事件监听机制


当一个事件源产生事件时,它通过事件发布器ApplicationEventPublisher发布事件,然后事件广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster会去事件注册表ApplicationContext中找到事件监听器 ApplicationListnener,并且逐个执行监听器的onApplicationEvent方法,从而完成事件监听器的逻辑。
Spring框架早已提供了完善的事件监听机制,在Spring框架中实现事件监听的流程如下:
1) 自定义事件,继承org. springframework . context.ApplicationEvent抽象类
2) 定义事件监听器,实现org. springframework . context.ApplicationListener接口
3) 在Spring容器中发布事件
提供了四种实现监听的方式:
1) 自定义类实现ApplicationListenser接口,并且在入口主函数中使用ConfigurableApplicationContext容器装载监听
ListenerApplication.java
package com.duing;import com.duing.listener.CustomListener1;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class ListenerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取启动后的容器,加载自定义监听器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(ListenerApplication.class, args);context.addApplicationListener(new CustomListener1());}}
CustomEvent.java
package com.duing.event;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;public class CustomEvent extends ApplicationEvent {public CustomEvent(Object source) {super(source);}public void printMessage(String msg){System.out.println("自定义事件"+msg);}}
CustomListener1.java
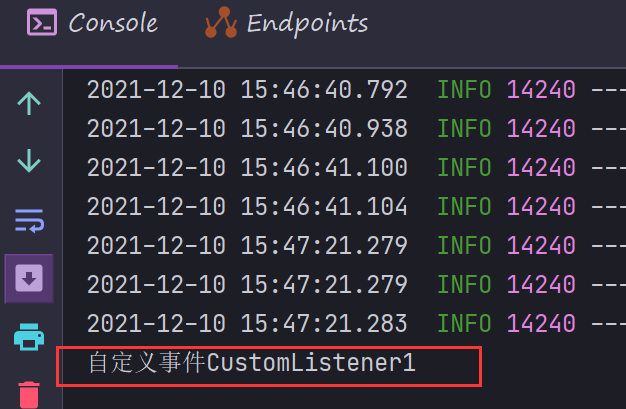
package com.duing.listener;import com.duing.event.CustomEvent;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;public class CustomListener1 implements ApplicationListener<CustomEvent> {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(CustomEvent customEvent) {customEvent.printMessage("CustomListener1");}}
EventController.java
package com.duing.controller;import com.duing.event.CustomEvent;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class EventController {@Autowiredprivate ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;@RequestMapping("/event")public String event(){publisher.publishEvent(new CustomEvent(this));return "Success";}}
2) 自定义类实现ApplicationListenser接口,在接口上注解@Component
CustomListener2.java
package com.duing.listener;import com.duing.event.CustomEvent;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 方式二通过@Component声明这是一个需要加载的监听器* 不需要在入口类加载*/@Componentpublic class CustomListener2 implements ApplicationListener<CustomEvent> {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(CustomEvent customEvent) {customEvent.printMessage("CustomListener2");}}
3) 自定义类不需要实现接口,在方法上标明@EventListener注解 (主要通过EventListenerMethodProcessor扫描出所有带有此注解的方法,然后动态构造事件监听器,并将监听器托 管到Spring应用上文中)
CustomListener3.java
package com.duing.listener;import com.duing.event.CustomEvent;import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 方式三:* 不需要实现ApplicationListener接口* 但是要先声明当前类是@Component组件,需要被加载* 通过在方法上添加@EventListener注解,声明这是一个监听组件,监听的事件是方法的参数*/@Componentpublic class CustomListener3 {@EventListenerpublic void eventListener(CustomEvent customEvent){customEvent.printMessage("CustomListener3");}}
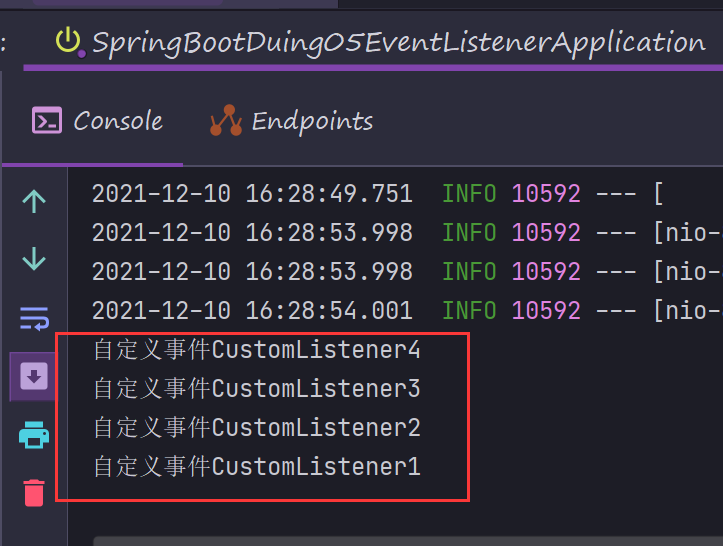
4)在application.properties/yml中配置context.listener. classes (DelegatingApplicationListener,该类的作用是从application.properties/yml中读取配置context.listener. classes,并将事件广播给这些配置的监听器)
CustomListener4.java
package com.duing.listener;import com.duing.event.CustomEvent;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;public class CustomListener4 implements ApplicationListener<CustomEvent> {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(CustomEvent customEvent) {customEvent.printMessage("CustomListener4");}}
application.yml
server:port: 8090context:listener:classes: com.duing.listener.CustomListener4

1)run方法的执行过程
//加载一系列的配置 准备一系列的环境 打印一系列的日志 开始创建容器启动监听
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//创建应用上下文/容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//加载配置
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取监听器 从META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取的
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
//传递命令行参数,创建应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建容器
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
//计时结束 启动完成
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//广播started方法对应的事件
listeners.started(context);
//回调runner的方法 分别是ApplicationRunner CommandLineRunner
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
...
try {
//启动监听器
listeners.running(context);
}
...
//返回容器
return context;
}
2)准备容器的工作
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置环境参数
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//应用初始化器
applyInitializers(context);
//广播容器准备方法对应的事件
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
//增加特殊的单例的bean
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
//加载sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//容器真正的加载逻辑 比如扫描注解 创建bean 关联bean的关系等等
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//广播 容器加载对应的事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
3)以LoggingApplicationListener为例
public class LoggingApplicationListener implements GenericApplicationListener {
//public interface GenericApplicationListener extends //ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>, Ordered {
//这是一个 springboot定义的监听器
//这是它订阅的事件类型 这是容器启动过程中会广播的不同事件
private static final Class<?>[] EVENT_TYPES = { ApplicationStartingEvent.class,
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class, ApplicationPreparedEvent.class, ContextClosedEvent.class,
ApplicationFailedEvent.class };
//接收事件时执行的方法
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) {
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent
&& ((ContextClosedEvent) event).getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
onContextClosedEvent();
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent();
}
}

