1、昨日复习
画出如下几行代码的内容结构:
String s1 = “hello”;
String s2 = “hello”;
String s3 = new String(“hello”);
s1 += “world”;如何理解String类的不可变性
String类是否可以被继承?为什么?
String s = new String(“hello”);在内存中创建了几个对象?请说明String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder三者的对比
String的常用方法有哪些?(至少7个)
length() / charAt() / equals() / compareTo() / startsWith() / endsWith()
containts() / indexOf() / lastIndexOf() / getBytes() / toCharArray() / valueOf() / ….2、常见算法题目
```java package com.atguigu.java;
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
- 1.模拟一个trim方法,去除字符串两端的空格。
- 2.将一个字符串进行反转。将字符串中指定部分进行反转。比如将“abcdefg”反转为”abfedcg”
- 3.获取一个字符串在另一个字符串中出现的次数。
比如:获取“ab”在 “cdabkkcadkabkebfkabkskab”
中出现的次数
4.获取两个字符串中最大相同子串。比如:
str1 = “abcwerthelloyuiodef“;str2 = “cvhellobnm”//10
提示:将短的那个串进行长度依次递减的子串与较长
的串比较。
5.对字符串中字符进行自然顺序排序。”abcwerthelloyuiodef” 提示: 1)字符串变成字符数组。 2)对数组排序,选择,冒泡,Arrays.sort(str.toCharArray()); 3)将排序后的数组变成字符串。
*/ public class StringExer {
// 第1题public String myTrim(String str) {if (str != null) {int start = 0;// 用于记录从前往后首次索引位置不是空格的位置的索引int end = str.length() - 1;// 用于记录从后往前首次索引位置不是空格的位置的索引while (start < end && str.charAt(start) == ' ') {start++;}while (start < end && str.charAt(end) == ' ') {end--;}if (str.charAt(start) == ' ') {return "";}return str.substring(start, end + 1);}return null;}// 第2题// 方式一:public String reverse1(String str, int start, int end) {// start:2,end:5if (str != null) {// 1.char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();// 2.for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {char temp = charArray[i];charArray[i] = charArray[j];charArray[j] = temp;}// 3.return new String(charArray);}return null;}// 方式二:public String reverse2(String str, int start, int end) {// 1.String newStr = str.substring(0, start);// ab// 2.for (int i = end; i >= start; i--) {newStr += str.charAt(i);} // abfedc// 3.newStr += str.substring(end + 1);return newStr;}// 方式三:推荐 (相较于方式二做的改进)public String reverse3(String str, int start, int end) {// ArrayList list = new ArrayList(80);// 1.StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(str.length());// 2.s.append(str.substring(0, start));// ab// 3.for (int i = end; i >= start; i--) {s.append(str.charAt(i));}// 4.s.append(str.substring(end + 1));// 5.return s.toString();}@Testpublic void testReverse() {String str = "abcdefg";String str1 = reverse3(str, 2, 5);System.out.println(str1);// abfedcg}// 第3题// 判断str2在str1中出现的次数public int getCount(String mainStr, String subStr) {if (mainStr.length() >= subStr.length()) {int count = 0;int index = 0;// while((index = mainStr.indexOf(subStr)) != -1){// count++;// mainStr = mainStr.substring(index + subStr.length());// }// 改进:while ((index = mainStr.indexOf(subStr, index)) != -1) {index += subStr.length();count++;}return count;} else {return 0;}}@Testpublic void testGetCount() {String str1 = "cdabkkcadkabkebfkabkskab";String str2 = "ab";int count = getCount(str1, str2);System.out.println(count);}@Testpublic void testMyTrim() {String str = " a ";// str = " ";String newStr = myTrim(str);System.out.println("---" + newStr + "---");}// 第4题// 如果只存在一个最大长度的相同子串public String getMaxSameSubString(String str1, String str2) {if (str1 != null && str2 != null) {String maxStr = (str1.length() > str2.length()) ? str1 : str2;String minStr = (str1.length() > str2.length()) ? str2 : str1;int len = minStr.length();for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {// 0 1 2 3 4 此层循环决定要去几个字符for (int x = 0, y = len - i; y <= len; x++, y++) {if (maxStr.contains(minStr.substring(x, y))) {return minStr.substring(x, y);}}}}return null;}// 如果存在多个长度相同的最大相同子串// 此时先返回String[],后面可以用集合中的ArrayList替换,较方便public String[] getMaxSameSubString1(String str1, String str2) {if (str1 != null && str2 != null) {StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();String maxString = (str1.length() > str2.length()) ? str1 : str2;String minString = (str1.length() > str2.length()) ? str2 : str1;int len = minString.length();for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {for (int x = 0, y = len - i; y <= len; x++, y++) {String subString = minString.substring(x, y);if (maxString.contains(subString)) {sBuffer.append(subString + ",");}}System.out.println(sBuffer);if (sBuffer.length() != 0) {break;}}String[] split = sBuffer.toString().replaceAll(",$", "").split("\\,");return split;}return null;}// 如果存在多个长度相同的最大相同子串:使用ArrayList
// public List
@Testpublic void testGetMaxSameSubString() {String str1 = "abcwerthelloyuiodef";String str2 = "cvhellobnmiodef";String[] strs = getMaxSameSubString1(str1, str2);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs));}// 第5题@Testpublic void testSort() {String str = "abcwerthelloyuiodef";char[] arr = str.toCharArray();Arrays.sort(arr);String newStr = new String(arr);System.out.println(newStr);}
}
<a name="ltRH1"></a># 3、**java.text.SimpleDateFormat类**Date类的API不易于国际化,大部分被废弃了,**java.text.SimpleDateFormat**类是一个不与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。 <br />它允许进行**格式化:日期》文本**、**解析:文本》日期 **<br />**格式化: **<br />**SimpleDateFormat() **:默认的模式和语言环境创建对象 <br />**public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern):**该构造方法可以用参数pattern指定的格式创建一个对象,该对象调用: **public String format(Date date):**方法格式化时间对象date <br />**解析: **<br />**public Date parse(String source):**从给定字符串的开始解析文本,以生成一个日期。---SimpleDateFormat的使用:SimpleDateFormat对日期Date类的格式化和解析<br />1、两个操作:<br />1.1 格式化:日期--->字符串<br />1.2 解析:格式化的逆过程,字符串--->日期<br />2、SimpleDateFormat的实例化```java@Testpublic void test1() throws ParseException {SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();//格式化Date date = new Date();System.out.println(date);String format = sdf.format(date);System.out.println(format);//解析String str = "2022-1-16 下午3:25";Date date1 = sdf.parse(str);System.out.println(date1);System.out.println("********************************");//指定方式格式化,调用带参的构造器SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//格式化String s = sdf1.format(date);System.out.println(s);//解析:要求字符串必须是符合SimpleDateFormat识别的格式(通过构造器参数体现),否则抛异常Date date2 = sdf1.parse("2019-11-28 16:44:25");System.out.println(date2);}
/*练习一:字符串“2020-09-08”转换为java.sql.Date*/@Testpublic void test2() throws ParseException {String birth = "2020-09-08";SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");Date date = sdf.parse(birth);// System.out.println(date);java.sql.Date birthDate = new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());System.out.println(birthDate);}
4、java.util.Calendar(日历)类
Calendar是一个抽象基类,主用用于完成日期字段之间相互操作的功能。
获取Calendar实例的方法
使用Calendar.getInstance()方法
调用它的子类GregorianCalendar的构造器。
一个Calendar的实例是系统时间的抽象表示,通过get(int field)方法来取得想要的时间信息。比如YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_WEEK、HOUR_OF_DAY 、MINUTE、SECOND
public void set(int field,int value)
public void add(int field,int amount)
public final Date getTime()
public final void setTime(Date date)
注意:
获取月份时:一月是0,二月是1,以此类推,12月是11
获取星期时:周日是1,周二是2 , 。。。。周六是7
@Testpublic void test1(){// Calendar的使用// 1、实例化// 方式一:创建其子类(GregorianCalendar)的对象// 方式二:调用其静态方法getInstance();Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();System.out.println(calendar.getClass());//class java.util.GregorianCalendarCalendar calendar1 = new GregorianCalendar();// 2、常用方法// get()int days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days);//16System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));//16//// set()calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,5);days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days);//5//// add()calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,-3);days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days);//2//// getTime():日历类———>DateDate date = calendar.getTime();System.out.println(date.getTime());//1641111904994System.out.println(date);//Sun Jan 02 16:25:04 CST 2022//setTime():Date———>日历类Date date1 = new Date();calendar.setTime(date1);days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days);//16}}
5、JDK8中新日期时间API
Java 8 吸收了 Joda-Time 的精华,以一个新的开始为 Java 创建优秀的 API。
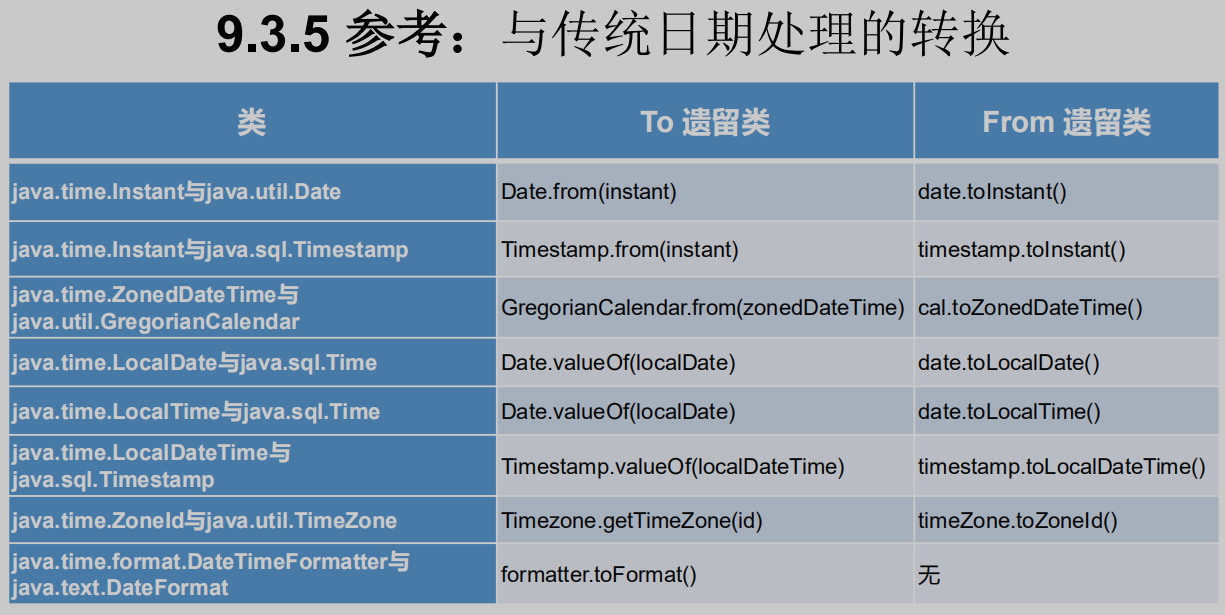
新的 java.time 中包含了所有关于本地日期(LocalDate)、本地时间(LocalTime)、本地日期时间(LocalDateTime)、时区(ZonedDateTime) 和持续时间(Duration)的类。历史悠久的 Date 类新增了 toInstant() 方法, 用于把 Date 转换成新的表示形式。这些新增的本地化时间日期 API 大大简 化了日期时间和本地化的管理。
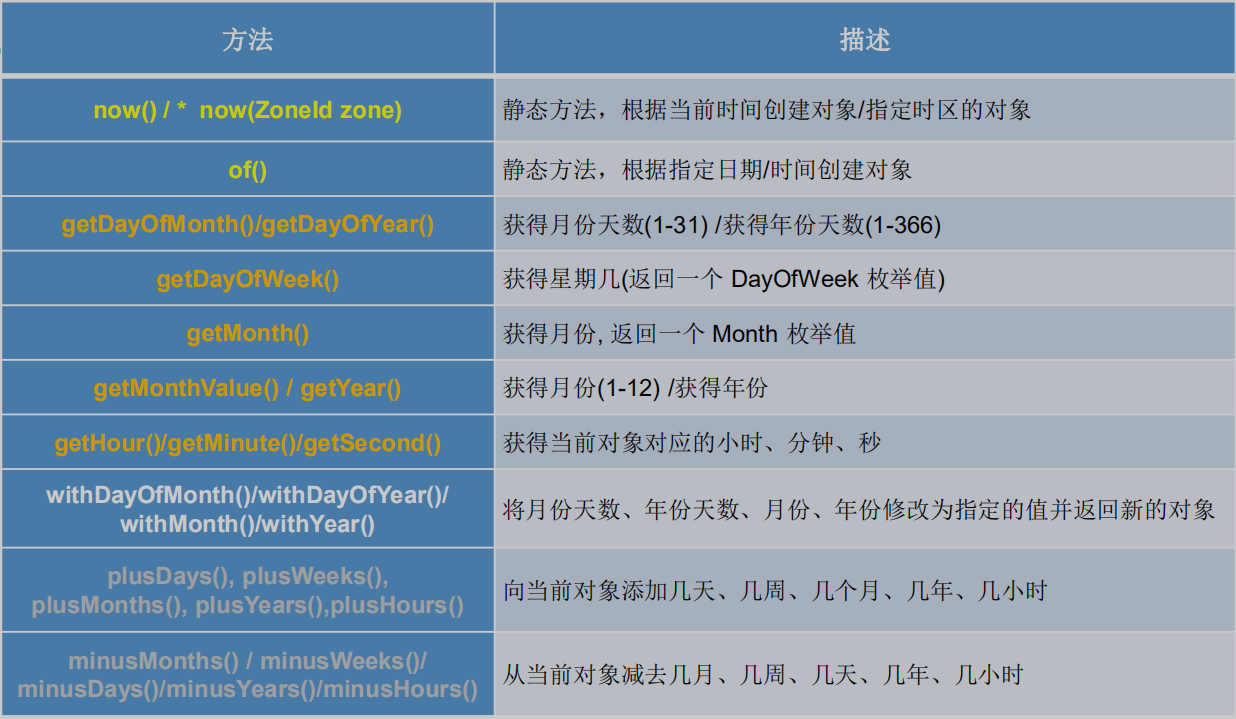
5.1 LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime
package com.atguigu.java1;import org.junit.Test;import java.time.LocalDate;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.time.LocalTime;public class JDK8DateTimeTest {/*说明:1、LocalDateTime相较于LocalDate、LocalTime,使用频率要更高2、类似于Calendar*/@Testpublic void test1(){//now():获取当前的日期、时间、日期+时间LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println(localDate);System.out.println(localTime);System.out.println(localDateTime);//of():设置指定的年月日,时分秒,没有偏移量。LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2022, 1, 16, 17, 31, 54);System.out.println(localDateTime1);//getXxx():获取相关的属性System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfWeek());System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfMonth());System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonth());System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonthValue());System.out.println(localDateTime.getMinute());//体现不可变性//withXxx():设置相关的属性LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.withDayOfMonth(22);System.out.println(localDate);System.out.println(localDate1);LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.withHour(4);System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(localDateTime2);//plusXxx():LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime.plusMonths(3);System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(localDateTime3);//minusXxx():LocalDateTime localDateTime4 = localDateTime.minusDays(6);System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(localDateTime4);}}
5.2 瞬时:Instant
Instant:时间线上的一个瞬时点。 这可能被用来记录应用程序中的事件时间戳。 
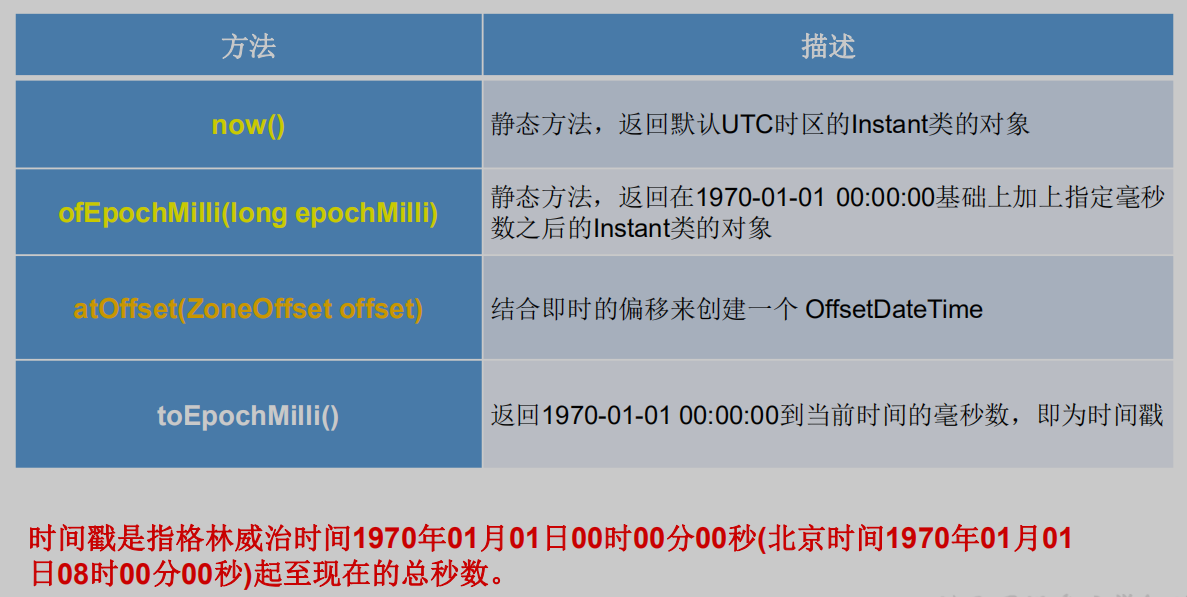
/*Instant的使用类似于java.util.Date类*/@Testpublic void test2(){//now():获取本初子午线对应的标准时间Instant instant = Instant.now();System.out.println(instant);//添加时间的偏移量OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));System.out.println(offsetDateTime);//toEpochMilli():获取自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒(UTC)开始的毫秒数-->Date类的getTime()long milli = instant.toEpochMilli();System.out.println(milli);//ofEpochMilli():通过给定的毫秒数,获取Instant实例-->Date(long millis)Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1642330764482L);System.out.println(instant1);}
5.3 格式化与解析日期或时间
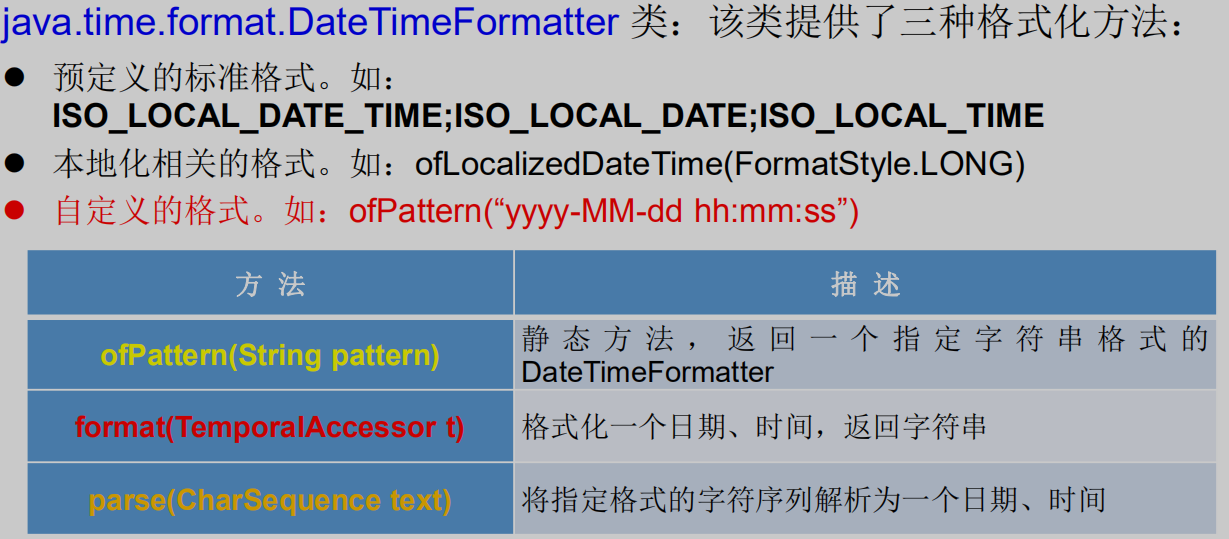
/*DateTimeFormatter:格式化与解析日期或时间类似于SimpleDateFormat*/@Testpublic void test3(){// 预定义的标准格式。ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIMEDateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;//格式化:日期-->字符串LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();String str1 = formatter.format(localDateTime);System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(str1);//解析:字符串-->日期TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse("2022-01-16T19:15:43.29");System.out.println(parse);// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG)DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);//格式化String str2 = formatter1.format(localDateTime);System.out.println(str2);DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);//格式化String str3 = formatter2.format(LocalDate.now());System.out.println(str3);// 重点 自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)DateTimeFormatter formatter3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//格式化String str4 = formatter3.format(LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(str4);//解析TemporalAccessor accessor = formatter3.parse("2022-01-16 19:32:46");System.out.println(accessor);}
5.4 其它API
6、 Java比较器
Java实现对象排序的方式有两种:
自然排序:java.lang.Comparable
定制排序:java.util.Comparator
package com.atguigu.java2;public class Goods implements Comparable {private String name;private double price;public Goods() {}public Goods(String name, double price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Goods{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Object o) {if (o instanceof Goods) {Goods goods = (Goods) o;//方式一if (this.price > goods.price) {return 1;} else if (this.price < goods.price) {return -1;} else {return 0;}//方式二// return Double.compare(this.price, goods.price);}throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不一致!");}}
package com.atguigu.java2;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Comparator;/*** 一、说明:java中的对象,正常情况下,只能进行比较:==或!=。不能使用</或>的* 但是在开发场景中,我们需要对多个对象进行排序,言外之意,就需要比较对象的大小。* 如何实现?使用两个接口中的任何一个:Comparable或Comparator* 二、Comparable接口与Comparator的使用对比:* Comparable接口的方式一旦指定,保证Comparable接口实现类的对象在任何位置都可以比较大小* Comparator接口属于临时性的比较。***/public class ComparaTest {/*Comparable接口的使用举例:自然排序1、像String、包装类等实现了Comparable接口,重写了compareTo()方法,给出了比较两个对象大小的方式2、像String、包装类等重写compareTo(obj)方法以后,进行了从小到大的排序3、重写compareTo(obj)方法的规则:如果当前对象this大于形参对象obj,则返回正整数,如果当前对象this小于形参对象obj,则返回负数如果当前对象this等于形参对象obj,则返回零。4、对于自定义类来说,如果需要排序,我们可以让自定义类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj)方法。在compareTo(obj)方法中指明如何排序*/@Testpublic void test1() {String[] arr = new String[]{"AA", "CC", "MM", "GG", "JJ", "DD", "KK"};Arrays.sort(arr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}@Testpublic void test2() {Goods[] arr = new Goods[5];arr[0] = new Goods("lianxiangMouse", 34);arr[1] = new Goods("dellMouse", 43);arr[2] = new Goods("xiaomiMouse", 12);arr[3] = new Goods("huaweiMouse", 65);arr[4] = new Goods("microsoftMouse", 43);Arrays.sort(arr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}/*Comparator接口的使用举例:定制排序1、背景:当元素的类型没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口而又不方便修改代码,或者实现了java.lang.Comparable接口的排序规则不适合当前的操作,那么可以考虑使用 Comparator 的对象来排序。2、重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。*/@Testpublic void test3() {String[] arr = new String[]{"AA", "CC", "MM", "GG", "JJ", "DD", "KK"};Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<String>() {//按照字符串从大到小的顺序排列@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {if (o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String) {String s1 = (String) o1;String s2 = (String) o2;return -s1.compareTo(s2);}throw new RuntimeException("输入的数据类型不一致");}});}@Testpublic void test4(){Goods[] arr = new Goods[6];arr[0] = new Goods("lianxiangMouse", 34);arr[1] = new Goods("dellMouse", 43);arr[2] = new Goods("xiaomiMouse", 12);arr[3] = new Goods("huaweiMouse", 65);arr[4] = new Goods("huaweiMouse", 224);arr[5] = new Goods("microsoftMouse", 43);Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Goods>() {//指明商品比较大小的方式:按照产品名称从低到高排序,再按照价格从高到低排序@Overridepublic int compare(Goods o1, Goods o2) {if (o1 instanceof Goods && o2 instanceof Goods) {Goods g1 = (Goods) o1;Goods g2 = (Goods) o2;if (g1.getName().equals(g2.getName())){return -Double.compare(g1.getPrice(), g2.getPrice());}else{return g1.getName().compareTo(g2.getName());}}throw new RuntimeException("输入的数据类型不一致");}});System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}}
7、System类

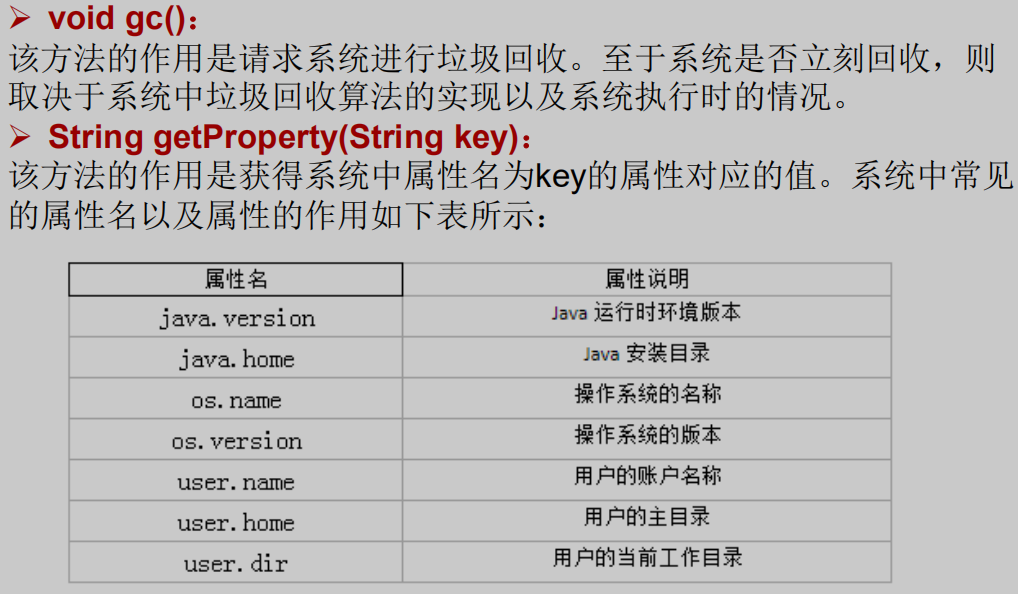
package com.atguigu.java2;import org.junit.Test;/*其他常用类的使用1、System2、Math3、BigInteger 和BigDecimal*/public class OtherClassTest {@Testpublic void test1() {String javaVersion = System.getProperty("java.version");System.out.println("java的version:" + javaVersion);String javaHome = System.getProperty("java.home");System.out.println("java的home:" + javaHome);String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println("os的name:" + osName);String osVersion = System.getProperty("os.version");System.out.println("os的version:" + osVersion);String userName = System.getProperty("user.name");System.out.println("user的name:" + userName);String userHome = System.getProperty("user.home");System.out.println("user的home:" + userHome);String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");System.out.println("user的dir:" + userDir);}}
8、Math类
9、BigInteger类和BigDecimal类



@Testpublic void test2() {BigInteger bi = new BigInteger("12433241123");BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");System.out.println(bi);// System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2));System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, 15, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));}}