输出流介绍
输入输出用在什么地方?
◆复制粘贴文件。
◆修改文件
Java中的输入输出流
◆ System。out;printIng;/将数据输出到屏幕上
◆ new Scanner(System.in)next;/获取输入流的数据
File类的使用
File类的介绍
什么是文件?
◆文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合
◆举例
◆文件、文件夹都是文件
◆Java中使用 java.io.Fie类
◆对文件进行操作
File类的常见方法

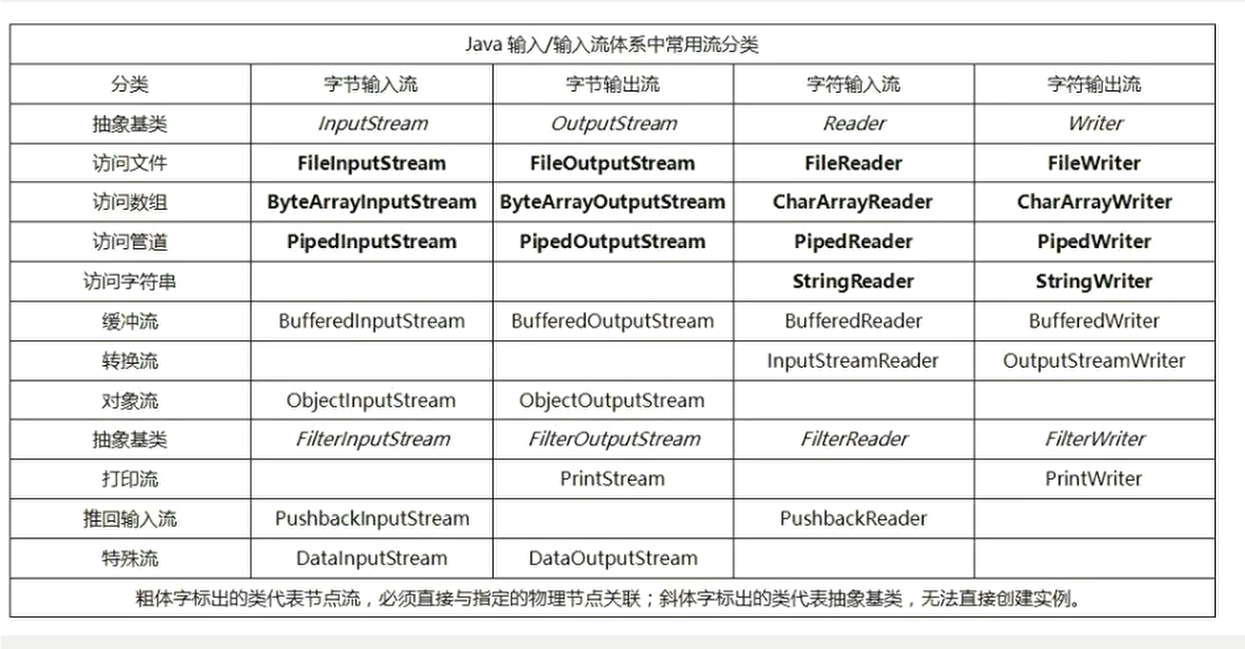
字节流
字节输入流 EInputstream
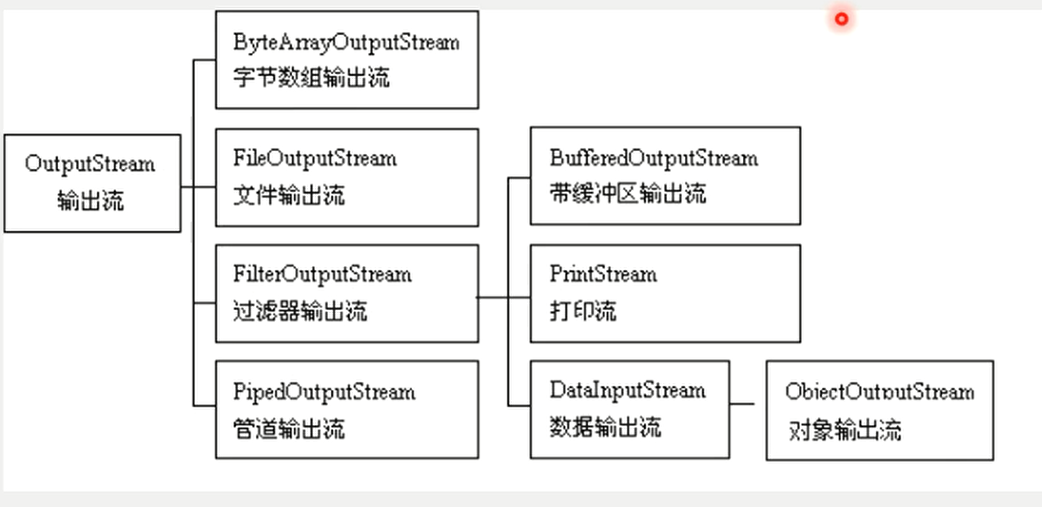
字节输出流 OutputStream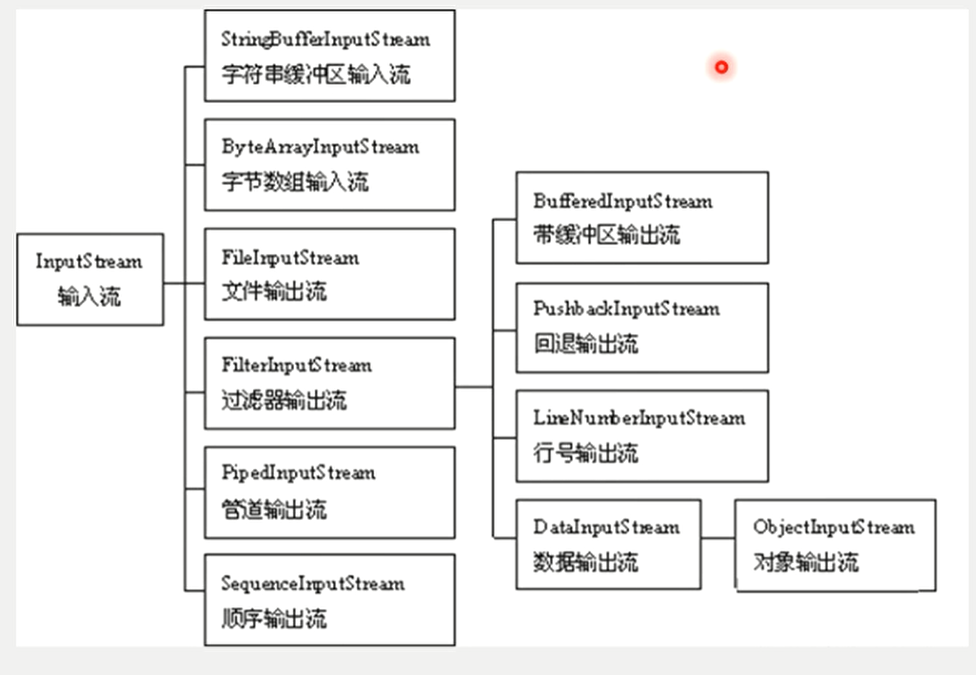
FileInputStream
从文件系统中的某个文件中获取输入字节
用于读取文件、图像等数据的原始字节流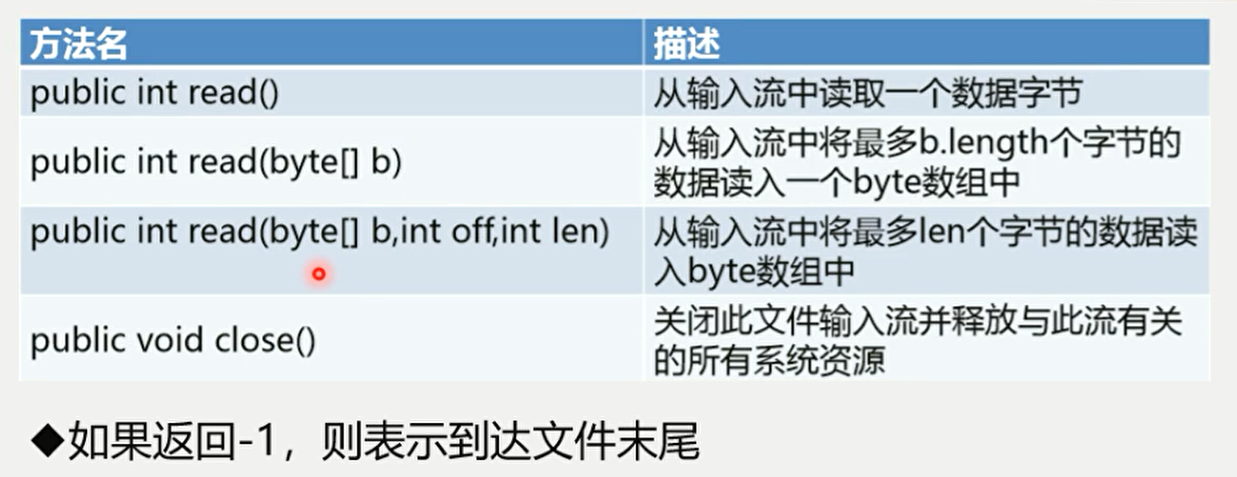
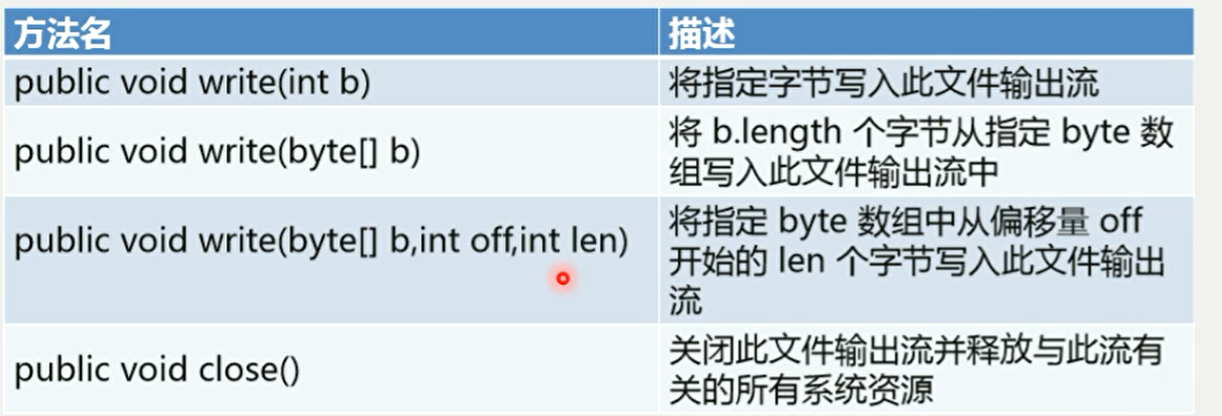
FileOutputStream
public class FileCtrl {// 创建文件public static File CreateFile(String filePath){// 1. 创建文件对象File file = new File(filePath);// 2. 判断文件是否存在if(!file.exists()){try {file.createNewFile();return file;} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;}}return file;}public static String ReadFile(File file){try {// 1. 创建文件输入流对象FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);// 2. 循环读取ByteArrayOutputStream arrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();byte bytes[] = new byte[10 24];// 缓冲数组int nRet = 0; //读取的返回字节数while (true){nRet = inputStream.read(bytes,0,1024);if(nRet==-1)break;arrayOutputStream.write(bytes,0,nRet);}inputStream.close();//记得关闭文件return new String(arrayOutputStream.toString());} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return null;}public static boolean WriteFile(File file,String content){boolean bRet = false;try {// 1. 创建文件输出流对象FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);// 2. 写入数据byte bytes[] = content.getBytes();fileOutputStream.write(bytes);bRet = true;fileOutputStream.close();//记得关闭文件} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return bRet;}public static String DeleteFile(File file){if (file.exists()){// 删除文件if (file.isFile()){file.delete();}// 删除目录else if (file.isDirectory()){// 删除目录下的每一个文件File[] files = file.listFiles();for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {// 递归删除DeleteFile(files[i]);}// 删除目录file.delete();}}return null;}}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = FileCtrl.CreateFile("1.txt");FileCtrl.WriteFile(file,"hello15pb");String content = FileCtrl.ReadFile(file);System.out.println(content);// FileCtrl.DeleteFile(file);}}
字符流
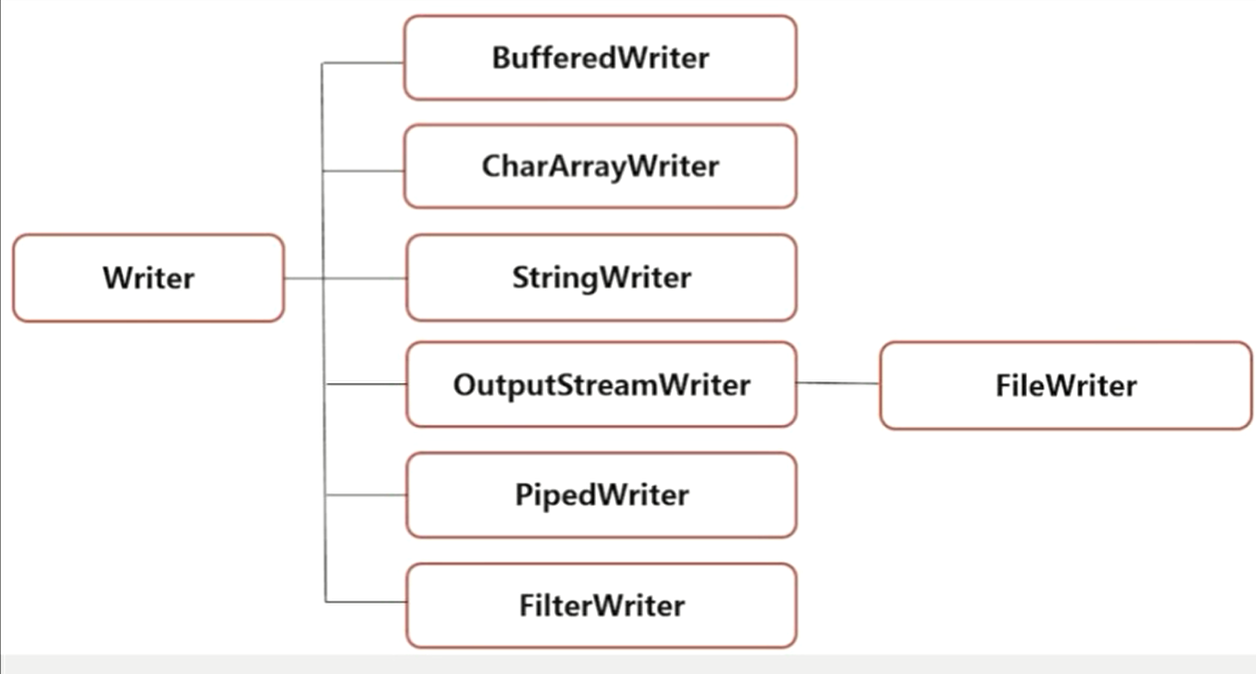
字符输入流 Reader
字符输出流 Writer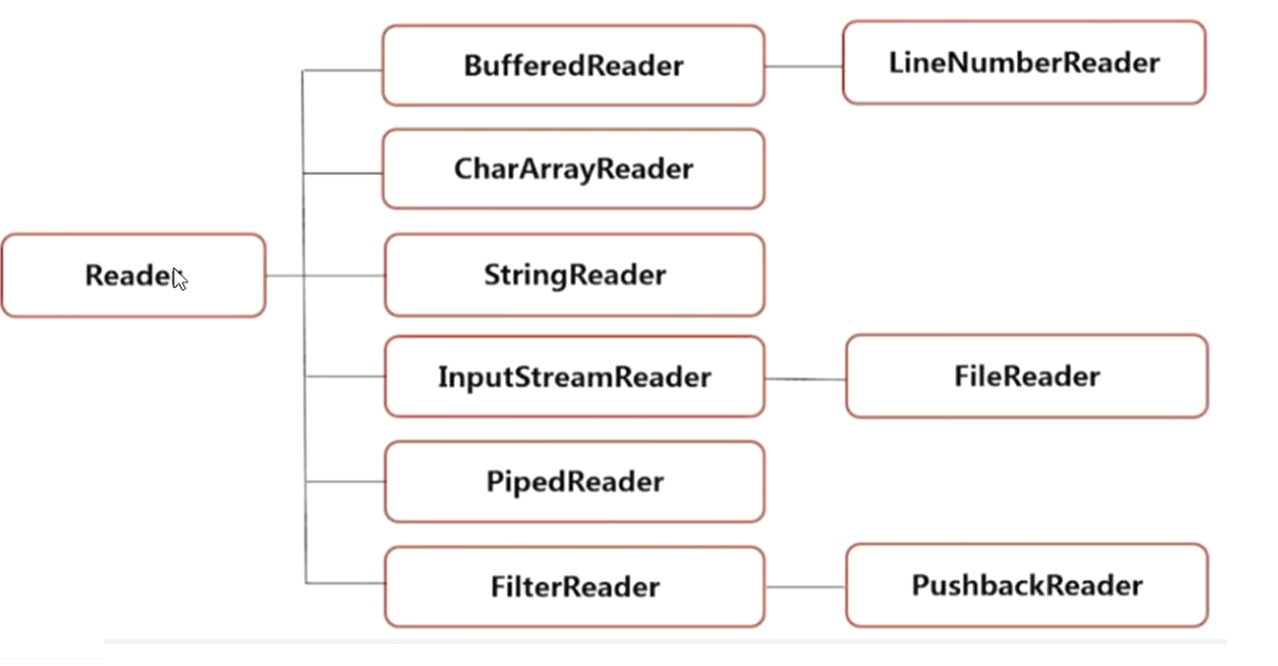
Java输入输出流体系
比较器
◆如果现在要想为一组对象进行排序,那么必须有一个可以区分出对象大小的关系操作,而这个操作在Java之中就是利用比较器完成的常用比较器:Comparable如果要为对象指定比较规则,那么对象所在的类必须实现 Comparable接口,下面首先来看一下这个接口的定义:
public interface Comparable<T>{public int compareTo(T o);}
根据文档的要求:要排序的数组所在的类一定要实现此接口,此接口返回的是int型数据,而用户覆写此方法的时候只需要返回三种结果:1(>0)、-1(<0)、0(=0)即可。
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}private String name ;private int age ;public Person(String name,int age) {this.name = name ;this.age = age ;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n";}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Person o) {if (this.age > o.age) {return 1;} else if (this.age < o.age) {return -1;} else {return 0;}}}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Person per[] = new Person[] {new Person("张三", 20),new Person("李四", 19),new Person("王五", 21)};Arrays.sort(per) ; // 排序System.out.println(Arrays.toString(per));}}
挽救的比较器
之前使用的 Comparable实际上是在一个类定义的时候就已经具备的功能了但是如果说现在一个类已经定义完成了。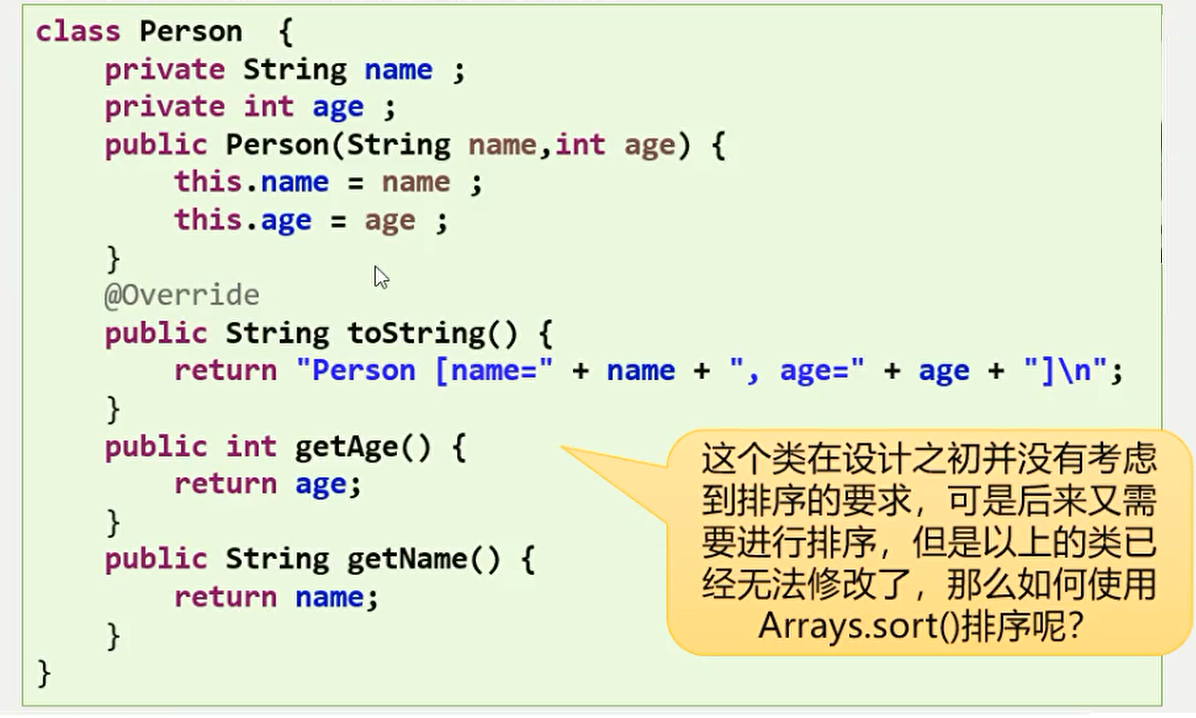
为了解决这样的问题,在java里面又提供了另外一个比较器接口java.util.Comparator接口,这个接口的定义如下:
public interface Comparator<T>{public int compare (t ol, T 02);public boolean equals(object obj);}
◆在 compare()方法上存在了两个参数用于比较大小,而要想使用这个接口,需要单独定义一个比较规则类
public class PersonComparator implements Comparator<Person> {@Overridepublic int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {if (o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()) {return 1;} else if (o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()) {return -1;} else {return 0;}}}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Person per[] = new Person[] {new Person("张三", 20),new Person("李四", 19),new Person("王五", 21)};Arrays.sort(per, new PersonComparator()); // 排序System.out.println(Arrays.toString(per));}}

