目录
- 通信底层介绍
- 通信整体流程
- 惊艳的设计
**
通信底层介绍
xxl-job 使用 netty http 的方式进行通信,虽然也支持 Mina,jetty,netty tcp 等方式,但是代码里面固定写死的是 netty http。
**
通信整体流程
我以调度器通知执行器执行任务为例,绘制的活动图:
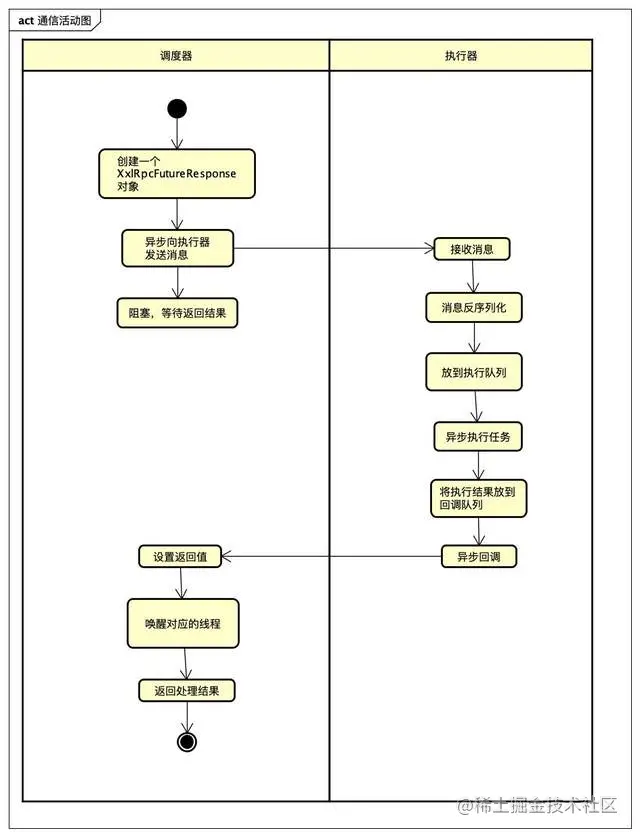
活动图
**
惊艳的设计
看完了整个处理流程代码,设计上可以说独具匠心,将 netty,多线程的知识运用得行云流水。
我现在就将这些设计上出彩的点总结如下:
| 使用动态代理模式,隐藏通信细节
xxl-job 定义了两个接口 ExecutorBiz,AdminBiz,ExecutorBiz 接口中封装了向心跳,暂停,触发执行等操作,AdminBiz 封装了回调,注册,取消注册操作,接口的实现类中,并没有通信相关的处理。
XxlRpcReferenceBean 类的 getObject() 方法会生成一个代理类,这个代理类会进行远程通信。
| 全异步处理
执行器收到消息进行反序列化,并没有同步执行任务代码,而是将任务信息存储在 LinkedBlockingQueue 中,异步线程从这个队列中获取任务信息,然后执行。
而任务的处理结果,也不是说处理完之后,同步返回的,也是放到回调线程的阻塞队列中,异步的将处理结果返回回去。
这样处理的好处就是减少了 netty 工作线程的处理时间,提升了吞吐量。
| 对异步处理的包装
对异步处理进行了包装,代码看起来是同步调用的。
我们看下调度器,XxlJobTrigger 类触发任务执行的代码:
public static ReturnT<String> runExecutor(TriggerParam triggerParam, String address){ReturnT<String> runResult = null;try {ExecutorBiz executorBiz = XxlJobScheduler.getExecutorBiz(address);//这里面做了很多异步处理,最终同步得到处理结果runResult = executorBiz.run(triggerParam);} catch (Exception e) {logger.error(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job trigger error, please check if the executor[{}] is running.", address, e);runResult = new ReturnT<String>(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, ThrowableUtil.toString(e));}StringBuffer runResultSB = new StringBuffer(I18nUtil.getString("jobconf_trigger_run") + ":");runResultSB.append("<br>address:").append(address);runResultSB.append("<br>code:").append(runResult.getCode());runResultSB.append("<br>msg:").append(runResult.getMsg());runResult.setMsg(runResultSB.toString());return runResult;}
ExecutorBiz.run 方法我们说过了,是走的动态代理,和执行器进行通信,执行器执行结果也是异步处理完,才返回的,而这里看到的 run 方法是同步等待处理结果返回。
我们看下xxl-job是如何同步获取处理结果的:调度器向执行器发出消息后,该线程阻塞。等到执行器处理完毕后,将处理结果返回,唤醒被阻塞的线程,调用处拿到返回值。
动态代理代码如下:
//代理类中的触发调用if (CallType.SYNC == callType) {// future-response setXxlRpcFutureResponse futureResponse = new XxlRpcFutureResponse(invokerFactory, xxlRpcRequest, null);try {// do invokeclient.asyncSend(finalAddress, xxlRpcRequest);// future getXxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = futureResponse.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);if (xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg() != null) {throw new XxlRpcException(xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg());}return xxlRpcResponse.getResult();} catch (Exception e) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-rpc, invoke error, address:{}, XxlRpcRequest{}", finalAddress, xxlRpcRequest);throw (e instanceof XxlRpcException)?e:new XxlRpcException(e);} finally{// future-response removefutureResponse.removeInvokerFuture();}}
XxlRpcFutureResponse 类中实现了线程的等待,和线程唤醒的处理:
//返回结果,唤醒线程public void setResponse(XxlRpcResponse response) {this.response = response;synchronized (lock) {done = true;lock.notifyAll();}}@Overridepublic XxlRpcResponse get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {if (!done) {synchronized (lock) {try {if (timeout < 0) {//线程阻塞lock.wait();} else {long timeoutMillis = (TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS==unit)?timeout:TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(timeout , unit);lock.wait(timeoutMillis);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw e;}}}if (!done) {throw new XxlRpcException("xxl-rpc, request timeout at:"+ System.currentTimeMillis() +", request:" + request.toString());}return response;}
有的同学可能会问了,调度器接收到返回结果,怎么确定唤醒哪个线程呢?
每一次远程调用,都会生成 uuid 的请求 id,这个 id 是在整个调用过程中一直传递的,就像一把钥匙,在你回家的的时候,拿着它就带开门。
这里拿着请求 id 这把钥匙,就能找到对应的 XxlRpcFutureResponse,然后调用 setResponse 方法,设置返回值,唤醒线程。
public void notifyInvokerFuture(String requestId, final XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse){// 通过requestId找到XxlRpcFutureResponse,final XxlRpcFutureResponse futureResponse = futureResponsePool.get(requestId);if (futureResponse == null) {return;}if (futureResponse.getInvokeCallback()!=null) {// callback typetry {executeResponseCallback(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {if (xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg() != null) {futureResponse.getInvokeCallback().onFailure(new XxlRpcException(xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg()));} else {futureResponse.getInvokeCallback().onSuccess(xxlRpcResponse.getResult());}}});}catch (Exception e) {logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);}} else {// 里面调用lock的notify方法futureResponse.setResponse(xxlRpcResponse);}// do removefutureResponsePool.remove(requestId);}

