- 函数
- Tracer">type Tracer
- Span">type Span
- SpanContext">type SpanContext
- SpanReference">type SpanReference
- StartSpanOption">type StartSpanOption
- StartSpanOptions">type StartSpanOptions
- Tag">type Tag
- Tags">type Tags
- HTTPHeadersCarrier">type HTTPHeadersCarrier
- TextMapCarrier">type TextMapCarrier
- BuiltinFormat">type BuiltinFormat
- TextMapReader">type TextMapReader
- TextMapWriter">type TextMapWriter
- 使用
- 简单例子:
文档:https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go
函数
func GlobalTracer() Tracer
- GlobalTracer返回全局单例“Tracer”实现
- 在“SetGlobalTracer()”被调用之前,“GlobalTracer()”是一个noop实现,它会删除传递给它的所有数据
func SetGlobalTracer(tracer Tracer)
- SetGlobalTracer设置了[单例]opentracing,由GlobalTracer()返回的跟踪程序
- 在调用下面的StartSpan全局函数之前,应该在main()中尽可能早地调用SetGlobalTracer
- 在调用“SetGlobalTracer”之前,任何通过“StartSpan”(etc)全局变量启动的span都是noops
func ContextWithSpan(ctx context.Context, span Span) context.Context
- 返回一个新的context,它持有对span的引用
- 如果span为nil,则返回一个没有活动span的新上下文
func StartSpan(operationName string, opts …StartSpanOption) Span
- 创建一个span
func SpanFromContext(ctx context.Context) Span
SpanFromContext返回先前与’ ctx ‘关联的’ Span ‘,如果找不到,则返回’ nil
func StartSpanFromContext(ctx context.Context, operationName string, opts …StartSpanOption) (Span, context.Context)StartSpanFromContext启动并返回一个带有‘operationName’的Span,使用‘ctx’中找到的任何Span作为ChildOfRef
如果找不到父节点,StartSpanFromContext创建一个根(无父节点)Span。
SomeFunction(ctx context.Context, ...) {sp, ctx := opentracing.StartSpanFromContext(ctx, "SomeFunction")defer sp.Finish()...}
type Tracer
Tracer是一个用于创建Span和传播SpanContext的简单、简洁的接口
type Tracer interface {// Create, start, and return a new Span with the given `operationName` and// incorporate the given StartSpanOption `opts`. (Note that `opts` borrows// from the "functional options" pattern, per// http://dave.cheney.net/2014/10/17/functional-options-for-friendly-apis)//// A Span with no SpanReference options (e.g., opentracing.ChildOf() or// opentracing.FollowsFrom()) becomes the root of its own trace.//// Examples://// var tracer opentracing.Tracer = ...//// // The root-span case:// sp := tracer.StartSpan("GetFeed")//// // The vanilla child span case:// sp := tracer.StartSpan(// "GetFeed",// opentracing.ChildOf(parentSpan.Context()))//// // All the bells and whistles:// sp := tracer.StartSpan(// "GetFeed",// opentracing.ChildOf(parentSpan.Context()),// opentracing.Tag{"user_agent", loggedReq.UserAgent},// opentracing.StartTime(loggedReq.Timestamp),// )//StartSpan(operationName string, opts ...StartSpanOption) Span// Inject() takes the `sm` SpanContext instance and injects it for// propagation within `carrier`. The actual type of `carrier` depends on// the value of `format`.//// OpenTracing defines a common set of `format` values (see BuiltinFormat),// and each has an expected carrier type.//// Other packages may declare their own `format` values, much like the keys// used by `context.Context` (see https://godoc.org/context#WithValue).//// Example usage (sans error handling)://// carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)// err := tracer.Inject(// span.Context(),// opentracing.HTTPHeaders,// carrier)//// NOTE: All opentracing.Tracer implementations MUST support all// BuiltinFormats.//// Implementations may return opentracing.ErrUnsupportedFormat if `format`// is not supported by (or not known by) the implementation.//// Implementations may return opentracing.ErrInvalidCarrier or any other// implementation-specific error if the format is supported but injection// fails anyway.//// See Tracer.Extract().Inject(sm SpanContext, format interface{}, carrier interface{}) error// Extract() returns a SpanContext instance given `format` and `carrier`.//// OpenTracing defines a common set of `format` values (see BuiltinFormat),// and each has an expected carrier type.//// Other packages may declare their own `format` values, much like the keys// used by `context.Context` (see// https://godoc.org/golang.org/x/net/context#WithValue).//// Example usage (with StartSpan):////// carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)// clientContext, err := tracer.Extract(opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)//// // ... assuming the ultimate goal here is to resume the trace with a// // server-side Span:// var serverSpan opentracing.Span// if err == nil {// span = tracer.StartSpan(// rpcMethodName, ext.RPCServerOption(clientContext))// } else {// span = tracer.StartSpan(rpcMethodName)// }////// NOTE: All opentracing.Tracer implementations MUST support all// BuiltinFormats.//// Return values:// - A successful Extract returns a SpanContext instance and a nil error// - If there was simply no SpanContext to extract in `carrier`, Extract()// returns (nil, opentracing.ErrSpanContextNotFound)// - If `format` is unsupported or unrecognized, Extract() returns (nil,// opentracing.ErrUnsupportedFormat)// - If there are more fundamental problems with the `carrier` object,// Extract() may return opentracing.ErrInvalidCarrier,// opentracing.ErrSpanContextCorrupted, or implementation-specific// errors.//// See Tracer.Inject().Extract(format interface{}, carrier interface{}) (SpanContext, error)}
type Span
type Span interface {// 设置结束时间戳并结束Span状态,每个span必须调用Finish()// 类似于Finish(),但是具有显式的控制时间戳和日志数据FinishWithOptions(opts FinishOptions)// Context() yields the SpanContext for this Span. Note that the return// value of Context() is still valid after a call to Span.Finish(), as is// a call to Span.Context() after a call to Span.Finish().Context() SpanContext// 设置或更改操作名称SetOperationName(operationName string) Span// 为span新增tag,值类型限制为numeric types, strings, or bools.SetTag(key string, value interface{}) Span// LogFields is an efficient and type-checked way to record key:value// , though the programming interface is a little// more verbose than LogKV(). Here's an example:s//// span.LogFields(// log.String("event", "soft error"),// log.String("type", "cache timeout"),// log.Int("waited.millis", 1500))//LogFields(fields ...log.Field)// LogKV is a concise, readable way to record key:value logging data about// a Span, though unfortunately this also makes it less efficient and less// type-safe than LogFields(). Here's an example://// span.LogKV(// "event", "soft error",// "type", "cache timeout",// "waited.millis", 1500)//// For LogKV (as opposed to LogFields()), the parameters must appear as// key-value pairs, like//// span.LogKV(key1, val1, key2, val2, key3, val3, ...)//// The keys must all be strings. The values may be strings, numeric types,// bools, Go error instances, or arbitrary structs.//LogKV(alternatingKeyValues ...interface{})// SetBaggageItem在此Span及其SpanContext上设置一个键值对//它也会传播到这个Span的后代//// SetBaggageItem() enables powerful functionality given a full-stack// opentracing integration (e.g., arbitrary application data from a mobile// app can make it, transparently, all the way into the depths of a storage// system), and with it some powerful costs: use this feature with care.//// IMPORTANT NOTE #1: SetBaggageItem() will only propagate baggage items to// *future* causal descendants of the associated Span.//// IMPORTANT NOTE #2: Use this thoughtfully and with care. Every key and// value is copied into every local *and remote* child of the associated// Span, and that can add up to a lot of network and cpu overhead.//// Returns a reference to this Span for chaining.SetBaggageItem(restrictedKey, value string) Span// 根据key获取值BaggageItem(restrictedKey string) string// 返回创建此span的TracerTracer() Tracer}
type SpanContext
type SpanContext interface {// ForeachBaggageItem grants access to all baggage items stored in the// SpanContext.// The handler function will be called for each baggage key/value pair.// The ordering of items is not guaranteed.//// The bool return value indicates if the handler wants to continue iterating// through the rest of the baggage items; for example if the handler is trying to// find some baggage item by pattern matching the name, it can return false// as soon as the item is found to stop further iterations.ForeachBaggageItem(handler func(k, v string) bool)}
type SpanReference
SpanReference是一个StartSpanOption,它对一个SpanReferenceType和一个引用的SpanContext。有关支持的关系,请参阅SpanReferenceType文档。如果SpanReference是用ReferencedContext==nil创建的,那么它没有作用。因此,它允许使用更简洁的语法来启动span ```go type SpanReference struct { Type SpanReferenceType ReferencedContext SpanContext }
sc, _ := tracer.Extract(someFormat, someCarrier) span := tracer.StartSpan(“operation”, opentracing.ChildOf(sc))
func ChildOf(sc [SpanContext](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#SpanContext)) [SpanReference](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#SpanReference)- 返回StartSpanOption,将新建的span作为父span(sc)的后代,如果sc == nil,则该选项无效<br />func FollowsFrom(sc [SpanContext](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#SpanContext)) [SpanReference](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#SpanReference)- 返回StartSpanOption,将新建的span作为父span(sc)的后代,但不直接依赖于它的结果- 如果sc == nil,则该选项无效<br />func (r [SpanReference](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#SpanReference)) Apply(o *[StartSpanOptions](https://godoc.org/github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go#StartSpanOptions)) 实现StartSpanOption接口<a name="afpmu"></a>#### type [FinishOptions](https://github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go/blob/master/span.go#L134)控制时间戳和日志数据```gotype FinishOptions struct {FinishTime time.TimeLogRecords []LogRecordBulkLogData []LogData}
type StartSpanOption
type StartSpanOption interface {Apply(*StartSpanOptions)}
type StartSpanOptions
type StartSpanOptions struct {// Zero or more causal references to other Spans (via their SpanContext).// If empty, start a "root" Span (i.e., start a new trace).References []SpanReference// StartTime overrides the Span's start time, or implicitly becomes// time.Now() if StartTime.IsZero().StartTime time.Time// Tags may have zero or more entries; the restrictions on map values are// identical to those for Span.SetTag(). May be nil.//// If specified, the caller hands off ownership of Tags at// StartSpan() invocation time.Tags map[string]interface{}}
type Tag
tag可以作为StartSpanOption传递给新的Span添加一个标签,或者它的Set方法可以用于将标签应用到现有的Span
type Tag struct {Key stringValue interface{}}
func (t Tag) Apply(o *StartSpanOptions) 实现StartSpanOption接口,在开启span时可做为参数传递过去
func (t Tag) Set(s Span) 将tag应用于现有的Span
type Tags
type Tags map[string]interface{}
func (t Tags) Apply(o *StartSpanOptions) 实现StartSpanOption接口,在开启span时可做为参数传递过去
type HTTPHeadersCarrier
HTTPHeadersCarrier满足了TextMapWriter 和 TextMapReader
如果多个服务都是http服务,可以直接使用HTTPHeadersCarrier作为Carrier
type HTTPHeadersCarrier http.Header
Example usage for server side:
carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)clientContext, err := tracer.Extract(opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)
Example usage for client side:
carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)err := tracer.Inject(span.Context(),opentracing.HTTPHeaders,carrier)
func (c HTTPHeadersCarrier) ForeachKey(handler func(key, val string) error) error 满足TextMapReader interface
func (c HTTPHeadersCarrier) Set(key, val string) 满足TextMapWriter interface
type TextMapCarrier
TextMapCarrier允许使用常规的map[string]string 作为TextMapWriter 和 TextMapReader
type TextMapCarrier map[string]string
func (c TextMapCarrier) ForeachKey(handler func(key, val string) error) error 满足TextMapReader interface
func (c TextMapCarrier) Set(key, val string) 满足TextMapWriter interface
type BuiltinFormat
BuiltinFormat用于划分包“opentrace”中的值,这些值将与trace . inject()和trace . extract()方法一起使用
type BuiltinFormat byte
const (// For Tracer.Inject(): the carrier must be an `io.Writer`.// For Tracer.Extract(): the carrier must be an `io.Reader`.Binary BuiltinFormat = iota// TextMap represents SpanContexts as key:value string pairs.// For Tracer.Inject(): the carrier must be a `TextMapWriter`.// For Tracer.Extract(): the carrier must be a `TextMapReader`.TextMap// HTTPHeaders represents SpanContexts as HTTP header string pairs.// For Tracer.Inject(): the carrier must be a `TextMapWriter`.// For Tracer.Extract(): the carrier must be a `TextMapReader`.//// See HTTPHeadersCarrier for an implementation of both TextMapWriter// and TextMapReader that defers to an http.Header instance for storage.// For example, Inject()://// carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)// err := span.Tracer().Inject(// span.Context(), opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)//// Or Extract()://// carrier := opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header)// clientContext, err := tracer.Extract(// opentracing.HTTPHeaders, carrier)//HTTPHeaders)
type TextMapReader
TextMapReader是TextMap内置格式的Extract()载体
type TextMapReader interface {// ForeachKey returns TextMap contents via repeated calls to the `handler`// function. If any call to `handler` returns a non-nil error, ForeachKey// terminates and returns that error.//// NOTE: The backing store for the TextMapReader may contain data unrelated// to SpanContext. As such, Inject() and Extract() implementations that// call the TextMapWriter and TextMapReader interfaces must agree on a// prefix or other convention to distinguish their own key:value pairs.//// The "foreach" callback pattern reduces unnecessary copying in some cases// and also allows implementations to hold locks while the map is read.ForeachKey(handler func(key, val string) error) error}
type TextMapWriter
TextMapWriter是TextMap内置格式的Inject()载体
type TextMapWriter interface {// Set a key:value pair to the carrier. Multiple calls to Set() for the// same key leads to undefined behavior.//// NOTE: The backing store for the TextMapWriter may contain data unrelated// to SpanContext. As such, Inject() and Extract() implementations that// call the TextMapWriter and TextMapReader interfaces must agree on a// prefix or other convention to distinguish their own key:value pairs.Set(key, val string)}
使用
使用context启动一个子span
func xyz(ctx context.Context, ...) {...span, ctx := opentracing.StartSpanFromContext(ctx, "operation_name")defer span.Finish()span.LogFields(log.String("event", "soft error"),log.String("type", "cache timeout"),log.Int("waited.millis", 1500))...}或者:func xyz(ctx context.Context, ...) {var parentCtx opentracing.SpanContextif parent := opentracing.SpanFromContext(ctx); parent != nil {parentCtx = parent.Context()}cliSpan := tracer.StartSpan("operation_name",opentracing.ChildOf(parentCtx),opentracing.Tag{Key: string(ext.Component), Value: "gRPC"},ext.SpanKindRPCClient,)defer cliSpan.Finish()}
创建一个空trace的root节点
func xyz() {...sp := opentracing.StartSpan("operation_name")defer sp.Finish()...}
给定父节点,创建一个子节点
func xyz(parentSpan opentracing.Span, ...) {...sp := opentracing.StartSpan("operation_name",opentracing.ChildOf(parentSpan.Context()))defer sp.Finish()...}
序列化到wire
func makeSomeRequest(ctx context.Context) ... {if span := opentracing.SpanFromContext(ctx); span != nil {httpClient := &http.Client{}httpReq, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", "http://myservice/", nil)// Transmit the span's TraceContext as HTTP headers on our// outbound request.opentracing.GlobalTracer().Inject(span.Context(),opentracing.HTTPHeaders,opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(httpReq.Header))resp, err := httpClient.Do(httpReq)...}...}
从wire虚拟化
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {var serverSpan opentracing.SpanappSpecificOperationName := ...wireContext, err := opentracing.GlobalTracer().Extract(opentracing.HTTPHeaders,opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(req.Header))if err != nil {// Optionally record something about err here}// Create the span referring to the RPC client if available.// If wireContext == nil, a root span will be created.serverSpan = opentracing.StartSpan(appSpecificOperationName,ext.RPCServerOption(wireContext))defer serverSpan.Finish()ctx := opentracing.ContextWithSpan(context.Background(), serverSpan)...}
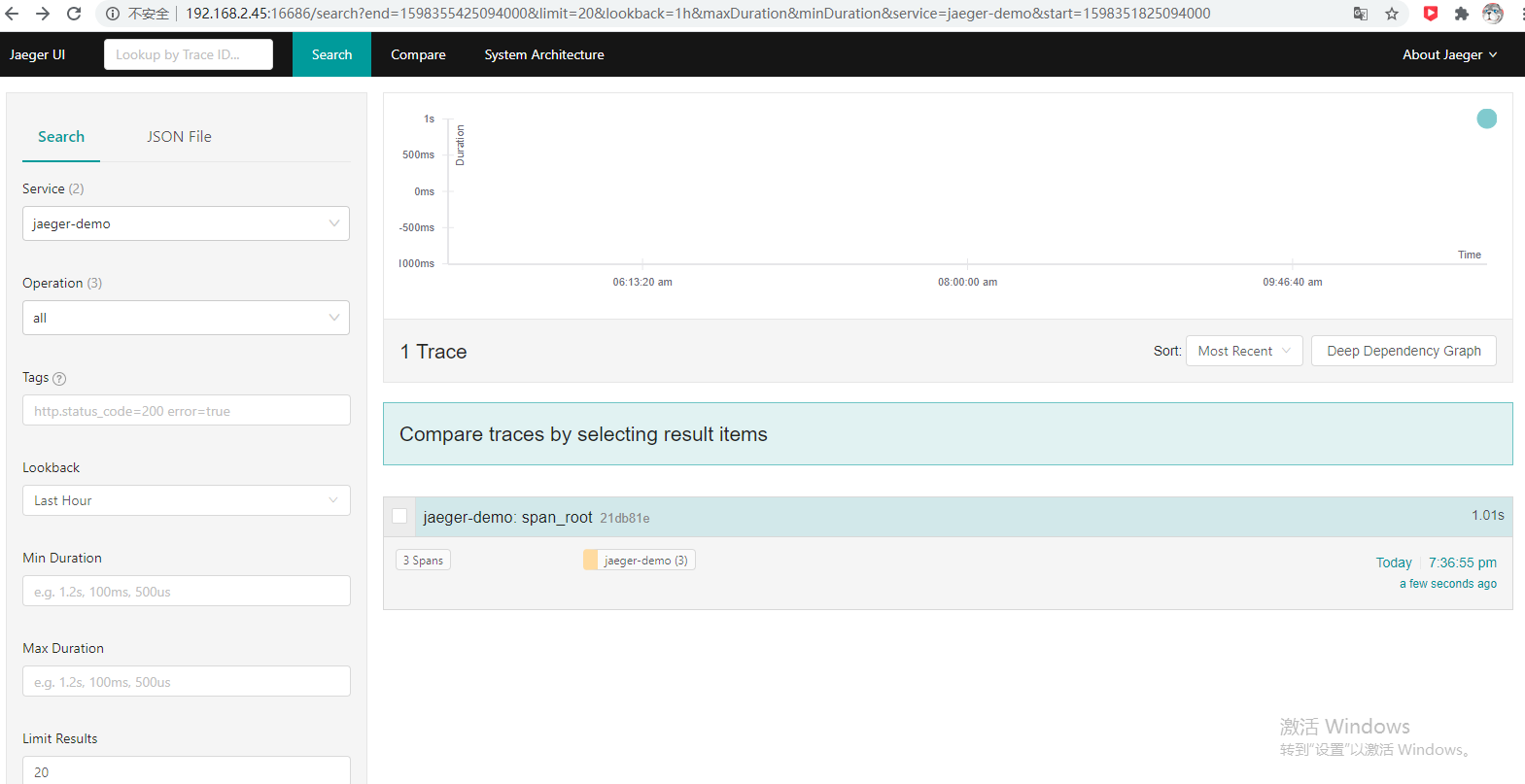
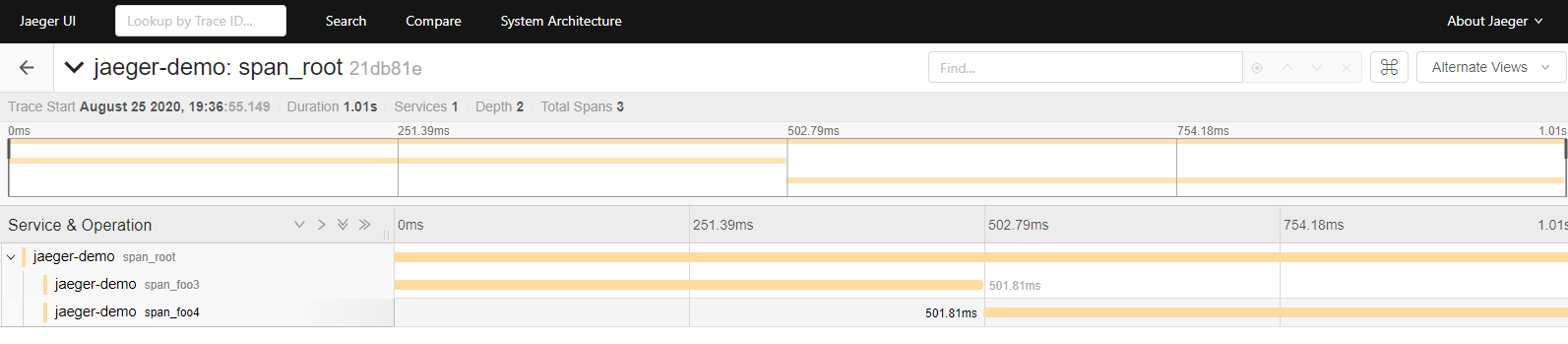
简单例子:
package mainimport ("context""fmt""github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go""github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go""github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go/config""io""time")func initJaeger(service string) (opentracing.Tracer, io.Closer) {cfg := &config.Configuration{ServiceName: service,Sampler: &config.SamplerConfig{Type: "const",Param: 1,},Reporter: &config.ReporterConfig{LogSpans: true,LocalAgentHostPort: "192.168.2.45:6831",},}tracer, closer, err := cfg.NewTracer(config.Logger(jaeger.StdLogger))if err != nil {panic(fmt.Sprintf("ERROR: cannot init Jaeger: %v\n", err))}return tracer, closer}func foo3(req string, ctx context.Context) (reply string) {//1.创建子spanspan, _ := opentracing.StartSpanFromContext(ctx, "span_foo3")defer func() {//4.接口调用完,在tag中设置request和replyspan.SetTag("request", req)span.SetTag("reply", reply)span.Finish()}()println(req)//2.模拟处理耗时time.Sleep(time.Second / 2)//3.返回replyreply = "foo3Reply"return}//跟foo3一样逻辑func foo4(req string, ctx context.Context) (reply string) {span, _ := opentracing.StartSpanFromContext(ctx, "span_foo4")defer func() {span.SetTag("request", req)span.SetTag("reply", reply)span.Finish()}()println(req)time.Sleep(time.Second / 2)reply = "foo4Reply"return}func main() {tracer, closer := initJaeger("jaeger-demo")defer closer.Close()opentracing.SetGlobalTracer(tracer) //StartspanFromContext创建新span时会用到span := tracer.StartSpan("span_root")defer span.Finish()ctx := opentracing.ContextWithSpan(context.Background(), span)r1 := foo3("Hello foo3", ctx)r2 := foo4("Hello foo4", ctx)fmt.Println(r1, r2)}