写于:2019-06-10 08:52:37
待整理
一、Hystrix 封装对象回顾
在 Hystrix工作流程解析 中,提到 Hystrix 提供了两种封装对象 HystrixCommand 和 HystrixObservableCommand。
它们分别提供了四种执行方式:
- execute()
- queue()
- observe()
- toObservable()
官方针对这四种执行方式给定了说明:
the first two are only applicable to simple HystrixCommand objects and are not available for the HystrixObservableCommand
通过查看源码也能够知道 execute() 和 queue() 只在 HystrixCommand 中有定义,是 HystrixCommand 的专属方法。而 HystrixObservalbeCommand 没有定义。
但是通过查看源码,我们能够得知:HystrixCommand 和 HystrixObservableCommand 都继承了抽象类 AbstractCommand。而 HystrixCommand 中的 execute() 和 queue() 最终调用的是 AbstractCommand 中的 toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture() 。
HystrixCommand 和 HystrixObservableCommand 都有各自的实现方式,但是最终都是调用的 AbstractCommand 中的方法实现。
二、测试数据准备
提供一个简单的 web 业务处理接口 http://localhost:9527/hello-world/{name}
@RequestMapping("/hello-world/{name}")public String helloWrold(@PathVariable String name){System.err.println("---->Hello world " + name);return "Hello World " + name;}
三、编码方式使用 HystrixCommand 和 HystrixObservableCommand
(基于 Hystrix 1.5.18)
3.1、HystrixCommand 包裹业务执行方法 “ 调用 hello-world 接口”
public class Case1 extends HystrixCommand<String> {private final String param;private RestTemplate restTemplate;/** 构造方法,传入 业务参数 和 http 请求方法 restTemplate **/public Case1(String param, RestTemplate restTemplate){super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));this.restTemplate = restTemplate;this.param = param;}/** 业务执行方法 **/@Overrideprotected String run() throws Exception {return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/"+ param,String.class);}/** 业务执行异常,调用方法 **/@Overrideprotected String getFallback() {return "出现异常执行 fallback";}}
进行单元测试
@Testpublic void testSynchronous(){assertEquals("Hello World World", new Case1("World",new RestTemplate()).execute());assertEquals("Hello World Bob", new Case1("Bob",new RestTemplate()).execute());}@Testpublic void testAsynchronous() throws Exception {assertEquals("Hello World World", new Case1("World",new RestTemplate()).queue().get());assertEquals("Hello World Bob", new Case1("Bob",new RestTemplate()).queue().get());}@Testpublic void testObserve() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// non-blockingObservable<String> ob = new Case1("World", new RestTemplate()).observe();ob.subscribe(new Observer<String>() {@Overridepublic void onCompleted() {System.err.println("-----> onCompleted");}@Overridepublic void onError(Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();}@Overridepublic void onNext(String s) {System.err.println("-----> onNext :" + s);}});ob.subscribe(new Action1<String>() {@Overridepublic void call(String s) {System.err.println("------> call:" + s);}});assertEquals("Hello World World", ob.toBlocking().toFuture().get());}@Testpublic void testToObservable(){// blockingObservable<String> ob = new Case1("World", new RestTemplate()).toObservable();assertEquals("Hello World World", new Case1("World",new RestTemplate()).toObservable().toBlocking().single());}
3.2、HystrixObservableCommand 包裹业务执行方法 “ 调用 hello-world 接口”
public class Case1_1 extends HystrixObservableCommand<String> {private final String name;private RestTemplate restTemplate;public Case1_1(String name,RestTemplate restTemplate) {super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));this.name = name;this.restTemplate = restTemplate;}@Overrideprotected Observable<String> construct() {return Observable.create(new Observable.OnSubscribe<String>() {@Overridepublic void call(Subscriber<? super String> observer) {try {if (!observer.isUnsubscribed()) {// a real example would do work like a network call hereString result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + name, String.class);observer.onNext(result);observer.onCompleted();}} catch (Exception e) {observer.onError(e);}}} ).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io());}@Overrideprotected Observable<String> resumeWithFallback() {return Observable.create(new Observable.OnSubscribe<String>(){@Overridepublic void call(Subscriber<? super String> subscriber) {try {if (!subscriber.isUnsubscribed()) {subscriber.onNext("fallback!");subscriber.onNext("失败异常!");subscriber.onCompleted();}} catch (Exception e) {subscriber.onError(e);}}}).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io());}}
执行单元测试
@Testpublic void tetObservable2(){Observable<String> observe = new Case1_1("World",new RestTemplate()).observe();Iterator<String> iterator = observe.toBlocking().getIterator();StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();while (iterator.hasNext()){sb.append(iterator.next());}assertEquals("Hello World World",sb.toString());}@Testpublic void testToObservable2(){Observable<String> observe = new Case1_1("World",new RestTemplate()).toObservable();Iterator<String> iterator = observe.toBlocking().getIterator();StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();while (iterator.hasNext()){sb.append(iterator.next());}assertEquals("Hello World World",sb.toString());}
在 web 开发中(spring mvc),我们来对比一下普通的业务调用和使用编码方式之后的业务调用。
@RequestMapping("/hystrix")public String command(){// 编码方式:使用 HystrixCommand 包装原始的接口调用,需要定义新的 HystrixCommand 包装对象。return new Case1("WTF名字好难取",restTemplate).execute();// 传统调用接口的方式//return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + "WTF名字好难取",String.class);}
使用 Hystrix 编码方式进行开发带来的问题:
- 1、耦合高。业务方法需要耦合到 HystrixCommand 对象中
- 2、代码量大。每一个使用 HystrixCommand 对象封装的 API 接口都需要定义一个新的 HystrixCommand封装类
四、注解方式使用 HystrixCommand 和 HystrixObservableCommand(基于 Hystrix 1.5.18,Spring Boot 2.1.5)
4.1、注解方式使用 HystrixCommand 封装业务接口
同步调用
/** sync **//** 注解方式,需要开启:@EnableCircuitBreaker **/@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "syncCommandFallback",commandProperties = {@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value = "1000")})@RequestMapping("/hystrix-sync/{param}")public Object syncCommand(@PathVariable String param,@RequestParam(value = "error",defaultValue = "1") int error,@RequestParam(value = "timeout",defaultValue = "100") int timeout) throws InterruptedException {// 模拟异常熔断int a = 1 / error;// 模拟超时Thread.sleep(timeout);return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + param,String.class);}/** <p> fallback 方法:需要与 注解方法参数对应 </p> **/public String syncCommandFallback(String param,int error,int timeout){return "syncCommandFallback";}
异步调用
/** async **//** 注解方式,需要开启:@EnableCircuitBreaker **/@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "case2Fallback")@RequestMapping("/hystrix-async/{param}")public Object asynccommand(@PathVariable String param, int error){int a = 1 / error;AsyncResult<String> asyncResult = new AsyncResult<String>() {@Overridepublic String invoke() {return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + param,String.class);}};return asyncResult;}/** <p> fallback 方法:需要与 注解方法参数对应 **/public String case2Fallback(String param,int error){return "case2Fallback";}
4.2、注解方式使用 HystrixObservableCommand
observe()
// HystrixObservableCommand 注解方式使用/** EAGER参数表示使用observe()方式执行 **/@HystrixCommand(observableExecutionMode = ObservableExecutionMode.EAGER,fallbackMethod = "case2Fallback") //使用observe()执行方式@RequestMapping("/hystrix-observer/{param}")public Observable<String> observer(@PathVariable String param, int error) {return Observable.create(new Observable.OnSubscribe<String>() {@Overridepublic void call(Subscriber<? super String> subscriber) {try {if(!subscriber.isUnsubscribed()) {int a = 1 / error;String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + param, String.class);subscriber.onNext(result);subscriber.onCompleted();}} catch (Exception e) {subscriber.onError(e);}}});}/** <p> fallback 方法:需要与 注解方法参数对应 **/public String case2Fallback(String param,int error){return "case2Fallback";}
toObservalbe()
/** LAZY参数表示使用toObservable()方式执行 **/@HystrixCommand(observableExecutionMode = ObservableExecutionMode.LAZY,fallbackMethod = "case2Fallback") //表示使用toObservable()执行方式@RequestMapping("/hystrix-to-observer/{param}")public Observable<String> toObserver(@PathVariable String param, int error) {return Observable.create(new Observable.OnSubscribe<String>() {@Overridepublic void call(Subscriber<? super String> subscriber) {try {if(!subscriber.isUnsubscribed()) {// 异常熔断控制int a = 1 / error;String results = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9527/hello-world/" + param, String.class);// 结果填入发送方subscriber.onNext(results);subscriber.onCompleted();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();subscriber.onError(e);}}});}/** fallback 方法:需要与 注解方法参数对应 **/public String case2Fallback(String param,int error){return "case2Fallback";}
五、Hystrix 集成 Feign (基于 spring boot 2.1.5 ,spring cloud Greenwich.SR1)
5.1、Feign 整合 hystrix
- step1、开启 feign 对于 hystrix 的支持
feign 手动开启 hystrix feign.hystrix.enabled=true
- step2、注解开启 feign 和 hystrix
- step3、feign 使用 hystrix 功能
声明方法调用熔断 fallback 方法
@Componentpublic class UserClientFallback implements FallbackFactory<UserClient> {@Overridepublic UserClient create(Throwable throwable) {return new UserClient() {@Overridepublic String saveUser(Long userId) {return "save faild";}@Overridepublic String queryUserByUserId(Long userId) {return "query faild";}};}}
feign 调用使用 hystrix fallback 方法
@FeignClient(name = "provider",fallbackFactory = UserClientFallback.class)public interface UserClient extends IUserController {}
5.2、通过全局配置 hystrix 策略
如:(更多配置参考 Hystrix 官方配置 )
hystrix 全局配置超时时间:1000ms hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds = 1000
5.3、针对特定接口进行细粒度控制
通过引入 feign 依赖和 hystrix 依赖,开启 feign 熔断之后,spring boot 会自动进行配置。
之后我们可以通过在 application.properties 或者 Bean 的方式进行 hystrix 的全局策略配置。
在开发过程中,大部分接口的配置使用相同的 hystrix 配置策略即可,但是在特定的场合中,如:某个接口的运行时间相对较长,超时时间1000ms 不够,这时候可以通过在接口上添加的自定义 HystrixCommand 来配置。
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "syncCommandFallback",commandProperties = {// 该接口调用时长较长,进行特殊配置 2000ms@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value = "2000")})@RequestMapping("/hystrix-sync/{param}")public Object syncCommand(......){......}
如果此时 hystrix 全局的超时时间配置为 1000ms ,此接口优先使用自定义的 hystrix 策略。
六、Hystrix 常用的配置策略
参考官方链接:Hystrix 配置
6.1、Execution 【HystrixCommand.run() 执行相关参数】
- hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy = Thread
配置线程隔离。两种:THREAD(线程池) 和 Semaphore (信号量)。默认:THREAD 线程池 - hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds = 1000
hystrixcommand 命令执行超时时间。默认:1000 ms。 - hystrix.command.default.execution.timeout.enabled = true
hystrixcommand 命令执行是否开启超时。默认:true - hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout = true
hystrixcommand 命令执行发生超时时是否中断执行操作。默认:true - hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests = 10
线程隔离为Semaphore 。允许的最大请求数。默认:10。
6.2、Fallback 【Fallback 相关参数】
- hystrix.command.default.fallback.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests = 10
线程隔离为Semaphore。fallback 信息允许的最大并发数。超过不会再走 fallback,直接抛出异常。默认:10。 - hystrix.command.default.fallback.enabled = true
是否开启异常自定义信息 fallback,不开启时异常直接抛出。默认:true。
6.3、Circuit Breaker 【Hystrix 熔断相关参数】
- hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.enabled = true
是否开启熔断机制。默认:true。 - hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage = 50
fallback 逻辑错误比率阈值,达到阈值会触发 fallback。默认:50。 - hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.forceOpen = false
强制开启熔断机制,相当于拒绝所有请求。默认:false。
6.4、Thread Pool Properties 【Hystrix 线程池相关参数】
- hystrix.threadpool.default.coreSize = 10
线程隔离为THREAD时,线程核心大小。默认:10. - hystrix.threadpool.default.maximumSize = 10
线程隔离为THREAD时,最大线程数据。默认:10。
注意:Hystrix 1.5.9 之前,coreSize == maximumSize 。Hystrix 1.5.9 后 hystrix.threadpool.default.allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize = true 时,可以分别设置 coreSize 和 maximumSize 为不同的值。
6.5、线程池相关配置策略选择
针对线程池相关的配置设置,Hystrix 官方给出了如下的计算公式:
requests per second at peak when healthy × 99th percentile latency in seconds + some breathing room
每秒正常的请求峰值 * 99%的请求延迟(也就是请求响应延迟) + 预留的缓冲
下图是 Hystrix 官方给出的一个例子。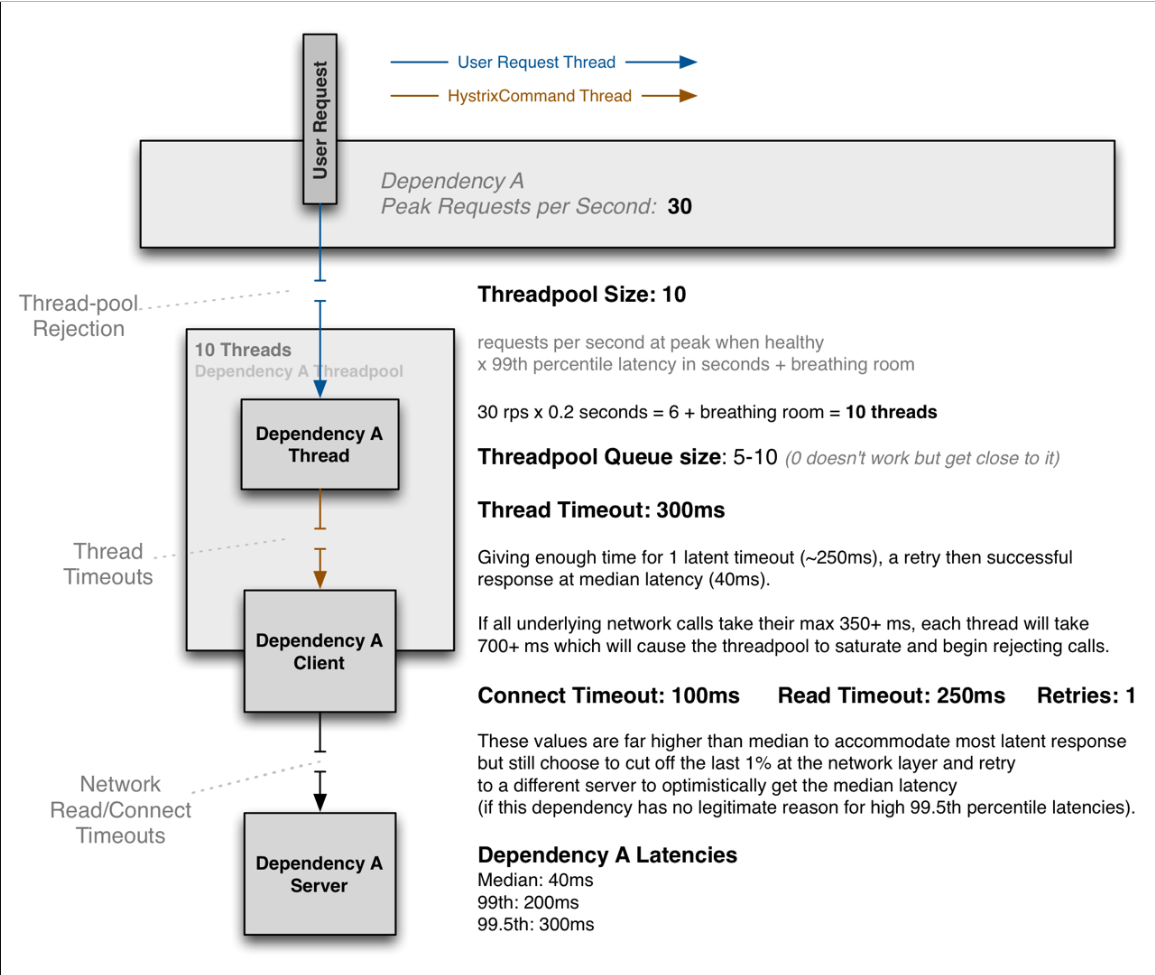
图中定义:每秒有30个峰值请求,每个请求的响应延迟为200ms(0.2s),预留 4 个线程。
所以 Hystrix 线程池配置 为 30 * 0.2 + 4 = 10
或者
每个线程每秒处理请求数:1000 /200 = 5 个请求
30个请求需要: 30 / 5 = 6 个线程
总线程数 = 峰值请求数所需线程 + 缓冲预留线程数 = 6 + 4 = 10 个线程。

