异常
什么是异常
在程序执行中,任何中断正常程序流程的条件就是错误或异常。例如,程序运行发生下列情况时,会出现异常:
1.想打开的文件不存在
2.网络连接中断
3.接受了不符合逻辑的操作数
4.系统资源不足
Throwable类是Java语言中所有错误或异常的超类。
Error、RuntimeException及其子类、其它异常表示一种运行时的困难,它通常由环境效果引起,可以进行处理。
在Java编程语言中,错误类(Error)定义被认为是不能恢复的严重错误条件(如资源耗尽)。在大多数情况下,当遇到这样的错误时,建议让程序中断,应用程序一般不对此问题进行处理。
异常处理允许程序捕获异常(Exception),处理它们,然后继续程序执行。它是分层把关,因此,错误情况不会介入到程序的正常流程中。
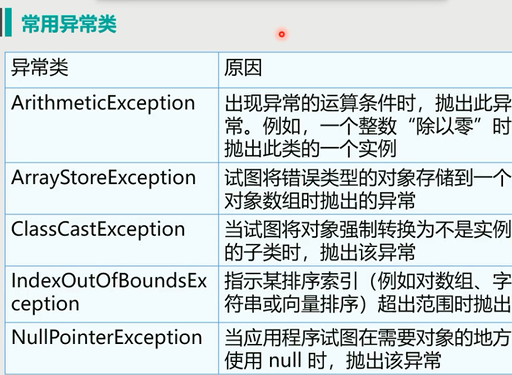
异常分类
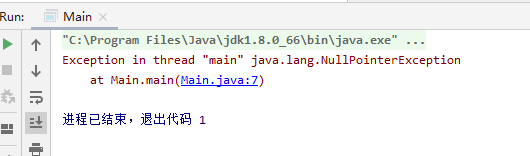
空指针异常
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = nul1;System.out.println(str.length());}}
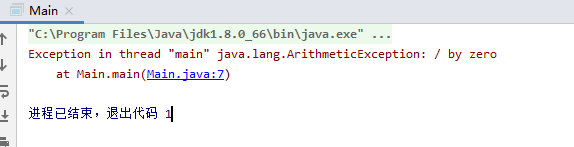
算数异常
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args){int divisor=10;double quotient =0d;quotient =divisor/0;System.out.println("quotient="+quotient);}}
程序中的异常从哪里来
1、程序运行过程中,运行环境检测到错误抛出的异常。
2、程序调用的方法可能会抛出异常。
如:File类的方法createTempFile
java语法中,有一些方法定义的时候有可能会出错,所以在编写的时候就有异常的提示
Ctrl+左键单击 可以进去看方法的定义
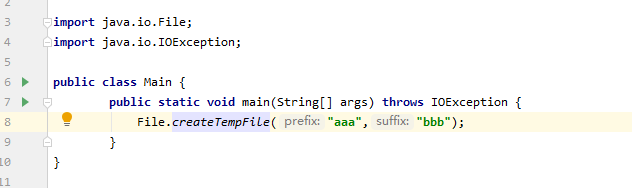
看到createTempFile方法定义中就抛出了异常,那我们就需要捕获异常(catch)或者向上抛(throw)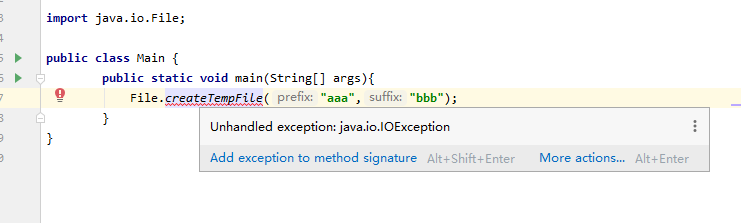
注:异常对象包含有关异常的信息,包括它的类型和出错时程序的状态。
向上抛异常:
这个有点不负责任,你写代码有可能会出错,谁调用了main方法才会去处理
import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File.createTempFile("aaa","bbb");}}
捕获异常:
就是在调用方法时,设置好异常捕获语句块,出了问题会直接进入异常处理
import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args){try {File.createTempFile("aaa","bbb");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
eg:
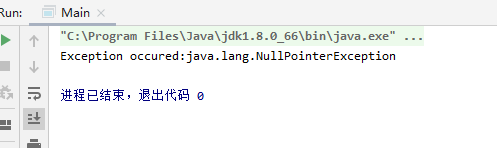
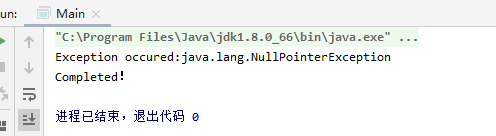
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = null;int length = 0;try {length = str.length();//空值调用方法System.out.println(length);} catch (NullPointerException e) {System.out.println("Exception occured:" + e);} finally {System.out.println("Completed!");}}}
eg:
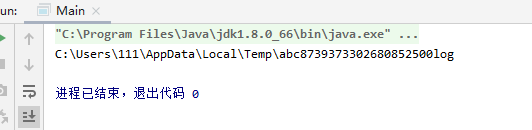
import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try{File tmp= File.createTempFile("abc","log");System.out.println(tmp. getAbsolutePath());} catch(IOException e){System. out. println(e. getMessage());}}}
使用try-catch捕获异常
使用try-catch捕获异常
语法格式:
try{//try代码块中的代码有可能抛出异常}catch(MyExceptionType e){//处理try代码块中抛出的MyExceptionType类型的异常实例e}finally{//无论是否有异常抛出,此部分代码总是被最后执行}
多异常情况下的catch
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = null;int length = 0;try {length = str.length();//空值调用方法System.out.printin(length);} catch (NullPointerException e) {System.out.println("Exception occured:" + e);} catch (ArithmeticException e) {System.out.println("Exception occured:" + e);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("Exception occured:" + e);}}}
finally语句
finally语句在try/catch/finally是一个可选的部分。
finally语句定义一个总是执行的代码块,而不考虑异常是否波捕获。所以它提供了在try/catch代码块执行结束后的后处里机制。下面一个用户登录验证的模拟过程:
try{查找用户;匹配密码}catch(AccountNotFoundException e){处理没有发现账号的异常;}catch(PasswordMismatchException e)处理账号密码不匹配的异常;}finally{登记本次访问;}
注意:一个try块可以不执行finally子句就能够退出的唯一方法是通过调用System.exit()方法来实现的。
捕获所有异常
所有异常使用Exception
catch(Exception e){...}
自定义异常
用户定义异常是通过扩展Exception类或子类来创建的一种具有特殊用途的子类,这种异常类可以包含一个“普通”类所包含的任何东西
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {class AccountNotFoundException extends Exception {String account;public AccountNotFoundException() {super("This account has not found.");}public AccountNotFoundException(String account) {super("This account about" + account + "has not found.");this.account = account;}public String getAccount () {return this.account;}}}}
方法声明中的异常
public class AccountNotFoundException extends Exception {String account;public AccountNotFoundException(){super("this account has not found");}public AccountNotFoundException(String account){super("this account about"+account+"has not found");}public String getAccount(){return this.account;}}
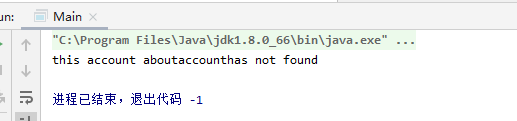
public class User {public void login(String account, String password)throws AccountNotFoundException {boolean accountExisted = false;//默认帐号不存在,改成true就登陆成功String otherPassword;//此处可插入查询帐号的代码if (false==accountExisted) {//如果帐号不存在,抛出异常,程序中断throw new AccountNotFoundException(account);}}}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {User user = new User();try {user.login("account", "password");} catch (AccountNotFoundException e) {//插入处理帐号不存在的代码System.out.println(e.getMessage());System.exit(-1);}//插入登陆成功的代码System.out.println("登陆成功/");}}
运行结果
public class Main {static void foo() throws Exception {throw new Exception();}public static void main(String args[]) {try {foo();} catch (Exception e) {System.exit(0);} finally {System.out.println("In finally");}}}
捕获异常的顺序
那个catch语句块在前面,谁先捕获