官方文档,官方文档已经写的非常完备,这里对官网内容进行讲解,演练,演练的样例数据使用《MySQL必知必会》上面的。
使用方式
Maven依赖
<dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.49</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis</artifactId><version>3.5.5</version></dependency>
添加MyBatis核心配置,一般命名为mybatis-config.xml,按照官方的命名方式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!-- 注意 XML 头部的声明,它用来验证 XML 文档的正确性。--><!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><!-- 环境 --><environments default="development"><!-- 开发环境(调试阶段) --><environment id="development"><!-- 采用JDBC的事务管理方法 --><transactionManager type="jdbc" /><!-- POOLED代表采取连接池的方式管理连接 --><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customer_test"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="root"/></dataSource></environment><!-- 生产环境(发布阶段) --><environment id="production"><!-- 采用JDBC的事务管理方法 --><transactionManager type="JDBC" /><!-- POOLED代表采取连接池的方式管理连接 --><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customer_test"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="root"/></dataSource></environment></environments></configuration>
集成druid连接池
有很多方式集成druid,其中一个比较简单的方式只需三步
第一步:添加依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.1.22</version></dependency>
第二步:新建一个类继承UnpooledDataSourceFactory
public class DruidDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {public DruidDataSourceFactory() {this.dataSource = new DruidDataSource();}}
第三步:在MyBatis核心配置文件中修改环境配置
<environment id="development"><!-- 采用JDBC的事务管理方法 --><transactionManager type="jdbc" /><!-- com.lff.thirdPart.DruidDataSourceFactory为继承UnpooledDataSourceFactory的类 --><dataSource type="com.lff.thirdPart.DruidDataSourceFactory"><property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customer_test"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="root"/><property name="initialSize" value="5"/><property name="maxActive" value="10"/><property name="maxWait" value="5000"/></dataSource></environment>
映射文件
在MyBatis里面怎么写SQL呢?比如增、删、改、查。还有在查询数据库的时候,需要把查询的结果转为Java bean对象的,应该怎么转呢?这时就需要映射文件了。
映射文件也是一个XML文件,MyBatis也规定了其格式应该怎么写
我们通常在项目的resources目录下创建一个mappers文件夹,在里面写映射文件。比如要查询所有的顾客数据mappers/customers.xml
官方文档有详细的解释<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><select id="allCustomers" resultType="map">select * from customers</select></mapper>
namespace为命名空间,因为命名空间下面可能会有很多个语句,起到隔离的目的。
select的查询标签有个id,可以随便起一个,也称为语句名称。
resultType为返回数据的类型,这里返回map类型。
MyBatis怎么知道映射文件的存在呢?需要在MyBatis核心配置文件中加一下
<!-- 映射文件 --><mappers><mapper resource="mappers/customers.xml" /></mappers>
使用方式,官方文档对如何使用有超详细的介绍
import com.lff.Customers;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.Reader;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;public class customersTest {@Testpublic void getCustomerList() throws IOException {try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) { //加载MyBatis核心配置文件SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); //使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建工厂对象SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(reader);SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); //使用工厂对象生产SqlSession对象//customers.allCustomers为命名空间和select标签的idList<Map> customersList = session.selectList("customers.allCustomers");//使用SqlSession对象做增、删、改、查System.out.println(customersList);}}}
查询结果
[{cust_country=USA, cust_email=sales@villagetoys.com, cust_address=200 Maple Lane, cust_name=Village Toys, cust_state=MI, cust_contact=John Smith, cust_id=1000000001, cust_city=Detroit, cust_zip=44444},{cust_country=USA, cust_address=333 South Lake Drive, cust_name=Kids Place, cust_state=OH, cust_contact=Michelle Green, cust_id=1000000002, cust_city=Columbus, cust_zip=43333},{cust_country=USA, cust_email=jjones@fun4all.com, cust_address=1 Sunny Place, cust_name=Fun4All, cust_state=IN, cust_contact=Jim Jones, cust_id=1000000003, cust_city=Muncie, cust_zip=42222},{cust_country=USA, cust_email=dstephens@fun4all.com, cust_address=829 Riverside Drive, cust_name=Fun4All, cust_state=AZ, cust_contact=Denise L. Stephens, cust_id=1000000004, cust_city=Phoenix, cust_zip=88888},{cust_country=USA, cust_address=4545 53rd Street, cust_name=The Toy Store, cust_state=IL, cust_contact=Kim Howard, cust_id=1000000005, cust_city=Chicago, cust_zip=54545}]
现在结果已经查出来了,怎么把查询的结果映射到JavaBean 呢?
注意我们的表结构是这样的?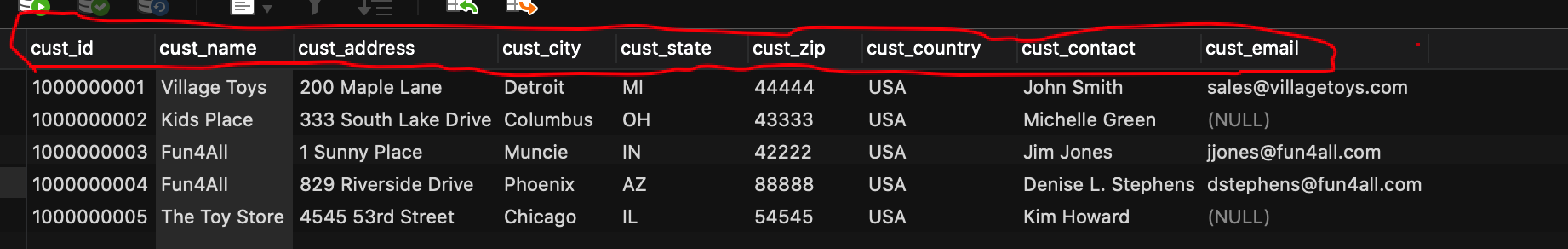
字段都是采用下划线标识的,这是数据库设计表的规范,但是我们bean对象里面的属性都是采用驼峰命名的,怎么才能对应其来呢?
方法一
MyBatis已经为我们处理了,只要在MyBatis的核心配置文件中显示的配置一下就好了
<settings><!-- 数据库表字段:my_first_name 映射到JavaBean 属性:myFirstName --><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/></settings>
是否开启驼峰命名自动映射,即从经典数据库列名 my_first_name 映射到经典 Java 属性名 myFirstName。默认为false
更新我们的映射文件,resultType改为我们的JavaBean对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><select id="allCustomers" resultType="com.lff.Customers">select * from customers</select></mapper>
外界使用
import com.lff.Customers;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.Reader;import java.util.List;public class customersTest {@Testpublic void getCustomerList() throws IOException {try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) { //加载MyBatis核心配置文件SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); //使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建工厂对象SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(reader);SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); //使用工厂对象生产SqlSession对象List<Customers> customersList = session.selectList("customers.allCustomers");//使用SqlSession对象做增、删、改、查for (Customers customers : customersList) {System.out.println(customers.getCustName());}}}}
打印结果
Village ToysKids PlaceFun4AllFun4AllThe Toy Store
方法二
如果不想在核心配置文件里面配置,我们也可以在映射文件里面配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><!-- resultMap的值是下面resultMap标签的id--><select id="allCustomers" resultMap="customers">SELECT * FROM customers</select><!-- type为我们要转化的Bean类--><resultMap id="customers" type="com.lff.Customers"><!-- property为Bean类中的属性名,column为数据库表里面对应的字段--><result property="custId" column="cust_id" /><!-- 如果是主键也可以使用id标签来指定--><!-- <id property="custId" column="cust_id"/>--><result property="custName" column="cust_name" /><result property="custAddress" column="cust_address" /><result property="custCity" column="cust_city" /><result property="custState" column="cust_state" /><result property="custZip" column="cust_zip" /><result property="custCountry" column="cust_country" /><result property="custContact" column="cust_contact" /><result property="custEmail" column="cust_email" /></resultMap></mapper>
外界使用的问题
在测试代码中,我们是这样写的
public class customersTest {@Testpublic void getCustomerList() throws IOException {try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) { //加载MyBatis核心配置文件SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); //使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建工厂对象SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(reader);SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); //使用工厂对象生产SqlSession对象//customers.allCustomers为mapper的namespace命名空间和select标签的id来执行语句List<Customers> customersList = session.selectList("customers.allCustomers");//使用SqlSession对象做增、删、改、查for (Customers customers : customersList) {System.out.println(customers.getCustName());}}}}
官方文档明确强调SqlSessionFactoryBuilder被创建完应该被丢弃、SqlSessionFactory的实例应该一直保存在内存里面、SqlSession每个线程都应该有它自己的 SqlSession 实例。我们根据官方文档上来操作,官方文档就是最佳实践。我们搞个工具类来直接获取SqlSession对象就可以了,拿到SqlSession对象来执行具体的sql语句。
package utils;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import java.io.Reader;public class MyBatisUtils {private static SqlSessionFactory factory;static {try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) {// 创建一个工厂构建器SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();// 创建一个工厂factory = builder.build(reader);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static SqlSession openSession() {return factory.openSession();}}
为了更加清晰的看到执行SQL的过程,我们需要查看打印信息。可以在Setting中开启打印日志功能。
<settings><!-- 数据库表字段:my_first_name 映射到JavaBean 属性:myFirstName --><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/><!-- 打印日志信息 --><setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" /></settings>
你也可以直接使用第三方的日志功能,只要在Maven中依赖即可,MyBatis会自动识别到。
<dependency><groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId><artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId><version>1.2.3</version></dependency>
参数传递
传递一个参数的情况
mapper文件,使用#{}的方式接受参数
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><select id="getOneCustomer" resultType="com.lff.Customers">SELECT * FROM customers where cust_id = #{id}</select></mapper>
{id}为参数占位符,名称任意。
外界使用
Customers customer = session.selectOne("customers.getOneCustomer","1000000001");
customers.getOneCustomer为mapper命名空间.select标签id
1000000001为传递的参数
传递多个参数
mapper文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><select id="getOneCustomer" resultType="com.lff.Customers">SELECT * FROM customers where cust_name = #{custName} AND cust_city like #{custCity}</select></mapper>
参数的含义
#{name}、#{city}要与外界传入的参数名称相同。
外界使用
public class customersTest {@Testpublic void getCustomerList() throws IOException {SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<>();params.put("custName","Fun4All");params.put("custCity","%ie%");List<Customers> customers = session.selectList("customers.getOneCustomer",params);for (Customers customer : customers) {System.out.println(customer.getCustCity());}}}
Map里面的name、city 要与映射文件里面的接受参数相同。
当然外界使用的时候也可以传入JavaBean对象。
public class customersTest {@Testpublic void getCustomerList() throws IOException {SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();Customers params = new Customers();params.setCustName("Fun4All");params.setCustCity("%ie%");List<Customers> customers = session.selectList("customers.getOneCustomer",params);for (Customers customer : customers) {System.out.println(customer.getCustCity());}}}
${}、#{}
{}为预编译传值,可以防止SQL注入。点击查看官方解释
${}直接文本替换。
多表查询
在《SQL必知必会》的表结构中,有一个产品表和供应商表,每一个产品都有一个供应商。
产品表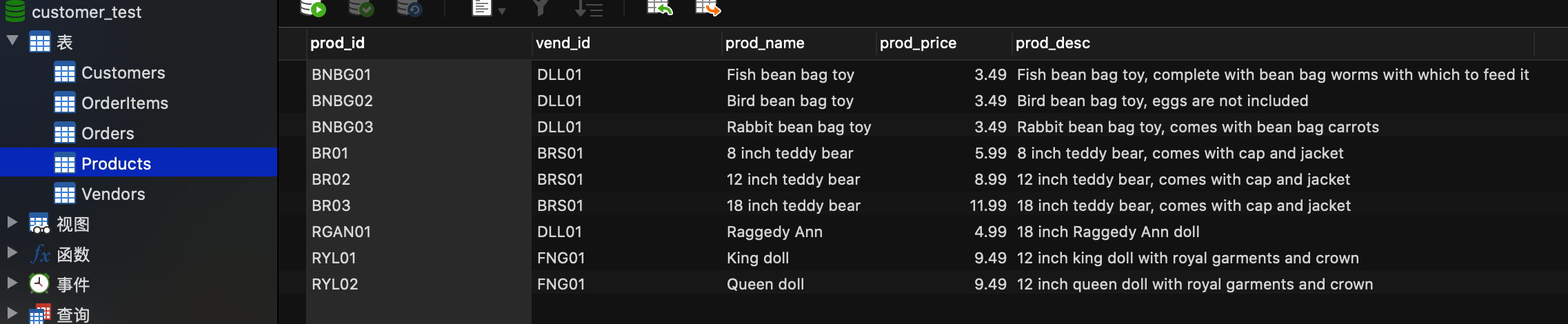
供应商表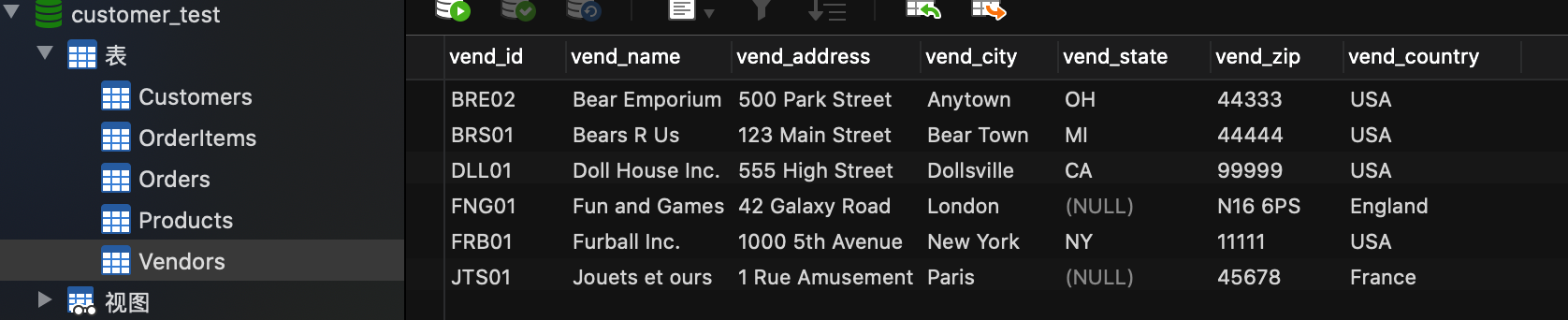
对应的JavaBean
package com.lff;public class Products {private String prodId;private String vendId;private String prodName;private String prodPrice;private String prodDesc;private Vendors vendors;public String getProdId() {return prodId;}public void setProdId(String prodId) {this.prodId = prodId;}public String getVendId() {return vendId;}public void setVendId(String vendId) {this.vendId = vendId;}public String getProdName() {return prodName;}public void setProdName(String prodName) {this.prodName = prodName;}public String getProdPrice() {return prodPrice;}public void setProdPrice(String prodPrice) {this.prodPrice = prodPrice;}public String getProdDesc() {return prodDesc;}public void setProdDesc(String prodDesc) {this.prodDesc = prodDesc;}public Vendors getVendors() {return vendors;}public void setVendors(Vendors vendors) {this.vendors = vendors;}}
供应商Bean
package com.lff;public class Vendors {private String vendId;private String vendName;private String vendAddress;private String vendCity;private String vendState;private String vendZip;private String vendCountry;public String getVendId() {return vendId;}public void setVendId(String vendId) {this.vendId = vendId;}public String getVendName() {return vendName;}public void setVendName(String vendName) {this.vendName = vendName;}public String getVendAddress() {return vendAddress;}public void setVendAddress(String vendAddress) {this.vendAddress = vendAddress;}public String getVendCity() {return vendCity;}public void setVendCity(String vendCity) {this.vendCity = vendCity;}public String getVendState() {return vendState;}public void setVendState(String vendState) {this.vendState = vendState;}public String getVendZip() {return vendZip;}public void setVendZip(String vendZip) {this.vendZip = vendZip;}public String getVendCountry() {return vendCountry;}public void setVendCountry(String vendCountry) {this.vendCountry = vendCountry;}}
我们根据以上条件查询一下产品表的数据。我们期望Products的vendors属性也能够有值。
mapper文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="productNameSpace"><select id="getProducts" resultType="com.lff.Products">SELECT Products.* ,Vendors.* FROM Products JOIN Vendors ON Vendors.vend_id=Products.vend_id;</select></mapper>
由于是新增的mapper,所以要在核心配置文件里面加上
<!-- 映射文件 --><mappers><mapper resource="mappers/customers.xml" /><mapper resource="mappers/products.xml" /></mappers>
外界使用
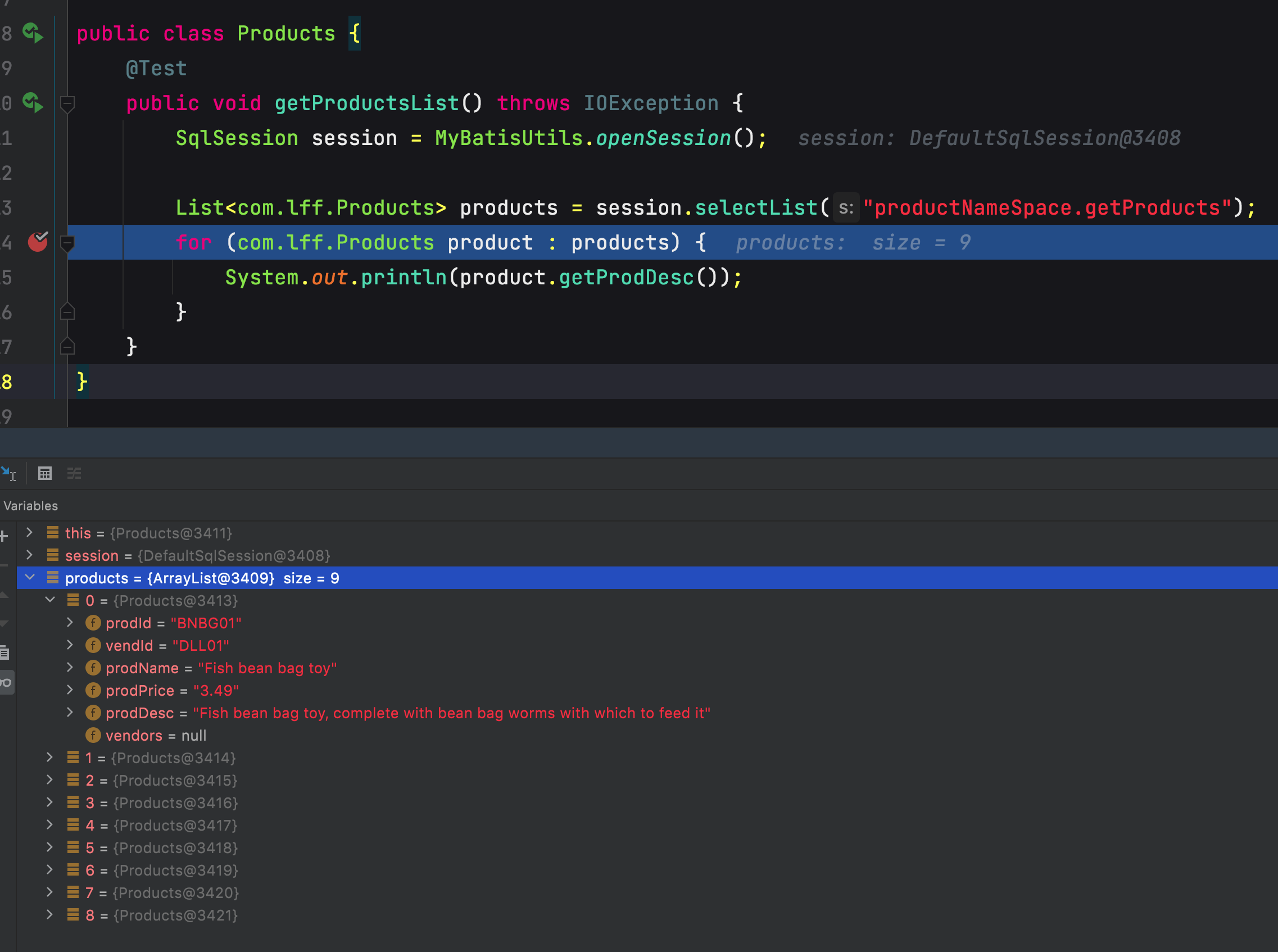
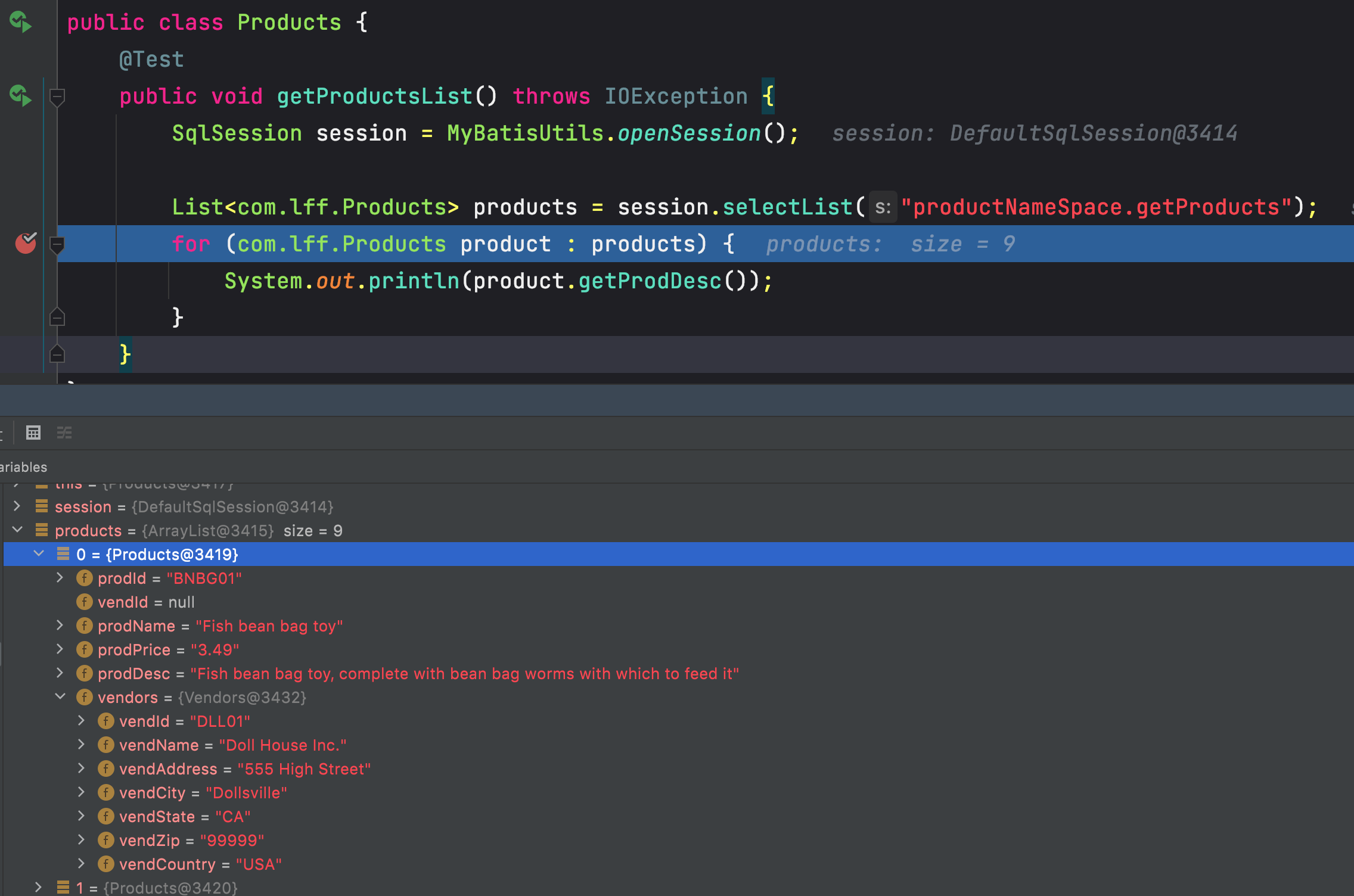
public class Products {@Testpublic void getProductsList() throws IOException {SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();List<com.lff.Products> products = session.selectList("productNameSpace.getProducts");for (com.lff.Products product : products) {System.out.println(product.getProdDesc());}}}
解决方案:
方法一:使用resultMap显示的声明
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="productNameSpace"><select id="getProducts" resultMap="product_vendors">SELECT Products.* ,Vendors.* FROM Products JOIN Vendors ON Vendors.vend_id=Products.vend_id;</select><!-- type为想要映射的JavaBean--><resultMap id="product_vendors" type="com.lff.Products"><!-- Products中有个属性叫vendors,vendors中有个属性叫vendId--><result property="vendors.vendId" column="vend_id" /><result property="vendors.vendName" column="vend_name" /><result property="vendors.vendAddress" column="vend_address" /><result property="vendors.vendCity" column="vend_city" /><result property="vendors.vendState" column="vend_state" /><result property="vendors.vendZip" column="vend_zip" /><result property="vendors.vendCountry" column="vend_country" /></resultMap></mapper>
也可以这样写更加清晰
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="productNameSpace"><select id="getProducts" resultMap="product_vendors">SELECT Products.* ,Vendors.* FROM Products JOIN Vendors ON Vendors.vend_id=Products.vend_id;</select><!-- type为想要映射的JavaBean--><resultMap id="product_vendors" type="com.lff.Products"><id property="prodId" column="prod_id"></id><result property="vendId" column="vend_id"></result><result property="prodName" column="prod_name"></result><result property="prodPrice" column="prod_price"></result><result property="prodDesc" column="prod_desc"></result><!-- 关联的属性vendors为Products的一个属性,类型为com.lff.Vendors。javaType表示关联的具体类型--><association property="vendors" javaType="com.lff.Vendors"><id property="vendId" column="vend_id" /><result property="vendName" column="vend_name" /><result property="vendAddress" column="vend_address" /><result property="vendCity" column="vend_city" /><result property="vendState" column="vend_state" /><result property="vendZip" column="vend_zip" /><result property="vendCountry" column="vend_country" /></association></resultMap></mapper>
只要看到column就是数据库查询出来的字段名称,property是指JavaBean中的属性名称。
外界使用
public class Products {@Testpublic void getProductsList() throws IOException {SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();List<com.lff.Products> products = session.selectList("productNameSpace.getProducts");for (com.lff.Products product : products) {System.out.println(product.getProdDesc());}}}
第二种方式
<select id="getProducts" resultType="com.lff.Products">SELECT Products.* ,Vendors.vend_id `vendors.vendId`,Vendors.vend_name `vendors.vendName`,Vendors.vend_address `vendors.vendAddress`,Vendors.vend_city `vendors.vendCity`,Vendors.vend_state `vendors.vendState`,Vendors.vend_zip `vendors.vendZip`,Vendors.vend_country `vendors.vendCountry`FROM Products JOIN Vendors ON Vendors.vend_id=Products.vend_id;</select>
在查询的时候直接将结果取别名,别名和JavaBean中的属性名相同。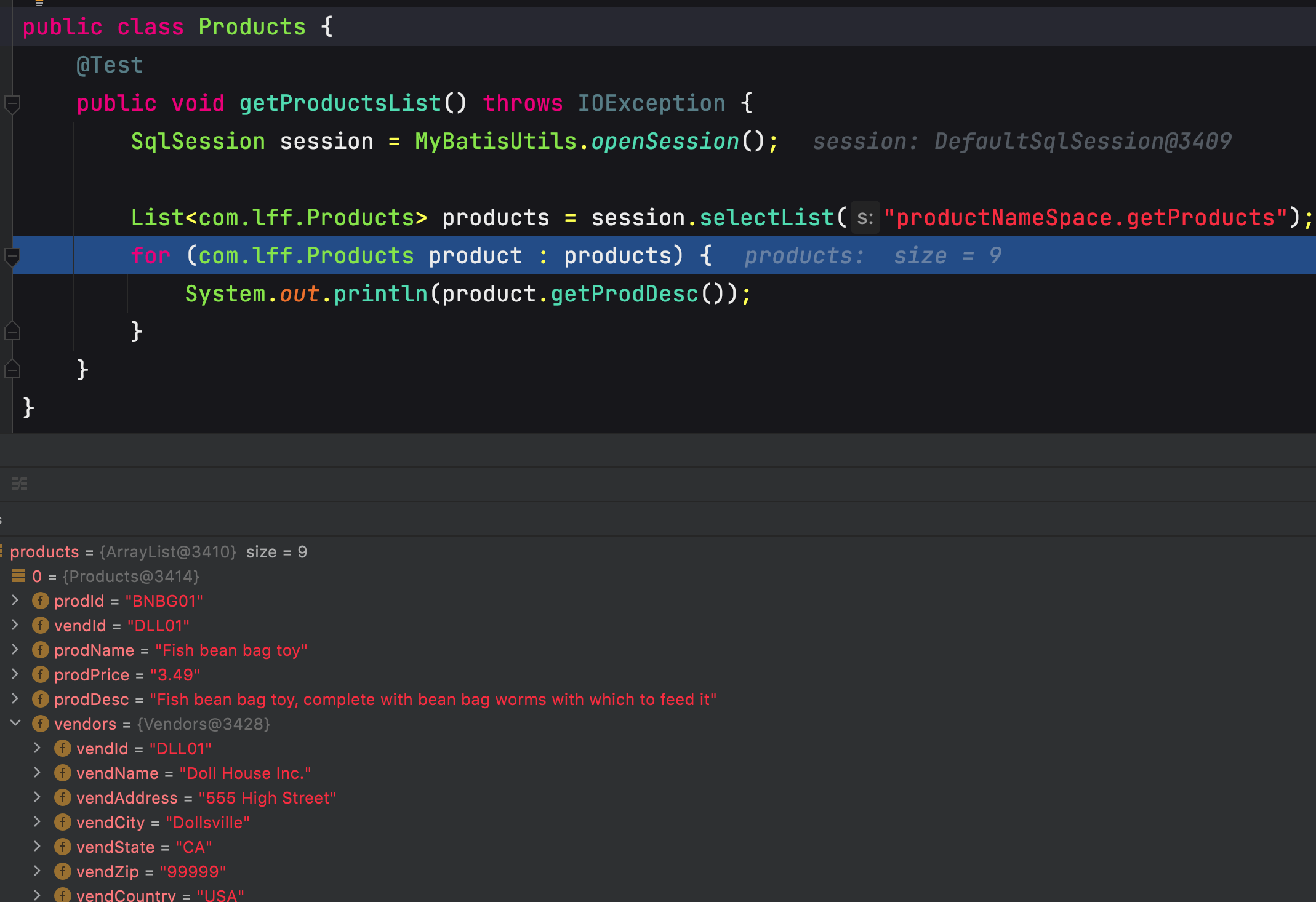
这种方式简单直接。
插入操作
mapper文件
<insert id="insertCustomer" parameterType="com.lff.Customers">INSERT INTO Customers(cust_id,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_contact,cust_email)VALUES(#{custId},#{custName},#{custAddress},#{custCity},#{custState},#{custZip},#{custContact},#{custEmail})</insert>
外界使用
public class customersTest {@Testpublic void insertCustomer(){SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();//传入JavaBeanCustomers customers = new Customers();customers.setCustId(1002);customers.setCustName("lff");customers.setCustCity("beijing");customers.setCustContact("Beijing");customers.setCustEmail("190000000@163.com");customers.setCustZip("10001");customers.setCustState("CN");customers.setCustAddress("Beijing");session.insert("customers.insertCustomer",customers);//对数据插入、更新、删除一定要提交事务。session.commit();}}
session对象的openSession方法的默认参数是false,默认不提交事务。
所以一定要手动的提交事务,否则MyBatis默认会回滚。
批量插入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="List">INSERT INTO Customers(cust_id,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_contact,cust_email)VALUES<foreach collection="list" item="cust" separator=",">(#{cust.custId},#{cust.custName},#{cust.custAddress},#{cust.custCity},#{cust.custState},#{cust.custZip},#{cust.custContact},#{cust.custEmail})</foreach></insert></mapper>
foreach中的collection=”list”,如果外界传入的参数是List 就写collection的值就是list,如果外界传入的是数组,collection的值写array
外界使用
public void batchInsertCustomer(){SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();List<Customers> customersList = new ArrayList<>();Customers customers = new Customers();customers.setCustId(1011);customers.setCustName("lff");customers.setCustCity("beijing");Customers customers1 = new Customers();customers1.setCustId(1012);customers1.setCustName("Mr Li");customers1.setCustCity("beijing");Customers customers2 = new Customers();customers2.setCustId(1013);customers2.setCustName("Mr Li");customers2.setCustCity("beijing");customersList.add(customers);customersList.add(customers1);customersList.add(customers2);session.insert("customers.batchInsert",customersList);session.commit();}
设置新插入的主键到参数中
更新
mapper文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="customers"><insert id="insertCustomer" parameterType="com.lff.Customers">INSERT INTO Customers(cust_id,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_contact,cust_email)VALUES(#{custId},#{custName},#{custAddress},#{custCity},#{custState},#{custZip},#{custContact},#{custEmail})</insert><update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.lff.Customers">UPDATE Customers SET cust_name=#{custName}, cust_address=#{custAddress} WHERE cust_id=#{custId}</update></mapper>
外界使用
public class customersTest {@Testpublic void insertCustomer(){SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();//传入JavaBeanCustomers customers = new Customers();customers.setCustId(1005);customers.setCustName("Mr Li");customers.setCustCity("beijing");customers.setCustContact("Beijing");customers.setCustEmail("190000000@163.com");customers.setCustZip("10001");customers.setCustState("CN");customers.setCustAddress("TianJing");session.insert("customers.updateCustomer",customers);//对数据插入、更新、删除一定要提交事务。session.commit();}}
删除
mapper文件
<delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="int">DELETE FROM Customers WHERE cust_id = #{custId}</delete>
外界使用
public void deleteCustomer(){SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();session.delete("customers.deleteCustomer",100);session.commit();}
批量删除
<delete id="batchDelete" parameterType="List">DELETE FROM Customers WHERE cust_id IN<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="item">#{item}</foreach></delete>
外界使用
public void batchDelete(){SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();List<Integer> params = new ArrayList<>();params.add(1008);params.add(1009);params.add(1010);session.delete("customers.batchDelete",params);session.commit();}