本文主要介绍两篇相关的文章,都是使用了动态滤波器的思想。
- (ICCV 2019) Dynamic Multi-scale Filters for Semantic Segmentation
- (CVPR 2019) Adaptive Pyramid Context Network for Semantic Segmentation
Dynamic Multi-scale Filters for Semantic Segmentation

Multi-scale representation provides an effective way to address scale variation of objects and stuff in semantic segmentation. Previous works construct multi-scale representation by utilizing different filter sizes, expanding filter sizes with dilated filters or pooling grids, and the parameters of these filters are fixed after training. These methods often suffer from heavy computational cost or have more parameters, and are not adaptive to the input image during inference.
多尺度表示为语义分割中对象和内容的尺度变化提供了一种有效的方法。以前的工作是通过利用不同的滤波器尺寸来构建多尺度表示,用扩张卷积或网格池化来扩展滤波器尺寸,并且这些滤波器的参数在训练后是固定的。这些方法往往计算成本较高或参数较多,在推理过程中不适应输入图像。
To address these problems, this paper proposes a Dynamic Multi-scale Network (DMNet) to adaptively capture multi-scale contents for predicting pixel-level semantic labels. DMNet is composed of multiple Dynamic Convolutional Modules (DCMs) arranged in parallel, each of which exploits context-aware filters to estimate semantic representation for a specific scale. The outputs of multiple DCMs are further integrated for final segmentation.
针对这些问题,本文提出了一种动态多尺度网络 (DMNet) 来自适应地捕获多尺度内容,用于预测像素级语义标签。DMNet 由多个并行排列的动态卷积模块 (DCMs) 组成,每个模块都利用上下文感知滤波器来估计特定尺度的语义表示。多个 DCMs 的输出进一步集成以进行最终分割。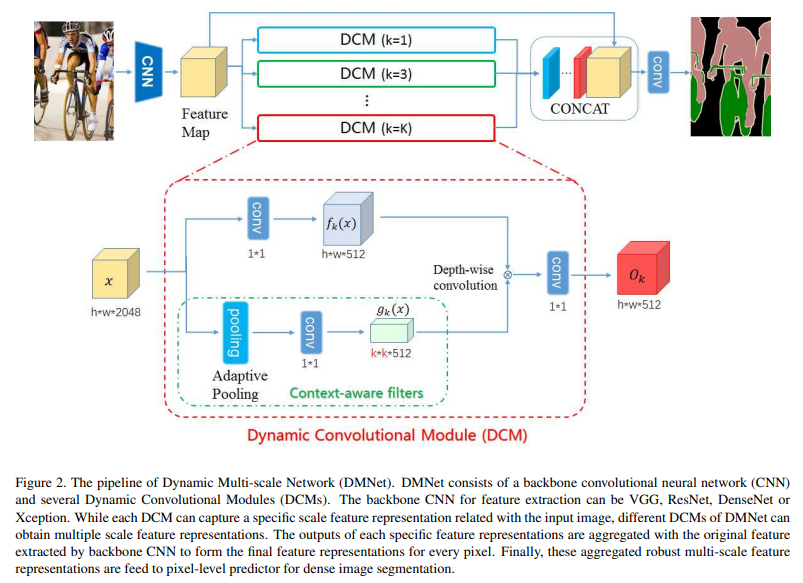
Adaptive Pyramid Context Network for Semantic Segmentation

Recent studies witnessed that context features can significantly improve the performance of deep semantic segmentation networks. Current context based segmentation methods differ with each other in how to construct context features and perform differently in practice. This paper firstly introduces three desirable properties of context features in segmentation task. Specially, we find that Global-guided Local Affinity (GLA) can play a vital role in constructing effective context features, while this property has been largely ignored in previous works.
最近的研究表明,上下文特征可以显著提高深度语义分割网络的性能。当前的基于上下文的分割方法在如何构造上下文特征彼此不同,并且在实践中表现不同。本文首先介绍了分割任务中上下文特征的三个期望性质。特别是,我们发现全局引导的局部亲和力 (GLA) 在构建有效的上下文特征方面发挥着至关重要的作用,而这个属性在以前的作品中已经被很大程度上忽略了。
Based on this analysis, this paper proposes Adaptive Pyramid Context Network (APCNet) for semantic segmentation. APCNet adaptively constructs multi-scale contextual representations with multiple welldesigned Adaptive Context Modules (ACMs). Specifically, each ACM leverages a global image representation as a guidance to estimate the local affinity coefficients for each sub-region, and then calculates a context vector with these affinities.
基于此分析,本文提出了用于语义分割的自适应金字塔上下文网络 (APCNet)。APCNet 通过多个精心设计的自适应上下文模块 (ACMs) 自适应地构建多尺度上下文表示。具体来说,每个 ACM 利用全局图像表示作为指导来估计每个子区域的局部亲和力系数,然后计算具有这些亲和力的上下文向量。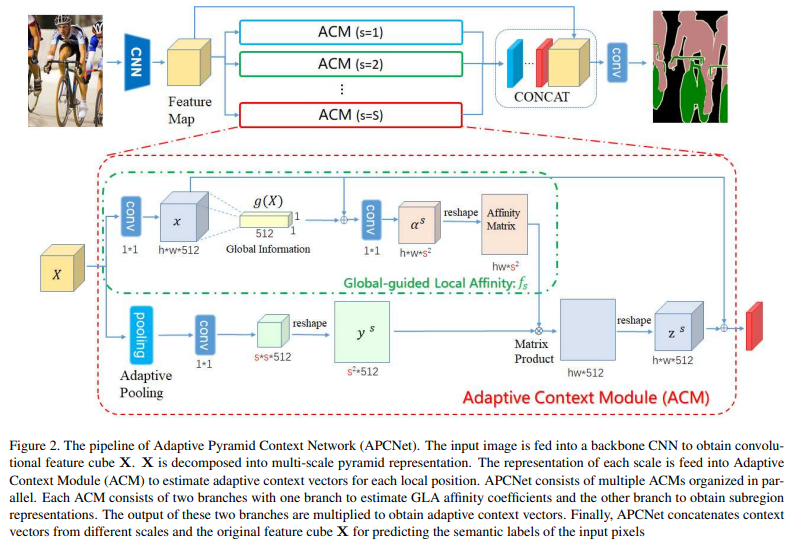
相关链接
- Dynamic Multi-scale Filters for Semantic Segmentation:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/He_Dynamic_Multi-Scale_Filters_for_Semantic_Segmentation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf
- Adaptive Pyramid Context Network for Semantic Segmentation:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/He_Adaptive_Pyramid_Context_Network_for_Semantic_Segmentation_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf

