- wait()、notify/notifyAll() 方法是Object的本地final方法,无法被重写。
- wait()使当前线程阻塞,前提是 必须先获得锁,一般配合synchronized 关键字使用,即,一般在synchronized 同步代码块里使用 wait()、notify/notifyAll() 方法。
- 当线程执行wait()方法时候,会释放当前的锁,然后让出CPU,进入等待状态。
- 只有当 notify/notifyAll() 被执行时候,才会唤醒一个或多个正处于等待状态的线程,然后继续往下执行,直到执行完synchronized 代码块的代码或是中途遇到wait() ,再次释放锁。
- 也就是说,notify/notifyAll() 的执行只是唤醒沉睡的线程,而不会立即释放锁,锁的释放要看代码块的具体执行情况。所以在编程中,尽量在使用了notify/notifyAll() 后立即退出临界区,以唤醒其他线程让其获得锁
- wait() 需要被try catch包围,以便发生异常中断也可以使wait等待的线程唤醒。
- notify 和wait 的顺序不能错,如果A线程先执行notify方法,B线程在执行wait方法,那么B线程是无法被唤醒的。
notify 和 notifyAll的区别
notify方法只唤醒一个等待(对象的)线程并使该线程开始执行。所以如果有多个线程等待一个对象,这个方法只会唤醒其中一个线程,选择哪个线程取决于操作系统对多线程管理的实现。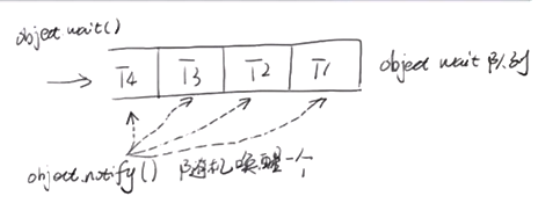
notifyAll 会唤醒所有等待(对象的)线程,尽管哪一个线程将会第一个处理取决于操作系统的实现。如果当前情况下有多个线程需要被唤醒,推荐使用notifyAll 方法。比如在生产者-消费者里面的使用,每次都需要唤醒所有的消费者或是生产者,以判断程序是否可以继续往下执行。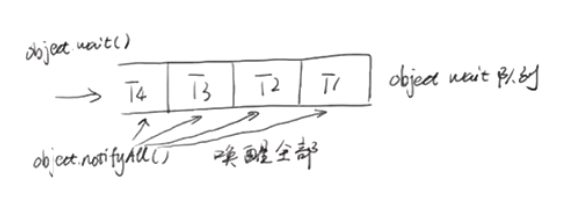
生产者消费者
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Product product = new Product();Producer producer = new Producer(product);Consumer consumer = new Consumer(product);new Thread(producer).start();new Thread(consumer).start();}}class Producer implements Runnable {private Product product;public Producer(Product product) {this.product = product;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (product) {while (true) {if (product.num >= 5) {try {product.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}product.num++;System.out.println("生产成功,商品总数:" + product.num);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}product.notifyAll();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {private Product product;public Consumer(Product product) {this.product = product;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (product) {while (true) {if (product.num <= 0) {try {product.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}product.num--;System.out.println("消费成功,商品总数为:" + product.num);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}product.notifyAll();}}}}class Product {int num = 0;}

