Chunk就是将大文件分成块,一个块对应着一个Http请求,然后会对每个Http进行编号,然后在接收方重组。
正常的Http请求都是客户端请求,服务器返回然后就结束了。而Chunk不会,是会一直等待服务器多次发送数据,发送数据完成后才会结束。
怎么判断一个Http是不是Chunk?
通过Header中的Transfer-Encoding = Chunked
怎么判断是否传输结束?
每个Http中的body中分为 length 和 chunked data 。length 就是传输的数据长度,chunked data就是实际的传输数据。二者通过换行符分隔。当收到length = 0的http时,就说明传输完成了。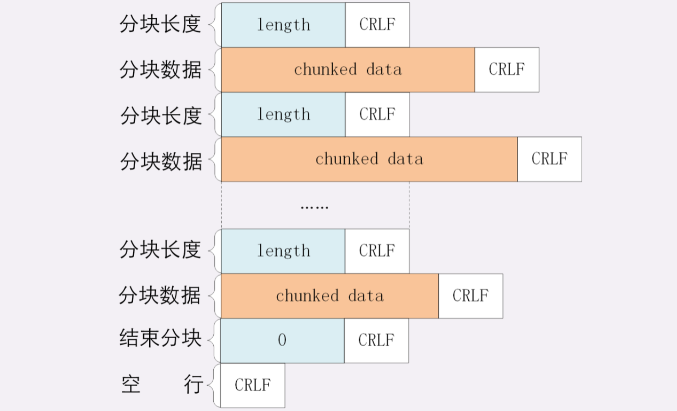
demo
package mainimport ("fmt""io""log""net/http""time")func httpServer() {http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {flusher, ok := w.(http.Flusher)if !ok {panic("expected http.ResponseWriter to be an http.Flusher")}for i := 1; i <= 10; i++ {w.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("rsp-%d", i)))flusher.Flush() // Trigger "chunked" encoding and send a chunk...time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)}})log.Print("Listening on localhost:8080")log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))}func httpClien() {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080")if err != nil {// handle error}fmt.Println(resp.Header)defer resp.Body.Close()var buf = make([]byte, 40960)for {n, err := resp.Body.Read(buf)fmt.Println(n, err)if n != 0 || err != io.EOF { // simplifiedfmt.Println(string(buf[:n]))}time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)}}func main() {go httpServer()go httpClien()time.Sleep(100 * time.Second)}

