1 if-else结构
如何从键盘获取不同类型的变量:需要使用Scanner类
具体实现步骤:
1、导包:import java.util.Scanner;
2、Scanner的实例化:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
3、调用Scanner的相关方法,来获取指定类型的变量
System.out.println("小鹏的期末成绩是(0-100):");Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int score = sc.nextInt();if (score == 100) {System.out.println("奖励一台BMW");} else if (score > 80 & score <= 99) {System.out.println("奖励一台iPhone");} else if (score >= 60 & score <= 80) {System.out.println("奖励一台iPad");} else {System.out.println("没有啥");}
课后练习题
int x = 4;int y = 1;if (x > 2) {if (y > 2)System.out.println(x + y);System.out.println("atguigu");} elseSystem.out.println("x is " + x);程序结果输出为:atguigu因为if处没有{}所以只会认为仅有 System.out.println(x + y);这一行代码。int x = 4;int y = 1;if (x > 2)if (y > 2)System.out.println(x + y);//System.out.println("atguigu");else//就近原则,与最近的if配对System.out.println("x is " + x);程序结果输出为:4
boolean b = true;if(b == false)System.out.println("a");else if(b)System.out.println("b");else if(!b)System.out.println("c");elseSystem.out.println("d");程序结果输出为:b//如果写成if(b=false)能编译通过吗?如果能,结果是?程序结果输出为:c
注意:if-else语句中范围大的写在前,范围小的写在后。
if-else语句可以嵌套,
package com.atguigu.study;public class Practice5 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*编写程序从1循环到150,并在每行打印一个值,另外在每个3的倍数行上打印出“foo”,在每个5的倍数行上打印“biz”,在每个7的倍数行上打印输出“baz”。*/for (int i = 1; i <= 150; i++) {System.out.print(i + " ");if (i % 3 == 0) {System.out.print("foo ");}if (i % 5 == 0) {System.out.print("biz ");}if (i % 7 == 0) {System.out.print("baz ");}System.out.println();}}}
2 switch-case
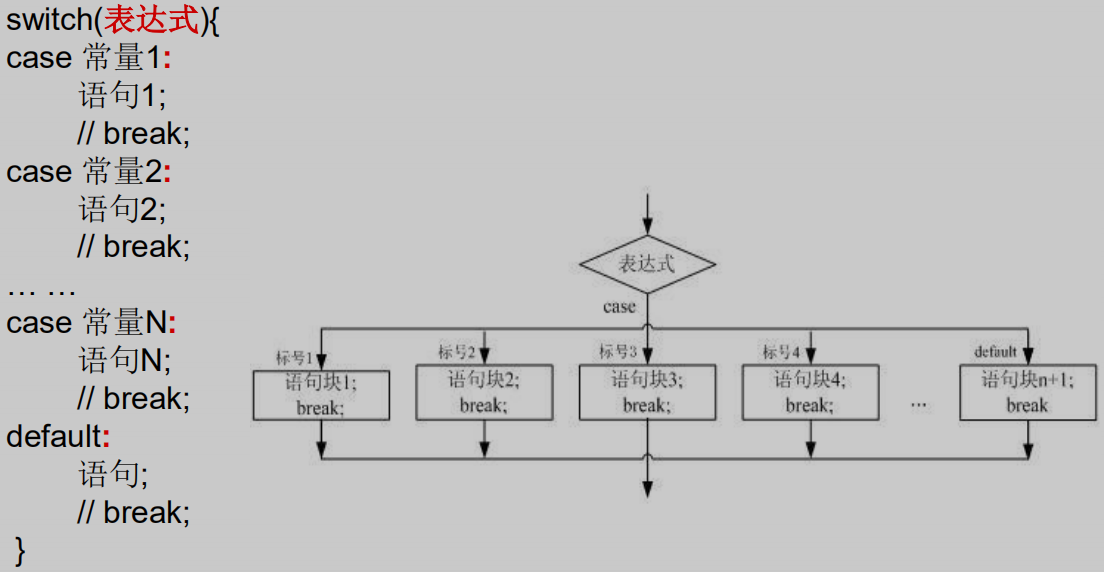
1、break的作用是跳出switch-case结构。
2、根据switch-case表达式的值,依次匹配各个case中的常量。一旦匹配成功,则进入相应的case结构中,调用其执行语句。当调用完执行语句后,则继续向下执行其他case结构的执行语句,直到遇到break或结构末尾才结束。
3、switch结构中的表达式,只能是如下的6种数据类型之一:byte、short、char、int、枚举类型(jdk 5.0)、String类型 (jdk 7.0)(重要)
4、case子句中的值必须是常量,不能是变量名或不确定的表达式值。
5、default子句是可任选的,相当于else。同时,位置是灵活的。当没有匹配的case时,执行default。
switch和if语句的对比
if和switch语句很像,具体什么场景下,应用哪个语句呢?
如果判断的具体数值不多,而且符合byte、short 、char、int、String、枚举等几种类型。虽然两个语句都可以使用,建议使用swtich语句。因为效率稍高。
其他情况:对区间判断,对结果为boolean类型判断,使用if,if的使用范围更广。也就是说,使用switch-case的,都可以改写为if-else。反之不成立。
package com.atguigu.study;import java.util.Scanner;public class Practice4 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*编写一个程序,为一个给定的年份找出其对应的中国生肖。中国的生肖基于12年一个周期,每年用一个动物代表:rat、ox、tiger、rabbit、dragon、snake、horse、sheep、monkey、rooster、dog、pig。提示:2019年:猪 2019 % 12 == 3*/Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入年份:");int year = sc.nextInt();switch (year%12){case 0:System.out.println("猴");break;case 1:System.out.println("鸡");break;case 2:System.out.println("狗");break;case 3:System.out.println("猪");break;case 4:System.out.println("鼠");break;case 5:System.out.println("牛");break;case 6:System.out.println("虎");break;case 7:System.out.println("兔");break;case 8:System.out.println("龙");break;case 9:System.out.println("蛇");break;case 10:System.out.println("马");break;case 11:System.out.println("羊");break;default:System.out.println("输入有问题");break;}}}
package com.atguigu.study;import java.util.Scanner;public class Practice3 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*从键盘分别输入年、月、日,判断这一天是当年的第几天注:判断一年是否是闰年的标准:1)可以被4整除,但不可被100整除或 2)可以被400整除*/Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入year:");int year = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入month:");int month = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入day:");int day = sc.nextInt();int sumDays = 0;switch (month) {case 12:sumDays += 31;case 11:sumDays += 31;case 10:sumDays += 30;case 9:sumDays += 31;case 8:sumDays += 31;case 7:sumDays += 30;case 6:sumDays += 31;case 5:sumDays += 30;case 4:sumDays += 31;case 3://sumDays+=28;if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) {sumDays += 29;} else {sumDays += 28;}case 2:sumDays += 31;case 1:sumDays += day;break;default:System.out.println("输入的月份有问题");break;}}}
3 循环结构
循环语句分类 :
for 循环
while 循环
do-while 循环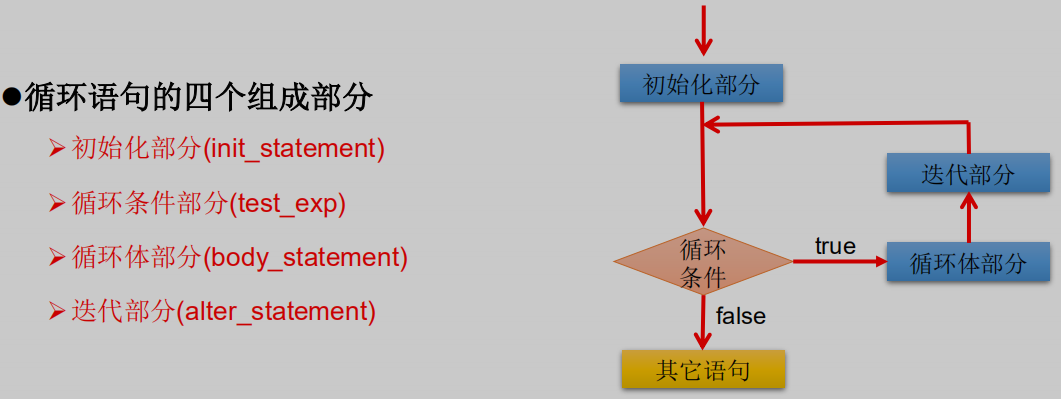
3.1 for循环
语法格式
for (①初始化部分; ②循环条件部分; ④迭代部分){
③循环体部分;
}
执行过程:
①-②-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…..-②
说明:
②循环条件部分为boolean类型表达式,当值为false时,退出循环
①初始化部分可以声明多个变量,但必须是同一个类型,用逗号分隔
④可以有多个变量更新,用逗号分隔
for(int i = 1;i<5;i++){System.out.println("1");}//int i,只在for中有效。
package com.atguigu.study;import java.util.Scanner;public class Practice6 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*题目:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。比如:12和20的最大公约数是4,最小公倍数是60。*/Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入正整数m:");int m = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入正整数n:");int n = sc.nextInt();int minBeiShu = m * n;if (m > n) {for (int yuShu = m % n; yuShu != 0; ) {m = n;n = yuShu;yuShu = m % n;}System.out.println("最大公约数是:" + n);System.out.println("最小公倍数是:"+(minBeiShu/n));} else {int temp = 0;temp = m;m = n;n = temp;for (int yuShu = m % n; yuShu != 0; ) {m = n;n = yuShu;yuShu = m % n;}System.out.println("最大公约数是:" + n);System.out.println("最小公倍数是:"+(minBeiShu/n));}}}//我写的,取巧了
package com.atguigu.study;import java.util.Scanner;/*题目:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。比如:12和20的最大公约数是4,最小公倍数是60。说明:break关键字的使用*/public class Practice9 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入第一个正整数:");int m = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入第二个正整数:");int n = sc.nextInt();int min = (m <= n) ? m : n;for (int i = min; i > 1; i--) {if (m % i == 0 && n % i == 0) {System.out.println("最大公约数:" + i);break;}}int max = (m >= n) ? m : n;for (int i = max; i <= m*n; i++) {if (i % m == 0 && i % n == 0) {System.out.println("最小公倍数:" + i);break;}}}}//老师写的
package com.atguigu.study;/*输出所有的水仙花数,所谓水仙花数是指一个3位数,其各个位上数字立方和等于其本身。例如: 153 = 1*1*1 + 3*3*3 + 5*5*5*/public class Practice10 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("水仙花数有:");for (int i = 100; i <= 999; i++) {int iBai = i / 100;int iGe = i % 10;int iShi = i / 10 % 10;if (iBai * iBai * iBai + iGe * iGe * iGe + iShi * iShi * iShi == i) {System.out.println(i);}}}}
3.2 while
语法格式
①初始化部分
while(②循环条件部分){
③循环体部分;
④迭代部分;
}
执行过程:
①-②-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…-②
说明:
注意不要忘记声明④迭代部分。否则,循环将不能结束,变成死循环。
for循环和while循环可以相互转换。
区别:for循环和while循环的初始化条件部分的作用范围不同。
3.2 do-while
语法格式
①初始化部分;
do{
③循环体部分
④迭代部分
}while(②循环条件部分);
执行过程:
①-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…②
说明:
do-while循环至少执行一次循环体。

