController),在ErrorController里面抛出异常,这样上面的异常处理拦截器就能拦截到异常,把异常信息返回到客户端了。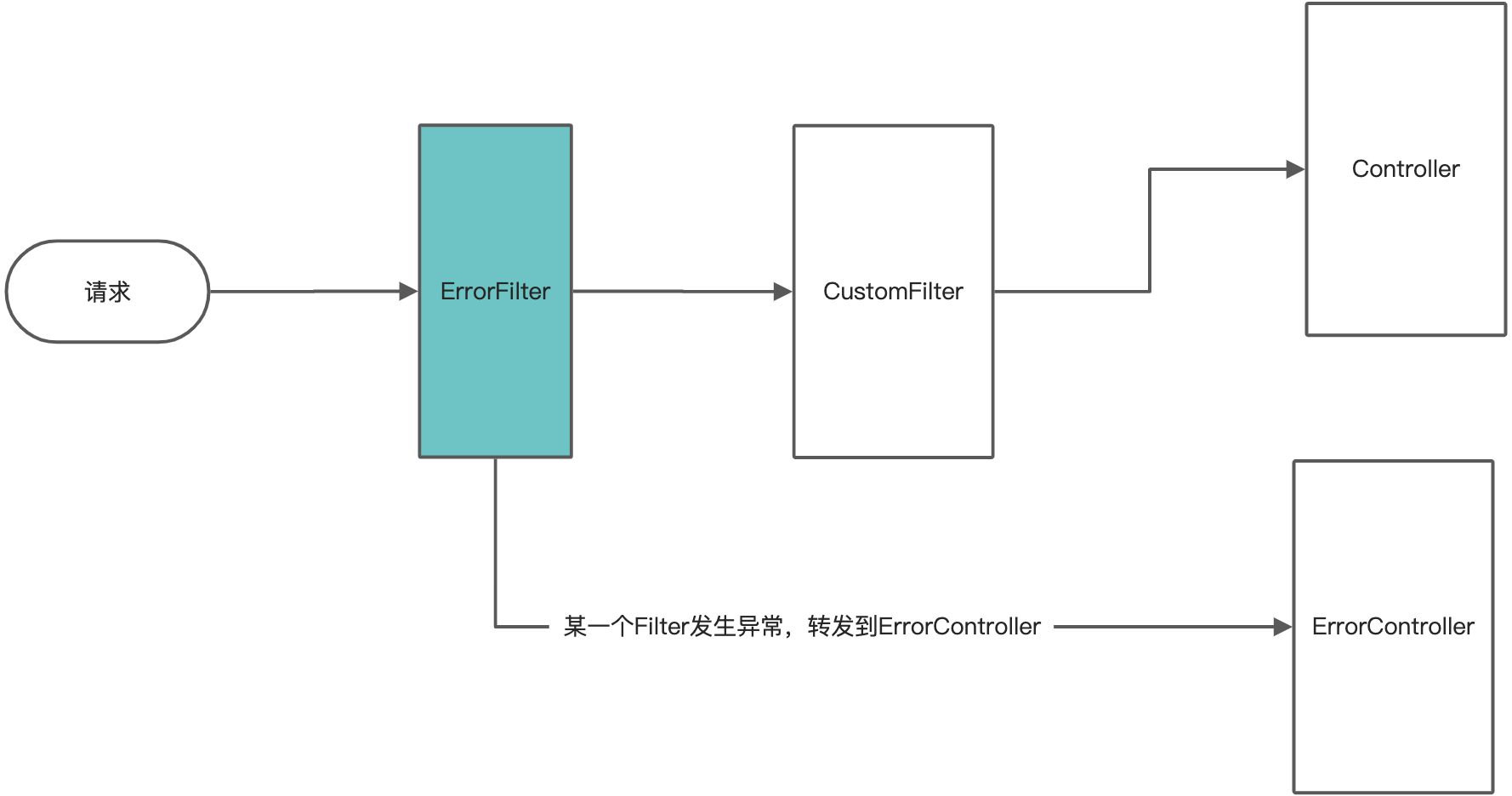
ErrorFilter示例代码
import javax.servlet.*;import java.io.IOException;public class ErrorFilter implements Filter {@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response,FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {try {chain.doFilter(request, response);} catch (Throwable e) {request.setAttribute("error_filter", e);request.getRequestDispatcher("/error/filter").forward(request, response);}}}
配置ErrorFilter为第一个处理请求的Filter
@Configurationpublic class WebCfg implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Beanpublic FilterRegistrationBean<Filter> filterRegistrationBean() {FilterRegistrationBean<Filter> bean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();bean.setFilter(new ErrorFilter());bean.addUrlPatterns("/*");// 最高权限bean.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);return bean;}}
处理错误ErrorFilterController代码如下
@RestControllerpublic class ErrorFilterController {@RequestMapping("/error/filter")public void handle(HttpServletRequest request) throws Throwable {throw (Throwable) request.getAttribute("error_filter");}}
外界直接用注解的方式使用即可
@RestController@RequestMapping("/sysUsers")@Api(tags = "系统用户")public class SysUserController {@GetMapping@ApiOperation("分页查询")@RequiresPermissions("user:list") //表示该方法必须有user:list权限@RequiresRoles("admin") //表示该方法必须有admin角色public ListJsonVo<SysUserVo> list(SysUserListReqVo reqVo) {}@GetMapping@ApiOperation("分页查询")@RequiresPermissions(value = {"user:list","user:update"},logical = Logical.AND) //多个权限使用方式public ListJsonVo<SysUserVo> list1(SysUserListReqVo reqVo) {return JsonVos.ok(service.list(reqVo));}}
整体执行流程
推荐学习视频
这套视频感觉比尚硅谷和黑马的教程讲的要清晰一些。
点击查看【bilibili】

