- 1、编写文档目的
- 2、OpenLDAP安装配置
- See slapd-config(5) for details on configuration options.
- This file should NOT be world readable.
- TLS settings
- Do not enable referrals until AFTER you have a working directory
- service AND an understanding of referrals.
- olcReferral: ldap://root.openldap.org
- Sample security restrictions
- Require integrity protection (prevent hijacking)
- Require 112-bit (3DES or better) encryption for updates
- Require 64-bit encryption for simple bind
- olcSecurity: ssf=1 update_ssf=112 simple_bind=64
- Load dynamic backend modules:
- - modulepath is architecture dependent value (32/64-bit system)
- - back_sql.la backend requires openldap-servers-sql package
- - dyngroup.la and dynlist.la cannot be used at the same time
- dn: cn=module,cn=config
- objectClass: olcModuleList
- cn: module
- olcModulepath: /usr/lib/openldap
- olcModulepath: /usr/lib64/openldap
- olcModuleload: accesslog.la
- olcModuleload: auditlog.la
- olcModuleload: back_dnssrv.la
- olcModuleload: back_ldap.la
- olcModuleload: back_mdb.la
- olcModuleload: back_meta.la
- olcModuleload: back_null.la
- olcModuleload: back_passwd.la
- olcModuleload: back_relay.la
- olcModuleload: back_shell.la
- olcModuleload: back_sock.la
- olcModuleload: collect.la
- olcModuleload: constraint.la
- olcModuleload: dds.la
- olcModuleload: deref.la
- olcModuleload: dyngroup.la
- olcModuleload: dynlist.la
- olcModuleload: memberof.la
- olcModuleload: pcache.la
- olcModuleload: ppolicy.la
- olcModuleload: refint.la
- olcModuleload: retcode.la
- olcModuleload: rwm.la
- olcModuleload: seqmod.la
- olcModuleload: smbk5pwd.la
- olcModuleload: sssvlv.la
- olcModuleload: syncprov.la
- olcModuleload: translucent.la
- olcModuleload: unique.la
- olcModuleload: valsort.la
- Schema settings
- Frontend settings
- Sample global access control policy:
- Root DSE: allow anyone to read it
- Subschema (sub)entry DSE: allow anyone to read it
- Other DSEs:
- Allow self write access
- Allow authenticated users read access
- Allow anonymous users to authenticate
- olcAccess: to dn.base=”” by * read
- olcAccess: to dn.base=”cn=Subschema” by * read
- olcAccess: to *
- by self write
- by users read
- by anonymous auth
- if no access controls are present, the default policy
- allows anyone and everyone to read anything but restricts
- updates to rootdn. (e.g., “access to by read”)
- rootdn can always read and write EVERYTHING!
- Configuration database
- Server status monitoring
- Backend database definitions
- 3、导入根域及管理员账号
- 4、导入基础文件及用户和用户组
- Default DNS domain
- Default base
- 5、OpenLDAP 客户端配置
- LDAP Defaults
- See ldap.conf(5) for details
- This file should be world readable but not world writable.
- BASE dc=example,dc=com
- URI ldap://ldap.example.com ldap://ldap-master.example.com:666
- SIZELIMIT 12
- TIMELIMIT 15
- DEREF never
- Turning this off breaks GSSAPI used with krb5 when rdns = false
- 6、Openldap 客户端常用管理命令
- ldappasswd -x -D ‘cm=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com’ -W ‘uid=ldapuser1,dc=macro,dc=com’ -S
#ldappasswd -H ldap://cdh1 -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W -S “uid=ldapuser1,ou=People,dc=macro,dc=com”
New password:
Re-enter new password:
1、编写文档目的
RedHat7下安装OpendLDAP并配置客户端
测试环境:
- RedHat7.4
-
2、OpenLDAP安装配置
2.1、下载OpenLDAP服务
下载
yum -y install openldap-clients openldap openldap-servers migrationtools openldap-devel nss-pam-ldapd bind-dyndb-ldap compat-openldap perl-LDAP krb5-server-ldap php-ldap openssl
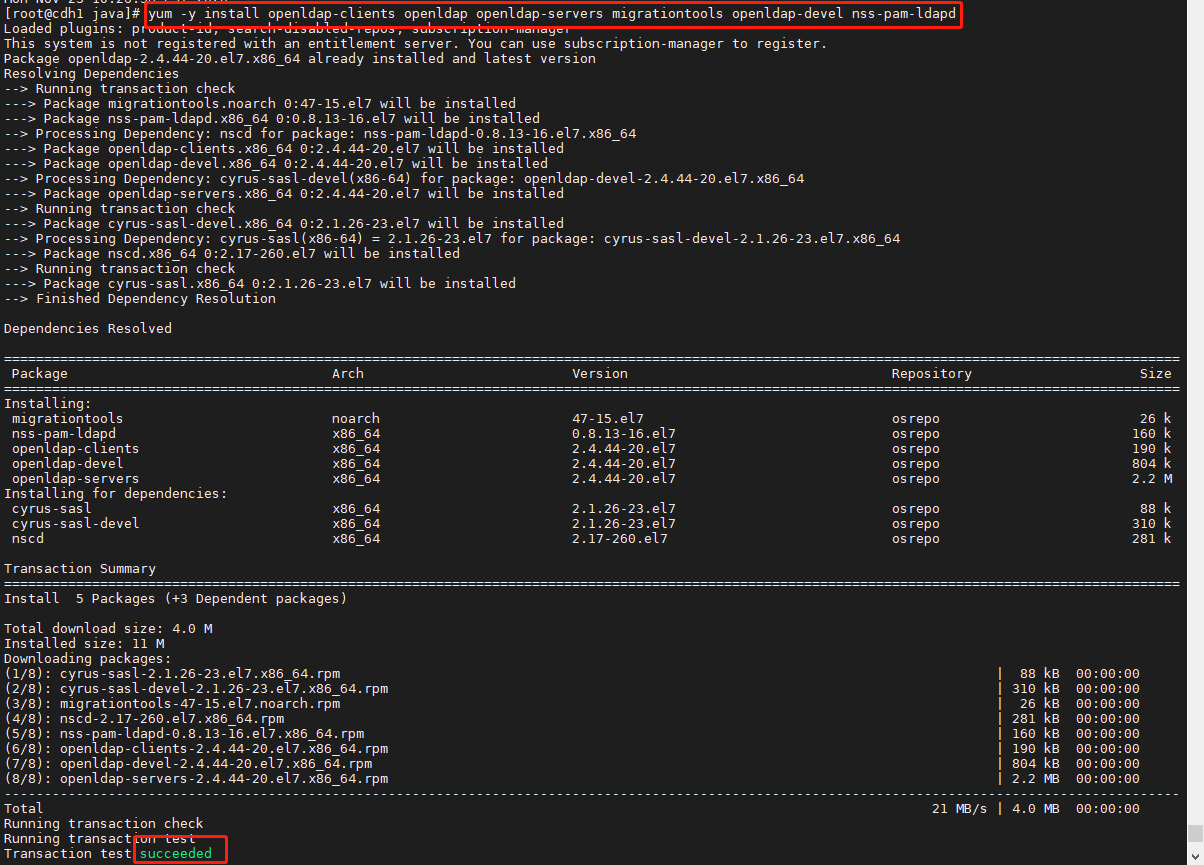
检查是否下载成功
rpm -qa | grep openldap
2.2、使用 openssl 生成 TLS 加密文件
生成服务器RSA私钥
openssl genrsa -out ldap.key 1024

生成签名文件
openssl req -new -key ldap.key -out ldap.csr
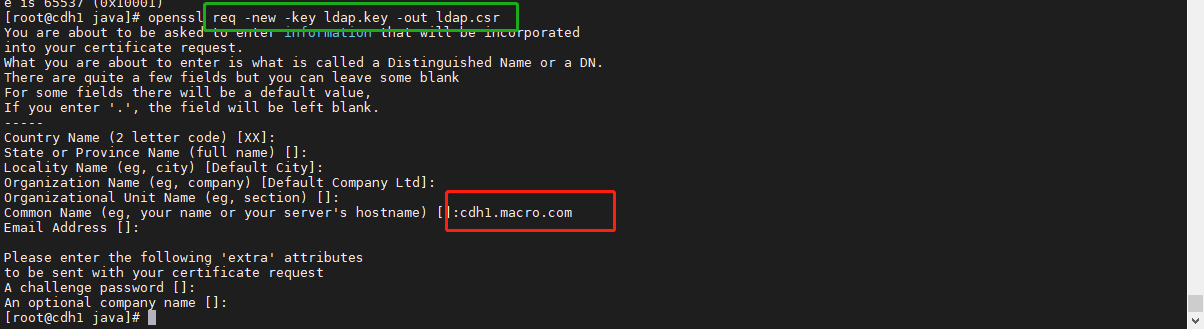
- 上图中红框处填写当前服务器的 hostname 其他地方留空
生成公钥文件
openssl x509 -req -days 3653 -in ldap.csr -signkey ldap.key -out ldap.crt

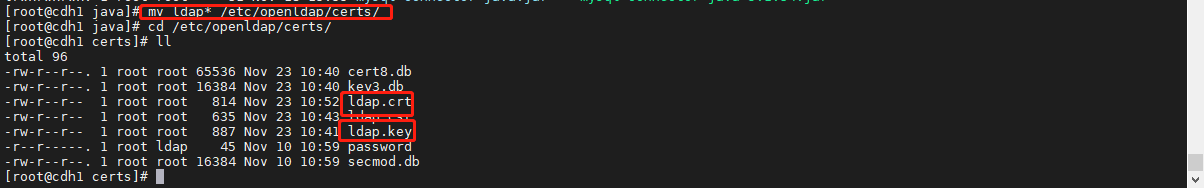
将生成的公钥文件和私钥拷贝至/etc/openldap/certs 目录下:
cp ldap.key ldap.crt /etc/openldap/certs/ll /etc/openldap/certs/
2.3、修改 OpenLDAP 的 slapd.ldif 配置文件
OpenLDAP服务配置文件默认地址:/usr/share/openldap-servers/
将 slapd.ldif 拷贝至/root 目录下
cd /usr/share/openldap-servers/llcp slapd.ldif /root/cd /rootll
2.3.3、修改 slapd.ldif 文件
增加 include 的文件及配置管理员账号和 OpenLDAP 的根域信息,文件全部内容如下:
vi /root/slapd.ldif
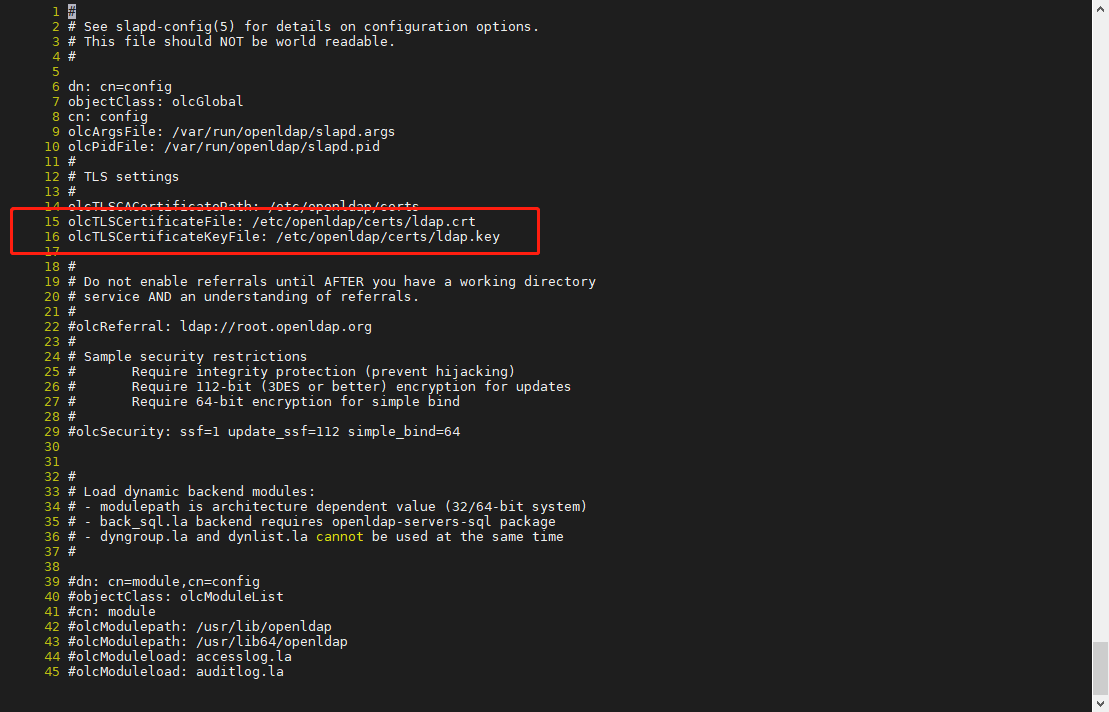
在15、16行添加openldap的公钥和私钥的路径地址
- 在84后添加file:///etc/openldap/schema/下的所有文件(OpenLDAP的根域信息)
- 文件末尾添加管理员账户。详细内容如下下
```shell
#
See slapd-config(5) for details on configuration options.
This file should NOT be world readable.
#
dn: cn=config objectClass: olcGlobal cn: config olcArgsFile: /var/run/openldap/slapd.args olcPidFile: /var/run/openldap/slapd.pid #
TLS settings
# olcTLSCACertificatePath: /etc/openldap/certs olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/openldap/certs/ldap.crt olcTLSCertificateKeyFile: /etc/openldap/certs/ldap.key #
Do not enable referrals until AFTER you have a working directory
service AND an understanding of referrals.
#
olcReferral: ldap://root.openldap.org
#
Sample security restrictions
Require integrity protection (prevent hijacking)
Require 112-bit (3DES or better) encryption for updates
Require 64-bit encryption for simple bind
#
olcSecurity: ssf=1 update_ssf=112 simple_bind=64
#
Load dynamic backend modules:
- modulepath is architecture dependent value (32/64-bit system)
- back_sql.la backend requires openldap-servers-sql package
- dyngroup.la and dynlist.la cannot be used at the same time
#
dn: cn=module,cn=config
objectClass: olcModuleList
cn: module
olcModulepath: /usr/lib/openldap
olcModulepath: /usr/lib64/openldap
olcModuleload: accesslog.la
olcModuleload: auditlog.la
olcModuleload: back_dnssrv.la
olcModuleload: back_ldap.la
olcModuleload: back_mdb.la
olcModuleload: back_meta.la
olcModuleload: back_null.la
olcModuleload: back_passwd.la
olcModuleload: back_relay.la
olcModuleload: back_shell.la
olcModuleload: back_sock.la
olcModuleload: collect.la
olcModuleload: constraint.la
olcModuleload: dds.la
olcModuleload: deref.la
olcModuleload: dyngroup.la
olcModuleload: dynlist.la
olcModuleload: memberof.la
olcModuleload: pcache.la
olcModuleload: ppolicy.la
olcModuleload: refint.la
olcModuleload: retcode.la
olcModuleload: rwm.la
olcModuleload: seqmod.la
olcModuleload: smbk5pwd.la
olcModuleload: sssvlv.la
olcModuleload: syncprov.la
olcModuleload: translucent.la
olcModuleload: unique.la
olcModuleload: valsort.la
#
Schema settings
#
dn: cn=schema,cn=config objectClass: olcSchemaConfig cn: schema
include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/corba.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/core.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/cosine.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/duaconf.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/dyngroup.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/inetorgperson.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/java.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/misc.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/nis.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/openldap.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/ppolicy.ldif include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/collective.ldif
#
Frontend settings
#
dn: olcDatabase=frontend,cn=config objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig objectClass: olcFrontendConfig olcDatabase: frontend #
Sample global access control policy:
Root DSE: allow anyone to read it
Subschema (sub)entry DSE: allow anyone to read it
Other DSEs:
Allow self write access
Allow authenticated users read access
Allow anonymous users to authenticate
#
olcAccess: to dn.base=”” by * read
olcAccess: to dn.base=”cn=Subschema” by * read
olcAccess: to *
by self write
by users read
by anonymous auth
#
if no access controls are present, the default policy
allows anyone and everyone to read anything but restricts
updates to rootdn. (e.g., “access to by read”)
#
rootdn can always read and write EVERYTHING!
#
#
Configuration database
#
dn: olcDatabase=config,cn=config objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig olcDatabase: config olcAccess: to by dn.base=”gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth” manage by none
#
Server status monitoring
#
dn: olcDatabase=monitor,cn=config objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig olcDatabase: monitor olcAccess: to by dn.base=”gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth” read by dn.base=”cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” read by none
#
Backend database definitions
#
dn: olcDatabase=hdb,cn=config objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig objectClass: olcHdbConfig olcDatabase: hdb olcSuffix: dc=macro,dc=com olcRootDN: cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com olcRootPW: 123456 olcDbDirectory: /var/lib/ldap olcDbIndex: objectClass eq,pres olcDbIndex: ou,cn,mail,surname,givenname eq,pres,sub olcDbIndex: uidNumber,gidNumber,loginShell eq,pres olcDbIndex: uid,memberUid eq,pres,sub olcDbIndex: nisMapName,nisMapEntry eq,pres,sub
<br />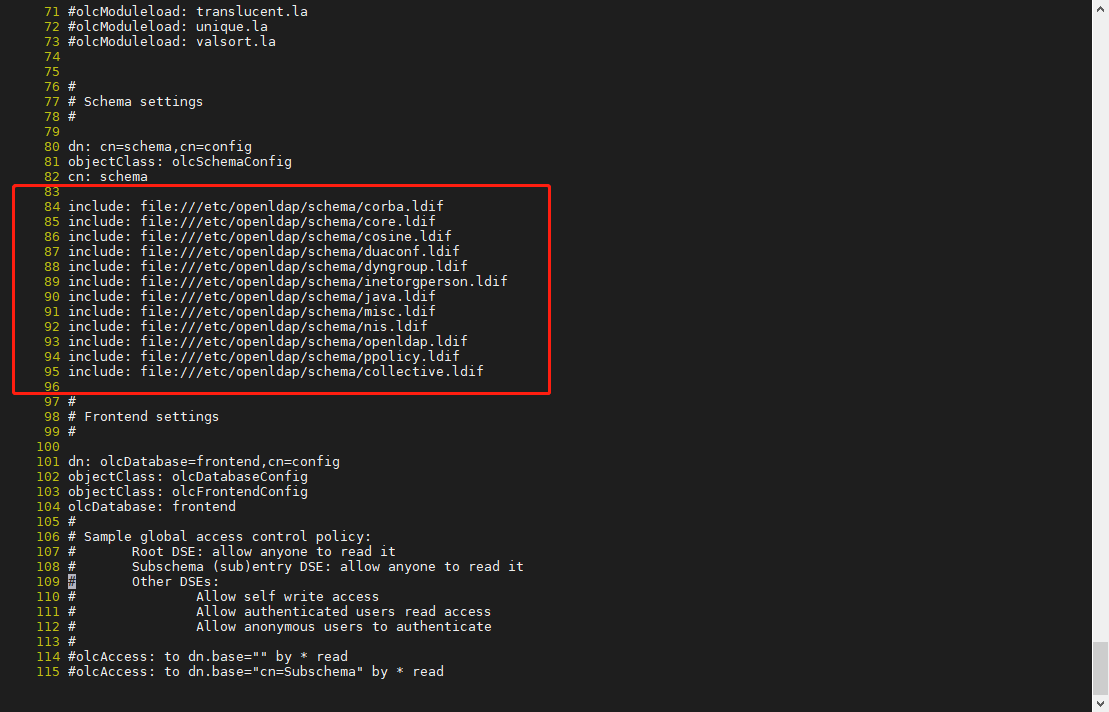<br />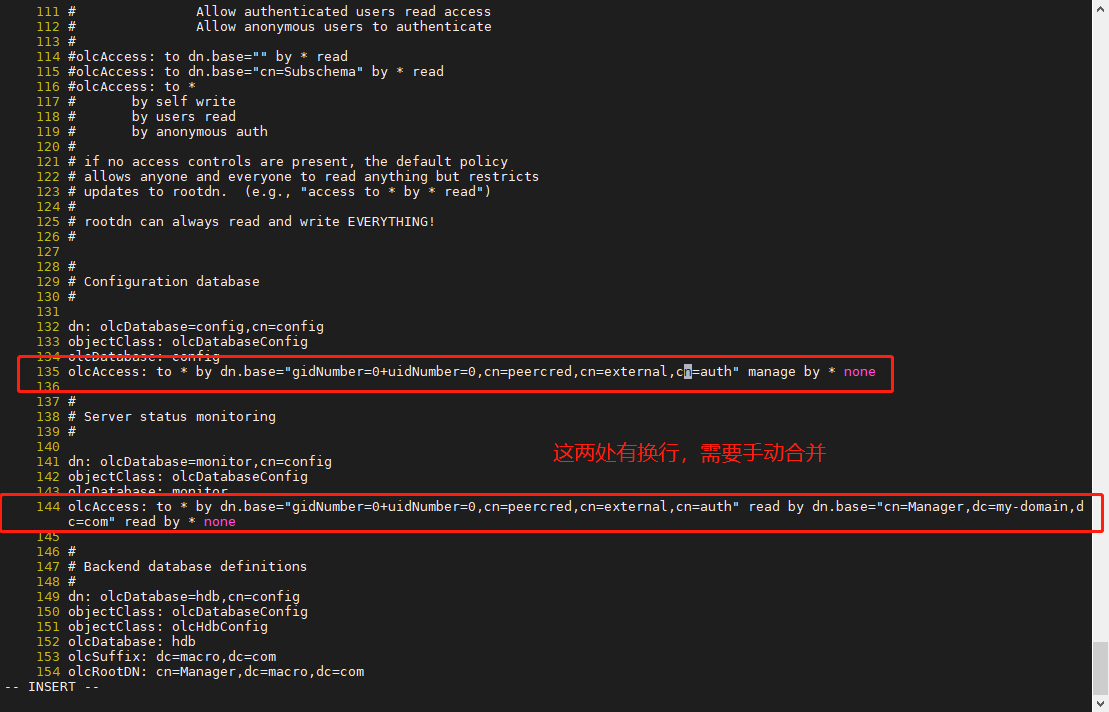<br />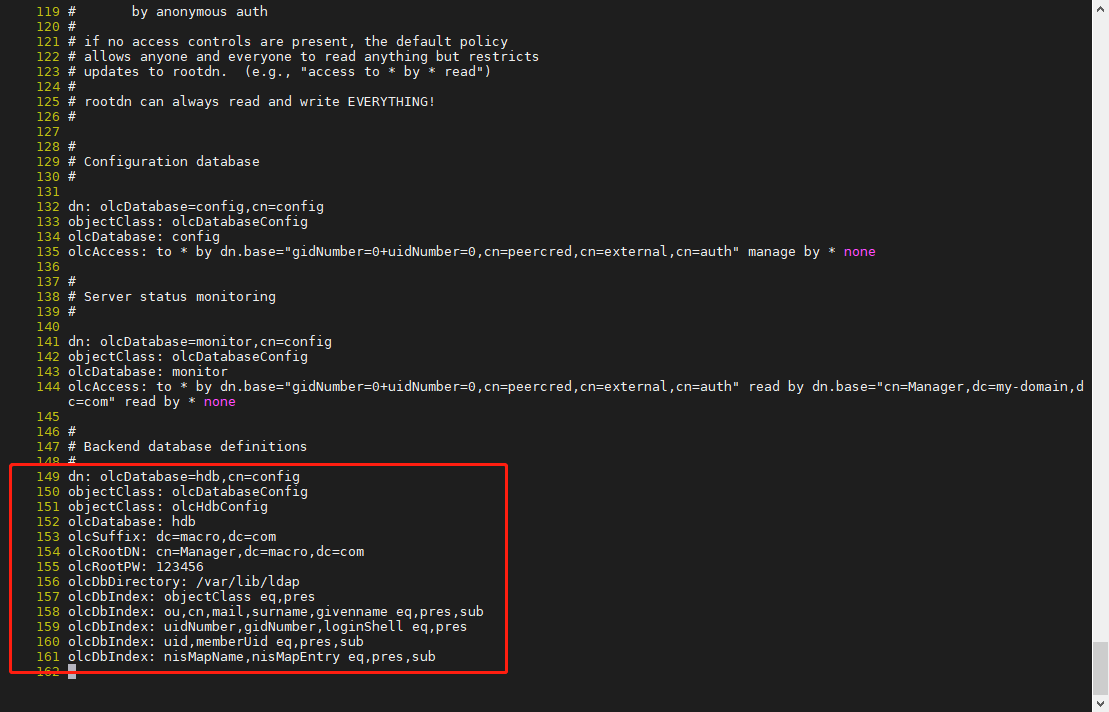<a name="agVX7"></a>## 2.4、新建 OpenLDAP 的配置1. 删除原配置,生成新配置```shellrm -rf /etc/openldap/slapd.d/*slapadd -F /etc/openldap/slapd.d -n 0 -l /root/slapd.ldifll /etc/openldap/slapd.d
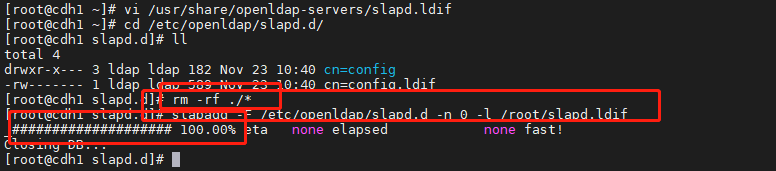
测试配置文件是否正确。succeeded为正确。
slaptest -u -F /etc/openldap/slapd.d

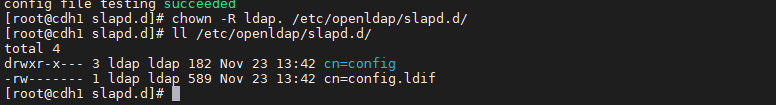
修改配置文件的属主,操作如下:
chown -R ldap. /etc/openldap/slapd.d/ll /etc/openldap/slapd.d/
2.5、安装OpenLDAP数据库文件
将/usr/share/openldap-servers/目录下的 DB_CONFIG.example 文件拷贝至/var/lib/ldap 目录下并重命名为 DB_CONFIG,操作如下:
cp /usr/share/openldap-servers/DB_CONFIG.example /var/lib/ldap/DB_CONFIGls /var/lib/ldap/
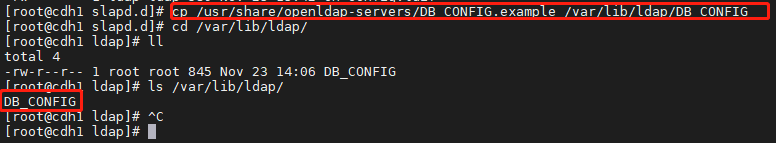
修改数据库文件属主
chown -R ldap. /var/lib/ldapll /var/lib/ldap/
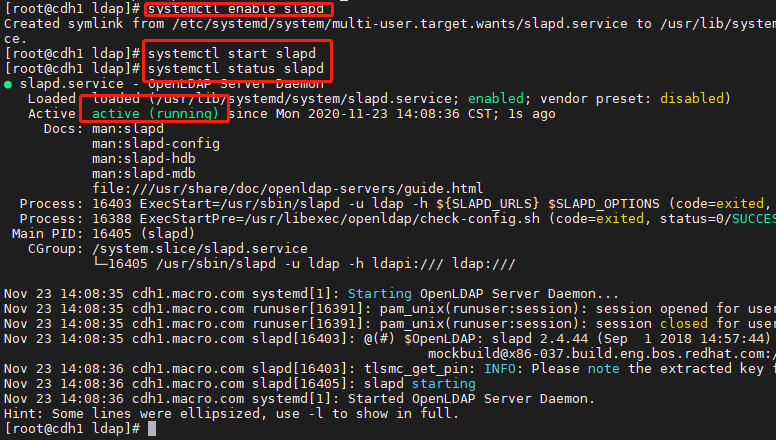
2.6、启动slapd服务并添加开机自启systemctl enable slapdsystemctl start slapdsystemctl status slapd
3、导入根域及管理员账号
创建root.ldif文件,内容如下 ```shell vi /root.ldif 复制如下内容:
dn: dc=macro,dc=com dc: macro objectClass: top objectClass: domain
dn: cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com objectClass: organizationalRole cn: Manager
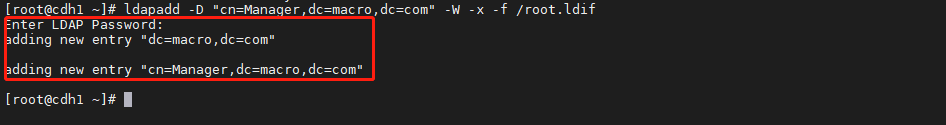
2. 导入根域及管理员信息到 OpenLDAP 服务中```shellldapadd -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W -x -f /root.ldif
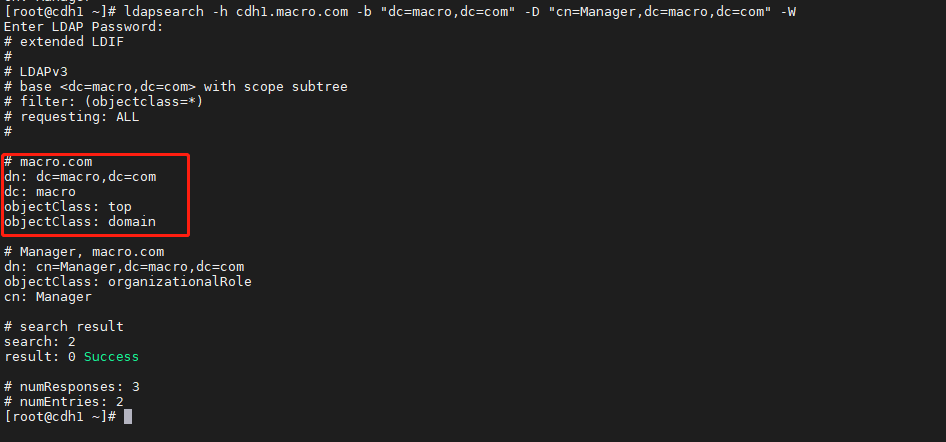
- 查看导入是否成功
ldapsearch -h cdh1.macro.com -b "dc=macro,dc=com" -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W
4、导入基础文件及用户和用户组
- 基于 migrationtools 服务已安装,通过该服务生成 OpenLDAP 的基础文件、用户和用户组的 ldif 文件
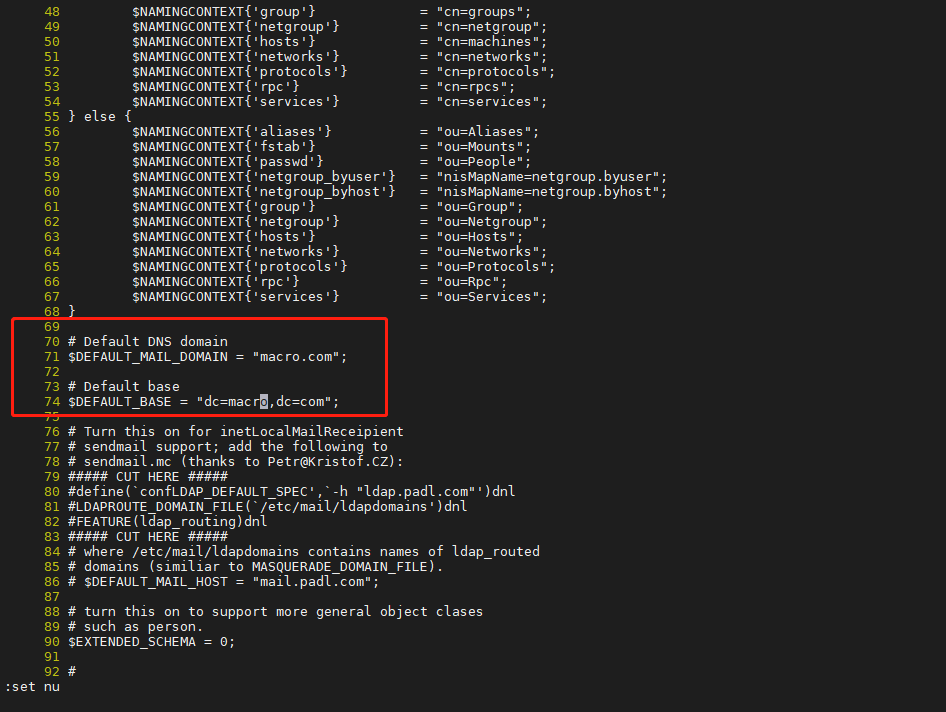
- 修改/usr/share/migrationtools/migrate_common.ph 文件,将文件中的$DEFAULT_MAIL_DOMAIN 和$DEFAULT_BASE 修改为自己 OpenLDAP 的域 ```shell vi /usr/share/migrationtools/migrate_common.ph 修改如下内容:
Default DNS domain
$DEFAULT_MAIL_DOMAIN = “macro.com”;
Default base
$DEFAULT_BASE = “dc=macro,dc=com”;
2. 使用如下命令导出 OpenLdap 的 base.ldif 文件```shell/usr/share/migrationtools/migrate_base.pl > base.ldif
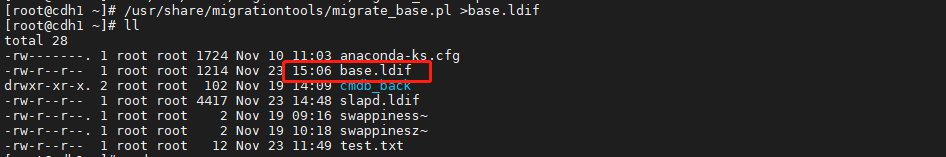
- 修改文件如下图,只保留下面两项

执行如下命令导出操作系统的 group.ldif 文件
/usr/share/migrationtools/migrate_group.pl /etc/group > group.ldif
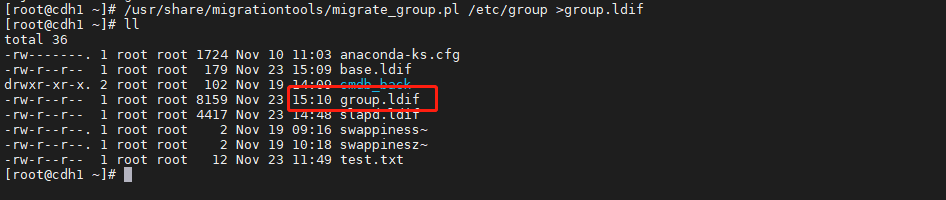
根据需要删除不需要导入 OpenLDAP 服务的 group
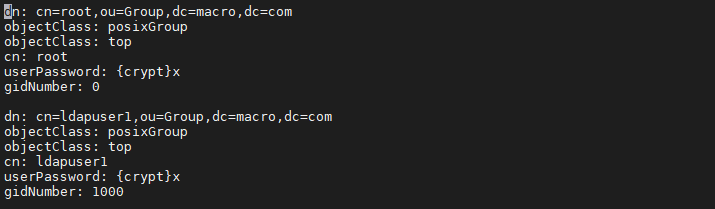
使用如下命令导出操作系统用户的 ldif 文件
/usr/share/migrationtools/migrate_passwd.pl /etc/passwd >user.ldif
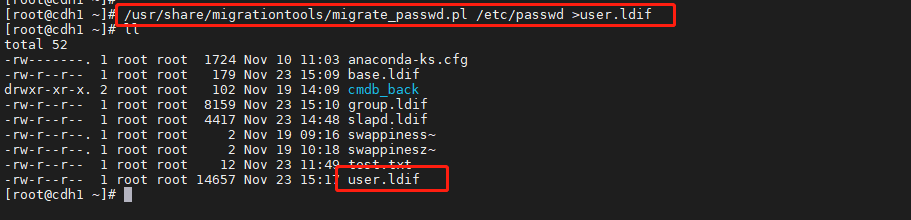
根据需要保留 user.ldif 文件中需要导入 OpenLDAP 服务的用户信息,注意用户信息与group.ldif 中组的对应,否则会出现用户无相应组的问题
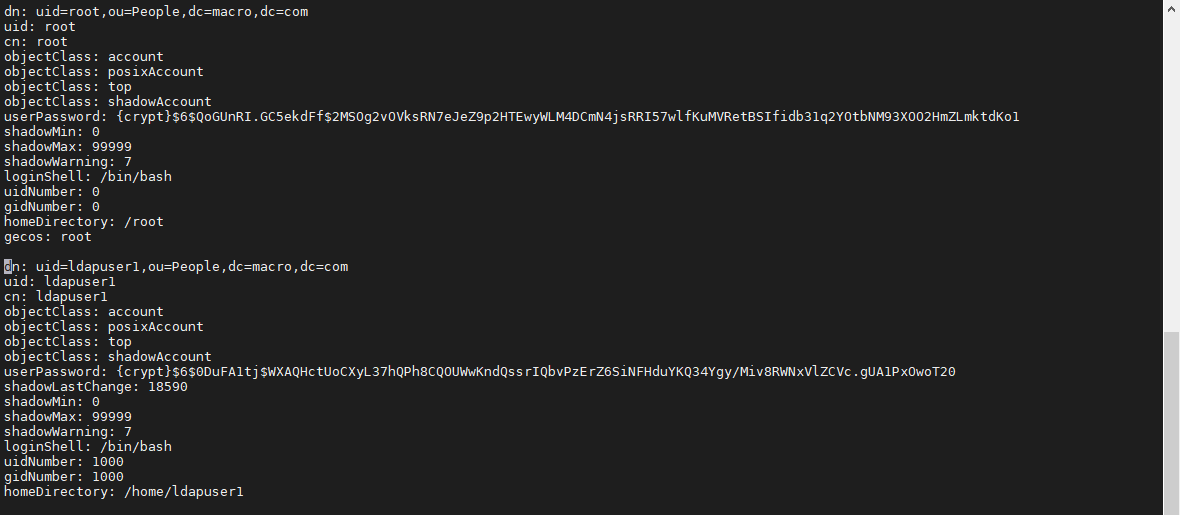
使用 ldapadd 命令将基础文件和用户和组导入 OpenLDAP
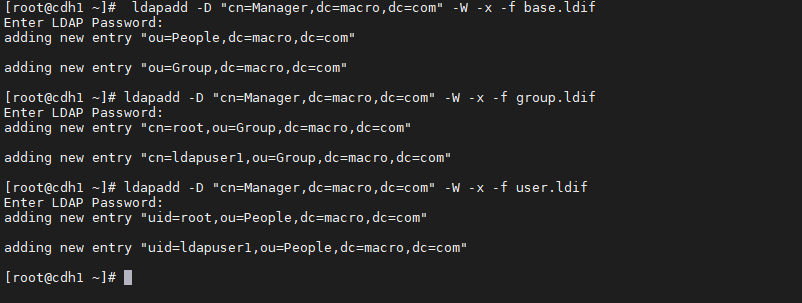
ldapadd -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W -x -f base.ldifldapadd -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W -x -f group.ldifldapadd -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W -x -f user.ldif
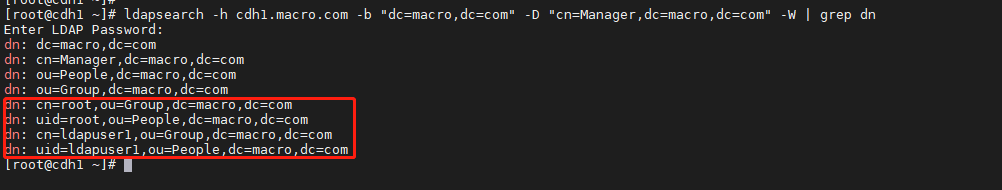
查看是否导入成功
ldapsearch -h cdh1.macro.com -b "dc=macro,dc=com" -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W | grep dn
5、OpenLDAP 客户端配置
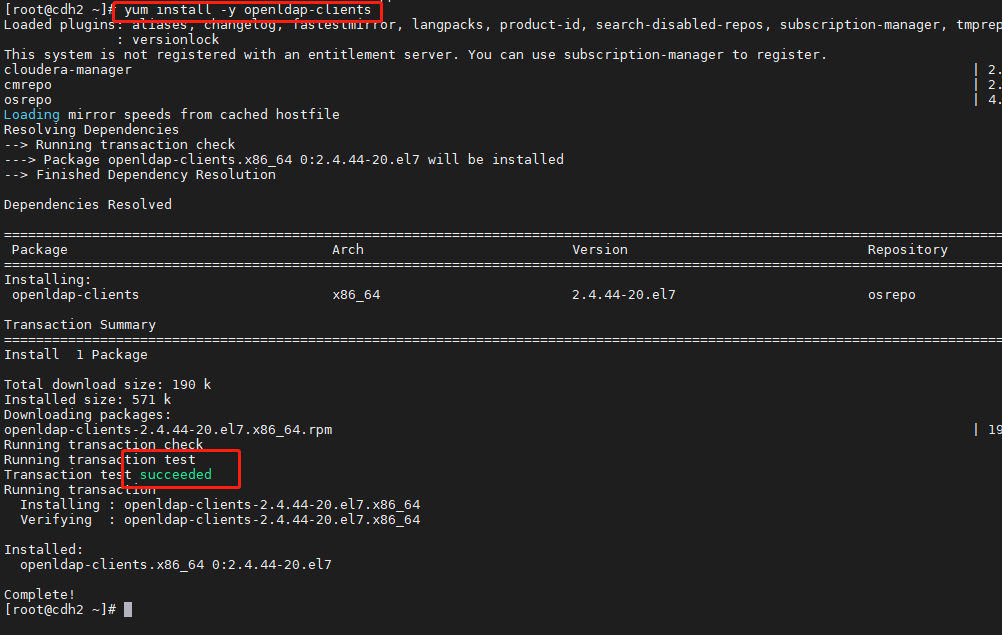
在客户端节点安装 OpenLDAP 的客户端软件包
yum install -y openldap-clients
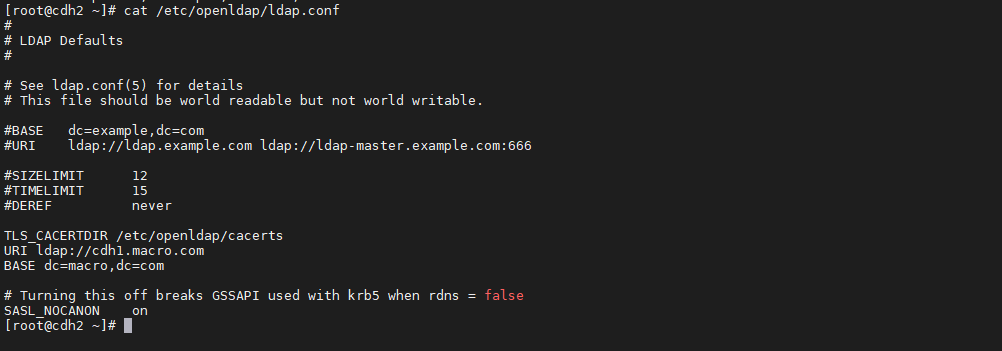
修改/etc/openldap/ldap.conf 文件,内容如下:
vim /etc/openldap/ldap.conf
```shell #
LDAP Defaults
#
See ldap.conf(5) for details
This file should be world readable but not world writable.
BASE dc=example,dc=com
URI ldap://ldap.example.com ldap://ldap-master.example.com:666
SIZELIMIT 12
TIMELIMIT 15
DEREF never
TLS_CACERTDIR /etc/openldap/certs URI ldap://cdh1.macro.com BASE dc=macro,dc=com
Turning this off breaks GSSAPI used with krb5 when rdns = false
SASL_NOCANON on
3. 测试客户端是否配置成功```shellldapsearch -D "cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com" -W |grep dn
6、Openldap 客户端常用管理命令
CN, OU, DC 都是 LDAP 连接服务器的端字符串中的区别名称(DN, distinguished name)
其中DN有三个属性,分别是CN,OU,DC
LDAP是一种通讯协议,如同HTTP是一种协议一样的!
在 LDAP 目录中,
- -x 进行简单认证
- -D 用来绑定服务器的DN
- -h 目录服务的地址
- -w 绑定DN的密码
- -f 使用ldif文件进行条目添加的文件
- 例子:
ldapadd -x -D “cn=root,dc=starxing,dc=com” -w secret -f /root/test.ldif
ldapadd -x -D “cn=root,dc=starxing,dc=com” -w secret (这样写就是在命令行添加条目)
6.2、ldapsearch (搜索)
-x 进行简单认证
-D 用来绑定服务器的DN
-w 绑定DN的密码
-b 指定要查询的根节点
-H 指定定要查询的服务器
ldapsearch -x -D “cn=root,dc=starxing,dc=com” -w secret -b “dc=starxing,dc=com”
使用简单认证,用 “cn=root,dc=starxing,dc=com” 进行绑定,
要查询的根是 “dc=starxing,dc=com”。这样会把绑定的用户能访问”dc=starxing,dc=com”下的
所有数据显示出来。
ldapsearch -x -W -D “cn=administrator,cn=users,dc=osdn,dc=zzti,dc=edu,dc=cn” -b “cn=administrator,cn=users,dc=osdn,dc=zzti,dc=edu,dc=cn” -h troy.osdn.zzti.edu.cn
ldapsearch -b “dc=canon-is,dc=jp” -H ldaps://192.168.0.92:636
6.3、ldapdelete (删除)
ldapdelete -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W “cn=ldapuser1,ou=Group,dc=macro,dc=com”
ldapdelete -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W “uid=ldapuser1,ou=People,dc=macro,dc=com”
ldapdelete -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W “cn=root,ou=Group,dc=macro,dc=com”
ldapdelete -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W “uid=root,ou=People,dc=macro,dc=com”
这样就可以删除’uid=zyx,dc=it,dc=com’记录了,应该注意一点,如果o或ou中有成员是不能删除的
6.4、ldapmodify常用Option
ldapmodify常用的Option的信息和用途整理如下:
| Option | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -H | ldapuri,格式为ldap://机器名或者IP:端口号,不能与-h和-p同时使用 |
| -h | LDAP服务器IP或者可解析的hostname,与-p可结合使用,不能与-H同时使用 |
| -p | LDAP服务器端口号,与-h可结合使用,不能与-H同时使用 |
| -x | 使用简单认证方式 |
| -D | 所绑定的服务器的DN |
| -w | 绑定DN的密码,与-W二者选一 |
| -W | 不输入密码,会交互式的提示用户输入密码,与-w二者选一 |
| -c | 出错后忽略当前错误继续执行,缺省情况下遇到错误即终止 |
| -n | 模拟操作但并不实际执行,用于验证,常与-v一同使用进行问题定位 |
| -v | 显示详细信息 |
| -d | 显示debug信息,可设定级别 |
| -e | 设置客户端证书 |
| -E | 设置客户端私钥 |
6.5、ldappasswd常用Option
ldappasswd常用的Option的信息和用途整理如下:
| Option | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -H | ldapuri,格式为ldap://机器名或者IP:端口号,不能与-h和-p同时使用 |
| -h | LDAP服务器IP或者可解析的hostname,与-p可结合使用,不能与-H同时使用 |
| -p | LDAP服务器端口号,与-h可结合使用,不能与-H同时使用 |
| -x | 使用简单认证方式 |
| -D | 所绑定的服务器的DN |
| -w | 绑定DN的密码,与-W二者选一 |
| -W | 不输入密码,会交互式的提示用户输入密码,与-w二者选一 |
| -n | 模拟操作但并不实际执行,用于验证,常与-v一同使用进行问题定位 |
| -v | 显示详细信息 |
| -d | 显示debug信息,可设定级别 |
| -S | 交互式进行密码的提示和输入以及Re-enter,与-s二者选一 |
| -s | 将指定内容设为密码,与-S二者选一 |
ldappasswd -x -D ‘cm=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com’ -W ‘uid=ldapuser1,dc=macro,dc=com’ -S
#ldappasswd -H ldap://cdh1 -x -D “cn=Manager,dc=macro,dc=com” -W -S “uid=ldapuser1,ou=People,dc=macro,dc=com”
New password:
Re-enter new password:
就可以更改密码了,如果原来记录中没有密码,将会自动生成一个userPassword。
-a 添加新的条目.缺省的是修改存在的条目.
-C 自动追踪引用.
-c 出错后继续执行程序并不中止.缺省情况下出错的立即停止.比如如果你的ldif 文
件内的某个条目在数据库内并不存在,缺省情况下程序立即退出,但如果使用了该参数,程
序忽略该错误继续执行.
-n 用于调试到服务器的通讯.但并不实际执行搜索.服务器关闭时,返回错误;服务器
打开时,常和-v 参数一起测试到服务器是否是一条通路.
-v 运行在详细模块.在标准输出中打出一些比较详细的信息.比如:连接到服务器的
ip 地址和端口号等.
-M[M] 打开manage DSA IT 控制. -MM 把该控制设置为重要的.
-f file 从文件内读取条目的修改信息而不是从标准输入读取.
-x 使用简单认证.
-D binddn 指定搜索的用户名(一般为一dn 值).
-W 指定了该参数,系统将弹出一提示入用户的密码.它和-w 参数相对使用.
-w bindpasswd 直接指定用户的密码. 它和-W 参数相对使用.
-H ldapuri 指定连接到服务器uri(ip 地址和端口号,常见格式为
ldap://hostname:port).如果使用了-H 就不能使用-h 和-p 参数.
-h ldaphost 指定要连接的主机的名称/ip 地址.它和-p 一起使用.
-p ldapport 指定要连接目录服务器的端口号.它和-h 一起使用.
如果使用了-h 和-p 参数就不能使用-H 参数.
-Z[Z] 使用StartTLS 扩展操作.如果使用-ZZ,命令强制使用StartTLS 握手成功.
-V 启用证书认证功能,目录服务器使用客户端证书进行身份验证,必须与-ZZ 强制启用
TLS 方式配合使用,并且匿名绑定到目录服务器.
-e 设置客户端证书文件,例: -e cert/client.crt
-E 设置客户端证书私钥文件,例: -E cert/client.key
#ldapmodify -x -D “cn=root,dc=it,dc=com” -W -f modify.ldif
将modify.ldif中的记录更新原有的记录。
清除全部缓存信息:
sss_cache -E1
清除指定用户的缓存信息:
sss_cache -u user1
删除缓存文件
这个方法简单有效,但是有一定的风险,需要谨慎操作。
操作方法如下:
systemctl stop sssdrm -rf /var/lib/sss/db/*systemctl restart sssd
重启SSSD服务后,可以使用linux的id命令查看用户信息,应该可以看到信息已更新