Explain有什么用
当Explain 与 SQL语句一起使用时,MySQL 会显示来自优化器关于SQL执行的信息。也就是说,MySQL解释了它将如何处理该语句,包括如何连接表以及什么顺序连接表等。
- 表的加载顺序
sql的查询类型- 可能用到哪些索引,哪些索引又被实际使用
- 表与表之间的引用关系
- 一个表中有多少行被优化器查询 …..
Explain有哪些信息
Explain执行计划包含字段信息如下:分别是id、select_type、table、partitions、type、possible_keys、key、key_len、ref、rows、filtered、Extra12个字段。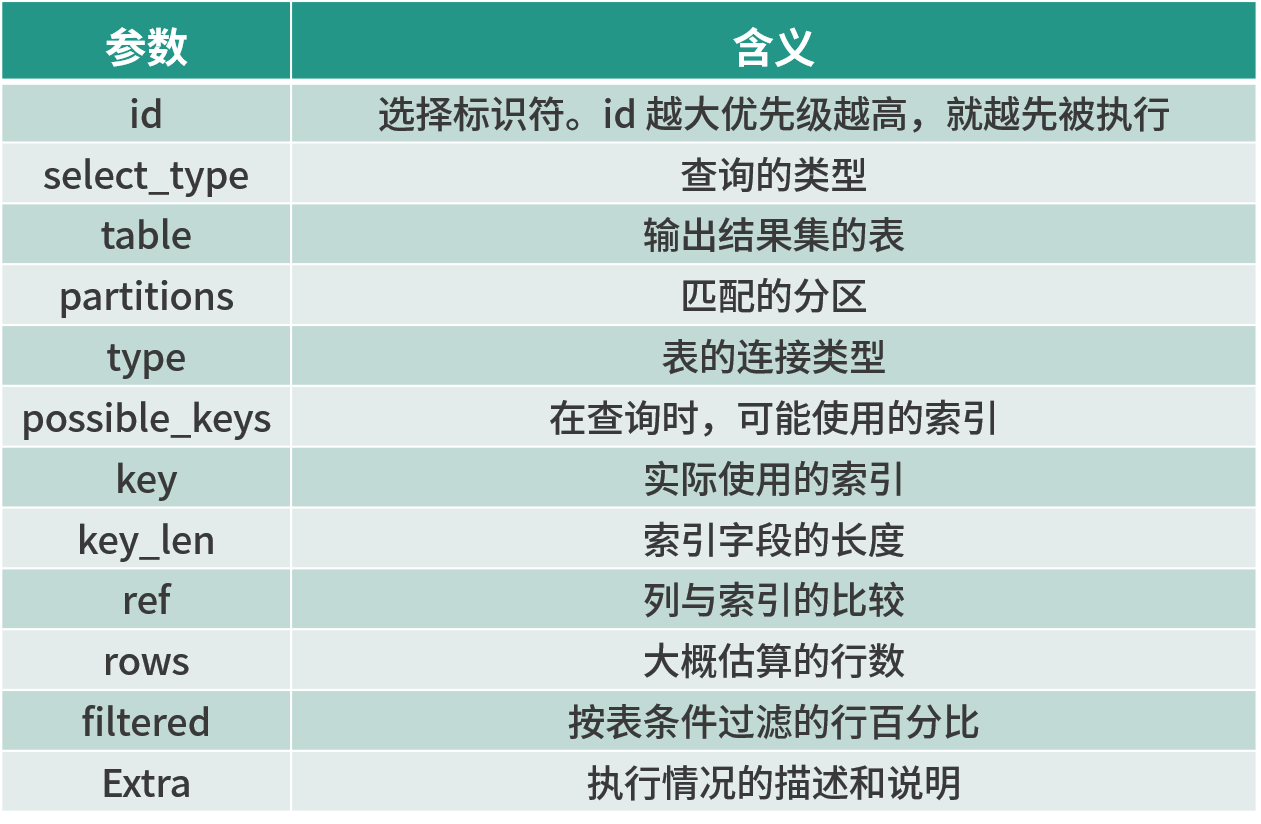
下边我们会结合具体的SQL示例,详细的解读每个字段以及每个字段中不同参数的含义,以下所有示例数据库版本为MySQL.5.7.17。
我们创建三张表mysql> select version() from dual;+------------+| version() |+------------+| 5.7.17-log |+------------+
one、two、three,表之间的关系one.two_id = two.two_id AND two.three_id = three.three_id。Explain执行计划详解
一、id
id::表示查询中执行select子句或者操作表的顺序,**id**的值越大,代表优先级越高,越先执行。id大致会出现 3种情况:1、
看到三条记录的id相同id都相同,可以理解成这三个表为一组,具有同样的优先级,执行顺序由上而下,具体顺序由优化器决定。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM one o,two t, three r WHERE o.two_id = t.two_id AND t.three_id = r.three_id;+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100 | NULL || 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) || 1 | SIMPLE | r | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | xin-slave.t.three_id | 1 | 100 | NULL |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2、
如果我们的id不同SQL中存在子查询,那么id的序号会递增,id值越大优先级越高,越先被执行 。当三个表依次嵌套,发现最里层的子查询id最大,最先执行。mysql> EXPLAIN select * from one o where o.two_id = (select t.two_id from two t where t.three_id = (select r.three_id from three r where r.three_name='我是第三表2'));+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | PRIMARY | o | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where || 2 | SUBQUERY | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where || 3 | SUBQUERY | r | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
3、以上两种同时存在
将上边的SQL稍微修改一下,增加一个子查询,发现id的以上两种同时存在。相同id划分为一组,这样就有三个组,同组的从上往下顺序执行,不同组id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行。mysql> EXPLAIN select * from one o where o.two_id = (select t.two_id from two t where t.three_id = (select r.three_id from three r where r.three_name='我是第三表2')) AND o.one_id in(select one_id from one where o.one_name="我是第一表2");+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | PRIMARY | o | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where || 1 | PRIMARY | one | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | xin-slave.o.one_id | 1 | 100 | Using index || 2 | SUBQUERY | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where || 3 | SUBQUERY | r | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+
二、select_type
select_type:表示select查询的类型,主要是用于区分各种复杂的查询,例如:普通查询、联合查询、子查询等。1、SIMPLE
SIMPLE:表示最简单的 select 查询语句,也就是在查询中不包含子查询或者union交并差集等操作。2、PRIMARY
PRIMARY:当查询语句中包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为PRIMARY。3、SUBQUERY
SUBQUERY:当select或where列表中包含了子查询,该子查询被标记为:SUBQUERY。4、DERIVED
DERIVED:表示包含在from子句中的子查询的select,在我们的from列表中包含的子查询会被标记为derived。5、UNION
UNION:如果union后边又出现的select语句,则会被标记为union;若union包含在from子句的子查询中,外层select将被标记为derived。6、UNION RESULT
UNION RESULT:代表从union的临时表中读取数据,而table列的<union1,4>表示用第一个和第四个select的结果进行union操作。 ```sql mysql> EXPLAIN select t.two_name, ( select one.one_id from one) o from (select two_id,two_name from two where two_name =’’) t union (select r.three_name,r.three_id from three r);
+———+———————+——————+——————+———-+———————-+————-+————-+———+———+—————+————————-+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+———+———————+——————+——————+———-+———————-+————-+————-+———+———+—————+————————-+
| 1 | PRIMARY | two | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50 | Using where |
| 2 | SUBQUERY | one | NULL | index | NULL | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 2 | 100 | Using index |
| 4 | UNION | r | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100 | NULL |
| NULL | UNION RESULT |
<a name="d0569dae"></a>### 三、table查询的表名,并不一定是真实存在的表,有别名显示别名,也可能为临时表,例如上边的 `DERIVED`、 `<union1,4>` 等。<a name="ee300575"></a>### 四、partitions查询时匹配到的分区信息,对于非分区表值为`NULL`,当查询的是分区表时,`partitions`显示分区表命中的分区情况。```sql+----+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | p201801,p201802,p201803,p300012 | index | NULL | PRIMARY | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
五、type
type:查询使用了何种类型,它在 SQL优化中是一个非常重要的指标,以下性能从好到坏依次是:system > const > eq_ref > ref > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL。
1、system
system:当表仅有一行记录时(系统表),数据量很少,往往不需要进行磁盘IO,速度非常快。
2、const
const:表示查询时命中 primary key 主键或者 unique 唯一索引,或者被连接的部分是一个常量(const)值。这类扫描效率极高,返回数据量少,速度非常快。
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from three where three_id=1;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+| 1 | SIMPLE | three | NULL | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100 | NULL |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
3、eq_ref
eq_ref:查询时命中主键primary key 或者 unique key索引, type 就是 eq_ref。
mysql> EXPLAIN select o.one_name from one o ,two t where o.one_id = t.two_id ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | index | PRIMARY | idx_name | 768 | NULL | 2 | 100 | Using index || 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | xin-slave.o.one_id | 1 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------+--------------------+------+----------+-------------+
4、ref
ref:区别于eq_ref ,ref表示使用非唯一性索引,会找到很多个符合条件的行。
mysql> select o.one_id from one o where o.one_name = "xin" ;+--------+| one_id |+--------+| 1 || 3 |+--------+mysql> EXPLAIN select o.one_id from one o where o.one_name = "xin" ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | ref | idx_name | idx_name | 768 | const | 1 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
5、ref_or_null
ref_or_null:这种连接类型类似于 ref,区别在于 MySQL会额外搜索包含NULL值的行。
mysql> EXPLAIN select o.one_id from one o where o.one_name = "xin" OR o.one_name IS NULL;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+--------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+--------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | ref_or_null | idx_name | idx_name | 768 | const | 3 | 100 | Using where; Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+--------------------------+
6、index_merge
index_merge:使用了索引合并优化方法,查询使用了两个以上的索引。
下边示例中同时使用到主键one_id 和 字段one_name的idx_name 索引 。
mysql> EXPLAIN select * from one o where o.one_id >1 and o.one_name ='xin';+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | index_merge | PRIMARY,idx_name | idx_name,PRIMARY | 772,4 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Using intersect(idx_name,PRIMARY); Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------------+
7、unique_subquery
unique_subquery:替换下面的 IN子查询,子查询返回不重复的集合。
value IN (SELECT primary_key FROM single_table WHERE some_expr)
8、index_subquery
index_subquery:区别于unique_subquery,用于非唯一索引,可以返回重复值。
value IN (SELECT key_column FROM single_table WHERE some_expr)
9、range
range:使用索引选择行,仅检索给定范围内的行。简单点说就是针对一个有索引的字段,给定范围检索数据。在where语句中使用 bettween...and、<、>、<=、in 等条件查询 type 都是 range。
举个栗子:three表中three_id为唯一主键,user_id普通字段未建索引。
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from three where three_id BETWEEN 2 AND 3;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | three | NULL | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
从结果中看到只有对设置了索引的字段,做范围检索 type 才是 range。
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from three where user_id BETWEEN 2 AND 3;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | three | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
10、index
index:Index 与 ALL 其实都是读全表,区别在于 index 是遍历索引树读取,而 ALL 是从硬盘中读取。
下边示例:three_id 为主键,不带 where 条件全表查询 ,type 结果为 index 。
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT three_id from three ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | three | NULL | index | NULL | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
11、ALL
ALL:将遍历全表以找到匹配的行,性能最差。
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from two ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| 1 | SIMPLE | two | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100 | NULL |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
六、possible_keys
possible_keys:表示在MySQL中通过哪些索引,能让我们在表中找到想要的记录,一旦查询涉及到的某个字段上存在索引,则索引将被列出,但这个索引并不定一会是最终查询数据时所被用到的索引。具体请参考上边的例子。
七、key
key:区别于 possible_keys,key 是查询中实际使用到的索引,若没有使用索引,显示为 NULL。具体请参考上边的例子。
当
type为index_merge时,可能会显示多个索引。
八、key_len
key_len:表示查询用到的索引长度(字节数),原则上长度越短越好 。
- 单列索引,那么需要将整个索引长度算进去;
- 多列索引,不是所有列都能用到,需要计算查询中实际用到的列。
注意:
key_len只计算where条件中用到的索引长度,而排序和分组即便是用到了索引,也不会计算到key_len中。
九、ref
ref:常见的有:const、func、null、字段名。
- 当使用常量等值查询,显示
const, - 当关联查询时,会显示相应关联表的
关联字段 - 如果查询条件使用了
表达式、函数,或者条件列发生内部隐式转换,可能显示为func - 其他情况
null十、rows
rows:以表的统计信息和索引使用情况,估算要找到我们所需的记录,需要读取的行数。
这是评估SQL性能的一个比较重要的数据,mysql需要扫描的行数,很直观的显示SQL性能的好坏,一般情况下rows值越小越好。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from three;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| 1 | SIMPLE | three | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100 | NULL |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
十一、filtered
filtered这个是一个百分比的值,表里符合条件的记录数的百分比。简单点说,这个字段表示存储引擎返回的数据在经过过滤后,剩下满足条件的记录数量的比例。
在MySQL.5.7版本以前想要显示filtered需要使用explain extended命令。MySQL.5.7后,默认explain直接显示partitions和filtered的信息。十二、Extra
Extra:不适合在其他列中显示的信息,Explain中的很多额外的信息会在Extra字段显示。1、Using index
Using index:我们在相应的select操作中使用了覆盖索引,通俗一点讲就是查询的列被索引覆盖,使用到覆盖索引查询速度会非常快,SQl优化中理想的状态。
什么又是覆盖索引?
一条SQL只需要通过索引就可以返回,我们所需要查询的数据(一个或几个字段),而不必通过二级索引,查到主键之后再通过主键查询整行数据(select *)。one_id表为主键
注意:想要使用到覆盖索引,我们在mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_id from one ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | index | NULL | idx_two_id | 5 | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
select时只取出需要的字段,不可select *,而且该字段建了索引。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * from one ;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100 | NULL |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
2、Using where
Using where:查询时未找到可用的索引,进而通过where条件过滤获取所需数据,但要注意的是并不是所有带where语句的查询都会显示Using where。
下边示例create_time并未用到索引,type为ALL,即MySQL通过全表扫描后再按where条件筛选数据。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_name from one where create_time ='2020-05-18';+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
3、Using temporary
Using temporary:表示查询后结果需要使用临时表来存储,一般在排序或者分组查询时用到。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_name from one where one_id in (1,2) group by one_name;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | range| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using temporary; Using filesort |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
4、Using filesort
Using filesort:表示无法利用索引完成的排序操作,也就是ORDER BY的字段没有索引,通常这样的SQL都是需要优化的。
如果mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_id from one ORDER BY create_time;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using filesort |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
ORDER BY字段有索引就会用到覆盖索引,相比执行速度快很多。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_id from one ORDER BY one_id;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | one | NULL | index | NULL | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
5、Using join buffer
Using join buffer:在我们联表查询的时候,如果表的连接条件没有用到索引,需要有一个连接缓冲区来存储中间结果。
先看一下有索引的情况:连接条件one_name、two_name都用到索引。
接下来删掉 连接条件mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_name from one o,two t where o.one_name = t.two_name;+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+--------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+--------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | index | idx_name | idx_name | 768 | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using where; Using index || 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ref | idx_name | idx_name | 768 | xin-slave.o.one_name | 1 | 100 | Using index |+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+--------------------------+
one_name、two_name的字段索引。发现Extra列变成Using join buffer,type均为全表扫描,这也是SQL优化中需要注意的地方。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_name from one o,two t where o.one_name = t.two_name;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100 | NULL || 1 | SIMPLE | o | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
6、Impossible where
Impossible where:表示在我们用不太正确的where语句,导致没有符合条件的行。mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT one_name from one WHERE 1=2;+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Impossible WHERE |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
7、No tables used
No tables used:我们的查询语句中没有FROM子句,或者有FROM DUAL子句。mysql> EXPLAIN select now();+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | No tables used |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
Extra列的信息非常非常多,这里就不再一一列举了,详见MySQL官方文档:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/explain-output.html

