前言
何人适合阅读这篇文章
- 基本的 JavaScript 知识。
- 知道一点点的数组及其用法。
同时,希望看完这篇文章的小伙伴掌握:
- 数组基本常识
- 数组的增删改查
- 数组的常用知识点
- 深入的理解js中数组这种常用的数据结构
- ES中新增的数据结构
文章有点长,预计阅读需要10-20分钟请耐心看完;
Question 1: 什么是数组(Array)?
我相信对于很多人来说,会有短暂的大脑空白,或者根本描述不清楚。那我们来看下数组的定义:
数组(**
array**)是一种线性表数据结构。它用一组连续的内存空间,来存储一组具有相同类型的数据。是按次序排列的一组值。每个值的位置都有编号(从0开始),整个数组用方括号[]表示 js中的数组有所不同,它实际上也是一种特殊的对象,数组中元素的下标(index)是key,而元素则是value。此外数组对象还有一个额外的属性, 即:“length”。 除了Object类型之外,Array类型恐怕是js中最常用的类型了,并且随着js的发展进步,数组中提供的方法也越来越来,对数组的处理也出现了各种骚操作。
如果对js原型/原型链不了解的可以移步__深入了解javascript原型/原型链,下面我们就来一起学习下js的数组。
Question 2:了解了什么是数组,那为什么用数组呢?
我们都知道学习数组的时候知道数组的优点是可以随机访问,比如你描述一个事物如猫
let Cat={name:'miaomiao',age: 1,color:'gray',breed:'Persian'}// 但当你想描述10条甚至100只更多毛毛的时候你改如何让表示呢// 这里数组的用处就体现出来了,let Cats=[{name:'miaomiao1',age: 1,color:'gray',breed:'Persian'},{name:'miaomiao3',age: 1,color:'gray',breed:'Persian'},...]
开启下一个灵魂拷问之前,先学习下js数组的基础操作及方法
如何创建一个数组呢?
let arr=[];let nextArr=new Array();
以上都是可以的;
我们也可以初始化+赋值;
let a = [1,2,3];let b = new Array(5);let b1 = new Array(5,6);let c = new Array([1, 2, 3]);let d = new Array(5).fill(1);let e = new Array(5).fill([]);
上面数组声明中,看下b1和b这两个数组的结果有啥不一样为什么呢?
console.log(b.length);//5console.log(b); //会生成一个length 为5,每一个都是undefined的数组console.log(b1.length);//2console.log(b1); //[5,6]
在使用构造函数创建数组时如果传入一个数字参数,则会创建一个长度为参数的数组,如果传入多个,则创建一个数组,参数作为初始化数据加到数组中
上图:理解js 的原型链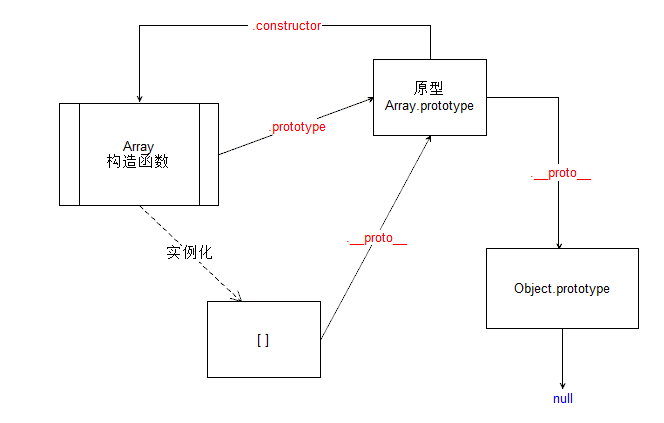
let a = [1, 2, 3]// 上面的数组可以表示为下面的形式let obj = {0: 1,1: 2,2: 3,length: 3}
我们再来说下数组访问和类型判断
数组访问
我们来看下数组对象的表示
let array = ['a']
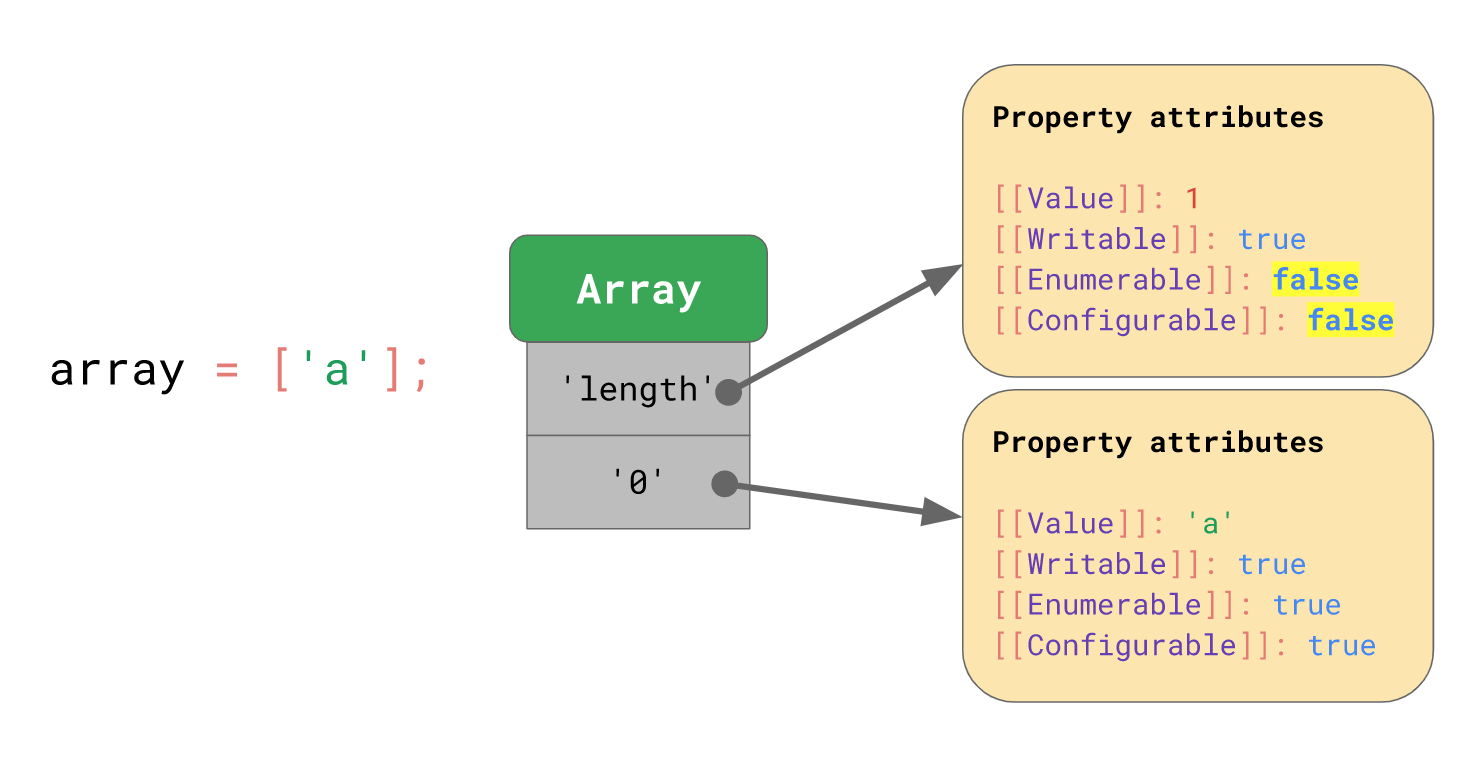
let a = [1,2,3];console.log(a[0]); //数组的下标是从 0 开始的console.log(a[1]);console.log(a[2]);//思考下我如果console.log(a[3]) // 会是什么结果?console.log(a[-1]) // 会是什么结果?
那么二维, 三维乃至多维数组该如何访问呢?
// 二维数组let arr = [[1,2],[2,3,4]]for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){for(var j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++){console.log(arr[i][j]);//}}// 三维数组let arr1 = [[1,2,['a','b','c']],[2,3,4,['a','b','c']]]for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){for(var j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++){for(var k=0;k<arr[i][j].length;k++){console.log(arr[i][j][k]);//}}// 多维参照上面自行思考
数组类型的判断
let arr= [];// instanceofconsole.log(arr instanceof Array); //true// Object.prototype.toString.callconsole.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arr).indexOf('Array')) // 8// Array.prototype.isPrototypeOfconsole.log(Array.prototype.isPrototypeOf(arr)) //true// constructorconsole.log(arr.constructor == Array); //true// Array.isArray
instanceof 和constructor 都存在一定的问题 ,因为constructor可以被重写,所以不能确保一定是数组
var str = 'abc';str.constructor = Array;str.constructor === Array // return true
instanceof操作符的问题在于,它假定只有一个全局环境。如果网页中包含多个框架,那实际上就存在两个以上不同的全局执行环境,从而存在两个以上不同版本的Array构造函数。
如果你从一个框架向另一个框架传入一个数组,那么传入的数组与在第二个框架中原生创建的数组分别具有各自不同的构造函数。
let iframe = document.createElement('iframe');document.body.appendChild(iframe);let arr = [1,2,3];fArr = window.frames[0].Array; //iframe中的构造函数let arr1 = new fArr(4,5,6);
数组的增删改查
数组的增加
let arr = ['a'];// 通过 push() 方法 向尾部添加arr.push('b'); // ['a','b']// 通过 length 属性arr[arr.length] = 'c'; // ['a','b','c']// 通过 unshift 向头部添加arr.unshift('0'); // ['0','a','b','c']// 通过 concat 拼接数组arr.concat([1,2,3]); // ['0','a','b','c',1,2,3]// 通过 splice 向任意位置添加数据arr.splice(1,0,'lala','lala'); // ['0','lala','lala','a','b','c',1,2,3]
数组的删除和修改
let arr=[{id:1,name:'balabala'},{id:2,name:'labala'},{id:3,name:'balla'}]// 通过splice 删除修改arr.slice(1,1); //从第二个开始删除1个arr.slice(1,1,'0'); //把第二个替换成'0'// 通过slice 删除修改arr.slice(0,2) // 从0开始截取两个返回// 通过filter 删除修改arr.filter(item=>item.id>=2)// 通过pop 删除 从尾部删除arr.pop()// 通过 shift 删除 从开头删arr.shift()// 通过 length 删除arr.length=arr.length-1
数组的查找及其他操作
// toStringlet arr = [1, 2, 3];arr.toString(); // '1,2,3'// joinlet arr=['1','2','3'];arr.join(','); // '1,2,3'// sort[2, 1, 3].sort(), // [1, 2, 3][2, 1, 3].sort((a, b) => b-a), // [3, 2, 1]['a', 'c', 'b'].sort(), // ['a', 'b', 'c']['cow', 'banana', 'apple'].sort(), // ['apple', 'banana', 'cow']// indexOf 方法返回调用 String 对象中第一次出现的指定值的索引。['2','a','c','a'].indexOf(1,'a') // 1// lastIndexOf 方法返回指定元素(也即有效的 JavaScript 值或变量)在数组中的最后一个的索引,如果不存在则返回 -1。['2','a','c','a'].lastIndexOf('c'); //2// forEachconst arr = ['0', '1', '2'];const cparr = [];// 使用 for 遍历for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {cparr.push(arr[i]);}// 使用 forEach 遍历arr.forEach(item=>{cparr.push(item);});// maparr.map(item=>{cparr.push(item);})// includes 方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,如果包含则返回 true,反之返回 false。// slice 方法提取一个字符串的一部分,并返回一新的字符串let arr = [{name: 'apples', id: 1},{name: 'bananas', id: 3},{name: 'cherries', id: 2}];arr.slice(0,2); // [{name: 'apples', id: 1},{name: 'bananas', id: 3}]// findlet arr = [{name: 'apples', id: 1},{name: 'bananas', id: 3},{name: 'cherries', id: 2}];function findCherries(fruit) {return fruit.id === 2;}arr.find(findCherries); // {name: "cherries", id: 2}// findIndex 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。否则返回-1。let arr=[1,2,3,4]arr.findIndex(item=>{return item===3;console.log(item); // 2})// reduce[1, 2, 3].reduce((prev, next) => {return prev + next;}); // 6// reverse 反转数组let arr = [1, 2, 3];arr.reverse(); // [3, 2, 1]// fill 填充let arr = [1, 2, 3];arr = new Array(arr.length).fill(0); // [0,0,0]// flat 数组扁平化let arr=[1,[2,3,[4,5,6],[7,9]],[0,1,2]]arr.flat(4); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 0, 1, 2]arr=new Set([...(arr.flat(4))]);Array.from(...arr); //[0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9]// copyWithin 浅复制数组的一部分到同一数组中的另一个位置,并返回它,不会改变原数组的长度const a = [1, 2, 3,4,5];a.copyWithin(-2); // [1, 2, 3, 1, 2]a.copyWithin(0, 3); // [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]a.copyWithin(0, 3, 4); // [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]// every 测试一个数组内的所有元素是否都能通过某个指定函数的测试。它返回一个布尔值。function comp(item, index, array) {return item >= 20;}[122, 20, 22, 990, 100].every(comp); // true// some 测试数组中是不是至少有1个元素通过了被提供的函数测试。它返回的是一个Boolean类型的值[1, 5, 9, 2, 4].some(comp); // false[1,5,9,10,22].some(comp); //true//reduceRight 从右向左累加,跟reduce相似let arr = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'];arr.reduceRight(function(prev, cur) { return prev + cur; }); // "54321"
构造函数扩展
// Array.of 简单理解就是创建一个新数组的实例,Array.of(5); // [5]Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]// 复制代码两者区别:Array.of(5) 创建一个具有单个元素 5 的数组,而 Array(5) 创建一个长度为7的空数组,这是指一个有5个空位(empty)的数组,而不是由7个undefined组成的数组)。Array(5); // [ , , , , ]Array(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]// Array.isArray 用于确定传递的值是否是一个 ArrayArray.isArray([1, 2, 3]); // trueArray.isArray({}); //false// Array.from 方法从一个类似数组或可迭代对象创建一个新的,浅拷贝的数组实例。const arr = Array.from(new Set([1,2,3,4,1,2,3]))
Question 3:JavaScript 中,数组为什么可以保存不同类型?
v8中数组
// The JSArray describes JavaScript Arrays// Such an array can be in one of two modes:// - fast, backing storage is a FixedArray and length <= elements.length();// Please note: push and pop can be used to grow and shrink the array.// - slow, backing storage is a HashTable with numbers as keys.class JSArray: public JSObject {public:// [length]: The length property.DECL_ACCESSORS(length, Object)// 。。。此处省略实现// Number of element slots to pre-allocate for an empty array.static const int kPreallocatedArrayElements = 4;};
如上我们可以看出 JSArray 是继承自 JSObject 的,所以在 JavaScript 中,数组可以是一个特殊的对象,内部也是以 key-value 形式存储数据,所以 JavaScript 中的数组可以存放不同类型的值。
Question 4:JavaScript 中,数组是如何存储的呢?
// The JSArray describes JavaScript Arrays// Such an array can be in one of two modes:// - fast, backing storage is a FixedArray and length <= elements.length();// Please note: push and pop can be used to grow and shrink the array.// - slow, backing storage is a HashTable with numbers as keys.class JSArray: public JSObject {public:// [length]: The length property.DECL_ACCESSORS(length, Object)// 。。。此处省略实现// Number of element slots to pre-allocate for an empty array.static const int kPreallocatedArrayElements = 4; // 这里可以看到数组默认初始大小为4};
注释上看到
数组分为两种实现模式
- 快数组 存储结构是 FixedArray时,length<= elements.length();请注意:push和pop可以用于增加和缩小数组
- 慢数组 存储结构是
HashTable(哈希表)时,数组下标作为key;
在v8实现的源码中fast 模式下数组在源码里面叫 FastElements ,而 slow 模式下的叫做 SlowElements
快数组(FastElements)
FixedArray 是 V8 实现的一个类数组(类似数组的类),它表示一段连续的内存,可以使用索引直接定位。当数组满(数组的长度达到数组在内存中申请的内存容量最大值)的时候,继续 push 时, JSArray 会进行动态的扩容,以存储更多的元素。fast是数组的创建的默认模式。
慢数组(SlowElements)
慢数组以哈希表的形式存储在内存空间里,它不需要开辟连续的存储空间,但需要额外维护一个哈希表,与快数组相比性能相对较差。
// src/objects/dictionary.hclass EXPORT_TEMPLATE_DECLARE(V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE) Dictionary: public HashTable<Derived, Shape> { //这里可以看出实现是的HashTableusing DerivedHashTable = HashTable<Derived, Shape>;public:using Key = typename Shape::Key;// Returns the value at entry.inline Object ValueAt(InternalIndex entry);inline Object ValueAt(const Isolate* isolate, InternalIndex entry);//...};
那么v8是什么时机来判断快慢数组的转换的呢?
- 当加入的索引值 index 比当前容量 capacity 差值大于等于 1024 时(index - capacity >= 1024)
- 快数组新容量是扩容后的容量 3 倍之多时
这两个条件就会把fast转为slow模式
源码如下:
// src/objects/js-objects.hstatic const uint32_t kMaxGap = 1024;// src/objects/dictionary.h// JSObjects prefer dictionary elements if the dictionary saves this much// memory compared to a fast elements backing store.static const uint32_t kPreferFastElementsSizeFactor = 3;// src/objects/js-objects-inl.h// If the fast-case backing storage takes up much more memory than a dictionary// backing storage would, the object should have slow elements.// staticstatic inline bool ShouldConvertToSlowElements(uint32_t used_elements,uint32_t new_capacity) {uint32_t size_threshold = NumberDictionary::kPreferFastElementsSizeFactor *NumberDictionary::ComputeCapacity(used_elements) *NumberDictionary::kEntrySize;// 快数组新容量是扩容后的容量3倍之多时,也会被转成慢数组return size_threshold <= new_capacity;}static inline bool ShouldConvertToSlowElements(JSObject object,uint32_t capacity,uint32_t index,uint32_t* new_capacity) {STATIC_ASSERT(JSObject::kMaxUncheckedOldFastElementsLength <=JSObject::kMaxUncheckedFastElementsLength);if (index < capacity) {*new_capacity = capacity;return false;}// 当加入的索引值 比当前容量capacity 大于等于 1024时, return trueif (index - capacity >= JSObject::kMaxGap) return true;*new_capacity = JSObject::NewElementsCapacity(index + 1);DCHECK_LT(index, *new_capacity);// TODO(ulan): Check if it works with young large objects.if (*new_capacity <= JSObject::kMaxUncheckedOldFastElementsLength ||(*new_capacity <= JSObject::kMaxUncheckedFastElementsLength &&ObjectInYoungGeneration(object))) {return false;}return ShouldConvertToSlowElements(object.GetFastElementsUsage(),*new_capacity);}
- 当慢数组的元素可存放在快数组中且长度在 smi 之间且仅节省了50%的空间,则会转变为快数组
static bool ShouldConvertToFastElements(JSObject object,NumberDictionary dictionary,uint32_t index,uint32_t* new_capacity) {// If properties with non-standard attributes or accessors were added, we// cannot go back to fast elements.if (dictionary.requires_slow_elements()) returnfalse;// Adding a property with this index will require slow elements.if (index >= static_cast<uint32_t>(Smi::kMaxValue)) returnfalse;if (object.IsJSArray()) {Object length = JSArray::cast(object).length();if (!length.IsSmi()) returnfalse;*new_capacity = static_cast<uint32_t>(Smi::ToInt(length));} elseif (object.IsJSArgumentsObject()) {returnfalse;} else {*new_capacity = dictionary.max_number_key() + 1;}*new_capacity = Max(index + 1, *new_capacity);uint32_t dictionary_size = static_cast<uint32_t>(dictionary.Capacity()) *NumberDictionary::kEntrySize;// Turn fast if the dictionary only saves 50% space.return2 * dictionary_size >= *new_capacity;}
Question 5:JavaScript 中,数组是如何动态扩容与减容的(灵魂拷问)?

上面我们得知数组初始大小为4,那我们就来看下数组是如何扩容的。
扩容
在 JavaScript 中,当数组执行 push 操作时,一旦发现数组内存不足,将进行扩容。
计算实现如下:
// js-objects.hstatic const uint32_t kMinAddedElementsCapacity = 16;// code-stub-assembler.ccNode* CodeStubAssembler::CalculateNewElementsCapacity(Node* old_capacity,ParameterMode mode) {CSA_SLOW_ASSERT(this, MatchesParameterMode(old_capacity, mode));Node* half_old_capacity = WordOrSmiShr(old_capacity, 1, mode);Node* new_capacity = IntPtrOrSmiAdd(half_old_capacity, old_capacity, mode);Node* padding =IntPtrOrSmiConstant(JSObject::kMinAddedElementsCapacity, mode);return IntPtrOrSmiAdd(new_capacity, padding, mode);}
push操作时,发现数组内存不足- 申请 new_capacity = old_capacity /2 + old_capacity + 16 那么长度的内存空间
- 将数组拷贝到新内存中
- 把新元素放在当前 length 位置
- 数组的 length + 1
-
减容回收
if (2 * length <= capacity) {// If more than half the elements won't be used, trim the array.isolate->heap()->RightTrimFixedArray(*backing_store, capacity - length);} else {// Otherwise, fill the unused tail with holes.BackingStore::cast(*backing_store)->FillWithHoles(length, old_length);}
当数组
pop后,如果数组容量大于等于 length 的 2 倍,则进行容量调整,使用RightTrimFixedArray函数,计算出需要释放的空间大小,做好标记,等待 GC 回收;如果数组容量小于 length 的 2 倍,则用 holes 对象填充 pop操作时,获取数组length- 获取
length - 1上的元素(要删除的元素) - 数组
length - 1 - 判断数组的总容量是否大于等于 length - 1 的 2 倍
- 是的话,使用
RightTrimFixedArray函数,计算出需要释放的空间大小,并做好标记,等待GC回收 - 不是的话,用
holes对象填充 - 返回要删除的元素
Question6: ArrayBuffer是啥?
首先看下ArrayBuffer是啥?
ES6推出了可以按照需要分配连续内存的数组,这就是ArrayBuffer。
ArrayBuffer会从内存中申请设定的二进制大小的空间,但是并不能直接操作它,需要通过ArrayBuffer构建一个视图,通过视图来操作这个内存
let arrbf = new ArrayBuffer(512);
这行代码就申请了 512b 的内存区域。但是并不能对 arrayBuffer 直接操作,需要将它赋给一个视图来操作内存
let buf = new Int32Array(arrbf);
视图还可以不通过ArrayBuffer对象,直接分配内存而生成
这里创建了有符号的32位的整数数组,每个数占 4 字节,length 也就是 512 / 4 = 128 个;
ArrayBuffer对象的byteLength属性,返回所分配的内存区域的字节长度;可以用来判断内存是否可分配
if (arrbf.byteLength === 512) {// 成功} else {// 失败}
byteOffset属性返回类型化数组从底层ArrayBuffer对象的哪个字节开始
let buf=Arraybuffer(32);let ar=Int32Array(buf,2);ar.byteOffset; //2
ArrayBuffer哪些视图
上面说了ArrayBuffer不能直接使用依赖视图的生成,下面看下都有哪些视图
Int8Array:8位有符号整数,长度1个字节。Uint8Array:8位无符号整数,长度1个字节。Int16Array:16位有符号整数,长度2个字节。Uint16Array:16位无符号整数,长度2个字节。Int32Array:32位有符号整数,长度4个字节。Uint32Array:32位无符号整数,长度4个字节。Float32Array:32位浮点数,长度4个字节。Float64Array:64位浮点数,长度8个字节
每一种视图都有一个BYTES_PER_ELEMENT常数,表示这种数据类型占据的字节数
Int8Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 1Uint8Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 1Int16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 2Uint16Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 2Int32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 4Uint32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 4Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 4Float64Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT // 8
DataView视图
读取内存
getInt8:读取1个字节,返回一个8位整数。getUint8:读取1个字节,返回一个无符号的8位整数。getInt16:读取2个字节,返回一个16位整数。getUint16:读取2个字节,返回一个无符号的16位整数。getInt32:读取4个字节,返回一个32位整数。getUint32:读取4个字节,返回一个无符号的32位整数。getFloat32:读取4个字节,返回一个32位浮点数。getFloat64:读取8个字节,返回一个64位浮点数。
写入内存
setInt8:写入1个字节的8位整数。setUint8:写入1个字节的8位无符号整数。setInt16:写入2个字节的16位整数。setUint16:写入2个字节的16位无符号整数。setInt32:写入4个字节的32位整数。setUint32:写入4个字节的32位无符号整数。setFloat32:写入4个字节的32位浮点数。setFloat64:写入8个字节的64位浮点数。
ArrayBuffer对象有一个slice方法,允许将内存区域的一部分,拷贝生成一个新的ArrayBuffer对象。 let buf=Arraybuffer(32); buf.slice(0,3);
普通数组和视图数组互转
let typedArr = new Uint8Array( [ 1, 2, 3 ] ); //普通数组转为视图数组let normalArr = Array.apply([], typedArr ); //类型数组转为普通数组
扩展 Set,Map,WeakMap,WeakSet,WeakRef
Set
定义:
Set对象是值的集合,你可以按照插入的顺序迭代它的元素。 Set中的元素只会出现一次,即 Set 中的元素是唯一的。
Set 本身是一种构造函数,用来生成 Set 数据结构。
new Set([iterable])//Set 对象允许你储存任何类型的唯一值,无论是原始值或者是对象引用。
Set的v8实现
就是一个OrderedHashTable 有序的hasTable 并且 each item is an offset
// OrderedHashTable is a HashTable with Object keys that preserves// insertion order. There are Map and Set interfaces (OrderedHashMap// and OrderedHashTable, below). It is meant to be used by JSMap/JSSet.//// Only Object* keys are supported, with Object::SameValue() used as the// equality operator and Object::GetHash() for the hash function.// Based on the "Deterministic Hash Table" as described by Jason Orendorff at// https://wiki.mozilla.org/User:Jorend/Deterministic_hash_tables// Originally attributed to Tyler Close.//// Memory layout:// [0]: bucket count// [1]: element count// [2]: deleted element count// [3..(NumberOfBuckets() - 1)]: "hash table", where each item is an offset// into the data table (see below) where the// first item in this bucket is stored.// [3 + NumberOfBuckets()..length]: "data table", an array of length// Capacity() * kEntrySize, where the first entrysize// items are handled by the derived class and the// item at kChainOffset is another entry into the// data table indicating the next entry in this hash// bucket.template<class Derived, int entrysize>class OrderedHashTable: public FixedArray {public:// Returns an OrderedHashTable with a capacity of at least |capacity|.static Handle<Derived> Allocate(Isolate* isolate, int capacity, PretenureFlag pretenure = NOT_TENURED);// Returns an OrderedHashTable (possibly |table|) with enough space// to add at least one new element, or returns a Failure if a GC occurs.// ...}
// 使用const s = new Set()[1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1].forEach(x => s.add(x))for (let i of s) {console.log(i) // 1 2 3 4}// 普通去重let arr=[1,3,2,3,4,5];arr= Array([...new Set(arr)];
当向 Set 加入值的时候,并不会发生类型转换,所以5和"5"是两个不同的值。
Set 内部判断两个值是否不同,使用的算法叫做“Same-value-zero equality”,它类似于精确相等运算符(===),主要的区别是Set 认为NaN等于自身,而精确相等运算符认为NaN不等于自身。
**
Set 实例属性
- constructor: 构造函数
- size:元素数量
Set的实例方法
```javascript //操作方法 let set = new Set() // add(value):新增,相当于 array里的push set.add(1).add(2).add(1)
// delete(value):存在即删除集合中value
set.delete(1)
set.has(1) // false
// has(value):判断集合中是否存在 value set.has(1) // true set.has(3) // false
// clear():清空集合 set.clear(); //
//Array.from 方法可以将 Set 结构转为数组 const items = new Set([1, 2, 3, 2]) const array = Array.from(items) console.log(array) // [1, 2, 3] // 或 const arr = […items] console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3]
//forEach(callbackFn, thisArg):用于对集合成员执行callbackFn操作,如果提供了 thisArg 参数,回调中的this会是这个参数,没有返回值 items.forEach((value, key) => { console.log(key + ‘ : ‘ + value) }) // 1 : 1 2 : 2 3 : 3
// values() 方法返回一个新的 Array Iterator 对象,该对象包含数组每个索引的值 arr.values();
// keys 方法返回一个包含数组中每个索引键的Array Iterator对象。 arr.keys();
// entries() 方法返回一个新的Array Iterator对象,该对象包含数组中每个索引的键/值对。 arr.entries();
<a name="4sL3f"></a>### Mapmap对象保存键值对,并且能够记住键的原始插入顺序。任何值(对象或者[原始值](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Glossary/Primitive)) 都可以作为一个键或一个值。一个Map对象在迭代时会根据对象中元素的插入顺序来进行 — 一个 [`for...of`](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/for...of) 循环在每次迭代后会返回一个形式为[key,value]的数组<br />Map 是一种叫做**字典**的数据结构;<a name="xl1Bu"></a>#### 集合 与 字典 的区别:- 共同点:集合、字典 可以储存不重复的值- 不同点:集合 是以 [value, value]的形式储存元素,字典 是以 [key, value] 的形式储存**任何具有 Iterator 接口、且每个成员都是一个双元素的数组的数据结构**都可以当作`Map`构造函数的参数,```javascriptconst set = new Set([['a', 1],['b', 2]]);const t1 = new Map(set);t1.get('a') // 1const t2 = new Map([['c', 3]]);const t3 = new Map(t2);t3.get('b') // 3
如果读取一个未知的键,则返回undefined。
new Map().get('babalalala')// undefined
注意,只有对同一个对象的引用,Map 结构才将其视为同一个键。这一点要注意。
const map = new Map();map.set(['a'], 1234);map.get(['a']) // undefined
Map 结构的默认遍历器接口(Symbol.iterator属性),就是entries方法。
map[Symbol.iterator] === map.entries; // true
与其他数据结构的相互转换
// Map 转 Arrayconst map = new Map([[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]])console.log([...map]) // [[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]]//. Array 转 Mapconst map = new Map([[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]])console.log(map) // Map {1 => 1, 2 => 2, 3 => 3}// Map 转 Object// 因为 Object 的键名都为字符串,而Map 的键名为对象,所以转换的时候会把非字符串键名转换为字符串键名。function mapToObj(map) {let obj = Object.create(null)for (let [key, value] of map) {obj[key] = value}return obj}const map = new Map().set('name', 'An').set('des', 'JS')mapToObj(map) // {name: "An", des: "JS"}// Object 转 Mapfunction objToMap(obj) {let map = new Map()for (let key of Object.keys(obj)) {map.set(key, obj[key])}return map}objToMap({'name': 'An', 'des': 'JS'}) // Map {"name" => "An", "des" => "JS"}// Map 转 JSONfunction mapToJson(map) {return JSON.stringify([...map])}let map = new Map().set('name', 'An').set('des', 'JS')mapToJson(map) // [["name","An"],["des","JS"]]// JSON 转 Mapfunction jsonToStrMap(jsonStr) {return objToMap(JSON.parse(jsonStr));}jsonToStrMap('{"name": "An", "des": "JS"}') // Map {"name" => "An", "des" => "JS"}
WeakMap
WeakMap 对象是一组键/值对的集合,其中的键是弱引用的。其键必须是对象,而值可以是任意的。
注意,WeakMap 弱引用的只是键名,而不是键值。键值依然是正常引用。
WeakMap 中,每个键对自己所引用对象的引用都是弱引用,在没有其他引用和该键引用同一对象,这个对象将会被垃圾回收(相应的key则变成无效的),所以,WeakMap 的 key 是不可枚举的。
属性:
- constructor:构造函数
方法:
- has(key):判断是否有 key 关联对象
- get(key):返回key关联对象(没有则则返回 undefined)
- set(key):设置一组key关联对象
- delete(key):移除 key 的关联对象
WeakSet
WeakSet 对象允许你将弱相关对象存储在一个集合中。如果传入一个可迭代对象作为参数, 则该对象的所有迭代值都会被自动添加进生成的 WeakSet 对象中。null 被认为是 undefined。
WeakSet 对象允许你将弱引用对象储存在一个集合中
WeakSet 与 Set 的区别:
- WeakSet 只能储存对象引用,不能存放值,而 Set 对象都可以
- WeakSet 对象中储存的对象值都是被弱引用的,即垃圾回收机制不考虑 WeakSet 对该对象的应用,如果没有其他的变量或属性引用这个对象值,则这个对象将会被垃圾回收掉(不考虑该对象还存在于 WeakSet 中),所以,WeakSet 对象里有多少个成员元素,取决于垃圾回收机制有没有运行,运行前后成员个数可能不一致,遍历结束之后,有的成员可能取不到了(被垃圾回收了),WeakSet 对象是无法被遍历的(ES6 规定 WeakSet 不可遍历),也没有办法拿到它包含的所有元素
属性:
- constructor:构造函数,任何一个具有 Iterable 接口的对象,都可以作参数
方法:
- add(value):在WeakSet 对象中添加一个元素value
- has(value):判断 WeakSet 对象中是否包含value
- delete(value):删除元素 value
WeakRef
WeakRef对象允许您保留对另一个对象的弱引用,而不会阻止被弱引用对象被GC回收
参考连接:
V8源代码,
MDN
「如果喜欢的话可以点赞👍👍👍/关注,支持一下,希望大家可以看完本文有所收获」
关注公众号,code本缘

