一道非常典型的并查集应用题
集合的简化表示
1. 未简化的表示方法
typedef struct{ /*数组类型:结构体*/ElementType Data; /*数据域Data*/int Parent; /*表示父结点位置的指针Parent*/} SetType;int Find(SetType S[], ElementType X){int i;for(i=0 ; i<MaxSize && S[i].Data != X ; i++); /*此行目的:想知道元素属于哪个集合的线性扫描*//*这样写非常浪费时间,最坏情况为O(n^2)*/if(i>=MaxSize) return -1;for(; S[i].Parent >= 0 ; i=S[i].Parent);return i;}
2. 化简思路
※ 任何有限集合的 N 个元素都可以被一一映射为整数 0 ~ N-1 ,
此处想法是 , 把集合中的每个元素直接用在数组里的下标来代表 , 只定义一个整型数组就可以表示集合了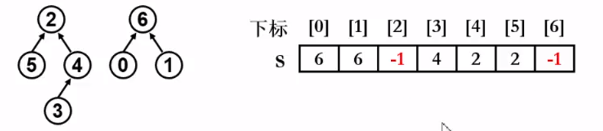
集合数 = 上图数组中 -1 的个数
3. 简化表示
typedef int ElementType; /*默认元素可以用非负整数表示*/typedef int SetNamel /*默认用根结点的下标作为集合名称*/typedef ElementType SetType[MaxSize];SetName Find( SetType S, ElementType X){/*默认集合元素全部初始化为-1*/for( ; S[X]>=0 ; X=S[X]); /*查找X在哪个集合*/return X;}void Union(SetType S, SetName Root1, SetName Root2){/*这里默认Root1和Root2是不同集合的根结点*/S[Root2] = Root1;}
题意理解
题目 :
输入样例1:5 /*有5台计算机*/C 3 2 /*C表示Check,查看2和3之间有没有连通(不连通,输出no)*/I 3 2 /*I表示添加网线,在2和3之间加网线使其连通*/C 1 5 /*查看1和5之间是否连通(不连通,输出no)*/I 4 5 /*在4和5之间加网线使其连通*/I 2 4 /*在4和2之间加网线使其连通*/C 3 5 /*查看3和5之间是否连通(连通,输出yes)*/S /*所有输入结束,对整个网络进行判断:一共有几个连通集*//*输出:There are 2 components*/
输入样例2:
5 /*有5台计算机*/
C 3 2 /*C表示Check,查看2和3之间有没有连通(不连通,输出no)*/
I 3 2 /*I表示添加网线,在2和3之间加网线使其连通*/
C 1 5 /*查看1和5之间是否连通(不连通,输出no)*/
I 4 5 /*在4和5之间加网线使其连通*/
I 2 4 /*在4和2之间加网线使其连通*/
C 3 5 /*查看3和5之间是否连通(连通,输出yes)*/
I 1 3
C 1 5
S /*输出:The network is connected */
代码
1. 程序框架搭建
int main () {
初始化集合;
do {
读入一条指令; (C 1 5)
处理指令;
} while (没结束) ;
return 0;
}
int main(){
SetType S;
int n;
char in;
/*初始化集合:①读入元素个数②初始化*/
scanf("%d\n",&n);
Initialization(S,n);
do{
scanf("%c",&in);
switch(in){
case 'I' : Input_connection(S);break; /*Input_connection:Union(Find)*/
case 'C' : Check_connection(S);break; /*Check_connection:Find*/
case 'S' : Check_network(S,n);break; /*Check_network:数一下一共有几个集合*/
}
} while(in != 'S');
return 0;
}
void Input_connection( SetType S){
ElementType u,v;
SetName Root1, Root2;
scanf("%d %d\n",&u,&v);
Root1 = Find(S,u-1);
Root2 = Find(S,v-1);
if(Root1 != Root2)
Union(S, Root1, Root2);
}
void Check_connection(SetType S){
ElementType u,v;
SetName Root1, Root2;
scanf("%d %d\n",&u, &v);
Root1 = Find(S, u-1);
Root2 = Find(S, v-1); /*从这往上与Input函数一样*/
if( Root1 == Root2 )
printf("yes\n");
else printf("no\n");
}
void Check_network(SetType S, int n){
int i, counter = 0;
for(i=0 ; i<n ; i++){
if( S[i] <0 ) counter++;
}
if( counter == 1 )
printf("The network is connected.\n");
else
prinf("There are &d components.\n", counter);
}
根据上面代码 , 可以看出运行效率主要取决于函数 Union 和 Find 的效率。
2. 简单实现
简单实现的话 , 运行速度很慢 , 在某些测试中会超时。
3. 按秩归并
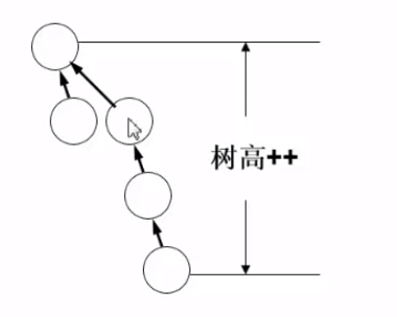
为什么需要按秩归并?

如上图 , 树会越长越高 , T(n) = O(n2)
不让树变高的方法
把矮的树贴到高树上 (需要添加一行对哪颗树高哪颗树矮的判断)
if (S[Root2] < S[Root1]) /*Root2高度 > Root1高度*/ S[Root1] = Root2; else{ if(S[Root1]==S[Root2]) S[Root1]--; /*两者等高,树高++*/ S[Root2] = Root1; }需要存储一下树的高度
树的高度存哪里 ?
S[Root] = -1 -> S[Root] = -树高 (仍初始化为 -1 )
另一种不让树变高的方法
比规模
- 把小树贴到大树上
S[Root] = -元素个数

