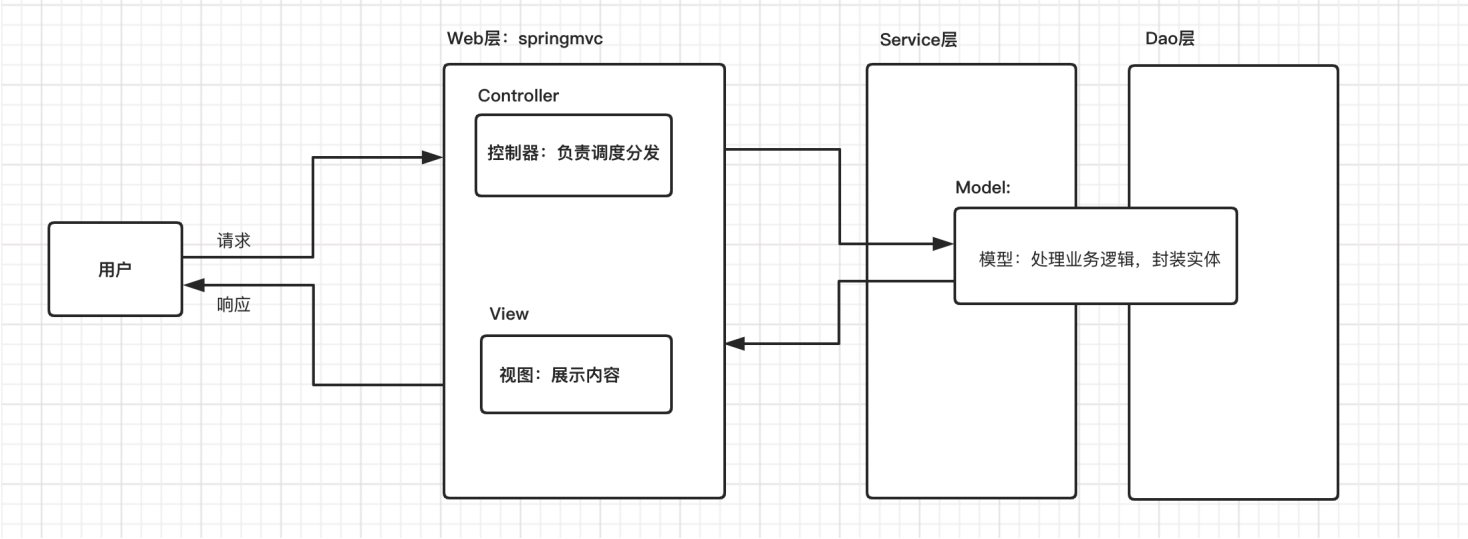
SpringMVC 是一种基于 Java 的实现 MVC 设计模式的轻量级 Web 框架,属于SpringFrameWork 的后续产品,已经融合在 Spring Web Flow 中。
SpringMVC 已经成为目前最主流的MVC框架之一,并且随着Spring3.0 的发布,全面超越 Struts2, 成为最优秀的 MVC 框架。它通过一套注解,让一个简单的 Java 类成为处理请求的控制器,而无须实现任何接口。同时它还支持 RESTful 编程风格的请求。 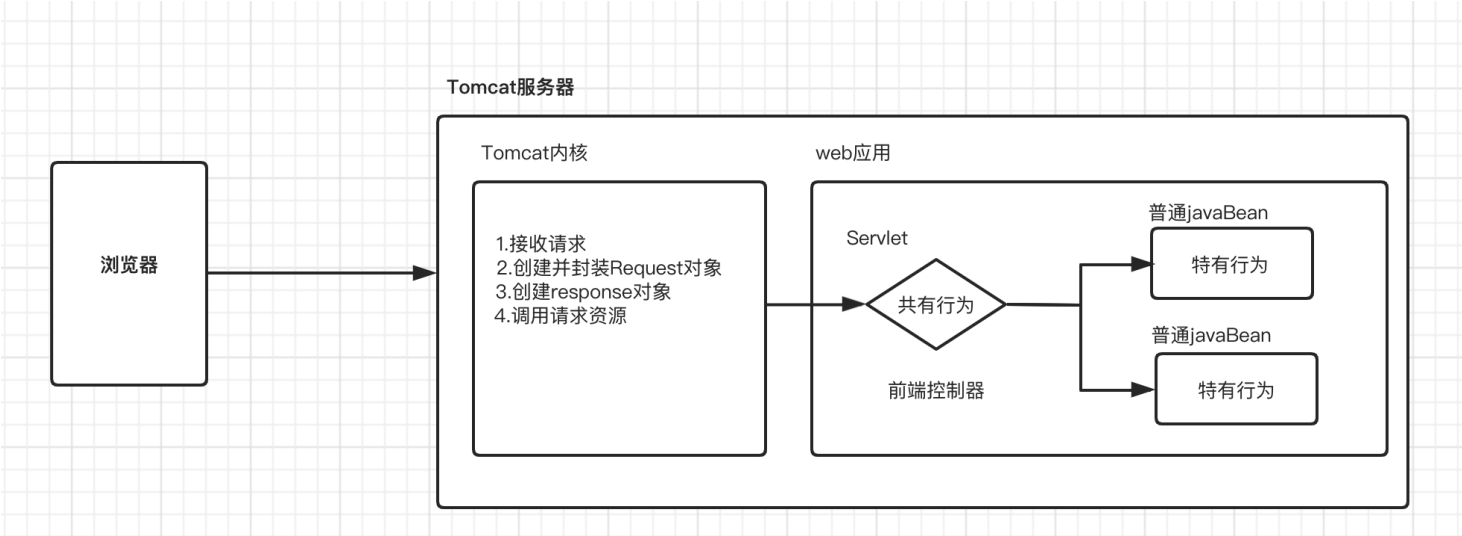
入门案例
客户端发起请求,服务器接收请求,执行逻辑并进行视图跳转。
步骤分析
- 创建web项目,导入SpringMVC相关坐标
- 配置SpringMVC前端控制器 DispathcerServlet
- 编写Controller类和视图页面
- 使用注解配置Controller类中业务方法的映射地址
- 配置SpringMVC核心文件 spring-mvc.xml
pom
<dependencies><!--springMVC坐标--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version></dependency><!--servlet坐标--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>3.1.0</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency><!--jsp坐标--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.2</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency></dependencies>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><servlet><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><!-- 这里url写细线,只能匹配到像/login /update这种,匹配不到/a.jsp这种。如果写/* 就什么都能匹配到--><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
spring-mvc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><context:component-scan base-package="com.ning"/></beans>
Controller
@Controllerpublic class UserController {@RequestMapping("/quick")public String quick() {System.out.println("quick running.....");return "/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp";}}
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>Success</title></head><body><h3>Spring MVC!</h3></body></html>
Web工程执行流程
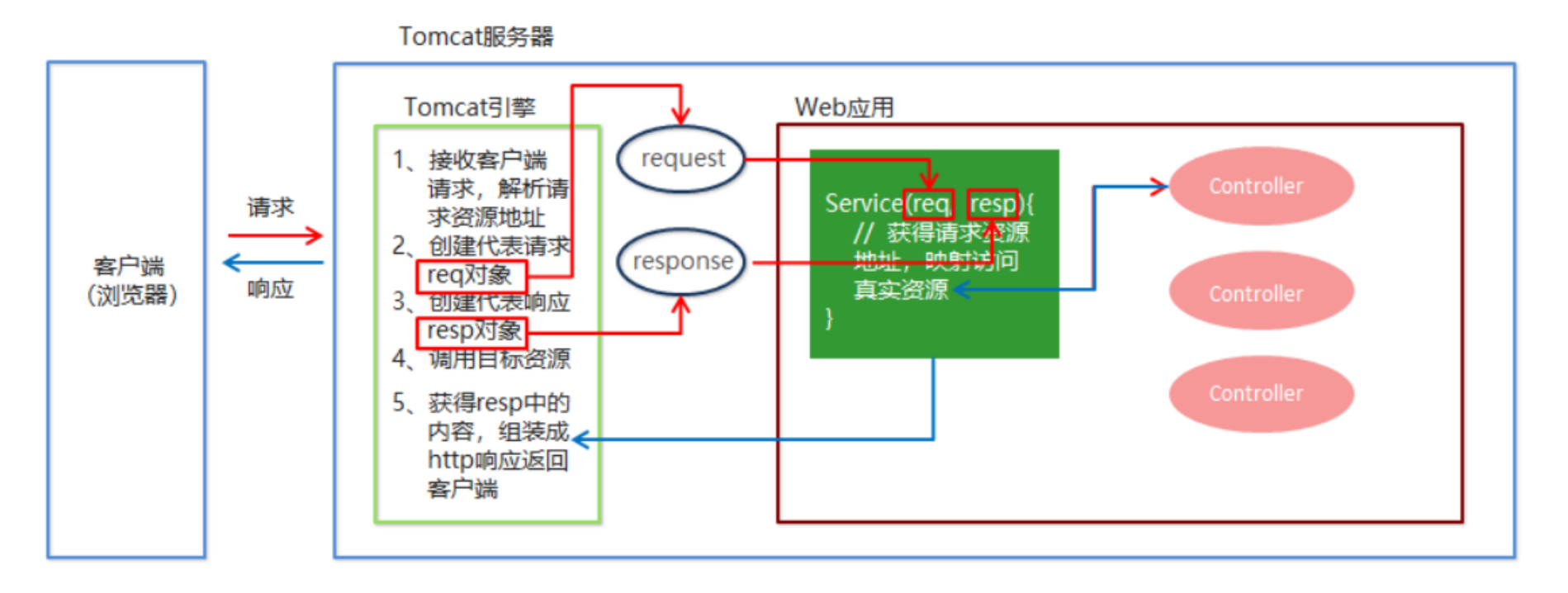
Spring MVC执行流程
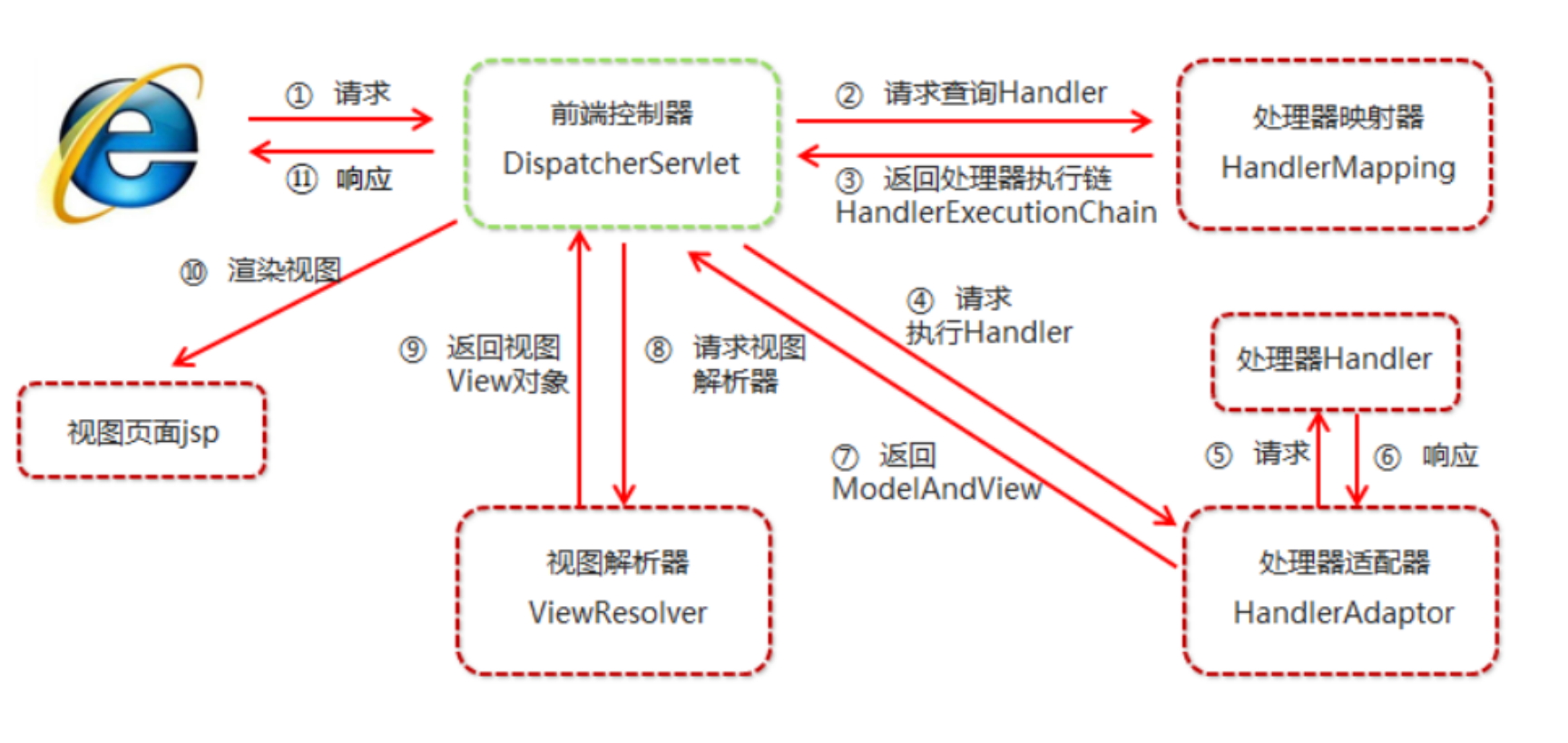
- 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
- 处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如
果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。 - DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
- HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
- Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
- HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
- ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
- DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
- DispatcherServlet将渲染后的视图响应响应用户。
Spring MVC组件详解
- 前端控制器:DispatcherServlet
用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于 MVC 模式中的 C,DispatcherServlet 是整个流程控制的
中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,DispatcherServlet 的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。 - 处理器映射器:HandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 负责根据用户请求找到 Handler 即处理器,SpringMVC 提供了不同的映射器
实现不同的映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。 - 处理器适配器:HandlerAdapter
通过 HandlerAdapter 对处理器进行执行,这是适配器模式的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型
的处理器进行执行。 - 处理器:Handler【开发者编写】
它就是我们开发中要编写的具体业务控制器。由 DispatcherServlet 把用户请求转发到
Handler。由Handler 对具体的用户请求进行处理。 - 视图解析器:ViewResolver
View Resolver 负责将处理结果生成 View 视图,View Resolver 首先根据逻辑视图名解析成物
理视图名,即具体的页面地址,再生成 View 视图对象,最后对 View 进行渲染将处理结果通过页面展示给
用户。 - 视图:View 【开发者编写】
SpringMVC 框架提供了很多的 View 视图类型的支持,包括:jstlView、freemarkerView、
pdfView等。最常用的视图就是 jsp。一般情况下需要通过页面标签或页面模版技术将模型数据通过页面展
示给用户,需要由程序员根据业务需求开发具体的页面。
*笔试题:springmvc中的三大组件是什么?
2 3 5
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><context:component-scan base-package="com.ning"/><!-- 配置了处理器适配器、映射器,还支持json的读写--><mvc:annotation-driven/><bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"></property><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property></bean></beans>
注解解析
@Controller
SpringMVC基于Spring容器,所以在进行SpringMVC操作时,需要将Controller存储到Spring容器中,如果使用@Controller注解标注的话,就需要使用:
<!--配置注解扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.ning.controller"/>
@RequestMapping
* 作用:用于建立请求 URL 和处理请求方法之间的对应关系* 位置:1.类上:请求URL的第一级访问目录。此处不写的话,就相当于应用的根目录。写的话需要以/开头。它出现的目的是为了使我们的URL可以按照模块化管理:用户模块/user/add/user/update/user/delete...账户模块/account/add/account/update/account/delete2.方法上:请求URL的第二级访问目录,和一级目录组成一个完整的 URL 路径。* 属性:1.value:用于指定请求的URL。它和path属性的作用是一样的2.method:用来限定请求的方式3.params:用来限定请求参数的条件例如:params={"accountName"} 表示请求参数中必须有accountNameprams={"money!100"} 表示请求参数中money不能是100
请求参数解析
客户端请求参数的格式是: name=value&name=value……
服务器要获取请求的参数的时候要进行类型转换,有时还需要进行数据的封装
SpringMVC可以接收如下类型的参数:
基本类型参数
对象类型参数
数组类型参数
集合类型参数
基本类型参数
Controller中的业务方法的参数名称要与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。并且能自动做类型转换;自动的类型转换是指从String向其他类型的转换。
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/simpleParam?id=1&username=杰克">基本类型</a>@RequestMapping("/simpleParam")public String simpleParam(Integer id,String username) {System.out.println(id);System.out.println(username);return "success";}
对象类型参数
Controller中的业务方法参数的POJO属性名与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/pojoParam" method="post">编号:<input type="text" name="id"> <br>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br><input type="submit" value="对象类型"></form>
public class User {Integer id;String username;// setter getter...}@RequestMapping("/pojoParam")public String pojoParam(User user) {System.out.println(user);return "success";}
当post请求时,数据会出现乱码,我们可以设置一个过滤器来进行编码的过滤。
可以把这一段加在web.xml里
<!--配置全局过滤的filter--><filter><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>UTF-8</param-value></init-param></filter><filter-mapping><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping>
数组类型参数
Controller中的业务方法数组名称与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/arrayParam">编号:<br><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="1">1<br><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="2">2<br><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="3">3<br><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="4">4<br><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="5">5<br><input type="submit" value="数组类型"></form>
@RequestMapping(path = "/arrayParam")public String arrayParam(Integer[] ids) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ids));return "success";}
集合(复杂)类型参数
获得集合参数时,要将集合参数包装到一个entity中才可以。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/queryParam" method="post">搜索关键字:<input type="text" name="keyword"> <br>user对象:<input type="text" name="user.id" placeholder="编号"><input type="text" name="user.username" placeholder="姓名"><br>list集合<br>第一个元素:<input type="text" name="userList[0].id" placeholder="编号"><input type="text" name="userList[0].username" placeholder="姓名"><br>第二个元素:<input type="text" name="userList[1].id" placeholder="编号"><input type="text" name="userList[1].username" placeholder="姓名"><br>map集合<br>第一个元素:<input type="text" name="userMap['u1'].id" placeholder="编号"><input type="text" name="userMap['u1'].username" placeholder="姓名"><br>第二个元素:<input type="text" name="userMap['u2'].id" placeholder="编号"><input type="text" name="userMap['u2'].username" placeholder="姓名"><br><input type="submit" value="复杂类型"></form>
public class QueryVo {private String keyword;private User user;private List<User> userList;private Map<String, User> userMap;}@RequestMapping("/queryParam")public String queryParam(QueryVo queryVo) {System.out.println(queryVo);return "success";}
自定义类型转换器
SpringMVC 默认已经提供了一些常用的类型转换器;
例如:客户端提交的字符串转换成int型进行参数设置,日期格式类型要求为:yyyy/MM/dd 不然的话会报错,对于特有的行为,SpringMVC提供了自定义类型转换器方便开发者自定义处理。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/converterParam">生日:<input type="text" name="birthday"><input type="submit" value="自定义类型转换器"></form>
@RequestMapping(path = "/converterParam")public String converterParam(Date birthday) {System.out.println(birthday);return "success";}
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {public Date convert(String dateStr) {//将日期字符串转换成日期对象 返回SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");Date date = null;try {date = format.parse(dateStr);} catch (ParseException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return date;}}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><context:component-scan base-package="com.ning"/><!-- 配置了处理器适配器、映射器,还支持json的读写--><!-- conversion service是让日期转换器生效--><mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionServiceFactoryBean"/><bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"></property><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property></bean><!-- 自定义日期转换器--><bean id="conversionServiceFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean"><property name="converters"><set><bean class="com.ning.converter.DateConverter"/></set></property></bean></beans>
其他注解
@RequestParam
当请求的参数name名称与Controller的业务方法参数名称不一致时,就需要通过@RequestParam注 解显示的绑定
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/findByPage?pageNo=2">分页查询</a>
/*@RequestParam() 注解defaultValue 设置参数默认值name 匹配页面传递参数的名称required 设置是否必须传递参数,默认值为true;如果设置了默认值,值自动改为false*/@RequestMapping("/findByPage")public String findByPage(@RequestParam(name = "pageNo", defaultValue = "1")Integer pageNum, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "5") Integer pageSize) {System.out.println(pageNum);System.out.println(pageSize);return "success";}
@RequestHeader
获取请求头的数据。
@RequestMapping("/requestHead")public String requestHead(@RequestHeader("cookie") String cookie) {System.out.println(cookie);return "success";}
@CookieValue
获取Cookie中的值
@RequestMapping("/cookieValue")public String cookieValue(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jesessionId) {System.out.println(jesessionId);return "success";}
获取Servlet API
@RequestMapping("/servletAPI")public String servletAPI(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponseresponse, HttpSession session) {System.out.println(request);System.out.println(response);System.out.println(session);return "success";}
SpringMVC的响应
页面跳转
- 返回字符串逻辑视图
- void原始ServletAPI
- ModelAndView
返回数据
- 直接返回字符串数据
- 将对象或集合转为json返回
//返回逻辑视图 会在配置文件里拼接前缀和后缀@RequestMapping("/returnString")public String returnString() {return "success";}
@RequestMapping("/returnVoid")public void returnVoid(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws Exception {// 1.通过response直接响应数据response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");response.getWriter().write("拉勾网");----------------------------------------request.setAttribute("username", "拉勾教育");// 2.通过request实现转发request.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp").forward(request,response);----------------------------------------// 3.通过response实现重定向response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");}
ModelAndView
方式一
在Controller中方法创建并返回ModelAndView对象,并且设置视图名称
@RequestMapping("/returnModelAndView1")public ModelAndView returnModelAndView1() {/*Model:模型 作用封装数据View:视图 作用展示数据*/ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();//设置模型数据modelAndView.addObject("username", " lagou");//设置视图名称 会去找/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp//写了forward或者redirect就不会去走视图解析器了。modelAndView.setViewName("success");return modelAndView;}
方式二
在Controller中方法形参上直接声明ModelAndView,无需在方法中自己创建,在方法中直接使用该对象设置视图,同样可以跳转页面
@RequestMapping("/returnModelAndView2")public ModelAndView returnModelAndView2(ModelAndView modelAndView) {//设置模型数据modelAndView.addObject("username", "itheima");//设置视图名称modelAndView.setViewName("success");return modelAndView;}
转发和重定向
企业开发我们一般使用返回字符串逻辑视图实现页面的跳转,这种方式其实就是请求转发。
我们也可以写成:forward转发 如果用了forward:则路径必须写成实际视图url,不能写逻辑视图。
它相当于:
request.getRequestDispatcher("url").forward(request,response)
使用请求转发,既可以转发到jsp,也可以转发到其他的控制器方法。
@RequestMapping("/forward")public String forward(Model model) {model.addAttribute("username", "拉勾招聘");return "forward:/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp";}
Redirect重定向
我们可以不写虚拟目录,springMVC框架会自动拼接,并且将Model中的数据拼接到url地址上
@RequestMapping("/redirect")public String redirect(Model model) {//底层使用的还是request.setAttribute() 所以不好用model.addAttribute("username", "拉勾教育");return "redirect:/index.jsp";}
@SessionAttributes
如果在多个请求之间共用数据,则可以在控制器类上标注一个 @SessionAttributes,配置需要在 session中存放的数据范围,Spring MVC将存放在model中对应的数据暂存到 HttpSession中。
@Controller@SessionAttributes("username") //向request域存入的key为username时,同步到session域中public class UserController {@RequestMapping("/forward")public String forward(Model model) {model.addAttribute("username", "子慕");return "forward:/WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp";}@RequestMapping("/returnString")public String returnString() {return "success";}}
静态资源访问的开启
当有静态资源需要加载时,比如jquery文件,通过谷歌开发者工具抓包发现,没有加载到jquery文 件,原因是SpringMVC的前端控制器DispatcherServlet的url-pattern配置的是 /(缺省),代表对所有的 静态资源都进行处理操作,这样就不会执行Tomcat内置的DefaultServlet处理,我们可以通过以下两种 方式指定放行静态资源:
方式一
<!--在springmvc配置文件中指定放行资源--><mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/js/"/><mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/"/><mvc:resources mapping="/img/**" location="/img/"/>
方式二
<!--在springmvc配置文件中开启DefaultServlet处理静态资源--><mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
Ajax异步交互
Springmvc默认用MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter对json数据进行转换,需要加入 jackson的包;同时使用
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId><version>2.9.8</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId><version>2.9.8</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId><version>2.9.0</version></dependency>
写个jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>ajax</title></head><body><script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/js/jquery-3.5.1.js"/><button id="btn1">ajax异步提交</button><script>$("btn1").click(function (){let url = '${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/ajaxRequest';let data = '[{"id":1, "username":"张三"},{"id":2, "username":"李四"}]';$.ajax({type: 'POST',url: url,data: data,contentType: 'application/json;charset=utf-8',success: function (resp) {alert(resp);}});});</script></body></html>
@RequestBody
该注解用于Controller的方法的形参声明,当使用ajax提交并指定contentType为json形式时,通过 HttpMessageConverter接口转换为对应的entity对象。
@RequestMapping("/ajaxRequest")public void ajaxRequest(@RequestBody List<User> list) {System.out.println(list);}
@ResponseBody
该注解用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过HttpMessageConverter接口转换为指定格式的数 据如:json,xml等,通过Response响应给客户端。
@RequestMapping("/ajaxRequest")@ResponseBodypublic List<User> ajaxRequest(@RequestBody List<User> list) {System.out.println(list);return list;}
REST ful
Restful是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。
主要用于客户端和服务器交互类的软件,基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存机制等。 Restful风格的请求是使用“url+请求方式”表示一次请求目的的,HTTP 协议里面四个表示操作方式的动词如下:
GET:读取(Read) POST:新建(Create) PUT:更新(Update) DELETE:删除(Delete) 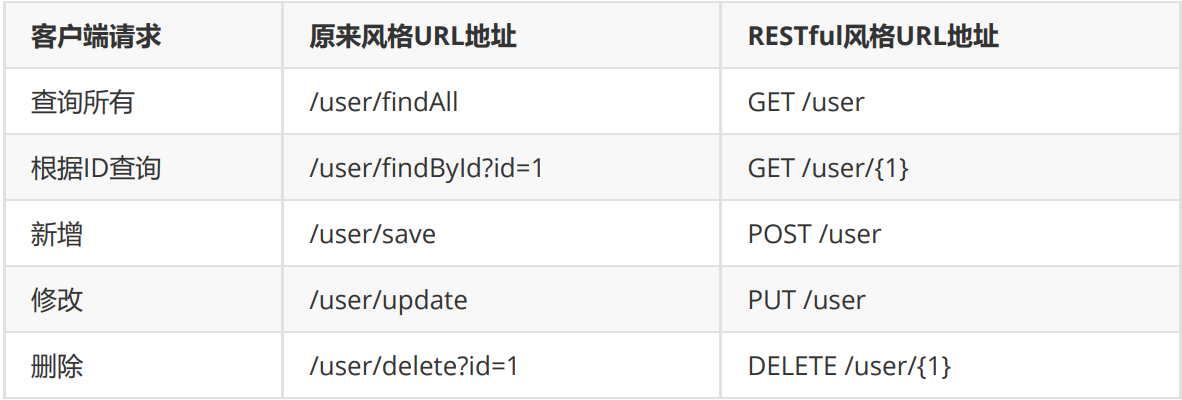
代码实现
@PathVariable 用来接收RESTful风格请求地址中占位符的值
@RestController RESTful风格多用于前后端分离项目开发,前端通过ajax与服务器进行异步交互,我们处理器通常返回的是json数据所以使用@RestController来替代@Controller和@ResponseBody两个注解。
// @Controller@RestControllerpublic class RestFulController {@GetMapping(value = "/user/{id}")// 相当于 @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)// @ResponseBodypublic String get(@PathVariable Integer id) {return "get:" + id;}@PostMapping(value = "/user")// @ResponseBodypublic String post() {return "post";}@PutMapping(value = "/user")// @ResponseBodypublic String put() {return "put";}@DeleteMapping(value = "/user/{id}")// @ResponseBodypublic String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {return "delete:"+ id;}}
文件上传
三要素
表单项 type=”file”
表单的提交方式 method=”POST”
表单的enctype属性是多部分表单形式 enctype=”multipart/form-data”
原理
当form表单修改为多部分表单时,request.getParameter()将失效。
当form表单的enctype取值为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 时,form表单的正文内容格式是: name=value&name=value
当form表单的enctype取值为 mutilpart/form-data 时,请求正文内容就变成多部分形式
实例(单文件上传)
<dependency><groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId><artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId><version>1.3.3</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>commons-io</groupId><artifactId>commons-io</artifactId><version>2.6</version></dependency>
配置解析器
<!--文件上传解析器--><bean id="multipartResolver"class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"><!-- 设定文件上传的最大值为5MB,5*1024*1024 --><property name="maxUploadSize" value="5242880"></property><!-- 设定文件上传时写入内存的最大值,如果小于这个参数不会生成临时文件,默认为10240 --><property name="maxInMemorySize" value="40960"></property></bean>
编码
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/fileUpload" method="post"enctype="multipart/form-data">名称:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>文件:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br><input type="submit" value="单文件上传"></form>
记得提前创建好文件夹
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload")public String fileUpload(String username, MultipartFile filePic) throwsIOException {System.out.println(username);// 获取文件名String originalFilename = filePic.getOriginalFilename();//保存文件filePic.transferTo(new File("d:/upload/"+originalFilename));return "success";}
多文件上传
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/filesUpload" method="post"enctype="multipart/form-data">名称:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>文件1:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br>文件2:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br><input type="submit" value="多文件上传"></form>
@RequestMapping("/filesUpload")public String filesUpload(String username, MultipartFile[] filePic) throwsIOException {System.out.println(username);for (MultipartFile multipartFile : filePic) {// 获取文件名String originalFilename = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();// 保存到服务器multipartFile.transferTo(new File("d:/upload/" + originalFilename));}return "success";}
异常处理
在Java中,对于异常的处理一般有两种方式:
一种是当前方法捕获处理(try-catch),这种处理方式会造成业务代码和异常处理代码的耦合。
另一种是自己不处理,而是抛给调用者处理(throws),调用者再抛给它的调用者,也就是一直向上抛。
在第二种方法的基础上,衍生出了SpringMVC的异常处理机制。 系统的dao、service、controller出现都通过throws Exception向上抛出,最后由springmvc前端控 制器交由异常处理器进行异常处理,如下图: 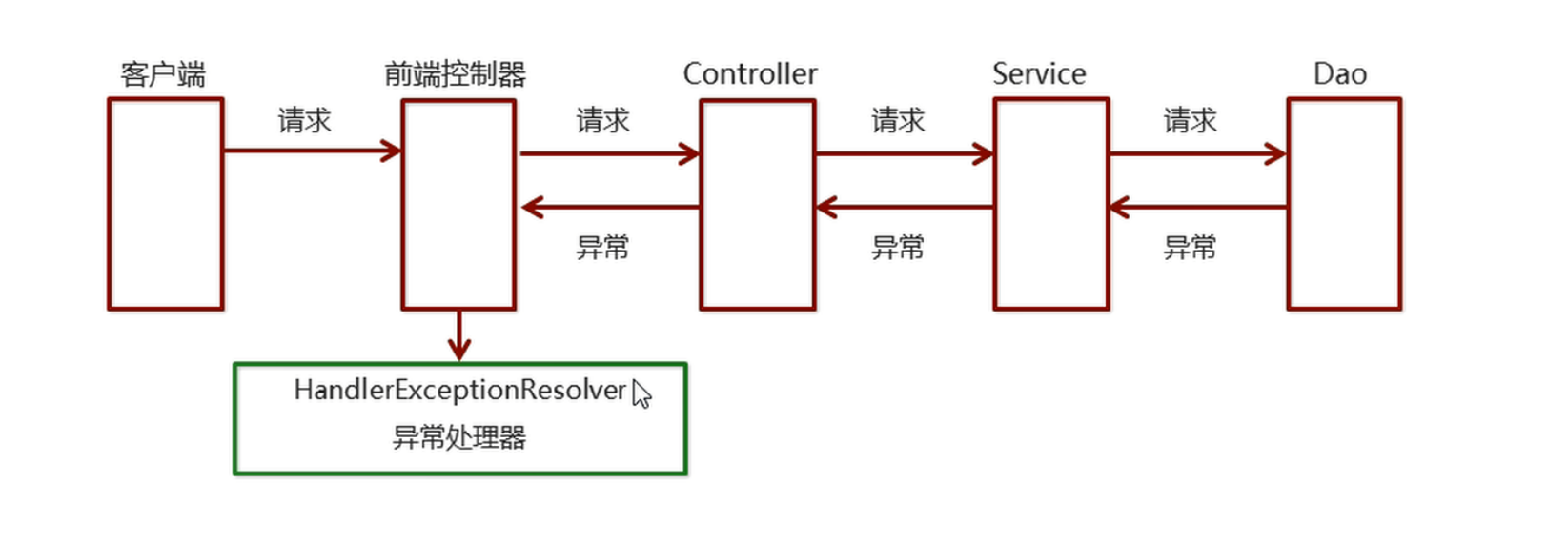
自定义异常处理器
- 创建异常处理器类实现HandlerExceptionResolver
- 配置异常处理器
- 编写异常页面
- 测试异常跳转
@Componentpublic class GlobalExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {@Overridepublic ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();modelAndView.addObject("error", ex.getMessage());modelAndView.setViewName("error");return modelAndView;}}
<bean id="globalExecptionResovler"class="com.ning.exception.GlobalExecptionResovler"></bean>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>error</title></head><body>出错啦!联系管理员!${error}</body></html>
<br />最后做个测试方法即可
@RequestMapping("/testException")public String testException() {int i = 1 / 0;return "success";}
Web异常处理机制
在web.xml里可以配置错误页面。这样404和500都可以处理的很好了。
<!--处理500异常--><error-page><error-code>500</error-code><location>/500.jsp</location></error-page><!--处理404异常--><error-page><error-code>404</error-code><location>/404.jsp</location></error-page>
拦截器
Spring MVC 的拦截器类似于 Servlet 开发中的过滤器 Filter,用于对处理器进行预处理和后处理。
将拦截器按一定的顺序联结成一条链,这条链称为拦截器链(InterceptorChain)。在访问被拦截的方法或字段时,拦截器链中的拦截器就会按其之前定义的顺序被调用。拦截器也是AOP思想的具体实现。
与filter的区别
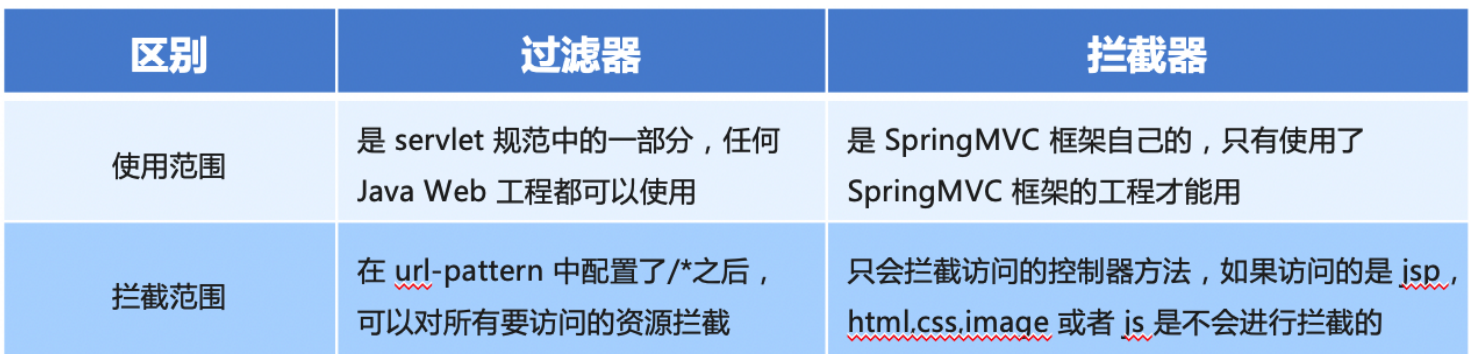
快速上手
- 创建拦截器类实现HandlerInterceptor接口
- 配置拦截器
- 测试拦截器的拦截效果
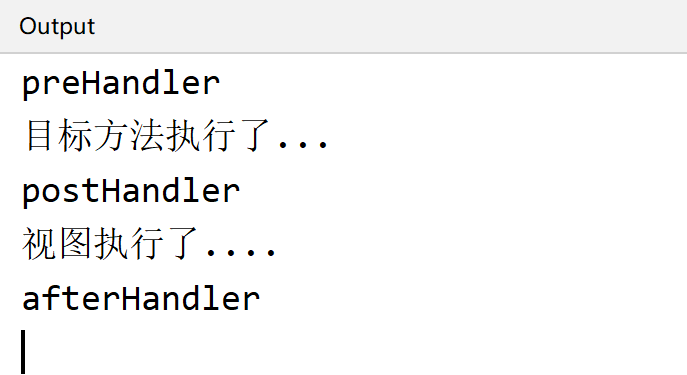
public class MyInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor {@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {System.out.println("preHandler");//返回false不放行return true;}//目标方法执行后,视图方法执行之前@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {System.out.println("postHandler");}@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {System.out.println("afterHandler");}}
<!--配置拦截器--><mvc:interceptors><mvc:interceptor><!--对哪些资源执行拦截操作--><mvc:mapping path="/**"/><bean class="com.lagou.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"/></mvc:interceptor></mvc:interceptors>
@Controllerpublic class TargetController {@RequestMapping("/target")public String targetMethod() {System.out.println("目标方法执行了...");return "success";}}
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>success</title></head><body><h3>success...</h3><% System.out.println("视图执行了....");%></body></html>
拦截器链
开发中拦截器可以单独使用,也可以同时使用多个拦截器形成一条拦截器链。
开发步骤和单个拦截器是一样的,只不过注册的时候注册多个,注意这里注册的顺序就代表拦截器执行的顺序。
同上,再编写一个MyHandlerInterceptor2操作,测试执行顺序:
<mvc:interceptors><mvc:interceptor><!--拦截器路径配置--><mvc:mapping path="/**"/><!--自定义拦截器类--><bean class="com.ning.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"></bean></mvc:interceptor><mvc:interceptor><!--拦截器路径配置--><mvc:mapping path="/**"/><!--自定义拦截器类--><bean class="com.ning.interceptor.MyInterceptor2"></bean></mvc:interceptor></mvc:interceptors>