1、昨日复习
- 一个IP对应着哪个类的一个对象?InetAddress
实例化这个类的两种方式是?
InetAddress.getByName(String host);
InetAddress.getLocalHost();//获取本地ip
两个常用的方法是?
getHostName();
getHostAddress();
2. 传输层的TCP协议和UDP协议的主要区别是?
TCP:可靠的数据传输(三次握手);进行大数据量的传输;效率低
UDP:不可靠;以数据报形式发送,数据报限定为64k;效率高
- 什么是URL,你能写一个URL吗?
URL:统一资源定位符
URL url = new
URL(“http://192.168.14.100:8080/examples/hello.txt?username=Tom”);
4. 谈谈你对对象序列化机制的理解
序列化过程:
反序列化过程:
5. 对象要想实现序列化,需要满足哪几个条件
1. 实现接口:Serializable 标识接口
2. 对象所在的类提供常量:序列版本号
3. 要求对象的属性也必须是可序列化的。(基本数据类型、String:本身就已经是可序列化的。)2、反射机制概述
Reflection(反射)是被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性及方法。
加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构。这个对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看
到类的结构,所以,我们形象的称之为:反射。
Java反射机制提供的功能
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
在运行时获取泛型信息
在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
在运行时处理注解
生成动态代理3、理解Class类并获取Class的实例
```java package com.atguigu.java1;
public class Person { private String name; public int age;
public Person() {System.out.println("我是空参构造器");}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}private Person(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public void show(){System.out.println("你好,我是一个人");}private String showNation(String nation){System.out.println("我的国籍是:"+nation);return nation;}
}
```javapackage com.atguigu.java1;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionTest {//反射之前,对于Person类的操作@Testpublic void test1() {//1、创建Person类的对象Person p1 = new Person("Tom", 12);//2、通过对象,调用其内部的属性、方法p1.age = 10;System.out.println(p1.toString());p1.show();//在Person类外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有结构//比如:name、showNation以及私有的构造器}//反射之后,对于Person类的操作@Testpublic void test2() throws Exception {Class clazz = Person.class;//1、通过反射创建Person类的对象Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);Object obj = cons.newInstance("Tom", 12);Person p = (Person) obj;System.out.println(p.toString());//2、通过反射,调用对象指定的属性、方法//调属性Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");age.set(p, 10);System.out.println(p.toString());//调方法Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");show.invoke(p);//通过反射,可以调用Person类的私有结构。比如:私有的构造器、方法、属性//调用私有的构造器Constructor cons1 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);cons1.setAccessible(true);Person p1 = (Person) cons1.newInstance("Jerry");System.out.println(p1);//调用私有的属性Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");name.setAccessible(true);name.set(p1,"HanMeimei");System.out.println(p1);//调用私有的方法Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class);showNation.setAccessible(true);String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(p1, "中国");//相当于p1.showNation("中国")System.out.println(nation);}//疑问1:通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中到底用哪个?//建议:直接new的方式。//什么时候会使用:反射的方式。反射的特征:动态性//疑问2:反射机制与面向对象的封装性是不是矛盾的?如何看待两个技术?//不矛盾。/*关于java.lang.Class类的理解1、类的加载过程:程序经过javac.exe命令以后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class结尾)。接着我们使用java.exe命令对某个字节码文件进行解释运行。相当于将某个字节码文件加载到内存中。此过程就称为类的加载。加载到内存中的类,我们就称为运行时类,此运行时类,就作为Class的一个实例。2、换句话说,Class的实例就对应着一个运行时类。3、加载到内存中的运行时类,会缓存一定的时间。在此时间之内,我们可以通过不同的方式来获取次运行时类。*///获取Class类的实例(四种方法)掌握@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {//方式一:调用运行时类的属性:.classClass clazz1 = Person.class;System.out.println(clazz1);//方式二:通过运行时类的对象Person p1 = new Person();Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();System.out.println(clazz2);//方式三:调用Class的静态方法:forName(String classPath)Class clazz3 = Class.forName("com.atguigu.java1.Person");System.out.println(clazz3);System.out.println(clazz1==clazz2);System.out.println(clazz1==clazz3);//方式四:使用类的加载器:ClassLoaderClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();Class clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.atguigu.java1.Person");System.out.println(clazz4);}//Class实例可以是哪些结构的说明@Testpublic void test4(){Class c1 = Object.class;Class c2 = Comparable.class;Class c3 = String[].class;Class c4 = int[][].class;Class c5 = ElementType.class;Class c6 = Override.class;Class c7 = int.class;Class c8 = void.class;Class c9 = Class.class;int[] a = new int[10];int[] b = new int[100];Class c10 = a.getClass();Class c11 = b.getClass();// 只要数组元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个ClassSystem.out.println(c10 == c11);}}
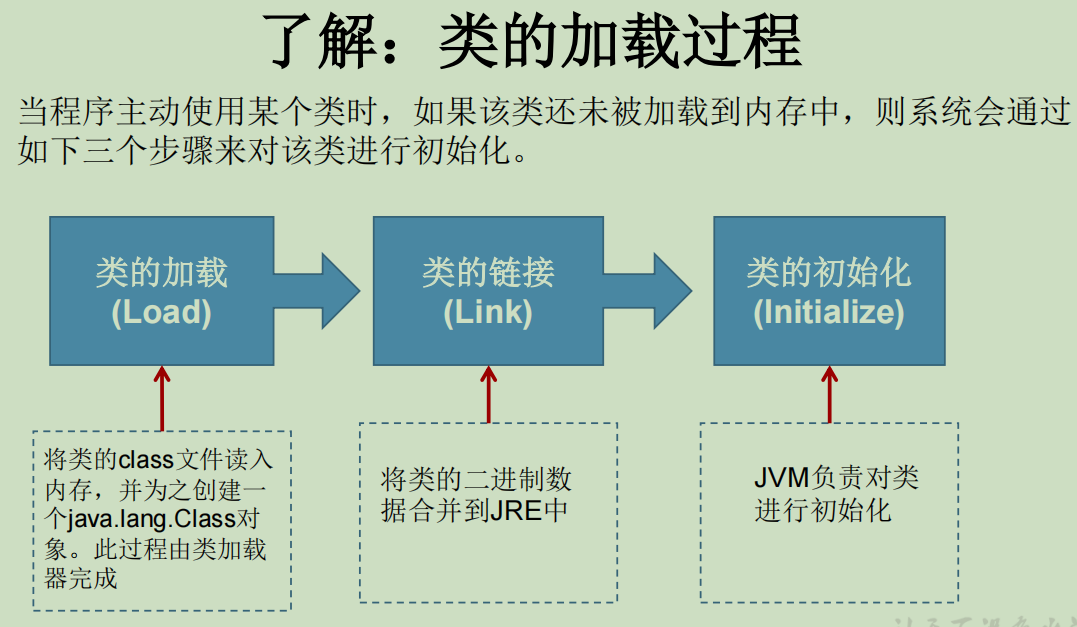
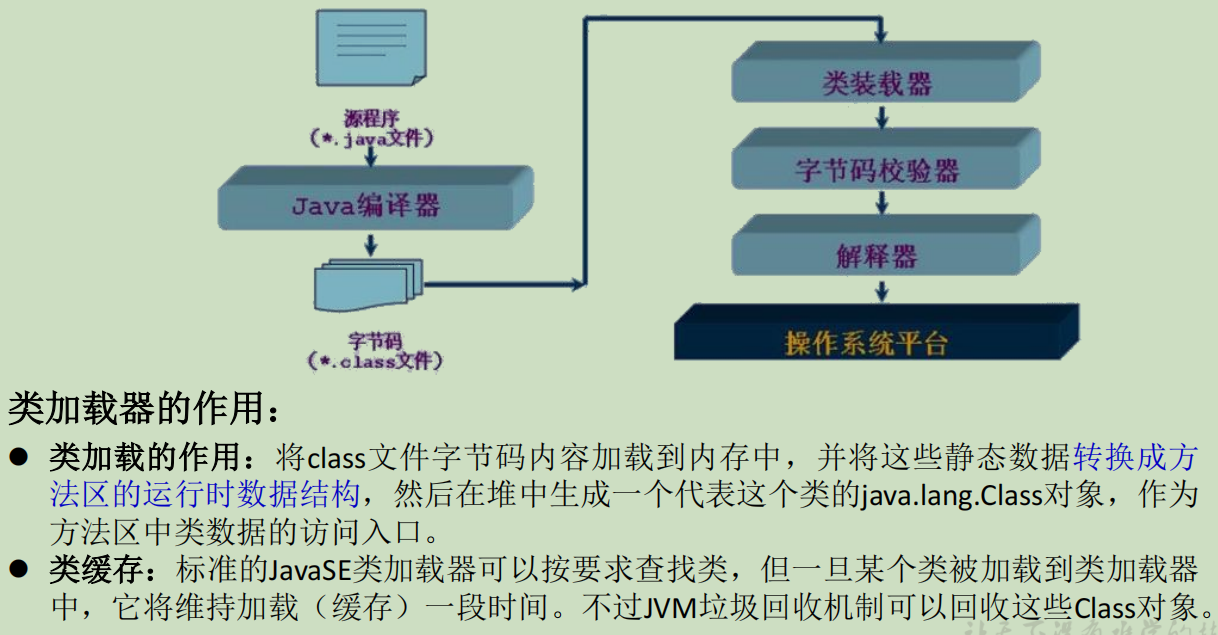
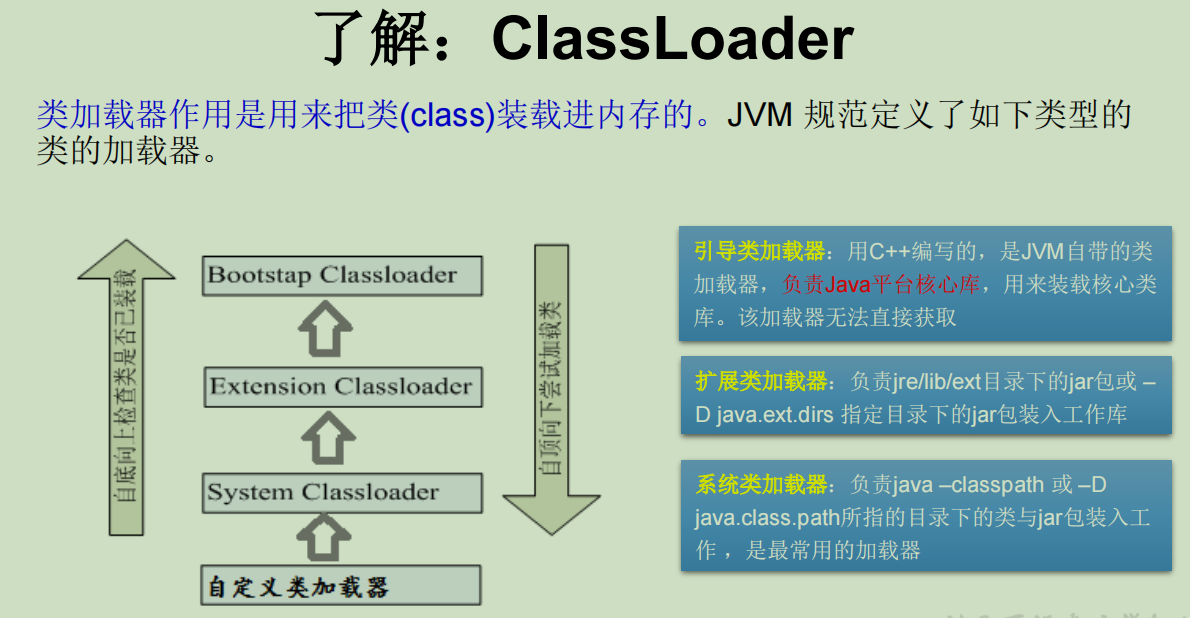
4、类的加载与ClassLoader的理解


package com.atguigu.java1;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.util.Properties;/*了解类的加载器*/public class ClassLoaderTest {@Testpublic void test1(){//对于自定义类,使用系统加载器进行加载ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();System.out.println(classLoader);//调用系统类加载器的getParent():获得扩展类加载器ClassLoader classLoader1 = classLoader.getParent();System.out.println(classLoader1);//调用扩展类加载器的getParent():无法获取引导类加载器//引导类加载器主要负责加载java的核心类库,无法加载自定义类的ClassLoader classLoader2 = classLoader1.getParent();System.out.println(classLoader2);ClassLoader classLoader3 = String.class.getClassLoader();System.out.println(classLoader3);}/*Properties:用来读取配置文件。*/@Testpublic void test2() throws IOException {Properties pros = new Properties();//此时文件默认在当前module下。//读取配置文件方式一:FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");pros.load(fis);//读取配置文件方式二:使用ClassLoader//配置文件默认识别为当前module的src下// ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();// InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc1.properties");// pros.load(is);String user = pros.getProperty("user");String password = pros.getProperty("password");System.out.println("user="+user+",password="+password);}}
5、创建运行时类的对象
package com.atguigu.java1;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Random;/*通过反射创建对应的运行时类的对象*/public class NewInstanceTest {@Testpublic void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {ClassLoader classLoader = NewInstanceTest.class.getClassLoader();Class<Person> clazz = (Class<Person>) classLoader.loadClass("com.atguigu.java1.Person");/*newInstance():调用此方法,创建对应的运行时类的对象。内部调用了运行时类的空参构造器要想此方法正常的创建运行时类的对象,要求:1、运行时类必须提供空参构造器2、空参的构造器的访问权限得够。通常,设置为public。在javabean中要求提供一个public的空参构造器。原因:1、便于通过反射,创建运行时类的对象2、便于子类继承此运行时类时,默认调用super()时,保证父类有此构造器*/Person obj = (Person) clazz.newInstance();System.out.println(obj);}//体会反射的动态性@Testpublic void test2() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {int num = new Random().nextInt(3);String classPath = "";switch (num) {case 0:classPath = "java.util.Date";break;case 1:classPath = "java.lang.Object";break;case 2:classPath = "com.atguigu.java1.Person";break;default:break;}try {Object obj = getInstance(classPath);System.out.println(obj);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*创建一个指定类的对象classPath:指定类的全类名*/public Object getInstance(String classPath) throws Exception {Class clazz = Class.forName(classPath);return clazz.newInstance();}}
6、获取运行时类的完整结构(了解)
package com.atguigu.java3;import com.atguigu.java2.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;/*获取当前运行时类的属性结构*/public class FileTest {@Testpublic void test1(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//获取属性结构//getFiles():获取当前运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();for (Field f:fields){System.out.println(f);}System.out.println("************************");//getDeclaredFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有的属性。(不包含父类中声明的属性)Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for (Field f:declaredFields){System.out.println(f);}}//权限修饰符 数据类型 变量名@Testpublic void test2(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for (Field f:declaredFields){//1、权限修饰符int modifiers = f.getModifiers();System.out.print(Modifier.toString(modifiers)+"\t");//2、数据类型Class<?> type = f.getType();System.out.print(type.getName()+"\t");//3、变量名String fName = f.getName();System.out.print(fName);System.out.println();}}}
package com.atguigu.java3;import com.atguigu.java2.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;/*获取运行时类的方法结构*/public class MethodTest {@Testpublic void test1() {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//getMethods():获取当前运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public权限的方法Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();for (Method m : methods) {System.out.println(m);}System.out.println("************************************");//getDeclaredMethods():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有方法。(不包含父类中声明的方法)Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method m : declaredMethods) {System.out.println(m);}}/*权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 形参名1,.....) throws XxxException{}*/@Testpublic void test2() {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method m : declaredMethods) {//1、获取方法声明的注解Annotation[] annos = m.getAnnotations();for (Annotation a : annos) {System.out.println(a);}//2、获取权限修饰符System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()) + "\t");//3、返回值类型System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getName() + "\t");//4、方法名System.out.print(m.getName());System.out.print("(");//5、形参列表Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();if (!(parameterTypes == null && parameterTypes.length == 0)) {for (int i=0;i<parameterTypes.length;i++){if (i==parameterTypes.length-1){System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName()+" args_"+i);break;}System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName()+" args_"+i+",");}}System.out.print(")");//6、抛出的异常Class[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes();// if (!(exceptionTypes==null&&exceptionTypes.length==0)){// System.out.print("throws ");// for (int i = 0; i < exceptionTypes.length; i++) {// if (i==exceptionTypes.length-1){// System.out.println(exceptionTypes[i].getName());// break;// }// System.out.println(exceptionTypes[i].getName()+",");// }// }if (exceptionTypes.length>0){System.out.print("throws ");for (int i = 0; i < exceptionTypes.length; i++) {if (i==exceptionTypes.length-1){System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName());break;}System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName()+",");}}System.out.println();}}}
package com.atguigu.java3;import com.atguigu.java2.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;import java.lang.reflect.Type;public class OtherTest {/*获取构造器结构*/@Testpublic void test1() {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//getConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();for (Constructor c : constructors) {System.out.println(c);}System.out.println();//getDeclaredConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有构造器。Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();for (Constructor c : declaredConstructors) {System.out.println(c);}}/*获取运行时类的父类*/@Testpublic void test2() {Class<? extends Person> clazz = new Person().getClass();Class<?> superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();System.out.println(superclass);}/*获取运行时类的带泛型的父类*/@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.atguigu.java2.Person");Type superclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();System.out.println(superclass);}/*获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型代码: 逻辑性代码 vs 功能性代码*/@Testpublic void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.atguigu.java2.Person");Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();ParameterizedType parameterizedType= (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;Type[] actualTypeArguments = parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments();System.out.println(actualTypeArguments[0].getTypeName());}/*获取运行时类实现的接口*/@Testpublic void test5(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();for (Class c:interfaces){System.out.println(c);}System.out.println();//获取运行时类的父类的接口Class<?>[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();for (Class c:interfaces1){System.out.println(c);}}/*获取运行时类所在的包*/@Testpublic void test6(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Package pack = clazz.getPackage();System.out.println(pack);}/*获取运行时类声明的注解*/@Testpublic void test7(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();for (Annotation a:annotations){System.out.println(a);}}}
7、调用运行时类的指定结构
package com.atguigu.java3;import com.atguigu.java2.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/*调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器*/public class ReflectionTest {@Testpublic void test1() throws NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {Class clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();//获取指定的属性:要求运行时类中的属性声明为public//通常不采用此方法Field id = clazz.getField("id");/*设置当前属性的值set():参数1:指明设置哪个对象的属性 参数2:将此属性值设置为多少*/id.set(p, 1001);/*获取当前属性的值get():参数1:获取哪个对象的当前属性值*/int pId = (int) id.get(p);System.out.println(pId);}/*如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性---需要掌握*/@Testpublic void test2() throws Exception {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = clazz.newInstance();//1、getDeclaredField(String name) :获取当前运行时类中指定变量名的属性。Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");//2、保证当前属性是可访问的name.setAccessible(true);//3、获取、设置指定对象的此属性值name.set(p,"Tom");System.out.println(name.get(p));}/*如何操作运行时类中的指定的方法---需要掌握*/@Testpublic void test3() throws Exception {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = clazz.newInstance();//1、获取指定的某个方法getDeclaredMethod():参数1:指明获取的方法的名称 参数2:指明获取的方法的形参列表Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class);//2、保证当前方法是可访问的show.setAccessible(true);/*3、调用方法的invoke():参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参invoke()的返回值即为对应类中调用的方法的返回值。*/Object returnValue = show.invoke(p, "CHN");System.out.println(returnValue);System.out.println("*******************静态方法******************");Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc");showDesc.setAccessible(true);//如果调用的运行时类中的方法没有返回值,则此invoke()返回nullObject returnVal = showDesc.invoke(Person.class);System.out.println(returnVal);}/*如何操作运行时类中的指定的构造器*/@Testpublic void test4() throws Exception {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//1、获取指定的构造器getDeclaredConstructor():参数:指明构造器的参数列表Constructor<Person> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);//2、保证此构造器是可访问的constructor.setAccessible(true);//3、调用此构造器创建运行时类的对象Person p = constructor.newInstance("Tom");System.out.println(p);}}


