延迟加载
就是在需要用到数据时才进行加载,不需要用到数据时就不加载数据。延迟加载也称懒加载。
- 优点:
先从单表查询,需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。 - 缺点:
因为只有当需要用到数据时,才会进行数据库查询,这样在大批量数据查询时,因为查询工作也要消耗时间,所以可能造成用户等待时间变长,造成用户体验下降。 - 在多表中:
一对多,多对多:通常情况下采用延迟加载
一对一(多对一):通常情况下采用立即加载 - 注意:
延迟加载是基于嵌套查询来实现的
局部延迟加载
<!-- 开启一对多 延迟加载 --><resultMap id="userMap" type="user"><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="username" property="username"></result><result column="password" property="password"></result><result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result><!--fetchType="lazy" 懒加载策略fetchType="eager" 立即加载策略--><collection property="orderList" ofType="order" column="id"select="com.lagou.dao.OrderMapper.findByUid" fetchType="lazy"></collection></resultMap><select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">SELECT * FROM `user`</select>
注意这里使用了toString方法。 在你调用当前对象的 equals、clone、hashCode、toString方法时也会触发关联对象的查询。
我们可以在配置文件中使用lazyLoadTriggerMethods配置项覆盖掉上面四个方法。
<settings><!--所有方法都会延迟加载--><setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="toString()"/></settings>
全局延迟加载
<settings><!--开启全局延迟加载功能--><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
注意局部延迟加载属性优先级要高于全局延迟加载。所以如果你在局部配置eager,全局配置lazy,那就是eager起效果。
缓存
一级缓存
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存,是默认开启的
所以在参数和SQL完全一样的情况下,我们使用同一个SqlSession对象调用一个Mapper方法,往往只执行一次SQL,因为使用SelSession第一次查询后,MyBatis会将其放在缓存中,以后再查询的时候,如果没有声明需要刷新,并且缓存没有超时的情况下,SqlSession都会取出当前缓存的数据,而不会再次发送SQL到数据库。
具体地说,sqlSession里有一个map结构。这个map结构会存储sql语句+sql语句参数+其他乱七八糟参数 对应的查询结果。
每次执行查询之前,会先访问缓存。
一级缓存是SqlSession范围的缓存,执行SqlSession的C(增加)U(更新)D(删除)操作,或者调用clearCache()、commit()、close()方法,都会清空缓存。不清空的话很可能会出现脏读问题。
当然也可以在每次查询之后都清空缓存,方法是
<!-- 每次查询时,都会清除缓存 -->< select flushCache="true"></select>
二级缓存
二级缓存是namspace级别(跨sqlSession)的缓存,是默认不开启的
二级缓存的开启需要进行配置,实现二级缓存的时候,MyBatis要求返回的Entity必须是可序列化的。 也就是要求实现Serializable接口,配置方法很简单,只需要在映射XML文件配置 就可以开启二级缓存了。
mybatis开启了二级缓存后,查询顺序是:二级缓存—》一级缓存—》数据库 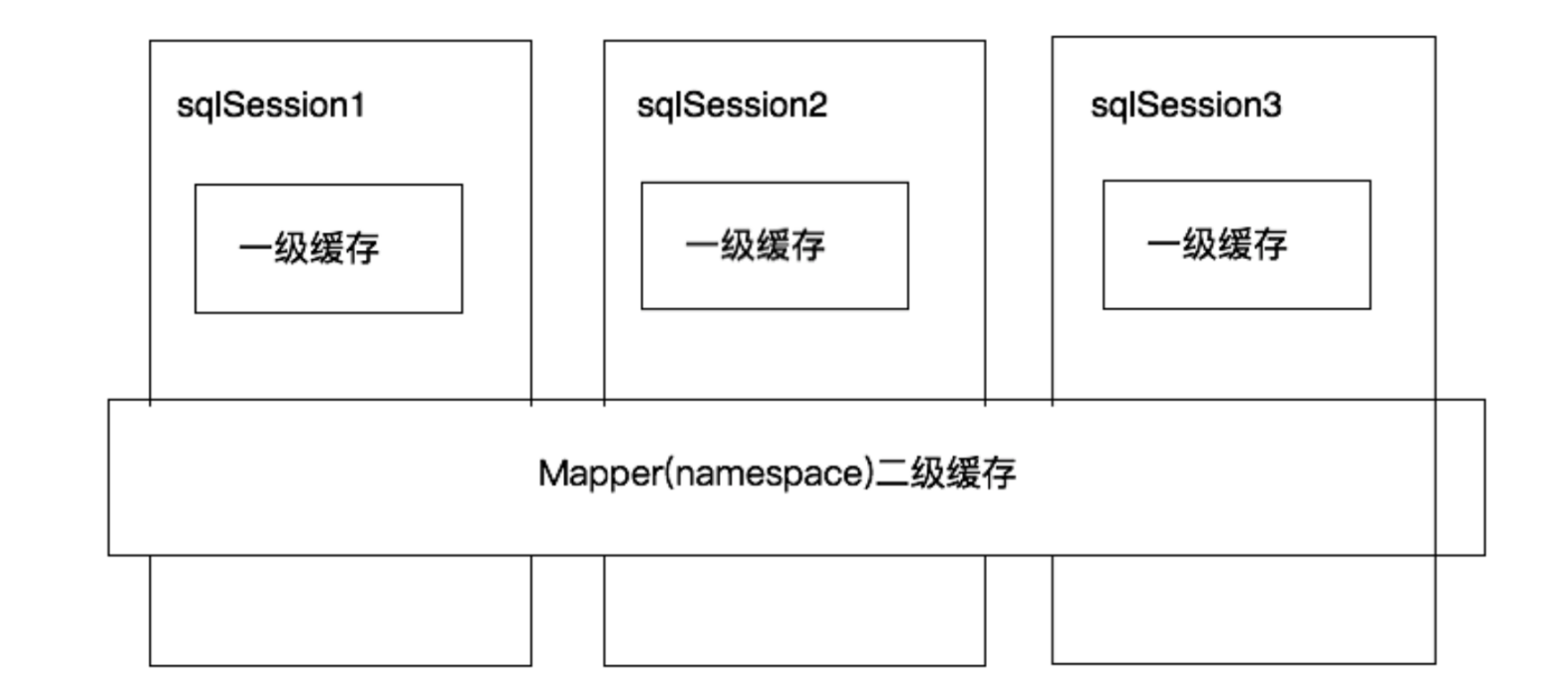
核心配置文件
<settings><!--因为cacheEnabled的取值默认就为true,所以这一步可以省略不配置。为true代表开启二级缓存;为false代表不开启二级缓存。--><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
映射配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.lagou.dao.UserMapper"><!--当前映射文件开启二级缓存--><cache></cache><!--<select>标签中设置useCache=”true”代表当前这个statement要使用二级缓存。如果不使用二级缓存可以设置为false注意:针对每次查询都需要最新的数据sql,要设置成useCache="false",禁用二级缓存。--><select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user" useCache="true">SELECT * FROM `user` where id = #{id}</select></mapper>
测试(注意此时的User类已经实现了Serializable接口)
@Testpublic void testTwoCache() throws Exception {SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);User user = userMapper.findById(41);System.out.println("第一次查询的用户:" + user);//SQLSession不关闭,数据就不会刷新到二级缓存里。sqlSession.close();SqlSession sqlSession1 = MyBatisUtils.openSession();UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);User user1 = userMapper1.findById(41);System.out.println("第二次查询的用户:"+user1);sqlSession1.close();}
二级缓存涉及多表查询和更新会有脏读问题。
实际开发中,最好不要用二级缓存。
基于注解的开发
简单案例
public interface UserMapper {@Select(value = "select * from user")List<User> findAll();@Insert(value = "insert into user(username, birthday, sex, address) values(#{username}, #{birthday}, #{sex}, #{address})")void save(User user);@Update(value = "update user set username = #{username}, birthday=#{birthday} where id = #{id}")void update(User user);@Delete(value = "delete from user where id = #{any}")void delete(int id);}
一对多查询案例
public interface UserMapper {@Select(value = "select * from user")List<User> findAll();@Insert(value = "insert into user(username, birthday, sex, address) values(#{username}, #{birthday}, #{sex}, #{address})")void save(User user);@Update(value = "update user set username = #{username}, birthday=#{birthday} where id = #{id}")void update(User user);@Delete(value = "delete from user where id = #{any}")void delete(int id);@Select(value = "select * from user where id = #{uid}")User findById(int uid);@Select("select * from user")@Results({@Result(property = "id", column = "id", id = true),@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),@Result(property = "birthday", column = "birthday"),@Result(property = "sex", column = "sex"),@Result(property = "address", column = "address"),@Result(property = "ordersList", javaType = List.class, column = "id", many = @Many(select = "com.ning.mapper.OrderMapper.findOrderByUid", fetchType = FetchType.EAGER))})List<User> findAllWithOrder();}
public interface OrderMapper {@Select(value = "select * from orders")@Results({@Result(property = "id", column = "id", id = true),@Result(property = "ordertime", column = "ordertime"),@Result(property = "total", column = "total"),@Result(property = "uid", column = "uid"),@Result(property = "user", javaType = User.class, column = "uid", one = @One(select = "com.ning.mapper.UserMapper.findById"))})List<Orders> findAllWithUser();@Select(value = "select * from orders where uid = #{uid}")List<Orders> findOrderByUid(int uid);}
多对多查询案例
@Select("select * from user")@Results({@Result(property = "id", column = "id", id = true),@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),@Result(property = "birthday", column = "birthday"),@Result(property = "sex", column = "sex"),@Result(property = "address", column = "address"),@Result(property = "roleList", javaType = List.class, column = "id", many = @Many(select = "com.ning.mapper.RoleMapper.findRoleById", fetchType = FetchType.EAGER))})List<User> findAllWithRole();@Select("select * from sys_role r inner join sys_user_role ur on ur.roleid = r.id where ur.userid = #{id}")List<Role> findRoleById(int id);
二级缓存注解
@CacheNamespace
在你想要开启二级缓存的mapper类上加这个注解
延迟加载
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY 表示懒加载fetchType = FetchType.EAGER 表示立即加载fetchType = FetchType.DEFAULT 表示使用全局配置

