迪克斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
- 赋权图
,求赋权图中指定的两个顶点
间的具有最小权的路,这条路称为
间的最短路,它的权称为
间的距离,记为
。
- 迪克斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法基本思想是每一次都走最短的路,可以处理有向图或无向图。
当权为负数时,不能使用Dijkstra算法,要使用Floyd算法。
例子
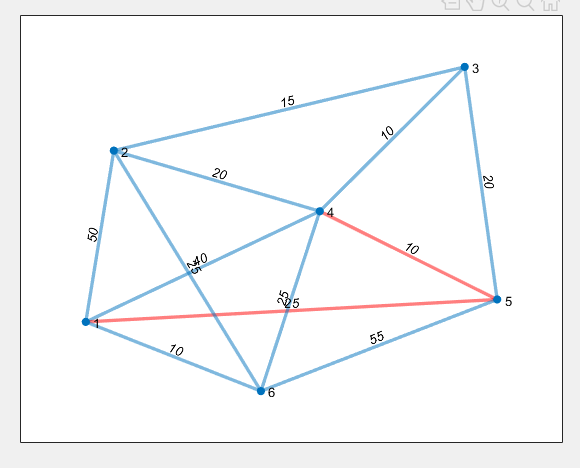
某公司在6个城市
有分公司,下表是两个城市之间的票价,若无直接航班,则为
。求
到其他城市的票价最便宜的路线图。
演示过程
[x] 先理解迪克斯特拉(Dojkstra)算法的思想,故演示如何寻找最短路径
初始化,visited是是否被标记为最优路径,distance是和初始节点的距离,parent_index是当前节点的父节点 | 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | | visited | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | distance | inf | inf | inf | inf | inf | inf | | parent_index | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 |
从节点1开始,当前节点为1 | 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | | visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | distance | 0 | inf | inf | inf | inf | inf | | parent_index | 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 |
将(未被访问节点的distance)和(当前节点的distance+当前节点到未被访问节点的距离)比较大小,由于40<inf,25<inf,10<inf,所以更新distance和parent_index | 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | | visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | distance | 0 | inf | inf | 40 | 25 | 10 | | parent_index | 1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
未被访问节点中节点6的distance最小,所以标记6为已访问,当前节点为6
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | inf | inf | 40 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
- 10+a(6,2)=10+25=35<inf,更新节点2的distance和parent_index
10+a(6,3)=10+inf,不更新节点3
10+a(6,4)=10+25=35<40,更新节点4的distance和parent_index
10+a(6,5)=10+55>25,不更新节点5
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | 35 | inf | 35 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | 6 | -1 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
未被访问节点中节点5的distance最小,所以标记5为已访问,当前节点为5
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | 35 | inf | 35 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | 6 | -1 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
- 25+a(5,2)=25+inf,不更新节点2
25+a(5,3)=25+20=45
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | 35 | 45 | 35 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
未被访问节点中节点2的distance最小,所以标记2为已访问,当前节点为2(2和4一样大,默认序号小的那个)
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | 35 | 45 | 35 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
同样的方法得到最终结果:
| 节点(index) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| visited | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| distance | 0 | 35 | 45 | 35 | 25 | 10 |
| parent_index | 1 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
matlab实现Dijkstra算法
clc,clear%% 初始化邻接矩阵a=zeros(6);%邻接矩阵初始化a(1,2)=50;a(1,4)=40;a(1,5)=25;a(1,6)=10;a(2,3)=15;a(2,4)=20;a(2,6)=25;a(3,4)=10;a(3,5)=20;a(4,5)=10;a(4,6)=25;a(5,6)=55;a=a+a';a(a==0)=inf;for i=1:length(a)a(i,i)=0;end%% 确定初始节点,初始化变量start_index=1;%初始节点temp=start_index;%当前节点distance=repelem(inf,length(a));%初始化所有节点和初始节点的距离distance(temp)=0;parent_index=repelem(-1,length(a));%父节点parent_index(temp)=1;visited=zeros(1,length(a));%节点是否已经被访问visited(temp)=1;%节点1被访问%%各节点到初始节点的最短距离while sum(visited)<length(a)%节点没有被访问完unvisited=find(visited==0);%将还没有被访问的节点索引放进unvisitedfor i=unvisitedif distance(temp)+a(temp,i)<distance(i)distance(i)=distance(temp)+a(temp,i);parent_index(i)=temp;endend[min_distance,index]=min(distance(unvisited));%找到未被访问的节点和当前节点的最近距离和节点temp=unvisited(index);%最小距离对应的下一个节点是unvisited中第index个值visited(temp)=1;enddisp(["各节点为" num2str([1:1:length(a)])]);disp(["各节点的父节点为" num2str(parent_index)]);disp(["各节点和初始节点的最短距离" num2str(distance)]);%%各节点到初始节点的最短路径for i=1:length(a)end_index=i;path=[end_index];while end_index ~= start_index && parent_index(end_index)~=-1path=[path,parent_index(end_index)];end_index=parent_index(end_index);endif parent_index(end_index)==-1disp([num2str(i) "无法到达初始节点"]);elsedisp([num2str(i) "到初始节点的最短路径" num2str(fliplr(path))]);%fliplr反转endend"各节点为" "1 2 3 4 5 6""各节点的父节点为" "1 6 5 6 1 1""各节点和初始节点的最短距离" "0 35 45 35 25 10""1" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1""2" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1 6 2""3" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1 5 3""4" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1 6 4""5" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1 5""6" "到初始节点的最短路径" "1 6"
python实现Dijkstra算法
a=np.array([[0,50,np.inf,40,25,10],[0,0,15,20,np.inf,25],[0,0,0,10,20,np.inf],[0,0,0,0,10,25],[0,0,0,0,0,55],[0,0,0,0,0,0]]);a=a+a.Ta## 确定初始节点,初始化变量start_index=0#初始节点temp=start_index#当前节点distance=np.array([float('inf')]*len(a))#初始化所有节点和初始节点的距离distance[temp]=0parent_index=np.array([-1]*len(a))#父节点parent_index[temp]=0visited=np.zeros(len(a))#节点是否已经被访问visited[temp]=1#节点1被访问## 各节点到初始节点的最短距离while np.sum(visited)<len(a):#节点没有被访问完unvisited=np.where(visited==0)[0]#将还没有被访问的节点索引放进unvisitedfor i in unvisited:if distance[temp]+a[temp,i]<distance[i]:distance[i]=distance[temp]+a[temp,i]parent_index[i]=tempmin_distance=min(distance[unvisited])index=np.where(distance[unvisited]==min_distance)[0][0] #第一个0是因为where得到的是一个元组,要把数组从元组里拿出来,#第二个0是当有多个索引时选择第一个temp=unvisited[index]#最小距离对应的下一个节点是unvisited中第index个值visited[temp]=1## 初始节点到某个节点的最短路径parent_index=list(parent_index)#转换成列表可以使用append方法,比较方便end_index=2path=[end_index]while end_index != start_index and parent_index[end_index]!=-1:path.append(parent_index[end_index])end_index=parent_index[end_index]if parent_index[end_index]==-1:print("初始节点%d无法到达节点%d"%(start_index,end_index))else:print("初始节点%d无法到达节点%d的最短路径为:"%(start_index,end_index))print(path[::-1])#path倒序输出
matlab自带最短路径函数
%% matlab自带算法s = [1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 5];t = [2 4 5 6 3 4 6 4 5 5 6 6];w = [50 40 25 10 15 20 25 10 20 10 25 55];G = graph(s,t,w);%无向图,digraph有向图plot(G, 'EdgeLabel', G.Edges.Weight, 'linewidth', 2) %画出图set( gca, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [] );[P,d] = shortestpath(G, 1, 4); %P是1到4的最短路径,d是最短距离,%无向图且所有边权重均为非负数时默认Dijkstra算法,具体情形可自行查询% 在图中高亮我们的最短路径myplot = plot(G, 'EdgeLabel', G.Edges.Weight, 'linewidth', 2); %首先将图赋给一个变量highlight(myplot, P, 'EdgeColor', 'r') %对这个变量即我们刚刚绘制的图形进行高亮处理(给边加上r红色)% 求出任意两点的最短路径矩阵D = distances(G);% 找出给定范围内的所有点 nearest(G,s,d)% 返回图形 G 中与节点 s 的距离在 d 之内的所有节点[nodeIDs,dist] = nearest(G, 2, 30);>> PP =1 5 4>> dd =35>> DD =0 35 45 35 25 1035 0 15 20 30 2545 15 0 10 20 3535 20 10 0 10 2525 30 20 10 0 3510 25 35 25 35 0>> nodeIDsnodeIDs =3465>> distdist =15202530
Floyd算法
- Floyd算法可以得到任意两个顶点之间的最短距离和路径
- 对于赋权图
,其中顶点集
,邻接矩阵
- Floyd算法的基本思想是递推产生一个矩阵序列
,
表示从顶点
到顶点
的路径上所经过的顶点序号不大于k的最短路径长度。
- 计算时用迭代公式
演示过程
同理,得
顶点 2 到顶点 5 得最短距离是,
,2——4——5
看2,4中间是否还有点,由于,所以没有其他点
看4,5中间是否还有点,由于,所以没有其他点
所以顶点 2 到顶点 5 得最短路径为:2——4——5
matlab代码
clc,clear%% 初始化邻接矩阵a=zeros(6);%邻接矩阵初始化a(1,2)=50;a(1,4)=40;a(1,5)=25;a(1,6)=10;a(2,3)=15;a(2,4)=20;a(2,6)=25;a(3,4)=10;a(3,5)=20;a(4,5)=10;a(4,6)=25;a(5,6)=55;a=a+a';a(a==0)=inf;for i=1:length(a)a(i,i)=0;end%% 初始化path矩阵n = size(a,1);dist = a;path = repelem(-1,n,n);%% 下面开始三个循环for k=1:n % 中间节点k从1- n 循环for i=1:n % 起始节点i从1- n 循环for j=1:n % 终点节点j从1-n 循环if dist(i,j)>dist(i,k)+dist(k,j) % 如果i,j两个节点间的最短距离大于i和k的最短距离+k和j的最短距离dist(i,j)=dist(i,k)+dist(k,j); % 那么我们就令这两个较短的距离之和取代i,j两点之间的最短距离path(i,j)=k; % 起点为i,终点为j的两个节点之间的最短路径要经过的节点更新为path(i,k)endendendend%% 找出任意两个顶点间的最短路劲sb=1;%起点db=6;%终点d=dist(sb,db);parent=path(sb,:);parent(parent==-1)=sb;mypath=db;t=db;while t~=sbp=parent(t);mypath=[p,mypath];t=p;end
该算法由matlab代码写出python代码就很简单了,不再展示