树
定义
A tree is a (possibly non-linear) data structure made up of nodes or vertices and edges without having any cycle. The tree with no nodes is called the null or empty tree. A tree that is not empty consists of a root node and potentially many levels of additional nodes that form a hierarchy.
树是由结点或顶点和边组成的(可能是非线性的)且不存在着任何环的一种数据结构。没有结点的树称为空(null或empty)树。一棵非空的树包括一个根结点,还(很可能)有多个附加结点,所有结点构成一个多级分层结构。
基本称呼
| Root | The top node in a tree. | 根 | 树的顶端结点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Child | A node directly connected to another node when moving away from the Root. | 孩子 | 当远离根(Root)的时候,直接连接到另外一个结点的结点被称之为孩子(Child); |
| Parent | The converse notion of a child. | 双亲 | 相应地,另外一个结点称为孩子(child)的双亲(parent)。 |
| Siblings | A group of nodes with the same parent. | 兄弟 | 具有同一个双亲(Parent)的孩子(Child)之间互称为兄弟(Sibling)。 |
| Ancestor | A node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent. | 祖先 | 结点的祖先(Ancestor)是从根(Root)到该结点所经分支(Branch)上的所有结点。 |
| Descendant | A node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child. | 子孙 | 以某结点为根的子树中的任一结点都称为该结点的子孙(后代)。 |
| Leaf | A node with no children. | 叶子(终端结点) | 没有孩子的结点(也就是度为0的结点)称为叶子(Leaf)或终端结点。 |
| Branch | A node with at least one child. | 分支(非终端结点) | 至少有一个孩子的结点称为分支(Branch)或非终端结点。 |
| Degree | The number of sub trees of a node. | 度 | 结点所拥有的子树个数称为结点的度(Degree)。(跟图的度不太一样) |
| Edge | The connection between one node and another. | 边 | 一个结点和另一个结点之间的连接被称之为边(Edge)。 |
| Path | A sequence of nodes and edges connecting a node with a descendant. | 路径 | 连接结点和其后代的结点之间的(结点,边)的序列。 |
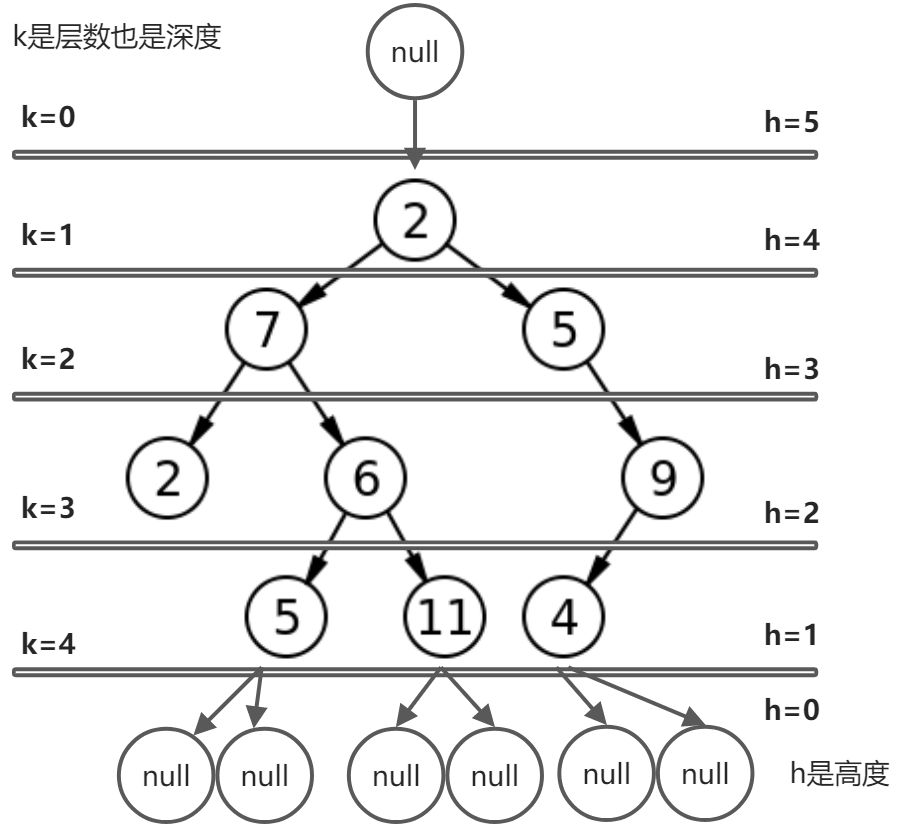
| Level | The level of a node is defined by 0 + (the number of connections between the node and the root). | 层次 | 结点的层次(Level)从根(Root)开始定义起,根为第0层,根的孩子为第1层。以此类推,若某结点在第i层,那么其子树的根就在第i+1层。 |
| Height of node | The height of a node is the number of edges on the longest path between that node and a leaf. | 结点的高度 | 结点的高度是该结点和某个叶子之间存在的最长路径上的边的个数。 |
| Height of tree | The height of a tree is the height of its root node. | 树的高度 | 树的高度是其根结点的高度。 |
| **Depth of node |
| The depth of a node is the number of edges from the tree’s root node to the node. | 结点的深度 | 结点的深度是从树的根结点到该结点的边的个数。 (注:树的深度指的是树中结点的最大层次。) | | Forest | A forest is a set of n ≥ 0 disjoint trees. | 森林** | 森林是n(>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合。 |
二叉树(Binary Tree)
定义
- 每个结点至多拥有两棵子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点),
-
性质
若二叉树的层次从1开始,则在二叉树的第i层至多有2^(i-1)个结点(i>=1)。
- 高度为k的二叉树最多有2^k- 1个结点(k>=0)。 (空树的高度为0)
- 对任何一棵二叉树,如果其叶子结点(度为0)数为m, 度为2的结点数为n, 则m = n + 1。
- 二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。也就是最长叶子节点的k
分类
完美二叉树PBT / 满二叉树
- 一个深度为k(>=-1)
- 且有2^(k+1) - 1个结点
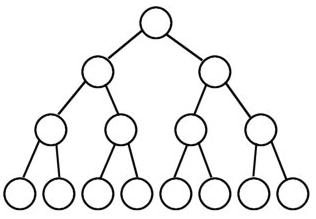
完全二叉树CBT
- 从根结点到倒数第二层满足完美二叉树,
- 最后一层可以不完全填充,其叶子结点都靠左对齐
换句话说,就是所有节点层序遍历编号连续。(一颗CBT就是从最右边取了几个元素的PBT)
优先级队列其实是一个堆,堆就是一棵完全二叉树,同时保证父子节点的顺序关系。
完满二叉树FBT
所有非叶子结点的度都是2。(只要你有孩子,你就必然是有两个孩子。) 
对比
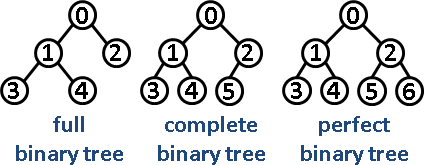
完满二叉树,完全二叉树,完美二叉树。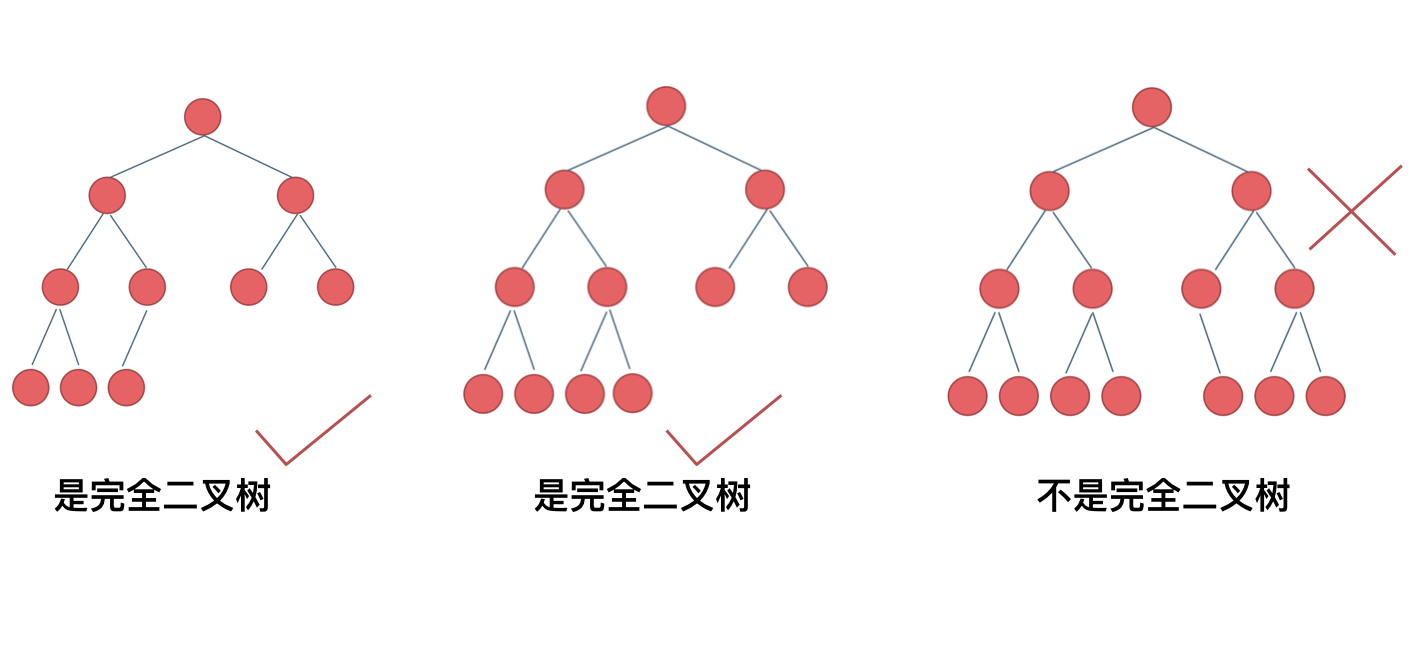
- 完美(Perfect)二叉树一定是完全(Complete)二叉树,但完全(Complete)二叉树不一定是完美(Perfect)二叉树。
- 完美(Perfect)二叉树一定是完满(Full)二叉树,但完满(Full)二叉树不一定是完美(Perfect)二叉树。
- 完全(Complete)二叉树可能是完满(Full)二叉树,完满(Full)二叉树也可能是完全(Complete)二叉树。
- 既是完全(Complete)二叉树又是完满(Full)二叉树也不一定就是完美(Perfect)二叉树。
二叉搜索树
有数值的二叉树 二叉查找树,又名二叉排序树,亦名二叉搜索树
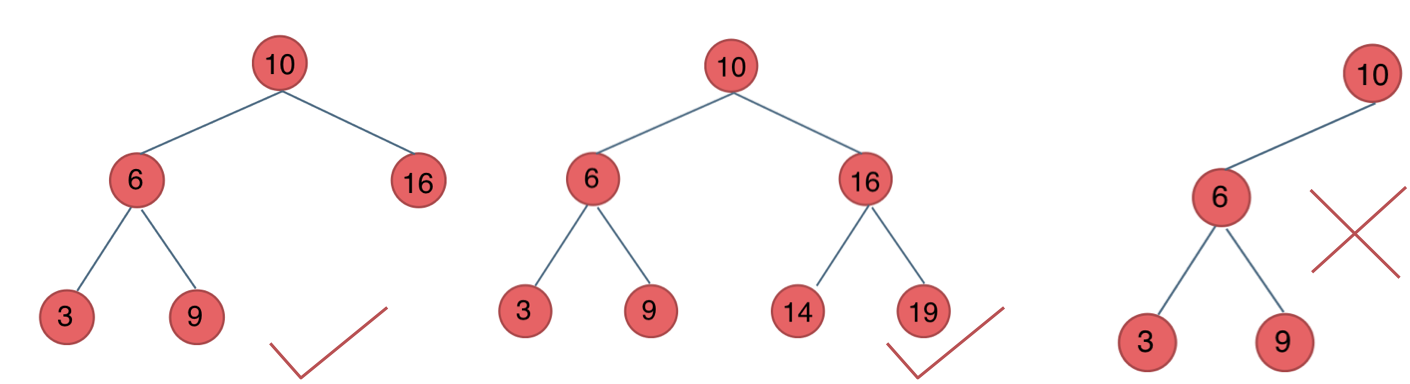
二叉搜索树是一个有序树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
平衡二叉搜索树 AVL
又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树
性质:
- 它是一棵空树
- 或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,
- 并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
:::info
C++中map、set、multimap,multiset的底层实现都是平衡二叉搜索树,所以map、set的增删操作时间时间复杂度是logn
unordered_map、unordered_map底层实现是哈希表。
:::
红黑树
见此 https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html
二叉树的存储
链式
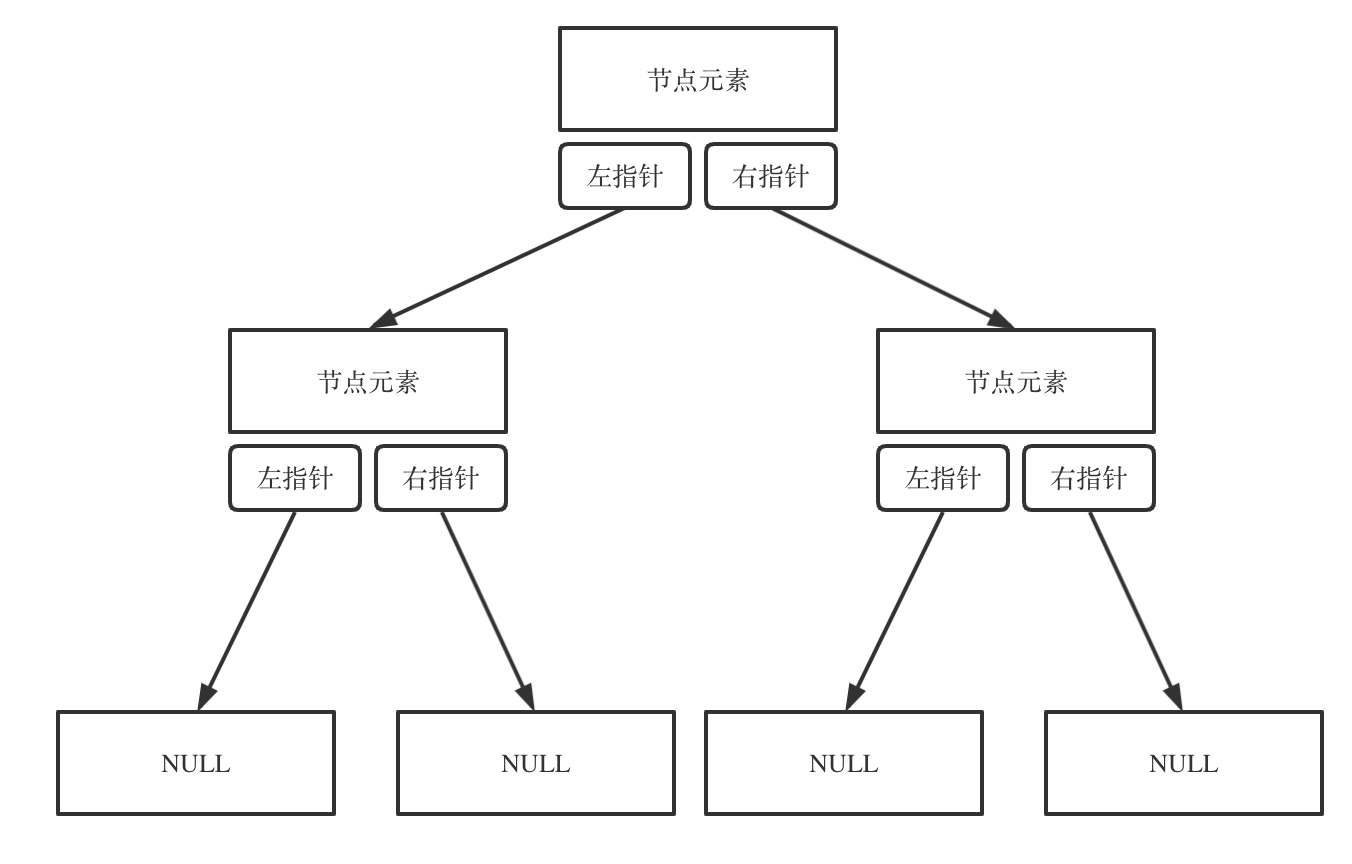
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}};
数组

如果父节点的数组下表是i,那么它的左孩子就是i * 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i * 2 + 2。
References:
https://www.cnblogs.com/idorax/p/6441043.html
https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E7%A7%8D%E7%B1%BB