Alias
在Nginx中的alias: 访问 /a 但是实际访问的内容文件在/b
应用的场景
代码目录结构发生了变化的项目
产品迭代: www.test.com/a —> www.test.com/b 当出现迭代的情况时,为了不影响现有业务,选择alias进行操作,虽然也可以发公告
seo : 之前做了seo推广的链接为 www.test.com/a 但是如果换成 www.test.com/b 则之前的全部失效了 这时候也选择alias
loaction /uri {alias /new_uri; # 这里填写文件新路径即可}
设置请求资源的目录root / alias
root:设置请求的根目录
| 语法 | root path; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | root html; |
| 位置 | http、server、location |
path为Nginx服务器接收到请求以后查找资源的根目录路径。
alias:用来更改location的URI
| 语法 | alias path; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | — |
| 位置 | location |
path为修改后的根路径。
root的处理结果是: root路径+location路径
alias的处理结果是:使用alias路径替换location路径
alias是一个目录别名的定义,root则是最上层目录的含义。
如果location路径是以/结尾,则alias也必须是以/结尾,root没有要求
网页跳转功能
return
return code; 返回状态
在这里可以定义任何响应码 500则返回服务器错误,302则跳转资源 200会下载状态码后的helloworld
server {listen 8080; #指定监听哪个端口server_name www.test.com; #访问该服务通过哪个域名来访问root /html/game; #存放源码的目录index tndex.html; #定义首页文件location /admin {autoindex on;auth_basic "please input passwd";auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/htpasswd;}location /status {stub_status;}location /test {return 302 "helloworld"; #为什么200会下载,因为在主配置文件中,我们配置了default_type application/octet-stream; 修改成application/json 即可文本解析}}
return url; 跳转到url
server {listen 8080; #指定监听哪个端口server_name www.test.com; #访问该服务通过哪个域名来访问root /html/game; #存放源码的目录index tndex.html; #定义首页文件location /admin {autoindex on;auth_basic "please input passwd";auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/htpasswd;}location /status {stub_status;}location /test {return http://baidu.com;}}
rewirte
应用的场景
用户访问http,跳转到https
针对SEO的url优化(伪静态)
类似alias
跳转的模式
break&last
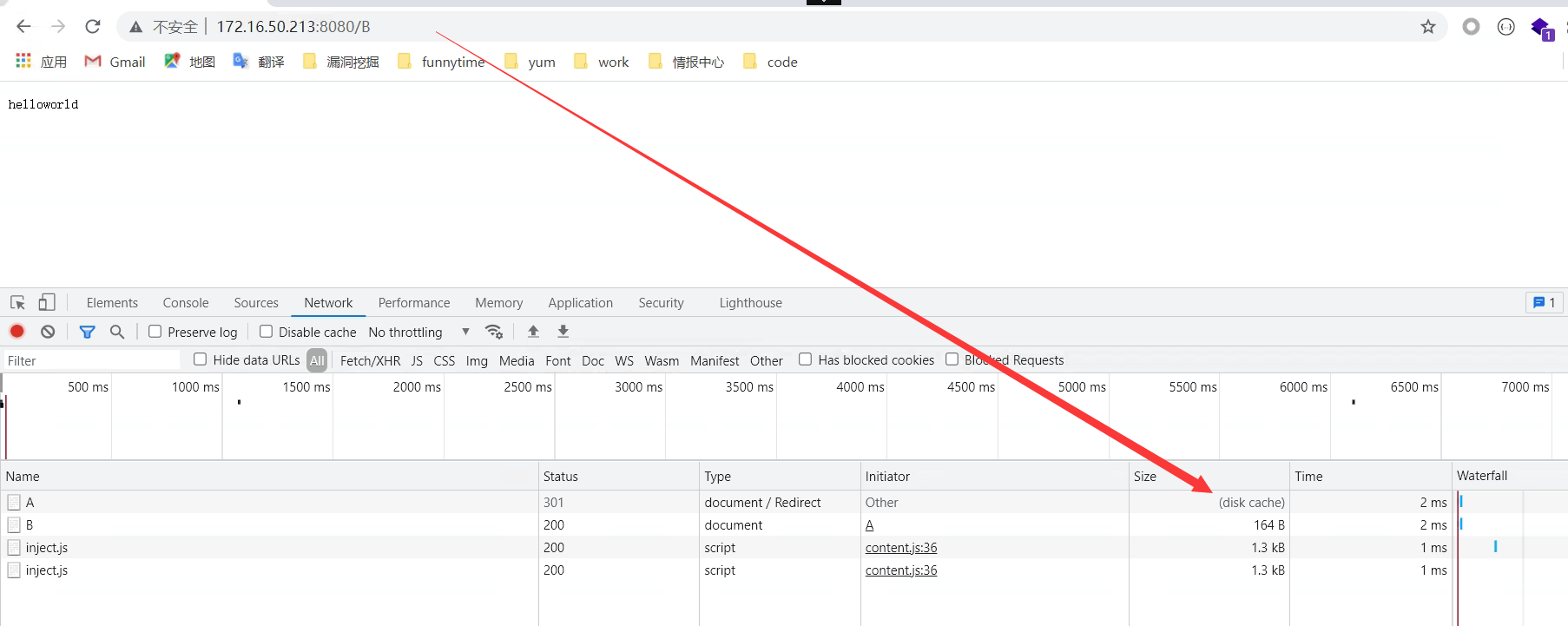
四种策略,两个方向方向一:break 将访问的URI信息进行直接跳转,不会重新发起连接请求last 当用户发送请求的时候,会重新让客户端根据新的URI,重新发起请求,匹配新的loacltion规则测试访问 /A 跳转到 /B 用break访问 /C 跳转到 /D 用lastserver {listen 8080; #指定监听哪个端口server_name www.test.com; #访问该服务通过哪个域名来访问root /html/game; #存放源码的目录index tndex.html; #定义首页文件location /admin {autoindex on;auth_basic "please input passwd";auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/htpasswd;}location /status {stub_status;}location /B {default_type application/json;return 200 "helloworld";}location /A {rewrite /A /B break;}location /C {rewrite /C /B last;}}
咱们来看一下结果,以及为什么
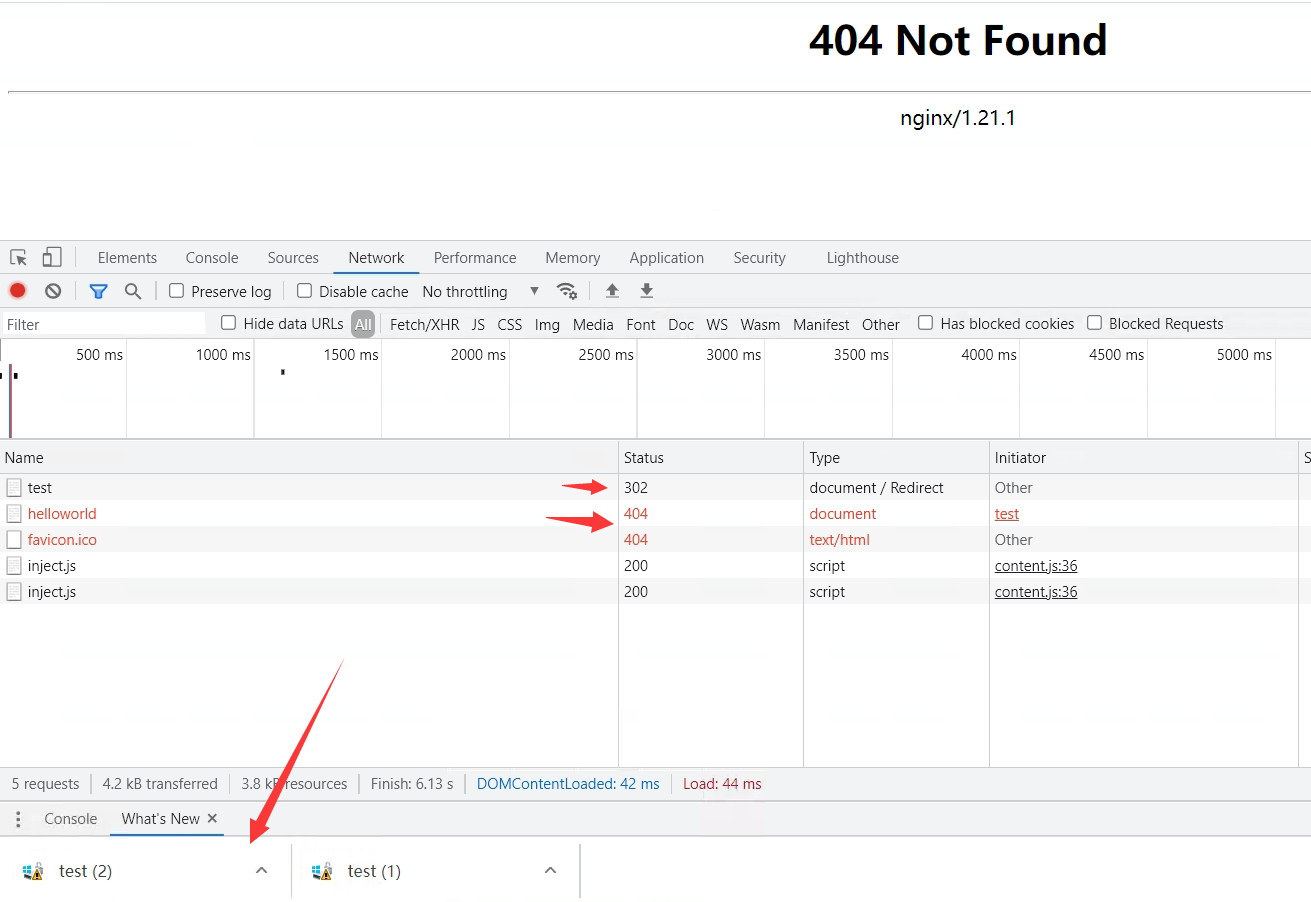
访问A — 404
为什么:因为不会发起新请求,所以nginx回去找配置文件中B的路径。也就是B在web的根目录下的路径,但是我们是location定义的 自然就没有这个路径,所以404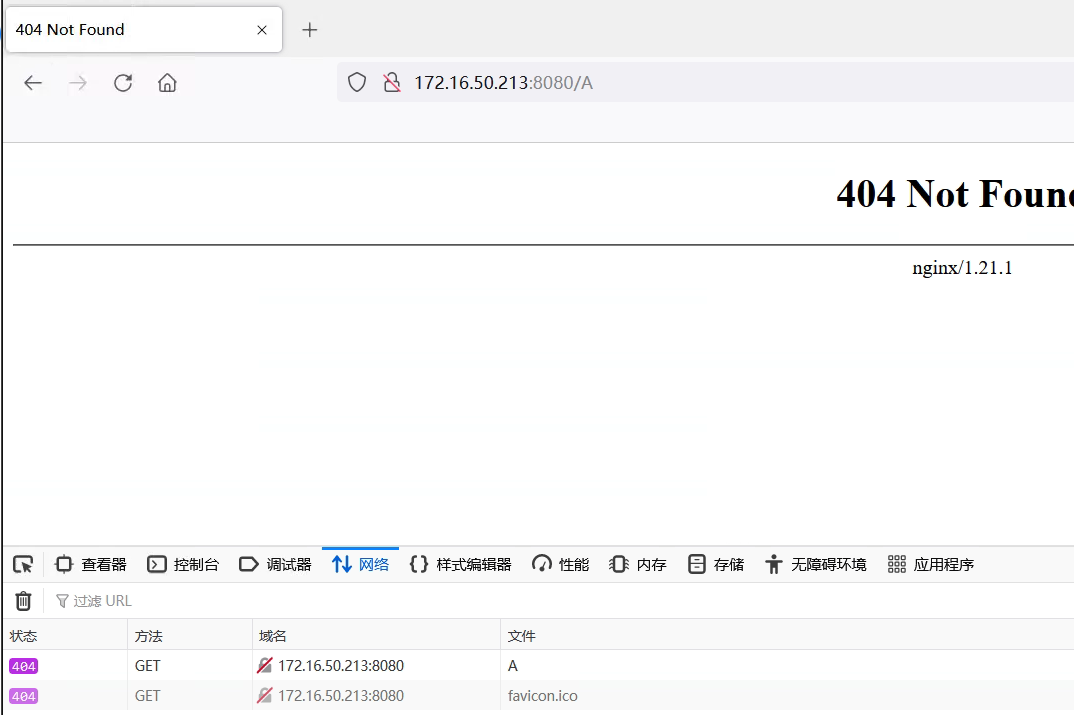
想要访问到,我们就得去根目录下创建B目录 这里URI会成为web根目录下的文件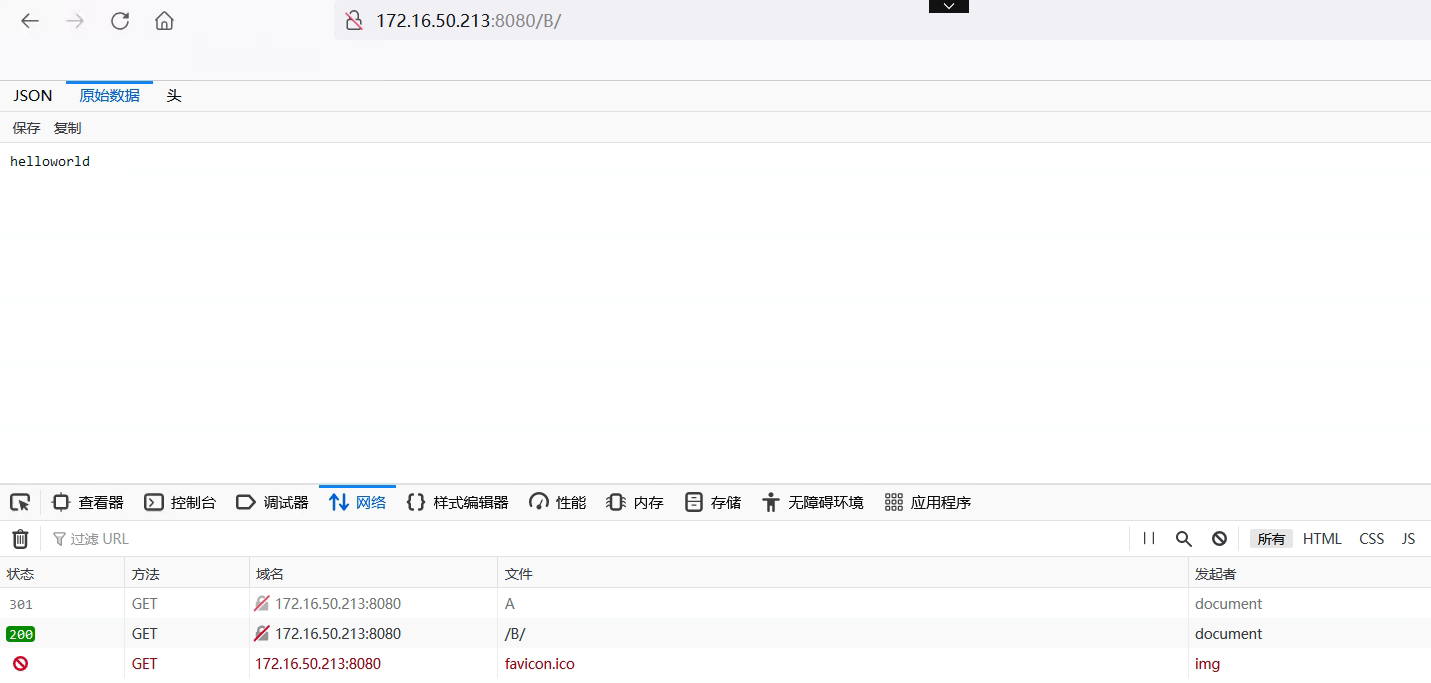
访问B
为什么:因为重新发起了请求
方向二:permanent 301 永久跳转 会将跳转过程保存在浏览器中redirect 302 临时跳转 不会保存过程在浏览器中,每次都是服务器端控制的测试:server {listen 8080; #指定监听哪个端口server_name www.test.com; #访问该服务通过哪个域名来访问root /html/game; #存放源码的目录index tndex.html; #定义首页文件location /admin {autoindex on;auth_basic "please input passwd";auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/htpasswd;}location /status {stub_status;}location /B {default_type application/json;return 200 "helloworld";}location /A {rewrite /A /B permanent;}location /C {rewrite /C /B redirect;}}
301 与 302 选择的场景
302 需要经常变化跳转路径的URI
301 基本不变的跳转URI 如 http - > https seo中 a.test.com - > b.test.com
针对SEO进行URL优化及安全策略
没有合适的环境 看老师的吧