背景
用 golang 写的数据库不多,boltdb 是一个非常优秀的开源项目,目前虽然是 achieve 不维护了,但是依然有很多项目都在使用,比如在云原生领域最火的 etcd。笔者一直想学习 etcd,借此先把它的底层存储 boltdb 搞定。
boltdb 是一个B+树实现的嵌入式数据库,里面实现了 ACID 事务,对于理解数据库实现,理解 golang 的指针操作有非常大的帮助。 关于 B+树的概念本篇文章不做赘述,可以去网上搜下具体的原理和使用场景。
架构
boltdb的核心代码在 5K 行左右,我这里 fork 的是 v1.3.1 版本。
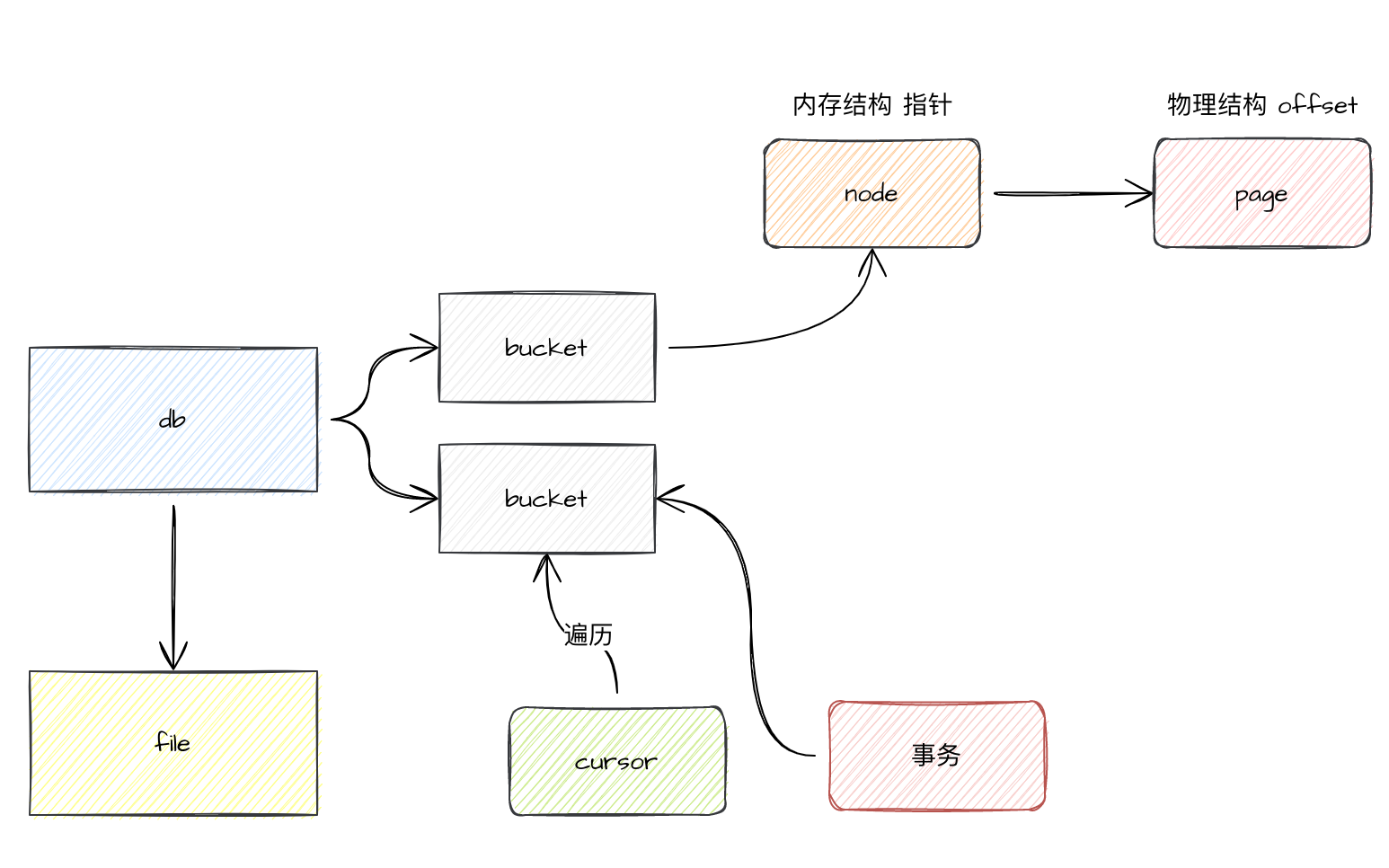
一个 db 一个文件,db 下可以有多个 bucket,bucket 类似于表,里面可以嵌套 bucket,也可以直接存放 kv 数据。一个 bucket 就是一颗 B+树,B+树的节点是 node,一个 node 可以存放多个 kv 数据,一个 kv 数据在内部是用 inode 来表示的,inode 映射到 page 的结构里,page 是直接和磁盘打交道的,也就是说在内存里的指针,在磁盘里就表现为 offset。
在 bucket 找数据,需要 cursor。 而数据的读和写需要事务,事务也是和 bucket 绑定的。接下来我们来一个个分析。
核心概念
page
首先先看下 page 的结构。
type pgid uint64type page struct {id pgidflags uint16count uint16overflow uint32ptr uintptr}// typ returns a human readable page type string used for debugging.func (p *page) typ() string {if (p.flags & branchPageFlag) != 0 {return "branch"} else if (p.flags & leafPageFlag) != 0 {return "leaf"} else if (p.flags & metaPageFlag) != 0 {return "meta"} else if (p.flags & freelistPageFlag) != 0 {return "freelist"}return fmt.Sprintf("unknown<%02x>", p.flags)}
page 可以存放很多结构类型的数据,在 boltdb 里,page 可以放 branch 枝干,leaf 叶子节点,可以放元信息,可以放特殊的 freelist 分配器。每个 page 都有唯一的 pageid。 ptr 指向的是 page 的数据内容,比如是kv 数据的话就代表 kv 数据的开始位置。
node
node 是 page 的内存结构,page 是非常底层的结构了,node 会更像 B+ 树的 node,可读性更好。一个 node 对应多个 page,持有 pageid 引用。
// node represents an in-memory, deserialized page.type node struct {bucket *BucketisLeaf boolunbalanced boolspilled boolkey []bytepgid pgid // 持有对应的 page 的 idparent *nodechildren nodesinodes inodes}
node 里面实际存放数据的是 inode。
// inode represents an internal node inside of a node.// It can be used to point to elements in a page or point// to an element which hasn't been added to a page yet.// inode 其实 node 的内部结构,才是持有 page 的 idtype inode struct {flags uint32 // 会存放好几种 flag,有 bucket 的 flagpgid pgidkey []byte // 存放了真实的数据value []byte}type inodes []inode
对于 node 的详细细节我这里不会描述的太多,很多时候我们只需要知道这个函数是做什么的就行了。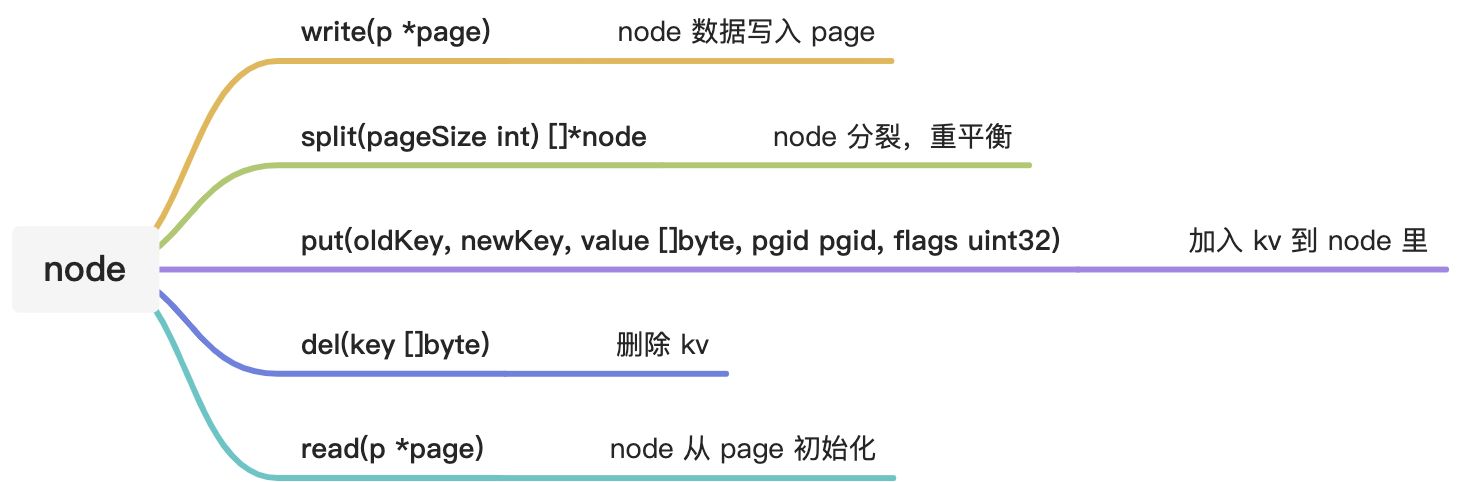
bucket
bucket 是表,一个 bucket 可以存放多个 kv 数据。
// Bucket represents a collection of key/value pairs inside the database.type Bucket struct {*buckettx *Tx // the associated transactionbuckets map[string]*Bucket // subbucket cachepage *page // inline page referencerootNode *node // materialized node for the root page.nodes map[pgid]*node // node cache// Sets the threshold for filling nodes when they split. By default,// the bucket will fill to 50% but it can be useful to increase this// amount if you know that your write workloads are mostly append-only.//// This is non-persisted across transactions so it must be set in every Tx.FillPercent float64}// bucket represents the on-file representation of a bucket.// This is stored as the "value" of a bucket key. If the bucket is small enough,// then its root page can be stored inline in the "value", after the bucket// header. In the case of inline buckets, the "root" will be 0.type bucket struct {root pgid // page id of the bucket's root-level pagesequence uint64 // monotonically incrementing, used by NextSequence()}
从代码可以看出,bucket 支持嵌套 bucket。一个 bucket 有一个 tx 事务绑定。bucket 的常用操作有如下。
// Cursor creates a cursor associated with the bucket.// The cursor is only valid as long as the transaction is open.// Do not use a cursor after the transaction is closed.func (b *Bucket) Cursor() *Cursor {// Update transaction statistics.b.tx.stats.CursorCount++// Allocate and return a cursor.return &Cursor{bucket: b,stack: make([]elemRef, 0),}}
遍历bucket,cursor 是每次需要的时候临时创建的,也就是说生命周期是跟一次遍历相同。
// Get retrieves the value for a key in the bucket.// Returns a nil value if the key does not exist or if the key is a nested bucket.// The returned value is only valid for the life of the transaction.func (b *Bucket) Get(key []byte) []byte {k, v, flags := b.Cursor().seek(key)// Return nil if this is a bucket.if (flags & bucketLeafFlag) != 0 {return nil}// If our target node isn't the same key as what's passed in then return nil.if !bytes.Equal(key, k) {return nil}return v}
从 bucket 里获取 KV 数据。可以看到获取是通过 cursor 游标来遍历的,这个就是 B+树的查找过程。
// Put sets the value for a key in the bucket.// If the key exist then its previous value will be overwritten.// Supplied value must remain valid for the life of the transaction.// Returns an error if the bucket was created from a read-only transaction, if the key is blank, if the key is too large, or if the value is too large.func (b *Bucket) Put(key []byte, value []byte) error {if b.tx.db == nil {return ErrTxClosed} else if !b.Writable() {return ErrTxNotWritable} else if len(key) == 0 {return ErrKeyRequired} else if len(key) > MaxKeySize {return ErrKeyTooLarge} else if int64(len(value)) > MaxValueSize {return ErrValueTooLarge}// Move cursor to correct position.// 找到合适的位置c := b.Cursor()k, _, flags := c.seek(key)// Return an error if there is an existing key with a bucket value.if bytes.Equal(key, k) && (flags&bucketLeafFlag) != 0 {return ErrIncompatibleValue}// Insert into node.// 插入到合适的 node 里key = cloneBytes(key)c.node().put(key, key, value, 0, 0)return nil}
插入操作也很简单,通过 cursor 找到 B+树合适的位置,返回 c,当前 c 持有的 node 就是合适的位置,把 kv 塞进去即可。
// Delete removes a key from the bucket.// If the key does not exist then nothing is done and a nil error is returned.// Returns an error if the bucket was created from a read-only transaction.func (b *Bucket) Delete(key []byte) error {if b.tx.db == nil {return ErrTxClosed} else if !b.Writable() {return ErrTxNotWritable}// Move cursor to correct position.c := b.Cursor()_, _, flags := c.seek(key)// Return an error if there is already existing bucket value.if (flags & bucketLeafFlag) != 0 {return ErrIncompatibleValue}// Delete the node if we have a matching key.c.node().del(key)return nil}
删除也很简单,通过 cursor 定位到数据,删掉即可。
// ForEach executes a function for each key/value pair in a bucket.// If the provided function returns an error then the iteration is stopped and// the error is returned to the caller. The provided function must not modify// the bucket; this will result in undefined behavior.func (b *Bucket) ForEach(fn func(k, v []byte) error) error {if b.tx.db == nil {return ErrTxClosed}c := b.Cursor()for k, v := c.First(); k != nil; k, v = c.Next() {if err := fn(k, v); err != nil {return err}}return nil}
遍历依然是通过 cursor,从第一个到最后一个,可以传入一个回调函数。
cursor
cursor 是操作 B+ 树的封装。 boltdb 的 B+树有一点不一样,叶子节点没有通过链表连起来,所以cursor 里有个 stack 结构,保存遍历的路径。
db
boltdb 的数据库操作封装为 db 结构,这个结构是文件的操作封装,在这里把文件操作变为内存操作。很有意思,我们先来看下。
首先是指定文件路径,然后通过mmap 把文件映射为内存结构。
// mmap opens the underlying memory-mapped file and initializes the meta references.// minsz is the minimum size that the new mmap can be.// 文件映射为内存结构func (db *DB) mmap(minsz int) error {db.mmaplock.Lock()defer db.mmaplock.Unlock()info, err := db.file.Stat()if err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("mmap stat error: %s", err)} else if int(info.Size()) < db.pageSize*2 {return fmt.Errorf("file size too small")}// Ensure the size is at least the minimum size.var size = int(info.Size())if size < minsz {size = minsz}size, err = db.mmapSize(size)if err != nil {return err}// Dereference all mmap references before unmapping.if db.rwtx != nil {db.rwtx.root.dereference()}// Unmap existing data before continuing.if err := db.munmap(); err != nil {return err}// Memory-map the data file as a byte slice.if err := mmap(db, size); err != nil {return err}// Save references to the meta pages.db.meta0 = db.page(0).meta()db.meta1 = db.page(1).meta()// Validate the meta pages. We only return an error if both meta pages fail// validation, since meta0 failing validation means that it wasn't saved// properly -- but we can recover using meta1. And vice-versa.err0 := db.meta0.validate()err1 := db.meta1.validate()if err0 != nil && err1 != nil {return err0}return nil}
默认文件大小是 16KB,boltdb 会扩容为 32KB,如果还是太小,会指数扩容到 1G,之后是 1G 的增幅扩大。
mmap 是通过系统调用,把文件的操作映射为内存的操作。读文件变成了读内存,大大提升了读效率。
// mmap memory maps a DB's data file.// DB 数据映射为内存结构func mmap(db *DB, sz int) error {// Map the data file to memory.b, err := syscall.Mmap(int(db.file.Fd()), 0, sz, syscall.PROT_READ, syscall.MAP_SHARED|db.MmapFlags)if err != nil {return err}// Advise the kernel that the mmap is accessed randomly.if err := madvise(b, syscall.MADV_RANDOM); err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("madvise: %s", err)}// Save the original byte slice and convert to a byte array pointer.db.dataref = bdb.data = (*[maxMapSize]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(&b[0]))db.datasz = szreturn nil}
读变成了读内存,所以性能提升,写是通过写文件直接写入,不是通过内存操作完成的。所以,如果 boltdb 有大量的写会导致大量的 IO 操作,并且会涉及到大量的 B+树平衡性调整,导致性能下降。
type DB struct {...ops struct {writeAt func(b []byte, off int64) (n int, err error) // hook 了文件的写入}}---// Default values for test hooksdb.ops.writeAt = db.file.WriteAt---// Write the buffer to our data file.// 真正落地到磁盘文件,还是在这里if _, err := db.ops.writeAt(buf, 0); err != nil {return err}
对外操作的函数。
| Begin() 返回事务操作封装 TX,自己独立去操作事务 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Update() 对写事务操作的封装 | ||
| View() 对读事务的封装 | ||
| Batch() 对批量操作的封装,可以减少 IO 的操作 |
事务
boltdb 的事务实现了 ACID,支持读读并发和一个读写,2 个可以并存。因为读操作是直接读的内存,而写操作直接写的是磁盘。
boltdb 的事务是通过 golang 的锁来实现的。写操作互斥用的是 rwlock 来实现的。
func (db *DB) beginRWTx() (*Tx, error) {// If the database was opened with Options.ReadOnly, return an error.if db.readOnly {return nil, ErrDatabaseReadOnly}// Obtain writer lock. This is released by the transaction when it closes.// This enforces only one writer transaction at a time.db.rwlock.Lock()// Once we have the writer lock then we can lock the meta pages so that// we can set up the transaction.db.metalock.Lock()defer db.metalock.Unlock()// Exit if the database is not open yet.if !db.opened {db.rwlock.Unlock()return nil, ErrDatabaseNotOpen}// Create a transaction associated with the database.t := &Tx{writable: true}t.init(db)db.rwtx = t// Free any pages associated with closed read-only transactions.var minid txid = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFfor _, t := range db.txs {if t.meta.txid < minid {minid = t.meta.txid}}if minid > 0 {db.freelist.release(minid - 1)}return t, nil}
写事务会加锁并且更新 meta 里的 txid。 在 db 的结构里获取到锁之后,会在 tx.go 里结束事务之后释放,或者是 rollback回滚之后释放。
func (tx *Tx) close() {if tx.db == nil {return}if tx.writable {// Remove transaction ref & writer lock.tx.db.rwtx = niltx.db.rwlock.Unlock()...} else {tx.db.removeTx(tx)}// Clear all references.tx.db = niltx.meta = niltx.root = Bucket{tx: tx}tx.pages = nil}
只读事务。
func (db *DB) beginTx() (*Tx, error) {// Lock the meta pages while we initialize the transaction. We obtain// the meta lock before the mmap lock because that's the order that the// write transaction will obtain them.db.metalock.Lock()// Obtain a read-only lock on the mmap. When the mmap is remapped it will// obtain a write lock so all transactions must finish before it can be// remapped.db.mmaplock.RLock()// Exit if the database is not open yet.if !db.opened {db.mmaplock.RUnlock()db.metalock.Unlock()return nil, ErrDatabaseNotOpen}// Create a transaction associated with the database.t := &Tx{}t.init(db)// Keep track of transaction until it closes.db.txs = append(db.txs, t)n := len(db.txs)// Unlock the meta pages.db.metalock.Unlock()// Update the transaction stats.db.statlock.Lock()db.stats.TxN++db.stats.OpenTxN = ndb.statlock.Unlock()return t, nil}
先获取meta 的 lock,避免这个时候写事务进入写了 meta。之后锁住 mmap 内存结构,避免 mmap 重新映射。所有的只读事务都在 txs 里。
事务的提交或回滚。
// Rollback closes the transaction and ignores all previous updates. Read-only// transactions must be rolled back and not committed.func (tx *Tx) Rollback() error {_assert(!tx.managed, "managed tx rollback not allowed")if tx.db == nil {return ErrTxClosed}tx.rollback()return nil}func (tx *Tx) rollback() {if tx.db == nil {return}if tx.writable {tx.db.freelist.rollback(tx.meta.txid)tx.db.freelist.reload(tx.db.page(tx.db.meta().freelist))}tx.close()}
如果是只读事务直接 close-remove 就好了,如果是读写事务,还需要更新 freelist 里的 page。总的来说,只读事务只是记录了 Tx 的结构体而已,多了一把 S 锁,而写事务是排它锁,串行的。
总结
boltDB是一个完全由go语言编写的基于B+树的kv数据库,其完全支持事务的ACID特性,整个数据库只有一个文件,且有较高的读性能与加载时间。etcd的后端存储使用的便是基于boltdb优化的kv存储 etcd-io/bbolt。
至此基本上把 boltdb 的核心功能梳理完成了,一个小小的开源项目把数据库的方方面面都涉及到了,非常值得多看几遍,不管是工程还是算法,都值得借鉴。
参考资料
https://github.com/etcd-io/bbolt
https://github.com/boltdb/bolt/tree/v1.3.1
https://www.qtmuniao.com/2021/04/02/bolt-transaction/
https://mrcroxx.github.io/posts/code-reading/boltdb-made-simple/0-introduction/

